Econ 1101
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Economy
Comes from the Greek word for “one who manages a household”
Economics
The study of how society manages its scare resources
Equity
Benefits of those resources shared fairly among the members of society
Opportunity Cost
Whatever must be giving up to obtain some item
Rational People
those who systematically and purposefully do their objectives
Market Economy
People and companies decide what to make, sell, and buy
Market Failure
When a market is left alone and fails to allocate resources efficiently caused by either externality or market power
Market Power
The ability of a single economic actor to have substantial influence on the market prices
Productivity
the quantity of goods and services produced per hour of worker’s time
Business Cycle
The economy's natural cycle of ups and downs over time
Externality
They are market failures that affect the uncompensated impact of one person’s actions on the well-being of a bystander
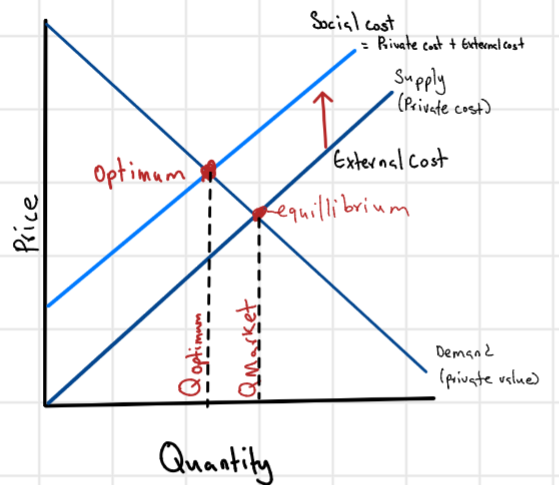
Negative Externalities
Lead markets to produce a larger quantity than is socially desirable.
Positive Externalities
Lead markets to produce a smaller quantity than is socially desirable
Internalized Externality
When incentives are altered in a way in which the external effects of their actions are accounted for
Corrective Taxes
Deal with the effects of negative externalities
Corrective subsidy
Equal the external benefit of positive externalities
Excludable Goods
Is the property of a good whereby a person can be prevented from using it.
Rival in Consumption
Is the property of a good whereby one person’s use diminishes other people’s use
Private Goods
Goods that are both excludable and rival in consumption.
A good that can be obtained through payment and once it’s paid for you are the only one with benefits
Examples of a private good
Ice Cream, Clothing, and Congested Toll Roads
Public Goods
Are neither excludable nor rival in consumption.
People cannot be prevented from using a good because one person’s use doesn’t reduce another’s ability to use it
Examples of public goods
Amber Alerts, National Defence, Uncongested Toll- Free Roads
Common Resources
Are rival in consumption but not excludable
Goods available to everyone but once taken by someone else it becomes unavailable
Examples of common resources
The Environment, Fish in the ocean, Congested Toll -Free roads
Club Goods
Are excludable but not rival in consumption
Your Access to the good doesn’t affect other’s use of the good
Examples of Club Goods
Wifi, Fire Protection, Uncongested Toll Roads
Industrial Organization
Is the study of how firms’ make decisions regarding prices and quantities depend on the market condition they face
Total Revenue for a Firm
Is the amount a firm receives for the sale of its output
Total Cost
Is the market value of inputs a firm uses in production
Profit
Total revenue minus total cost
Explicit costs
Input cost that require a momentary payment by the firms
Implicit Costs
Input Costs that do not require a monetary payment by the firm
Economic Profit
Total revenue - ( explicit + implicit costs )
Accounting Profit
Total revenue - explicit costs
Production Function
The relationship between the quantity of labour used to produce a good and the quantity of output of the good
Marginal Product
Is the increase in output that arises from an additional unit of input
Diminishing Marginal Product
The property whereby the marginal product of an input declines as the quantity of the input increases
Fixed Costs(FC)
Are costs that do not vary with the quantity of output produced
Variable Costs (VC)
Are costs that do vary with the quantity of output produced
Efficient Scale
Is the level of output that minimizes average total costs
Economies of Scale
occurs when LRATC decreases as the quantity of output increases.
Diseconomies of Scale
Occurs when LRATC increases as the quantity of output
increases.
Constant Returns to Scale
occurs when LRATC stays the same as the quantity of output changes.
Competitive Market
is a market in which there are many buyers and many sellers
so that each has a negligible impact on the market price
Average Revenue
Is the total revenue divided by quantity sold
Marginal Revenue
Is the change in total revenue from selling one more unit
Maximizing profit in a Competative Market
MR = MC
Characteristics of a Competitive Market
Many buyers and sellers
The goods offered by various sellers are identical
Firms can freely enter and exit the market
Price
MR & AR
Increase in Production
MC<MR
Decrease in Production
MC> MR
Circular- Flow Diagram
a visual model of the economy that shows how dollars flow through markets among households and firms
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
A graph that shows the maximum possible output combinations of two goods
Used to illustrate concepts like scarcity, opportunity cost, and efficiency
Positive statements
Claims that attempt to describe the world as it is
Normative Statements
Claims that attempt to prescribe how the world should be
Law of Demand
the claim that,other things equal, the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises
Normal Good
Is something people buy when their income goes up causing an increase in demand
Inferior Good
Goods that people buy less of when their income increases causing a decrease in demand
Why Price Elascity of demand matters
Helps firms make pricing descions which impacts their TR
Elasctity
Is the measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded/supplied to one of it’s detrminents
Determinants of Price elacticity
Availability of Substitutes
Porpotion spent on the Good
Time Elapsed since Price change
Luxuries vs Necessities
Price Ceiling
Is the legal maximum for a good designed to protect consumers from excessively high prices
Price floor
Is the Legal minimum price for a good designed to protect producers from excessively low prices
Binding
Market price is set at the price floor
Non- Binding
Market price remains at the equilibrium
Willingness to Pay
Is the maximum amount that a buyer is willing to pay for a good
Consumer surplus
Willingness to pay - Amount actually Paid
Producer Surplus
Market Price - Minimum accepted Price
Tax incidence
How the burnden of a tax is shared amoung participants in a market
Monopoly
A firm that is the sole seller of a product without close substitutes
Maxmizing Profit in a Monopolist market
P > MR = MC
Price Discrimination
Is the buisness practice of selling the same good at different prices for different customers
Natural Monopolies
Occurs when a single firm can produce a good to an entire market at a lower cost than 2 or more firms could
Consumer -Choice Theory
explains how consumers decide what to buy by analyzing the trade offs they face with the relationship between their income and spending