Python
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
Python lacks built-in syntax for constants, so how do you signal that a variable is unchangeable?
The convention in Python is to fully capitalise the name of the variable and use underscores for spaces to signify that the variable is to be treated as a constant (can’t be changed). This may also solely signify a Global Variable.

If __name__ == “__main__”:
When you import a module, Python executes all its code. This pattern checks if the file is being run directly versus imported. When run directly, a special variable equals "__main__", but when imported, it equals the module’s name instead. Code inside this conditional block only runs when executed directly, letting you include test/demo code that won’t run during imports.
How do you import the pi functionality from the math module?
from math import pi

What does the from keyword do when importing modules?
It allows us to import parts of a module's functionality.
How do we import multiple modules in the same import statement?
By placing a comma between the modules we're importing.
What's the statistics module for?
It provides methods to help with common statistical calculations.

In this scenario, why do we not need to state statistics.mean() to use the mean function from the statistics module?
Because we used the from keyword in the import statement to import the mean() function individually.
How do you import a specific function from a Python module without importing the whole function?
You use the from keyword with the import keyword.

How do you access the mean() function in Python?
You must import the statistics module.

Can we use modules to reuse other people's code?
Yes, modules are a way developers make their code available online for people to use.
What's the difference between a module and a class?
Modules usually contain lots of classes, while a class is singular.
What instruction can we use to find out the functionality a module has?
We use help(<moduleName>).
How do we use the .sqrt() method from Python’s built-in math module?
We state the module name, followed by the method name and the data we are accessing/modifying. For example, math.sqrt(16)

How do we gain access to a module so that we can use its features in our code?
To use a module, we import it with the keyword import followed by the module's name.
What data structure follows the FIFO (First in, First out) principle?
A queue
What is the use of a module in OOP?
Modules group related classes and data and make them accessible from one place.

What are the steps taken in the compiling process?
1 - Preprocessing step (takes care of any of the hash symbols in C, such as hashdefine)
2 - Compiling step (compiles your code into assembly code)
3 - Assembling step (converts that assembly code into machine code)
4 - Linking step (takes your machine code and combines it with your installed libraries to give you one executable program)
What is the largest number an 8-bit unsigned binary digit can represent?
255 (there’s 256 possibilities, but remember that we always start counting from 0)
How do we abstract a class?
Write a few core methods that handle low-level functions.

Call the method defined in the class using the drone variable.
drone.fly()

Fill in the missing code so that instances of Student receive a name property.
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name


Which methods does phone have?
call() and charge()
When a function is inside an object, what is it called?
A method.

How can we customize a Cowboy ' to have the same functionality as Person except greet() prints ‘Howdy!’ ?
Add a subclass of Person called Cowboy and change it to print Howdy! in greet ().
How does a subclass override its inherited methods?
Defining the inherited method in the subclass and changing the behavior.
Polymorphism refers to objects' ability to do which of the following?
Customize their implementation of an inherited behavior.

Instances of Electric will inherit the overridden method from Electric , not the original one from Car . What will tesla.drive() log?
Whirr!
What does Polymorphism ensure when an object’s/instance’s method is called?
Polymorphism ensures that the proper method will be executed based on the calling object’s class.
With inheritance, we can extend a child class's functionality. But what if we want to implement class behaviors differently from each other?
We can use something called polymorphism. This means a subclass can override the methods it inherits from its superclass. We simply set the same name method on the subclass.
In this example, in the Lion subclass, we are changing the behaviour of the speak() method Lion inherited from the Feline class. We do this my redefining the method with def speak(self):

Why is implementing abstraction important in OOP?
So others can use a class without knowing how it works.
How do we implement abstraction in OOP?
Write a few core methods that handle low-level functions.

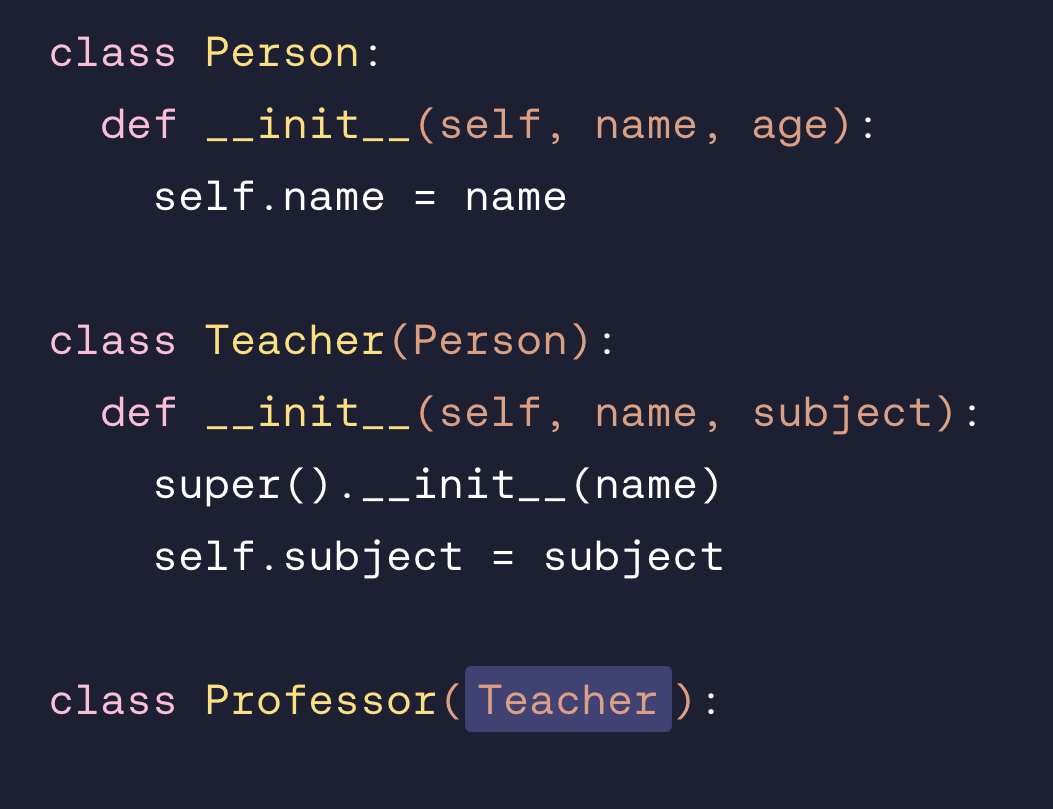
Choose the correct class so that instances of Professor can inherit both name and subject properties.
class Professor(Teacher):
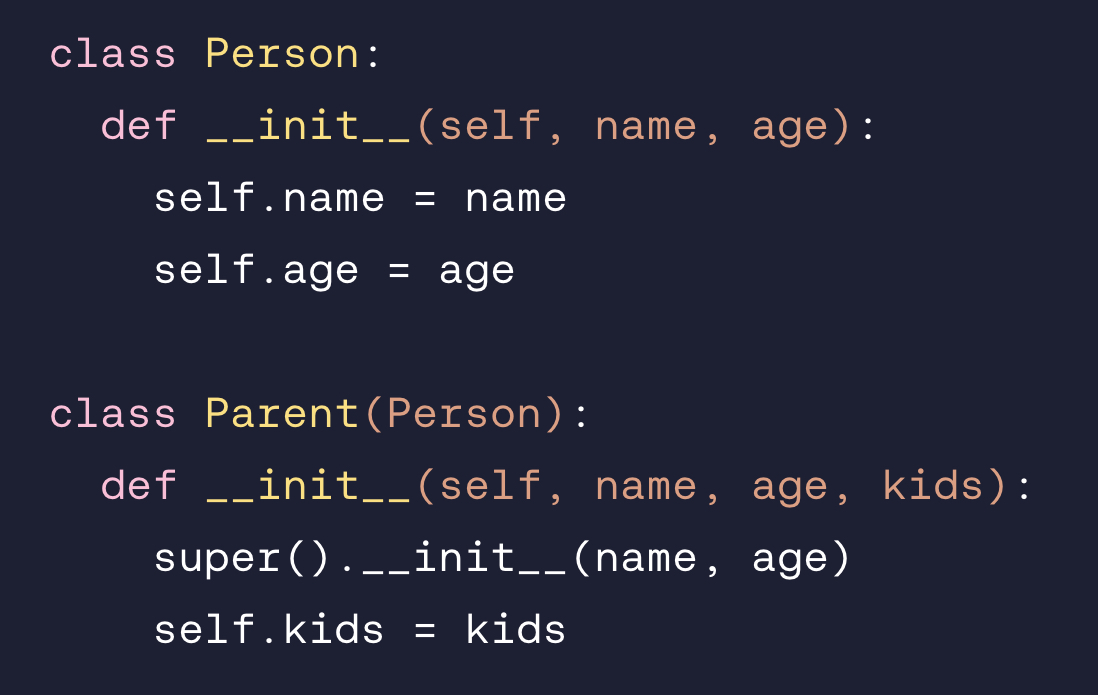
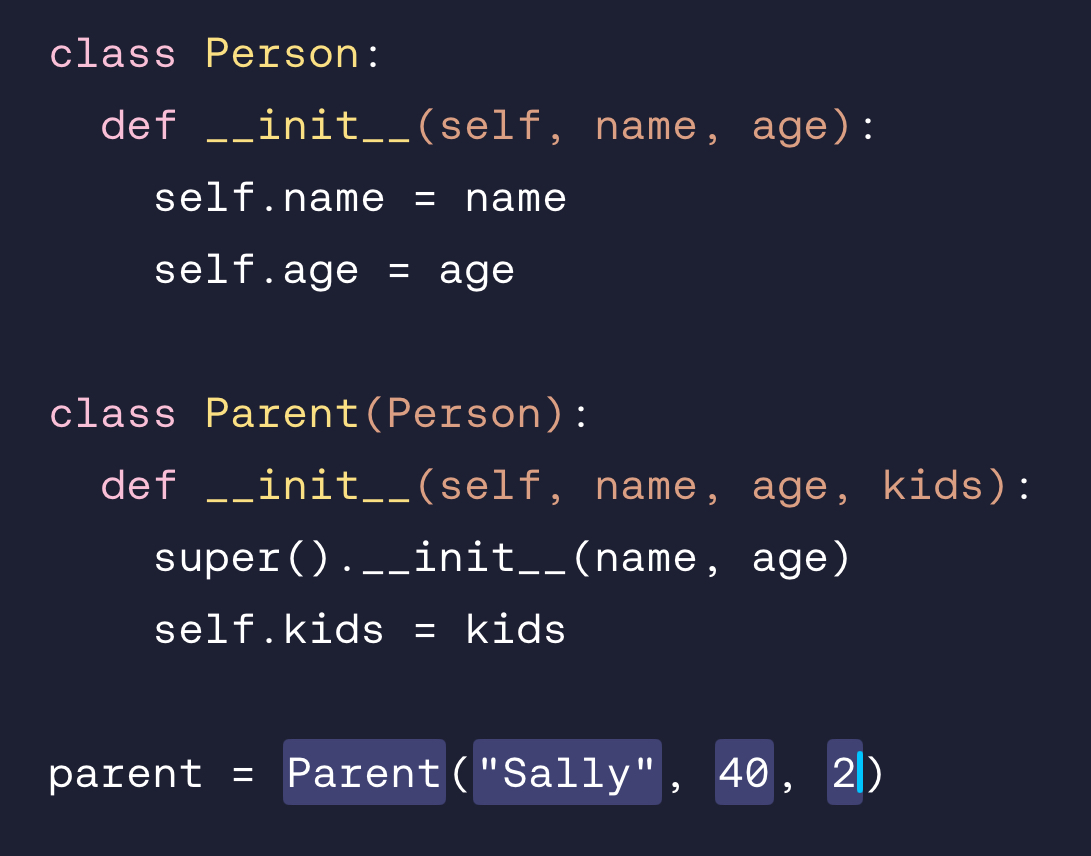
Sally is a 40-year-old mother of two kids. Create a new instance that encapsulates her information.
parent = Parent(“Sally”, 40, 2)
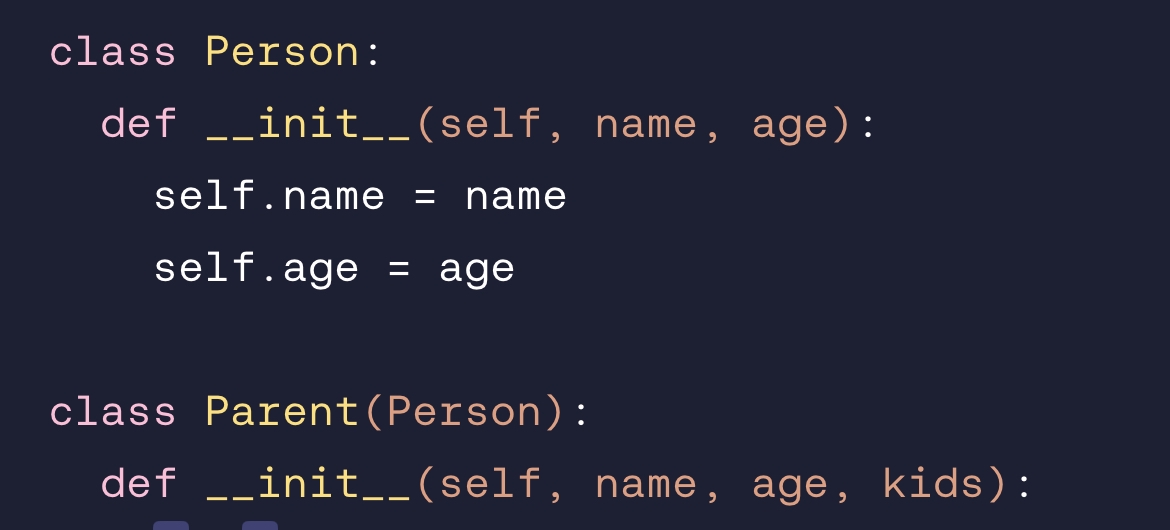
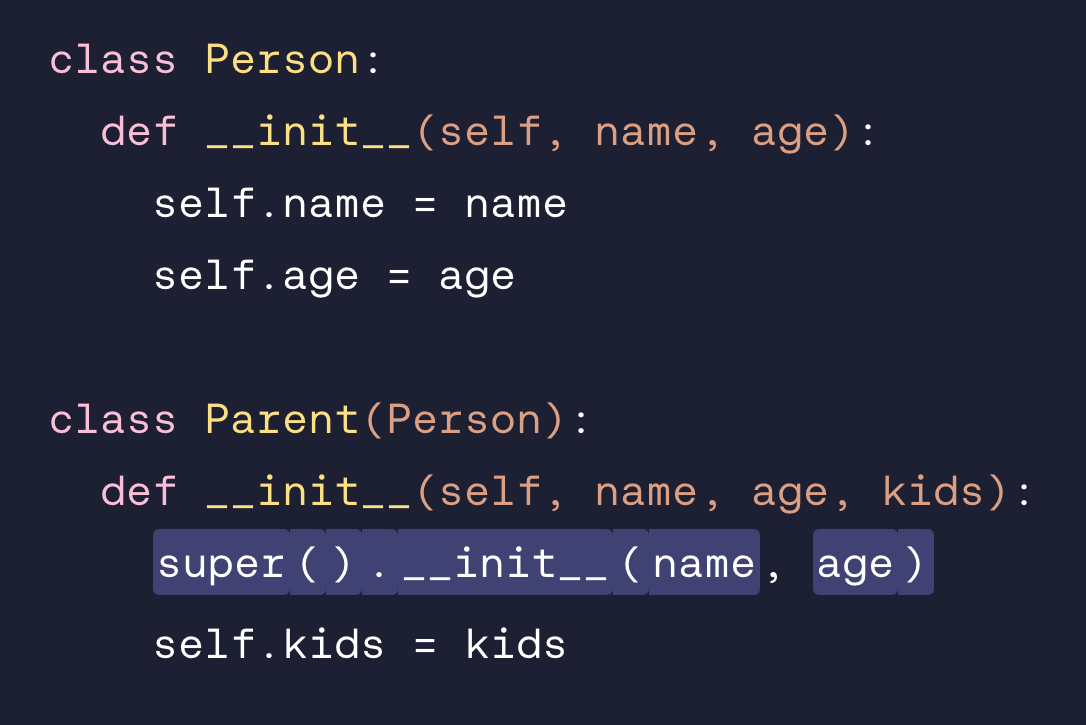
Call super().__init__ with name and age so that instances of Parent receive these properties.
super().__init__(name, age)

How would you create a subclass called Laptop that inherits the turnOn() method from Computer .
class Laptop(Computer):

Which methods can we call on the jet instance?
Both fly() and invert()

The dev instance is missing the company property. What line do we need to add to the Developer subclass?
super().__init__(company)
Which class method sets the properties of instances?
__init__()
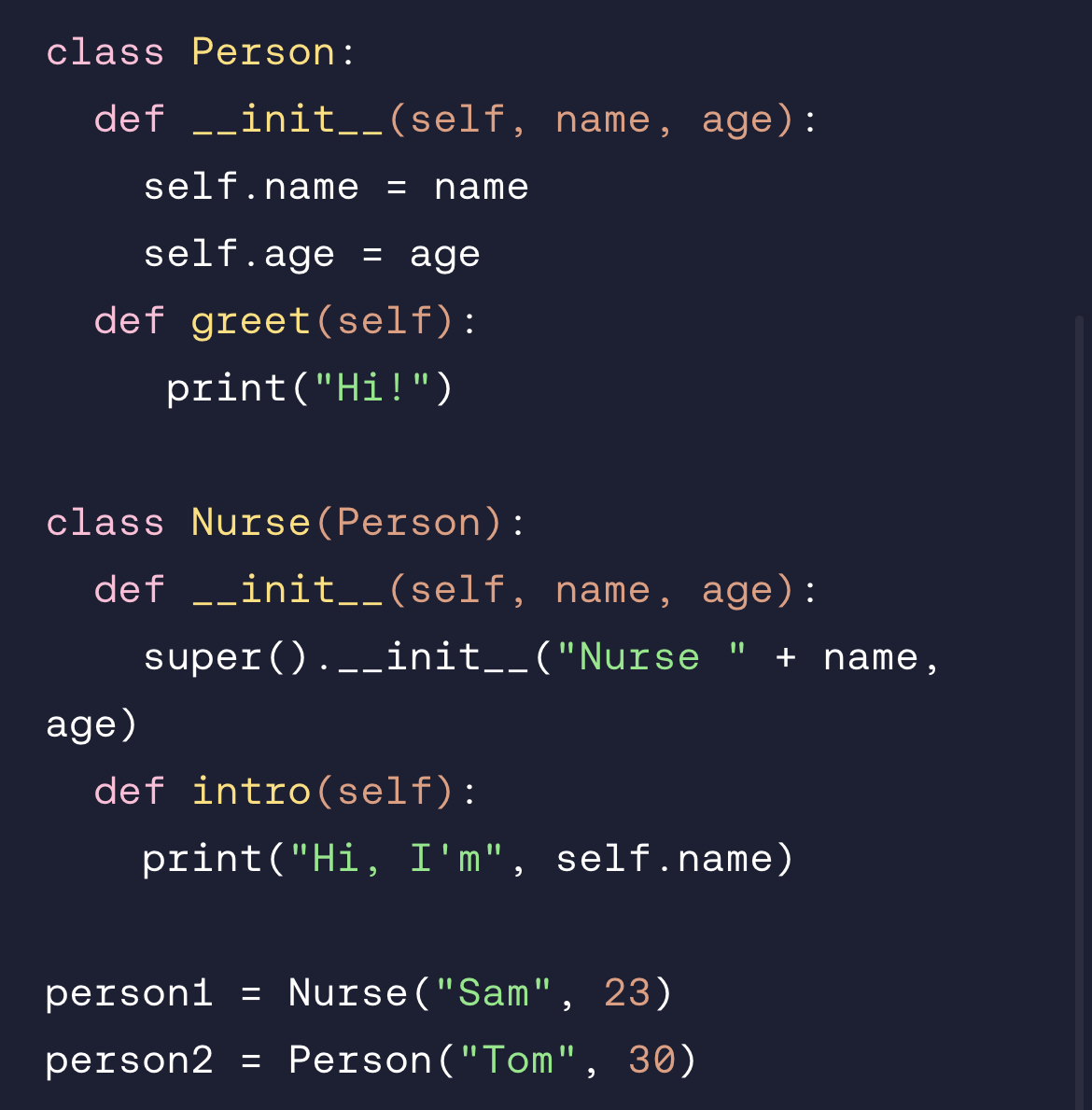
What is the super() function used for?
super() is a Python function that lets a child class access methods from its parent class. It’s used for inheritance.
So super().__init__ is used to modify the properties the child class inherited from its parent class.
How does inheritance make our OOP code more efficient?
Functions need to be set only once.
In OOP, what is it called when classes receive methods from other classes to improve efficiency?
Inheritance. Inheritance lets us create classes that have different properties and behaviours without coding each one from scratch.
Here we see that the Child class is inheriting the Parent class because it's inside the parentheses after the class name.

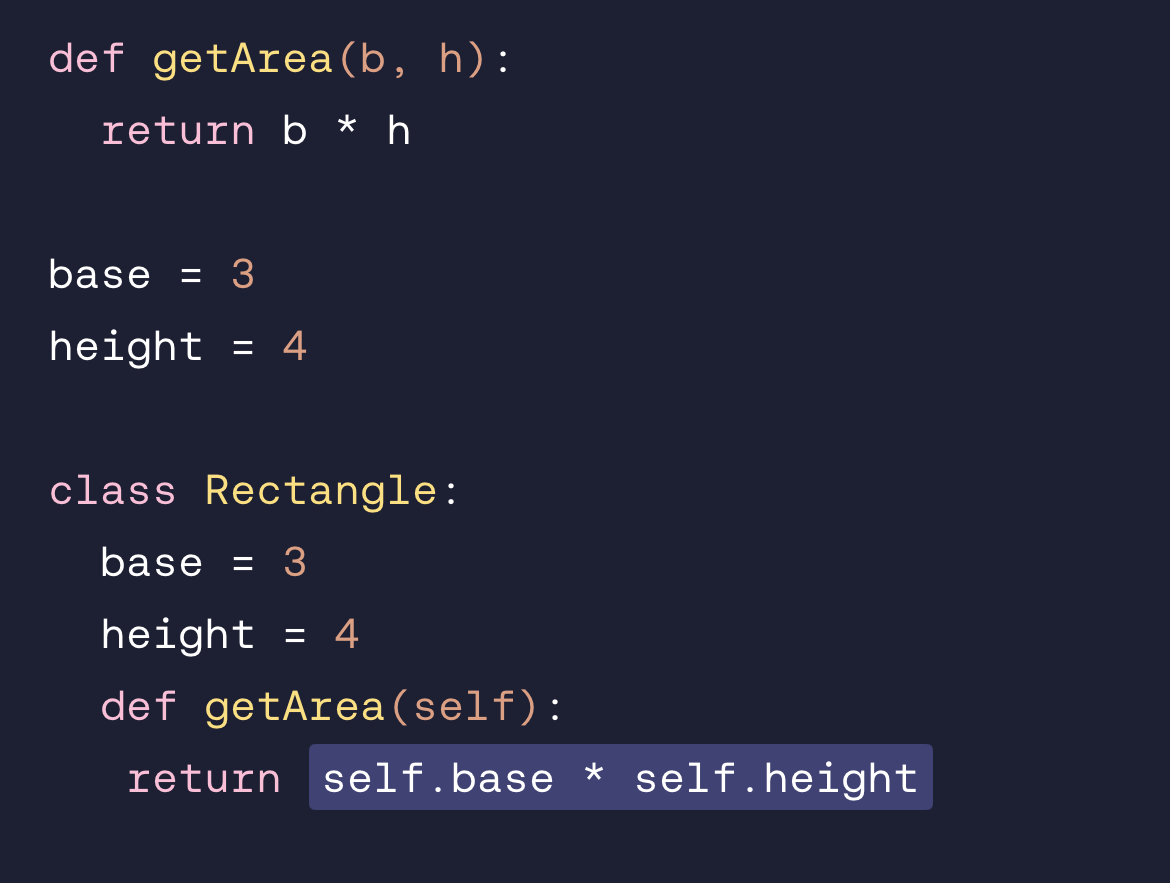
What is the point in the self keyword in the return statement?
When you write self.base inside the method, you’re saying “look for the base attribute on whatever instance (object using this class) eventually calls this method.”
So self is the mechanism that connects the method to the instance’s data (or the class’s data as a fallback).

In FP, code is not encapsulated. Can you explain why this code does not show encapsulation?
The data and the function are not grouped together in an object.

In OOP, what is it called when we group together related data and functions in the same object?
Encapsulation
What is the self parameter used for when creating an instance method?
In Python, self is a conventional name for the first parameter of instance methods in a class. It represents the instance of the class itself (the specific object that the method is being called on).
When you call a method on an object, Python automatically passes that object as the first argument to the method (self). The self parameter receives this object, allowing the method to access and modify the object’s/instance’s attributes and call other methods on that same instance.
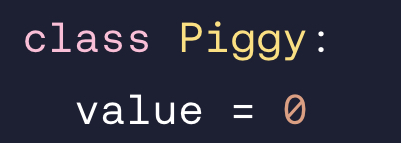
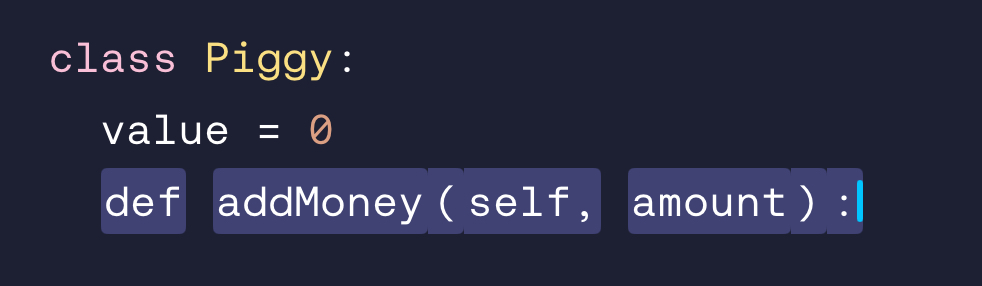
Write the code to add a method called addMoney() that accepts a parameter called amount:
def addMoney(self, amount):
What is object-oriented programming?
A programming style where we use objects to bundle together related data (properties) and functionality (methods).

Is this code an example of Functional Programming (FP) or Object-Oriented Programming?
It’s Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), where we group data and functionality as properties and methods inside objects, like Virtual_Pet here.
True or False, In the FP style, we keep data and functionality separate?
True, we pass data into functions whenever we want something.

Functional Programming (FP)
A programming paradigm focused on building applications by composing pure, mathematical functions, treating functions as first-class citizens (data) to avoid shared mutable state and side effects, resulting in declarative, modular, and often more predictable code, especially useful for complex tasks like big data and concurrency. It emphasizes immutability, expressions over statements, and uses recursion instead of loops.
What is object-oriented programming (OOP) and functional programming (FP) examples of?
Paradigms
What term is used to refer to different styles of coding?
Paradigms

What's wrong with this code?
self needs to be the first parameter of the __init__ method

What is the difference between name and self.name in the following code?
name refers to the value passed when the instance is created and self. name refers to the class variable, name
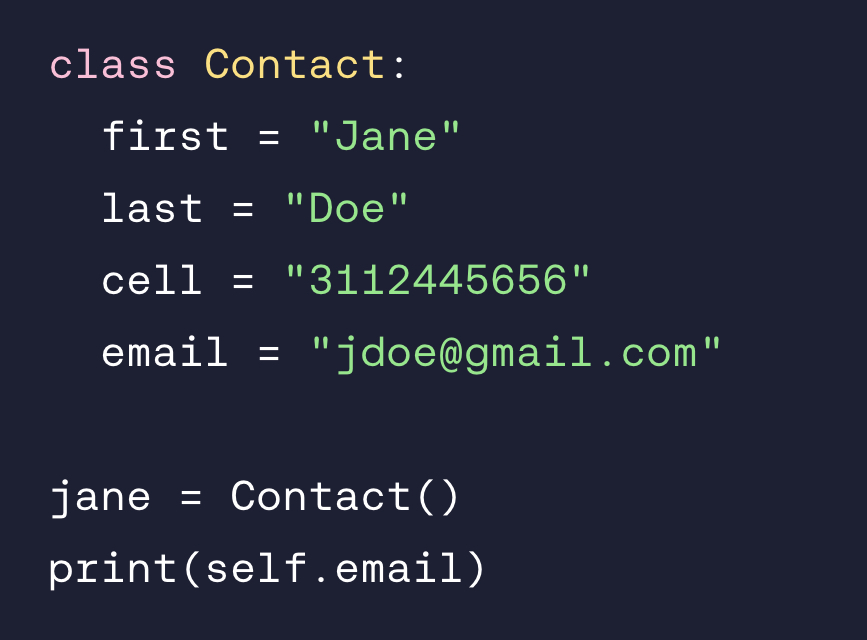
What’s wrong with this code?
print(self.email) should be print(jane.email) instead

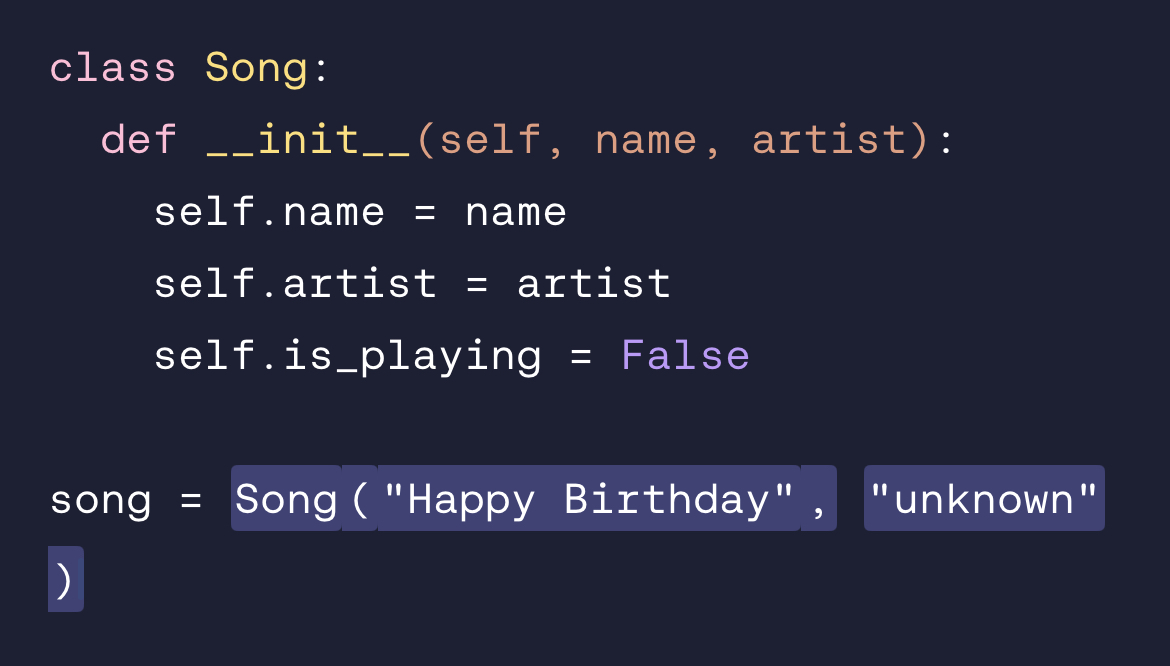
Create an instance called song of the class where name = "Happy Birthday" and artist = "unknown"
song = Song ( "Happy Birthday", "unknown")
How can we assign class variables a value when the class instance is being constructed?
By adding them as a parameter in the init function and setting the variable equal to the parameter value.

What is wrong with this code?
The class keyword is missing.
Following conventional naming syntax, what should a class name look like?
Class names usually have the first letter capitalized and the rest lowercase, like with Person here.

When defining the parameters of a function in its parenthesis, what does a -> signify after the closing parenthesis?
This is the start of a type hint, which tell you and other programmers what data types to expect. A -> and the data type following it tells you the type of data this function returns.

What are hash tables known as in Python?
Dictionaries or dict

Write a print statement that displays the first item of the class variable countries.
print(gymnastics.countries[0])
![<p>print(gymnastics.countries[0])</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/85eaf15f-b7a2-41b6-aeaf-6540297af911.jpg)
What are classes used for?
To reduce repeated code by grouping it into a class.
When do we use the keyword self ?
When we need to access class variables or methods inside the class definition.
How do we define the constructor method?
def __init__(self):
What is the purpose of a constructor?
To construct an instance of a class object with unique class variables.

How do we call the display_color function defined inside the Flower class?
We can use an instance of the class, a ., and then the name of the function. For example, rose_flower = Flower() & rose_flower.display_color()


What does the code self.color = color do in this example?
You’re storing the value of the parameter color inside the object as self.color, so it can be accessed later. We can then pass in a value to a specific class instance (rocky) using that parameter (with rocky = Virtual_Pet(“red”)).
What’s the difference between a variable defined in a class and a variable defined in a class by using a constructor method (__init__)?
A variable defined normally in the class body is a class variable, which is shared by all objects made from that class (the value of that class variable is also shared for the entire class, unless overridden).
A variable defined inside the constructor (__init__) is an instance variable, meaning each object gets its own separate copy that can be different for each instance.
What does the constructor method look like when creating a method for a class, and what does it do?
The constructor method looks like __init__() and allows us to set unique values for the class variables when we create an instance.

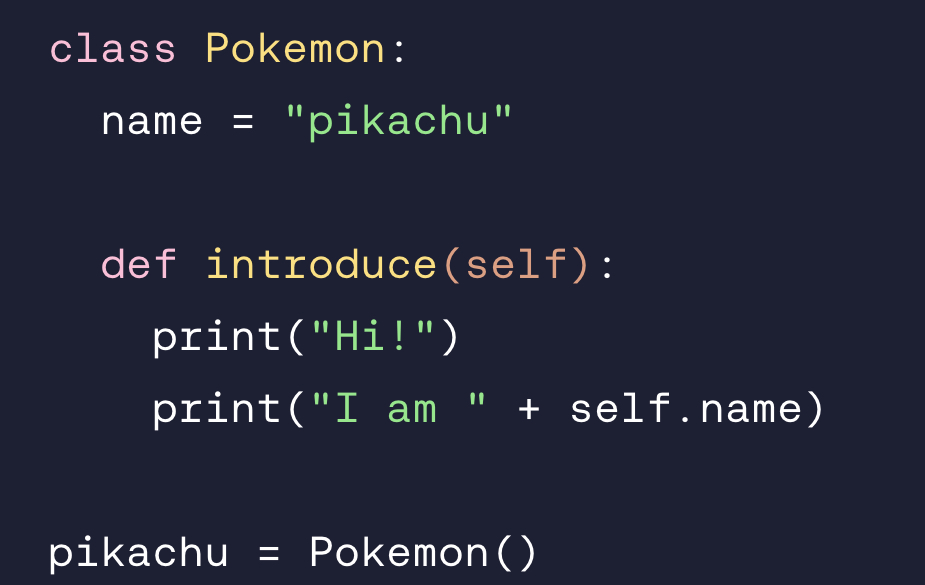
Access and call the method introduce using the class instance pikachu .
pikachu.introduce()

Do we still pass in self as the first parameter of a class method when it uses a constructor (__init__)?
Yes, you still include self as the first parameter.


How do we access rocky 's method print_color?
rocky.print_color()
What is the name of the first parameter we pass into a method? and what is its purpose?
self is the first parameter of any method. We use self as a parameter in class methods so that they can access the class variables (by making it within their scope).
What is a method in Python?
In Python, methods are functions that are defined as part of a class.
It is common practice that the first argument of any method that is part of a class is the actual object calling the method. This argument is usually called self.

Why do we need to store the class instance in a variable?
So we can access the class instance.
What syntax do you use to create a class object instance?
You need the class name followed by ().
What are variables inside a class used for?
To store data that is related to the given class.
What is a class?
A template that can have variables and functionality associated with it. Can be used to create class objects.

What does this code do?
We're defining a class (VirtualPet) and creating an instance (an object) of it (fluffy)
What is a class instance?
Instantiation is when you create an object (instance) from a class. When you store that instance (class object) inside a variable, it’s called an instance variable. It’s stored inside the object itself (usually created in __init__.
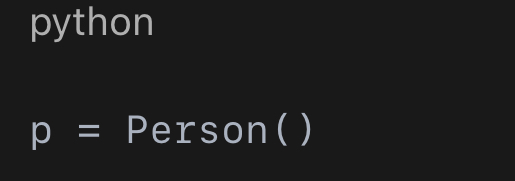
What is a class definition?
A class definition is the code that creates a new class. It describes what attributes and methods the class will have.

How do we access a class variable?
To access a class variable, we add the instance name (variable containing class definition), a . , and the name of the variable we want. Like skippy.wagging_tail here.


What are we doing here?
We are creating variables from the VirtualPet class template (these are called instances). So fluffy and benny are instances of the VirtualPet class (definition).
Instead of creating new variables for each of the different configurations for the same object (which will take a lot of time and could lead to mistakes), what could we use instead?
We can create classes instead to help us group data and functionality. A class is just a template that we use to create many similar but distinct things.


What happens when we slice a list with a step value but without providing a start position or stop position?
We can use the step value with no start or end value when slicing. By default, this will work from the start to the end of the full original list.
True or False, when using a negative step value when slicing, start needs to be either omitted or greater than stop to return elements?
True

What will this code return?
['B', 'D', 'F'] , we can use a different slicing format with two colons with [start:stop:step] , where the step determines how Python steps between start and end.
How can we start creating a template called Person via a class?
We add the keyword class followed by a name for class template (Person) and a colon.


What happens if the step value in a list slice is negative?
The step value can be negative, which allows us to use a start position larger than the end value. The order of the elements is reversed.


What temperatures will be printed?
All of them.
What does the del keyword do?
Allows us to delete objects, or items within a data structure.
What happens when we use the loop variable as the expression in a list comprehension?
We copy the original list.
![<p>Complete the list slicing in the code so that [3, 2, 1] is printed at the end.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b60f8443-3dab-45de-aa4b-f5b61e794ae2.jpg)
Complete the list slicing in the code so that [3, 2, 1] is printed at the end.
[::2]
![<p>[::2]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e0524bff-0a3b-4584-9c73-d3b51a59661a.jpg)
![<p>Complete the start:stop:step notation so that [5, 5, 5] is printed.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b3c823ba-0fe2-43a0-b691-72e821b4f4e0.jpg)
Complete the start:stop:step notation so that [5, 5, 5] is printed.
[-1:2:-2]
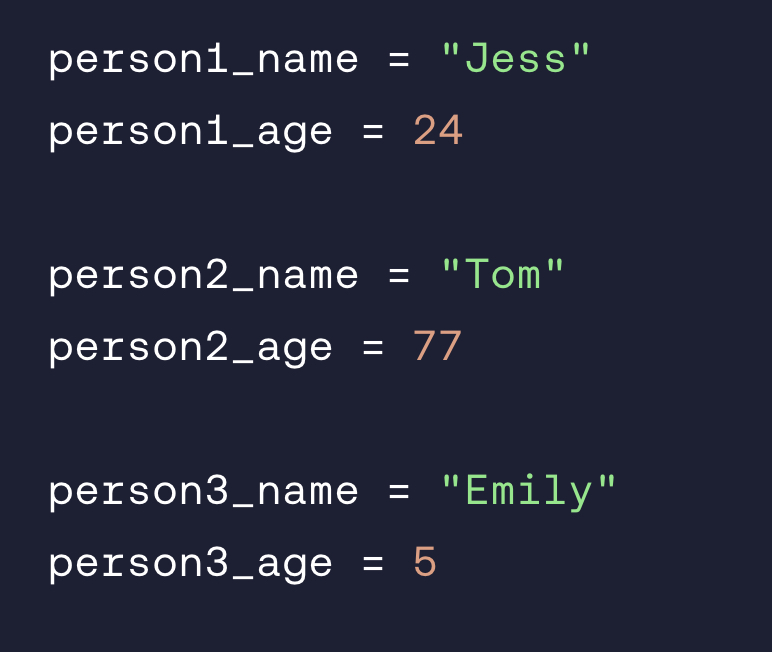
Should the following code be grouped into a class?
Yes, a class could group a Person with the variable's 'name' and 'age'.
Why would we use an if statement in a list comprehension?
We add in to the end of the list comprehension to filter the elements in the new list that meet a certain condition.
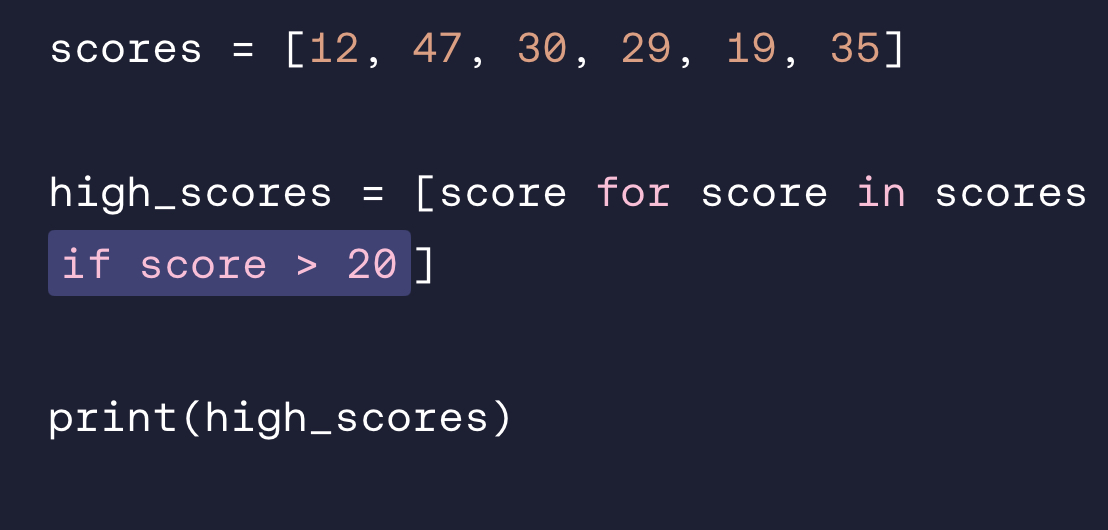

Why can’t we use this get_full_name() function inside a list comprehension?
Because it doesn’t have a return value.

What is the difference between the halved_lc variable and the halved_loop variable?
Both list variables contain the exact same values. However, halved_lc uses list comprehension to use a more compact version of the code in halved_loop
How do we conventionally indicate that something is a class?
Its name will start with a capital letter.