Ecology
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
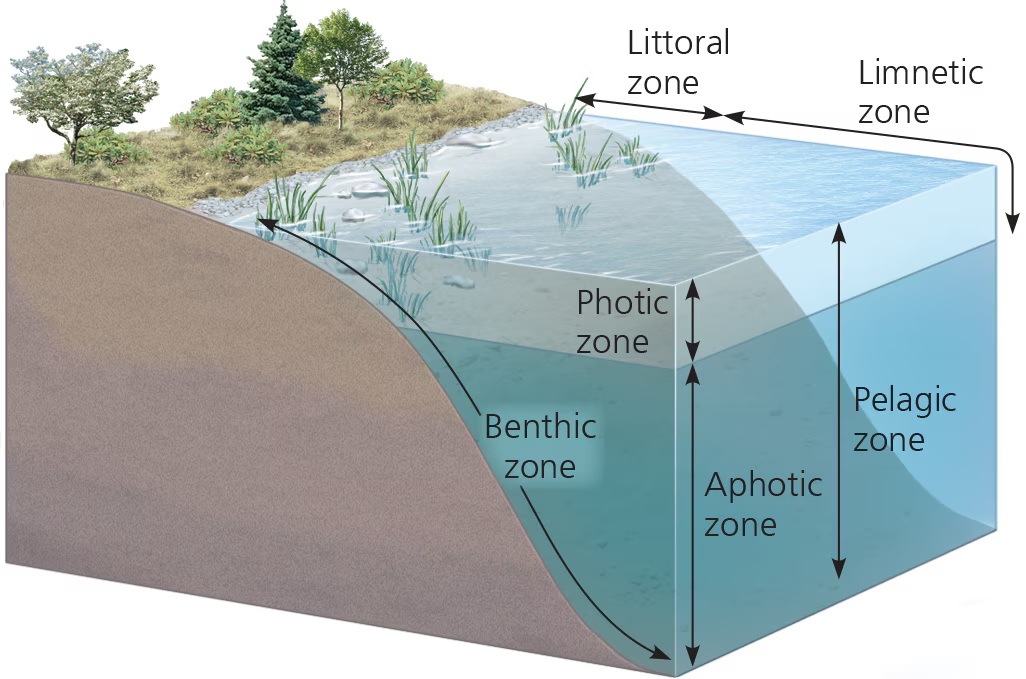
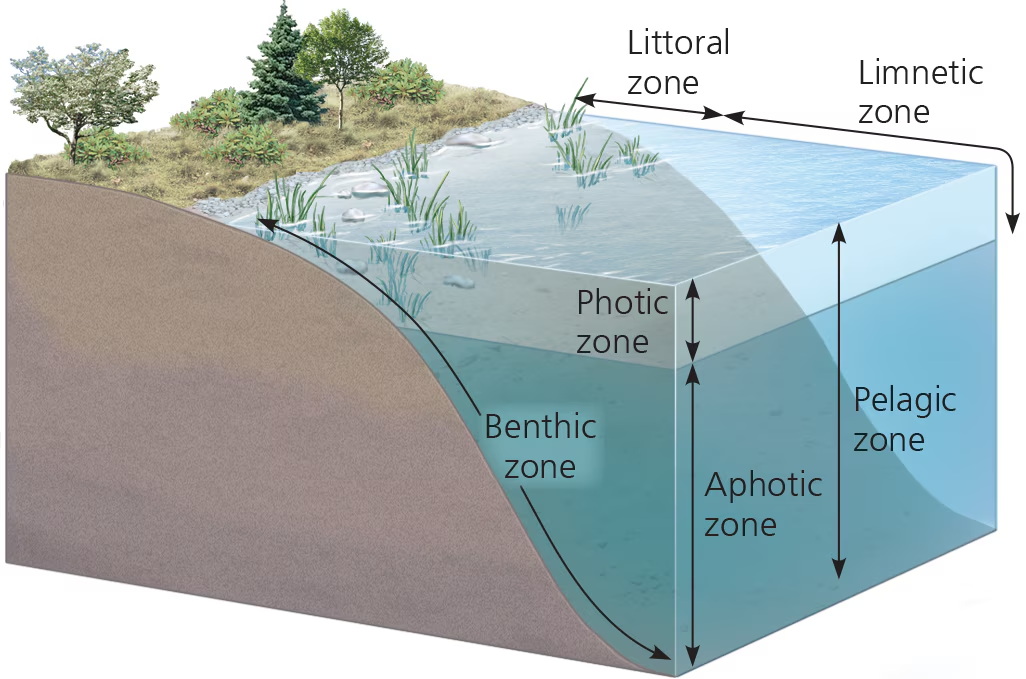
photic zone
water region w/ sufficient light for photosynth
Hadley Cell
0-30 degs (N and S of equator)
air warms @ equator → rises + releases moisture (over equator) → dry air masses around 30 degs, suck up moisture, create arid climate beneath → some descends back to Hadley, some descends into Ferrell
environment
surrounding conditions influencing life + behavior or orgs (biotic and biotic factors)
Ferrell Cell
30 - 60 degs latitude
air @ surface is pulled from high pressure area (30 degs) to lower pressure area (60 degs) → air warms and rises @ 60 degs → flows towards 30 degs and sinks again
Polar cells
60-70 degs latitude
cold air sinks near poles → rises around 60 degs latitude
structural hierarchy used to organize living systems (types of ecology)
Organismal
org’s structure and behavior meet environmental challenges
Population (one species)
factors affecting pop size/ changes and why
Community (2+ species)
how interactions b/w species affect community structure/ organization
Ecosystem (one place)
energy + chemical flow b/w orgs in environment
Landscape (many ecosystems)
energy, material, org exchanges across ecosystems
Global
regional E / material exchange influences fxn/ org distribution in biosphere
Type III survivorship curve
High early death rate then stabilization with age (ex. Oysters)
Type I survivorship curve
Low death, early midlife, sharp decline with age (large mammals)
density dependent factors of population growth
Affect larger pops. > smaller ones
1) Competition (limited resources- food, space, water)
2) Predation
3) Disease (spreads faster in crowded pops.)
density independent factors of population growth
affect all pops. equally regardless of density
1) natural disasters (wildfire, hurricane, flood)
2) climate change (drought, extreme temps)
3) humans (pollution, habitat destruction)
cohort
group of individuals of the same age in a population
seasonality
strong seasonal cycles in day length, temp, solar rad
Aquatic biomes
life zones characterized by their physical and chemical environment
communities distributed according to water depth, light penetration, distance from shore, open water/ bottom dwelling orgs
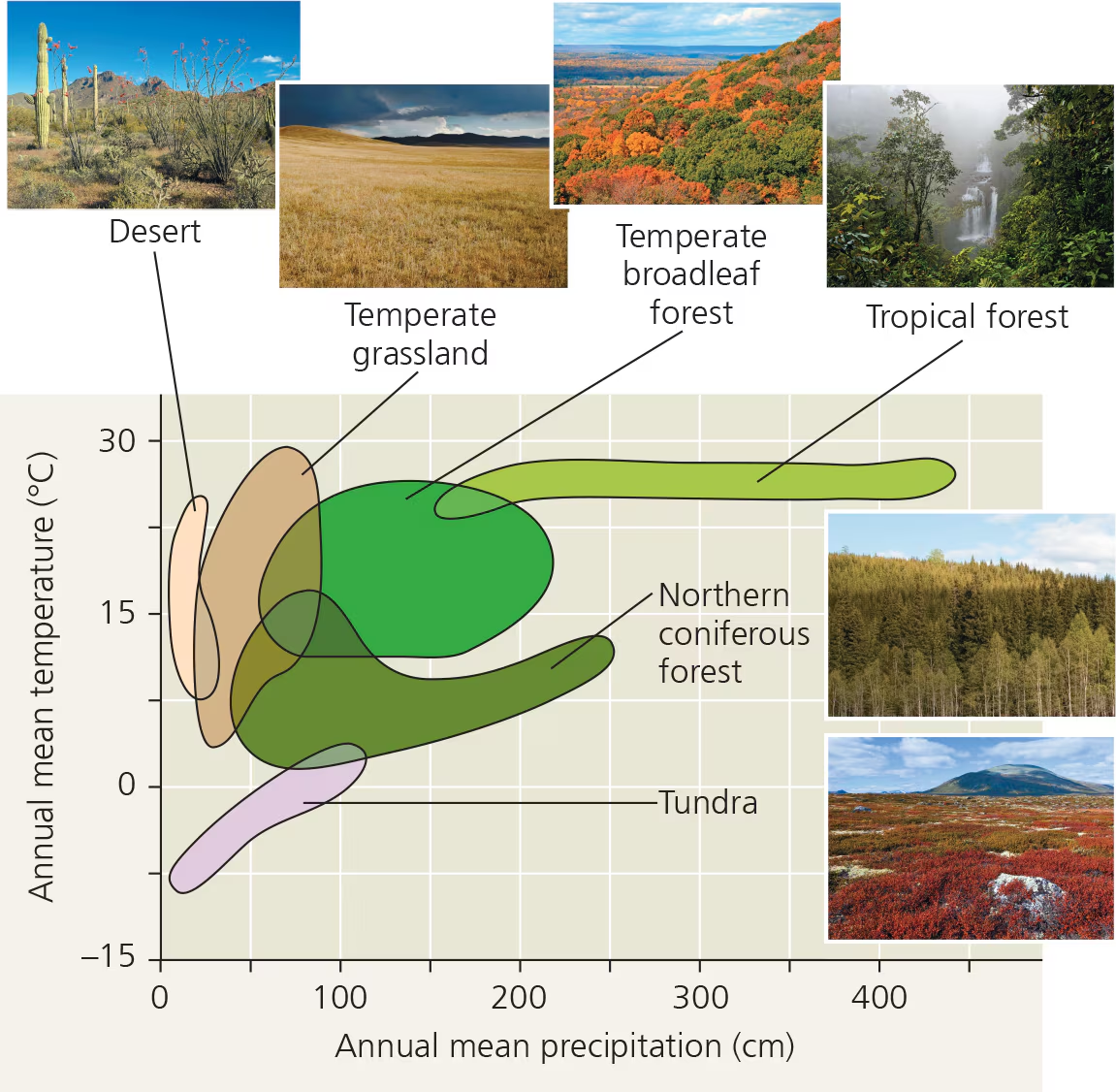
terrestrial biomes
major life zones characterized by climate and vegetation type (also animals, fungi, microrogs)
we live: Temperate Broadleaf forest
population
group of orgs of the SAME species living in same area; interact with one another
secondary succession
recolonization of an area where a disturbance removed some but NOT ALL orgs in that community
mutualism
both species benefit (+,+)
longevity
avg age ppl die in a particular country
commensalism
one species benefits; other unaffected (+,0)
predator-prey (species interxn)
one species preys on another (+,-)
Benthic zone
lowest level in aquatic biome; has organic + inorganic sediments; occupied by benthos
herbivory
animal consumes plant: (+,-) or (+,0)
TFR
Total fertility rate: avg # babies per woman in a particular country during her reproductive lifespan
primary succession
ecological succession in a lifeless area
ex. on volcanic islan
ecological succession
transition in a community’s species composition after a disturbance; establishment of a community in area w/ ~no life
amensalism
negatively effects one species; other is not affected (-, 0)
parasitism
Parasite benefits at host’s expense (+,-)
Endoparasites - live within
Ectoparasites - live on outer surface
parasites can change their host’s behavior to increase likelihood of transfer to another host
cryptic coloration
camouflage (a prey/ predator adaptation- falls under Exploitation)
interspecific interactions
relationships b/w species in the same community
K - Selection
reproductive strategy where species produce less offspring because they put more energy/ resources into raising them
typical in stable environments w/ high competition for resources
longer life spans, mature later
exponential growth
reproduction/ pop. growth w/ unlimited resources + w/out constraints
J curve
demography
study of changes overtime in vital statistics of populations (especially birth / death rates)
think Life Tables and Survivorship Curves
climograph
plot of annual mean temp (y-axis) and precipitation (x-axis) in a region
ecosystem
community of orgs in an area + the physical factors they interact with
Dispersion
the pattern of spacing among individuals within the boundaries of the population
Pattern types: clumped, uniform, random
species richness
number of species in a community
relative abundance
the proportional abundance of different species within a community
Trophic Structure
feeding relationships b/w orgs in a community
key factor affecting community structure
food chain
link trophic levels from producers to top carnivores (consumers)
trophic level
position an org occupies in food chain
food web
group of food chains linked by complex trophic interactions
arrows point: eaten → consumer
foundation species
have strong effects on their community due to their large size/ high abundance
ex. coral
keystone species
usually not abundant, control community structure through ecological roles
many = apex predators
critical to ecosystem diversity/ stability
removal would change type/ number of species/ their population size at multiple trophic levels
ecosystem engineers
physically change environment → affects community structure (ex. beavers)
ecological niche
specific set of abiotic + biotic resources an org uses in its environment
Resource partitioning
ecologically similar species coexist given one or more significant differences in their niches
related: fundamental and realized niches
Realized niche
actual resources a species uses given its environment / competition (not its ideal)
Fundamental niche
the potential/ ideal resources available for a species (no competition)
ecotone
transition area b/w ecosystems / biomes
disturbance
event that changes a community → removing organisms & changing resource availability
storm, fire, humans
biosphere
global ecosystem
phyllotaxy
way to classify trees
pattern of leaf arrangement on stem or branch
climate
long-term prevailing weather conditions in given area
Factors: temp, precip, sunlight, wind
determines distribution of terrestrial biomes/ where orgs can live
phytography
branch of botany for description, naming & classification of plants
biotic factors
LIVING parts of environment → influence distribution/ abundance of organisms
abiotic factors
NONLIVING chemical / physical attributes of environment → influence distribution/ abundance of organisms
were never living
Ecology
scientific study of interactions b/w organisms & their environment
greek: “home study”
estuary
region where fresh and salty marine waters mix
Chesapeake is largest estuary in US
Population Density
number of individuals of population / unit area (where they live)
what kinds of species tend to have stepwise survivorship curves? (?)
molting species (periods of vulnerability)
biggest cause of seasonality
earth’s tilted axis & its orbit around sun
two major climatic factors affecting org distribution in terrestrial ecosystems
temperature and precipitation
Carrying Capacity
(K) Max population size that can be supported by available resources in a habitat (given no degradation of that habitat)
what does r stand for in population growth models?
The per capita population growth rate (equal to per capita birth rate minus per capita death rate)
Type II survivorship curve
a constant decline with a constant death rate over the life span
Why do some invertebrates, such as lobsters, show a "stair-step" survivorship curve?
vulnerable to predation during molting when their shell is soft
Which of the biomes (of the 7) require periodic fires to maintain their existence? (?)
savanna, chaparral, temperate grassland, and coniferous forest
aphotic zone
water region w/ very little light (insufficient for photosynth)
orgs here have to rely on other energy gains (ex. chemosynth)
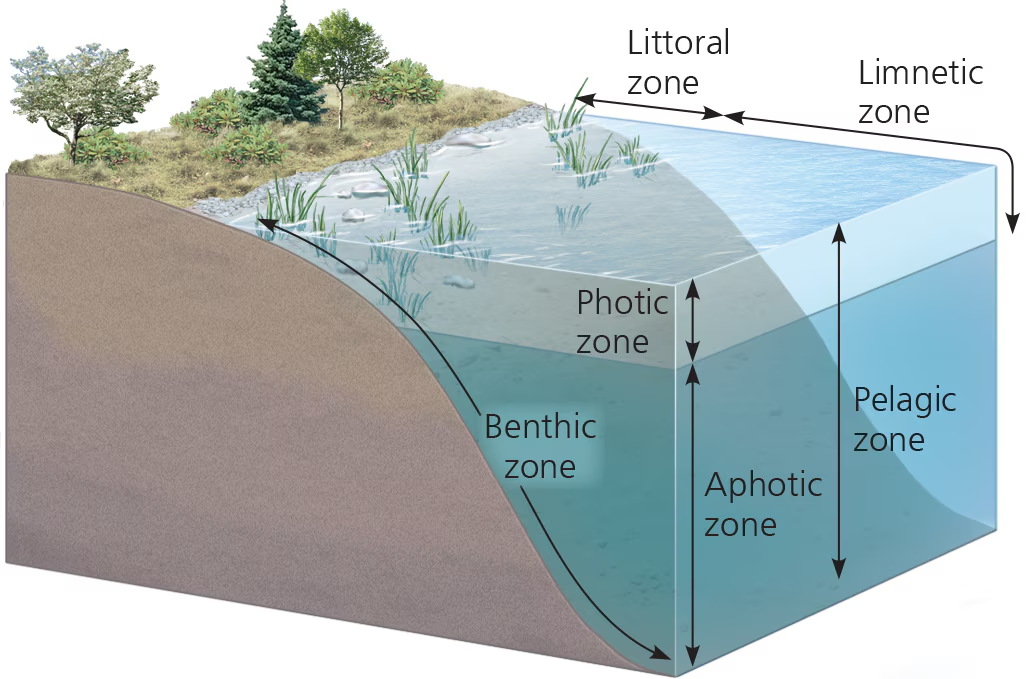
pelagic zone (aquatic)
the photic and aphotic zones together
covers the majority of the ocean
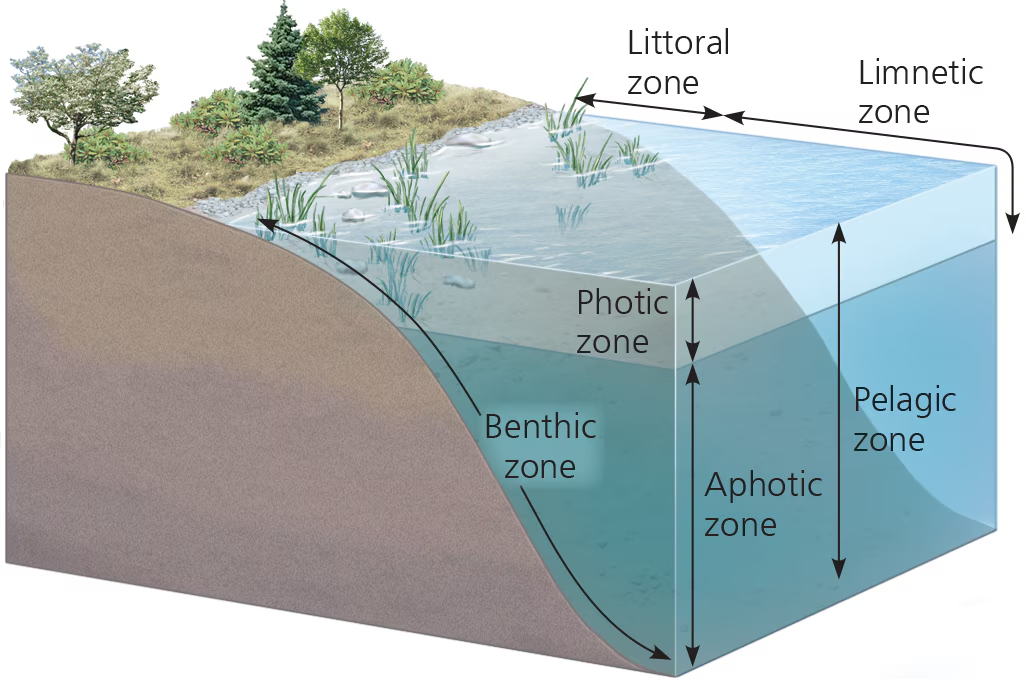
benthos
communities of orgs living on, in, or near bottom of aquatic biome (benthic zone)
Littoral zone (aquatic)
waters close to shore; shallow enough for rooted plants
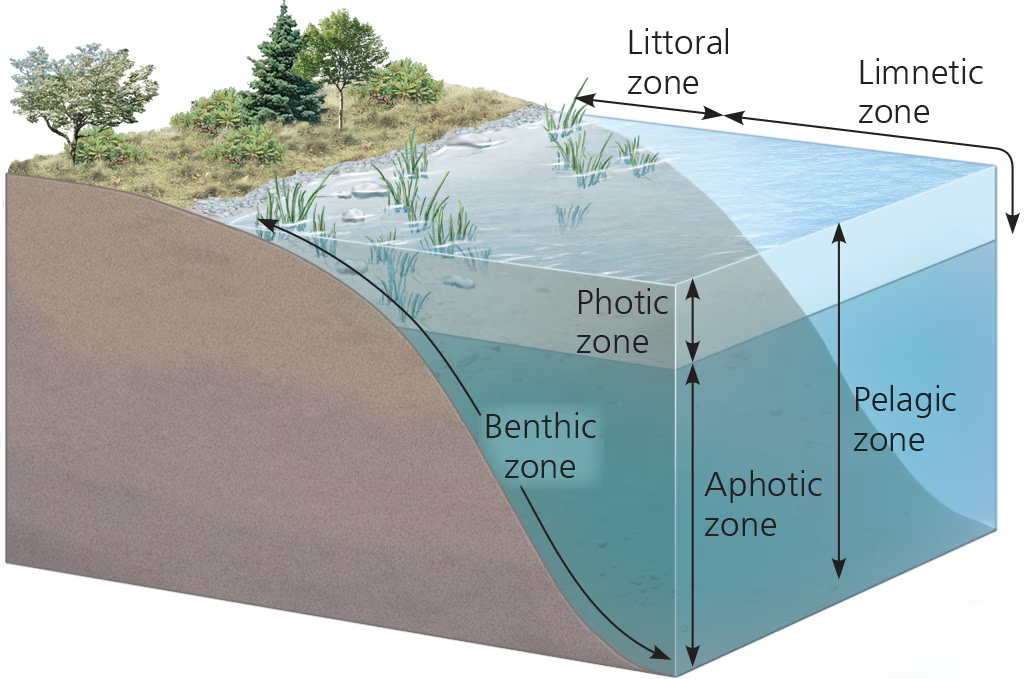
Limnetic zone (aquatic)
waters farther from shore; too deep for rooted plants
thermocline
narrow layer of abrupt temp change (in oceans / temperate lake zones)
Dispersal
movement of individuals or gametes away from their origin area / centers of high population
contributes to global distribution of organisms
Limiting Factors for Species distribution (?)
Dispersal
Biotic Factors (other species)
Abiotic Factors (temp, water, O2, salinity, sunlight, rocks/ soil)