Targeted drug delivery to the brain
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
The central nervous (CNS)
The CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord and its main role is to coordinate/control body functions through a network of nerves
The CNS is protected by a specialized structure known as the Blood Bran Barrier. The barrier tightly separates the CNS from the circulating blood. The aim is to:
Protect the brain from any harmful substance in the circulation ( microbes or toxins).
Shield the CNS and the body from the effect of chemokines.
Control the CNS environment and maintain homeostasis.
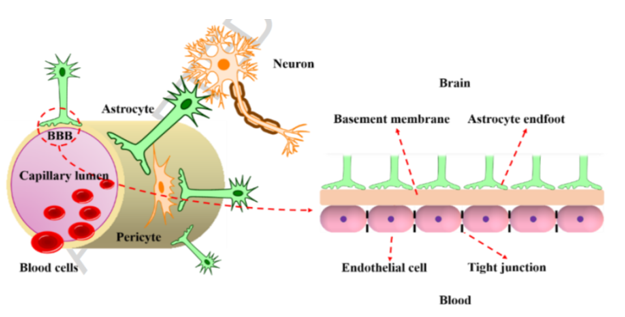
CNS
This efficient barrier function belongs to the anatomy. It consists of a basement membrane lined by endothelial cells with tight junction to control the movement of substance.
Endothelial cells with tight junction at the bottom, then the basement membrane and then astrocyte endfoot
CNS drugs
This unique anatomy and control of molecule transport into the brain created a challenge for CNs drug delivery
Different classes of pharmaceutical molecules target the CNS to achieve therapeutic response, these include:
Analgesics ( NSAID or Narcotics)
Anticonvulsants
Antiparkinsonian agents
Antiemetics
Anyxolyic, sedatives and hypnotics
CNS stimulants
General Anaesthetics
Antidepressant
Antibiotics
Targeted drug delivery to the /CNS is not an easy task this is mainly due to the presence of the BBB which protects the CNS by providing shielding effect from harmful molecules.
How does molecules move into the brain?
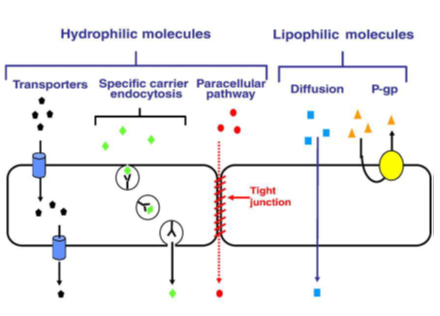
Two classes= either hydrophobic or hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Molecules
Carrier mediated for small molecules (amino acids, glucose)
Transporters (e.g. L-Dopa, Baclofen and Valproate)
Receptor-mediated transcytosis for large molecules such as hormones
Endocytosis (e.g. donepezil and Taxol)
Lipophilic Molecules crosses by Transcellular diffusion (e.g. benzodiazepines and barbiturates)
Passive diffusion (high volume of distribution and lower selectivity). Any lipophilic molecule can pass through into the CNS. It is non-specific. High volume of distribution for lipophilic molecules leading to a lower concentration into the CNS and getting to everywhere in the body. Can require an increase in dose of medication which could lead to side effects.
P-gp= Permeability glycoprotein. Recognises lipophilic molecules and collects them to kick them out. Prevents them getting into BBB
Medicinal drug properties for successful CNS delivery
The essential physical properties for a good absorption and permeability Include:
Lipophilicity
This is measured by Oil/water distribution coefficient or LogP.
If you mix water with oil in a 1:1 ratio there are two layers. Mix in potential drug molecule. Measure concentration of drug in each layer and get percentage of distribution in each layer.
If majority of molecule in oil layer so there is a high oil partition compared to the water layer then the drug is likely to be able to be delivered by passive diffusion
Optimal CNS drug permeation to the brain via passive diffusion when log P is between 1.5-2.7
However if molecule is lipophilic but doesn’t meet other specifications it won’t pass into the CNS
Molecular weight
Due to the anatomical barrier (BBB), the CNS drug molecules should be lower than others (400-500 Da). Smaller lipophilic molecules can move by passive diffusion into BBB if they fill all criteria
Hydrogen bonding
This should be kept below 5 for good CNS permeation
Increasing the number of H+ decreases drug penetration to the CNS
Medicinal Drug Properties for Successful CNS Delivery - Continued
Polar surface area
CNS drug molecules are expected to have low PSA values ( 60-70Å)
Charge
Better CNS drug penetration was evident with positively charged molecules at physiological pH(7-8).
Can adsorb into surface and pass by adsorption endocytosis
Pharmacokinetic properties
Metabolism, permeability, protein binding etc can also affect CNS drug permeation
Factors affecting CNS Drug delivery: Physiochemical properties
Lipophilicity
Molecular charge
Molecular weight
Chemical structure
Chemical conformation
Polymorph= arrangement of molecules in lattice which can have effect on properties of molecules
Factors affecting CNS Drug delivery: Bio pharm. & phk. factors
Systemic absorption
Membrane transport
Receptor/carriers affinity
Distribution
Metabolism
Clearance rate
Factors affecting CNS Drug delivery: Dosage form factors
Formulation & additives
Concentration gradient
Particle size
Dissolution rate
Factors affecting CNS Drug delivery: Biological factors
Physiological factors
Cerebral blood flow
Pathological status e.g. can change permeability of BBB
Strategies for CNS drug delivery
Invasive Techniques
Pharmacological Approaches
Physiological Methods
Miscellaneous
Invasive techniques: Intra-cerebro-ventricular (ICV) infusion
This method can be used for glycopeptide antibiotics (Vancomycin) or aminoglycoside antibiotics (gentamicin).
For large molecules that can’t get into the BBB by any other route
Diffusion of drug through a pump intrathecally into the CSF fluid
Or can be injected into a pre implanted reservoir which connects to ventricles
Intra-cerebral injection of implants (biodegradable carrier plus pharmaceutical molecules).
Direct injection into ventricles using a needle. Requires a special formulation with a biodegradable carrier loaded with the pharmaceutical molecule which allows slow release
Can be used for meningitis to get large concentration of antibiotic into brain
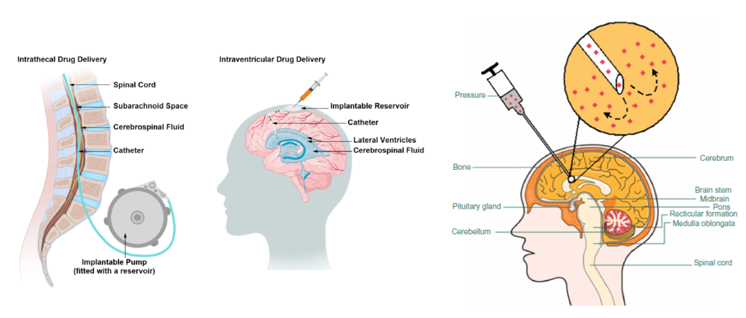
Invasive techniques: Convection enhanced delivery
Inserting a small diameter catheter into the tumour
Anti-cancer drug injected through catheter
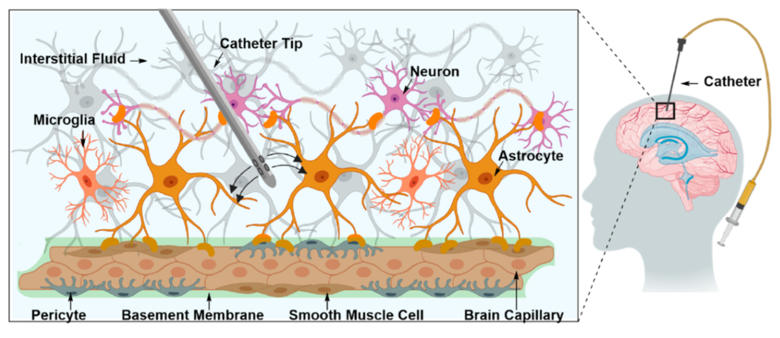
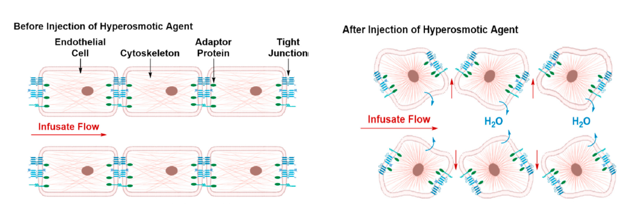
Invasive techniques: Disruption of the BBB
Causing osmotic disruption which shrinks the endothelial cells and disrupting the tight junctions to allow molecules to pass through
The disruption can be also the outcome during inflammation, hypertension and hypoxia
The shortcomings for the invasive procedures include:
The techniques are not cost effective and include anaesthesia and hospitalization.
It may lead to the spread of tumour cells
Another outcome could be a permeant damaged in the brain tissue
First picture shows tight junctions not allowing anything to pass, second picture shows tight junctions opening
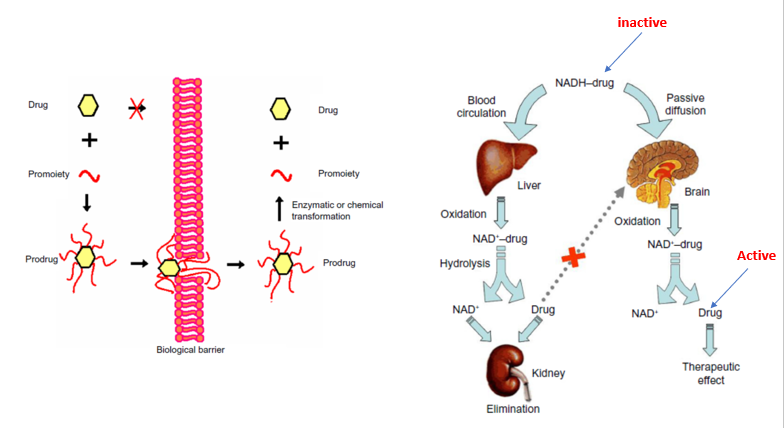
Pharmacological approaches: Chemical drug delivery
Involves increasing the drug lipophilicity by forming a prodrug to enhance CNS penetration.
Once the prodrug is inside the brain, it will be cleaved enzymatically yielding a less lipophilic / active drug molecules which will be trapped in the brain.
E.g. Ganciclovir, Benzylpenicillin and Zidovudine, Levodopa, GABA and Morphine
Figure on left:
Drug on its own cannot pass as it does not fulfil any criteria.
So it is attached to a promoiety to make it more lipophilic. It becomes a prodrug and crosses the BBB.
Once it has crossed it goes through enzymatic transformation and the active drug is released
Figure on right: Drug is attached to NADH, making it inactive
In circulation it will go to brain and metabolised at the same time
If it goes to the liver it will go through metabolism, cleaving the NADH moiety, leaving the active molecule which is excreted via kidney
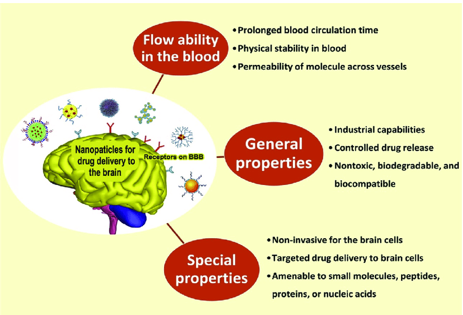
Physiological Methods (Nanoparticles and Liposomes)
Nanoparticles is another approach for targeted CNS delivery this involve
Adjusting the particle size (1-100nm) and drug - polymer ratio
Coating with surfactant, cell penetrating peptides or antibodies can enhance CNS penetration
Physiological Methods (Nanoparticles and Liposomes)
Liposomes are lipid vesicles have an aqueous core encircled by a lipid bilayer used for CNS drug delivery via passive diffusion (Taxol, Amphotericin B and Rivastigmine).
Targeted CNS delivery can be achieved by exploitation of endogenous pathway via binding with specific receptors (insulin or lipoprotein and transferrin receptors) which will facilitate drug delivery via endo/transcytosis
Brand Name | Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) | Application |
AMBISOME (Liposome) | Amphotericin B | Antifungal |
CASELYX (Liposome) | Doxorubicin | Brain Tumour |
ARICEPT (Liposome) | Donepezil | Alzheimer’s Disease |
AUROSHELL ( Nanoparticles) | Gold coated silica NPs | Solid Tumours |
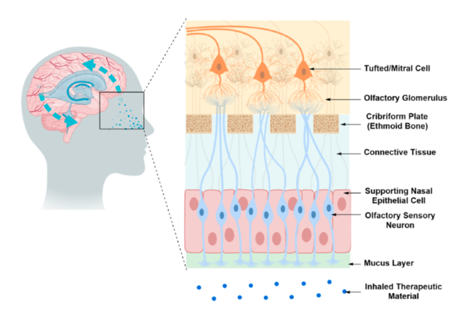
Miscellaneous approaches: Intranasal drug delivery
Intranasal drug delivery, the nasal mucosa offer direct delivery of the drug molecules to the CNS
This is a non invasive method which allows the drug to enter the CNS through or along the olfactory /trigeminal neural pathways.
Requires high solubility to deliver 20-30ul
pH and isotonicity are essential for successful drug delivery
Improper administration can send the drug to the lung or stomach
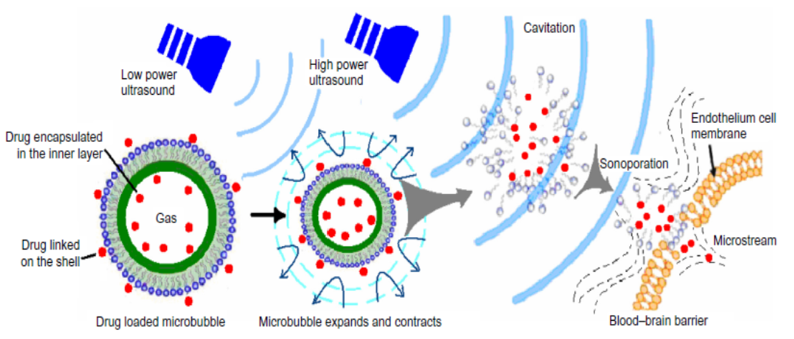
Miscellaneous approaches: Image-guided focused ultrasound
Injection of drug loaded microbubbles followed by exposure to ultrasound radiation to achieve temporarily disruption of the BBB and hence enhancing drug delivery to the brain