Chemistry Exam 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Hydrogen
H
Helium
He
Lithium
Li
Beryllium
Be
Boron
B
Carbon
C
Nitrogen
N
Oxygen
O
Fluorine
F
Neon
Ne
Sodium
Na
Magnesium
Mg
Aluminum
Al
Silicon
Si
Phosphorus
P
Sulfur
S
Chlorine
Cl
Argon
Ar
Potassium
K
Calcium
Ca
Titanium
Ti
Vanadium
V
Chromium
Cr
Manganese
Mn
Iron
Fe
Cobalt
Co
Nickel
Ni
Copper
Cu
Zinc
Zn
Bromine
Br
Krypton
Kr
Rubidium
Rb
Strontium
Sr
Silver
Ag
Cadmium
Cd
Tin
Sn
Iodine
I
Xenon
Xe
Barium
Ba
Gold
Au
Mercury
Hg
Lead
Pb
Radon
Rn
Uranium
U
What makes an atom
protons, neutrons, electrons
Atomic Number
number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Atomic Mass
the mass of an atom; the number of protons + neutrons in an atom
Molecule
Group of atoms bonded together
Ion
atom or group of atoms, has a net positive or negative charge
Isotope
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
Ionic Bond
exchange of an electron that holds atoms together
Covalent
Sharing of electrons
Cation
ion w/ positive charge; Neutral atom loses one or more electrons
Anion
ion w/ a negative charge; Neutral atom gains one or more electrons
Equation for Binding Energy
calculate difference in masses between the reactants + products
reactants minus products
convert from amu to kg (1 amu = 1.66 ×10^-27 kg)
Finally convert mass to energy using E=mc²
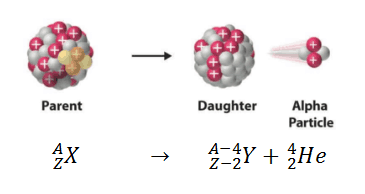
Alpha Decay
reactant (parent isotope) —> product (daughter) + 4/2 He (alpha expelled)
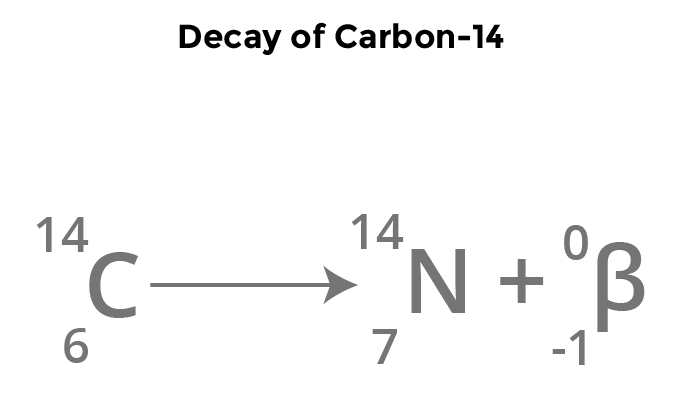
Beta Decay
1/0 n (in nucleus) —> 1/1 p (in nucleus) + 0/-1 B (Beta expelled)
Positron Emission
1/1 p (in nucleus) —>1/0 n (in nucleus) + 0/1 e (positron expelled)
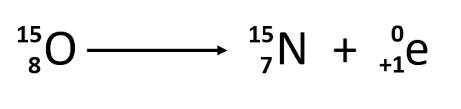
Electron Capture
0/-1 e + 1/1 p (in nucleus) —→ 1/0 n (in nucleus)
ON REACTANT SIDE
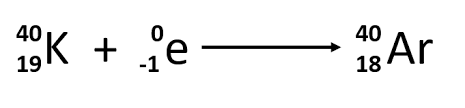
Ionic Compounds
often metal & nonmetal; anion (nonmetal), add -ide to element nature
generally solids
ex: K20: Potassium Oxide
Mg(OH)2: Magnesium Hydroxide
Transition Metal Ionic Compounds
indicate charge with Roman numerals. We don’t know transition charge so we have to indicate it.
ex: FeCl2: Iron (11) Chloride
Cr2S3: Chromium (111) sulfide
Molecular Compounds
nonmetals or nonmetals & metalloids
Element furthest left in periodic table is 1st & element closest to the bottom of group is 1st
If more than one compound can be formed from the same elements, use prefixes to indicate # of each kind of atom
last element ends in -ide
generally liquids or solids
Ex: NF3: Nitrogen trifluoride
N2Cl4: dinitrogen tetrachloride
Acid
substance that yields hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water
ex: Hydrogen chloride—> dissolved in water = hydrochloric acid
Oxoacid
acid that contains hydrogen, oxygen, and another element
HNO3: nitric acid
H2CO3: carbonic acid
Base
substance that yields hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water
NaOH: sodium hydroxide
Ba(OH)2: Barium hydroxide
Hydrates
compounds that have a specific number of water molecules attached to water
Avogadro’s Number
units in every mole: 6.022 × 10^ 23 units
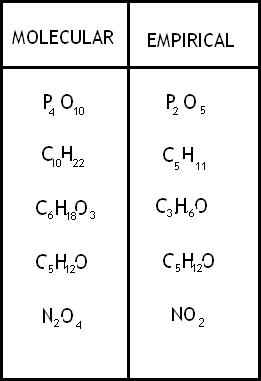
Molecular formula
shows the exact # of atoms of each element in the smallest unit of a substance
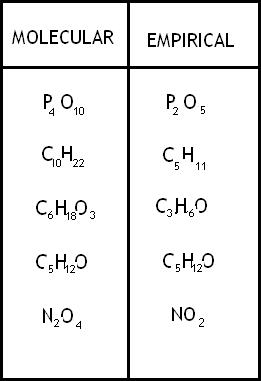
Empirical Formula
shows the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms in a substance
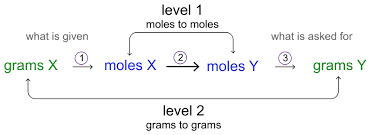
Solve Stoichiometry + Limiting Reagent Problems
need balanced rxns
convert given amount to moles
use rxn coefficients (molar ratios) to find # moles of wanted stuff
convert moles of wanted stuff to grams
Find limiting reagent
answer other Q’s