Genetics Chapter 10
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What are the criteria for a molecule to serve as the genetic material?
- Be replicated (copied and passed into daughter cells)
- Store information
-Be used to express information
- Allow variation by mutation
What is the source of variability in organisms?
Variations in the genetic material
What is the Central Dogma of molecular genetics?
DNA → RNA → protein
What was Crick's intention when he developed the Central Dogma of molecular genetics?
illustrate how the flow of genetic information occurs
Chromosomes contain both _____ and ______.
DNA and Protein
What are some exceptions to Crick's model?
- RNA viruses with double-stranded RNA genomes
- the existence of RNA as both genetic material and a catalyst (ribozymes)
- processes that deviate from the central dogma, such as the reverse transcription of RNA into DNA in retroviruses
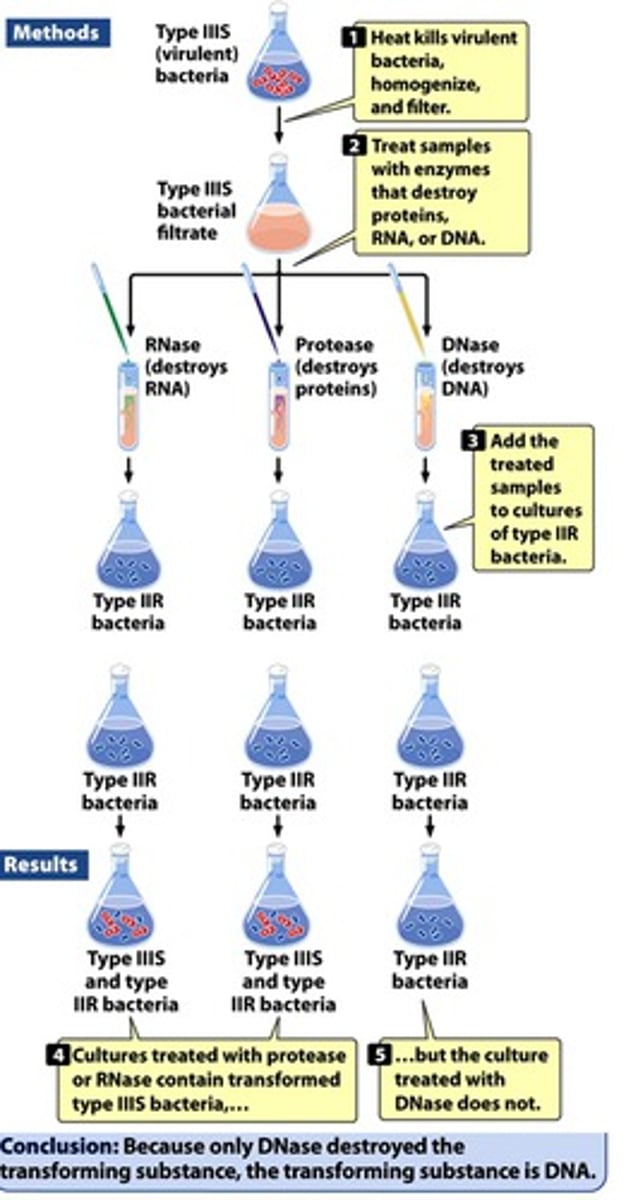
What did Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty do?
- tested whether destroying protein, DNA, or RNA would remove the transforming properties of the heat-killed bacteria
- Only treating it with DNase (an enzyme that destroys DNA) destroyed the transforming activity
- This demonstrated that DNA was the transforming material, and therefore likely to be the genetic material
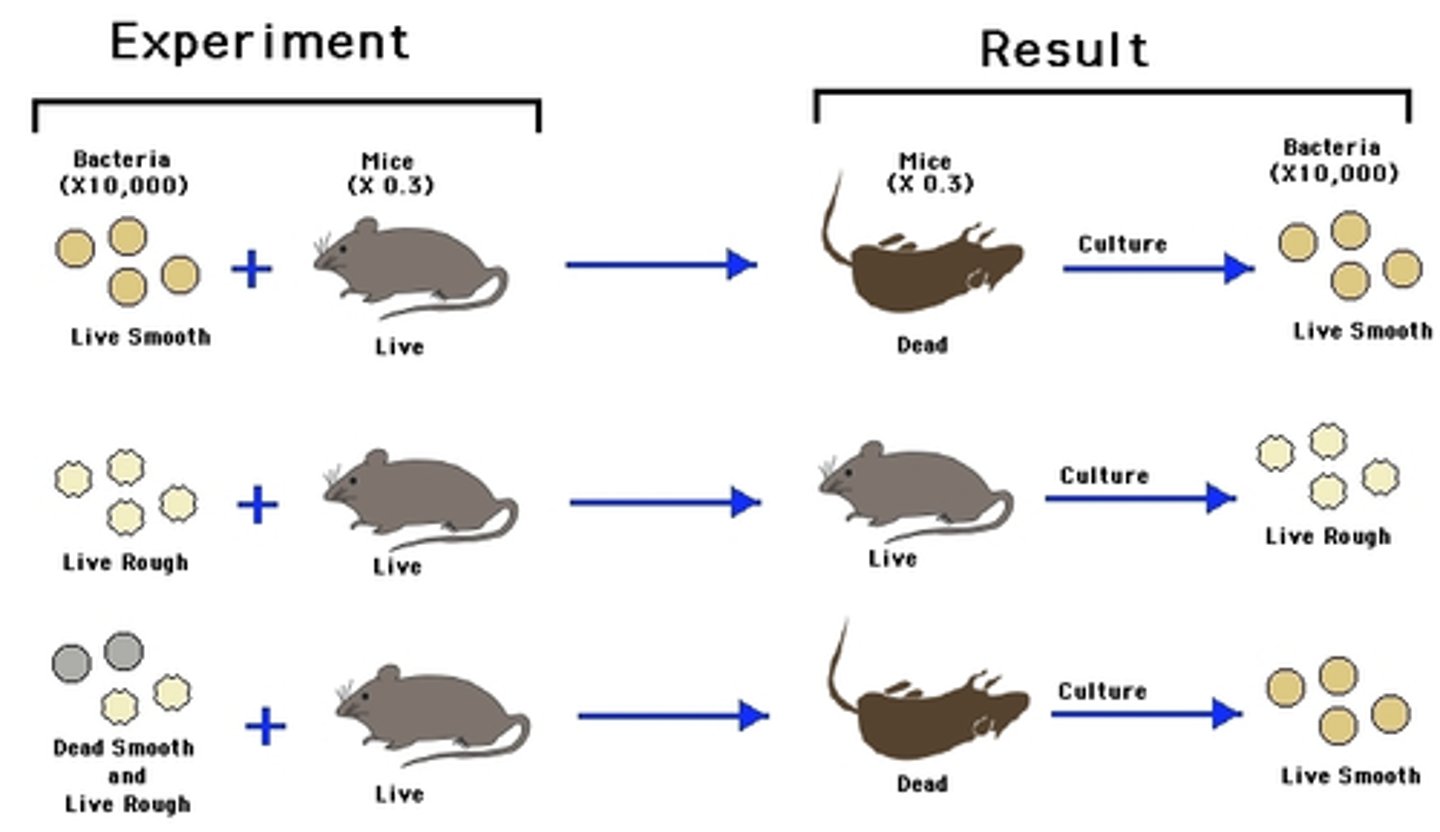
What are the findings of Frederick Griffith?
Showed that avirulent strains of Diplococcus pneumoniae could be transformed to virulence
- Speculated transforming principle could be part of a polysaccharide capsule or a compound required for capsule synthesis
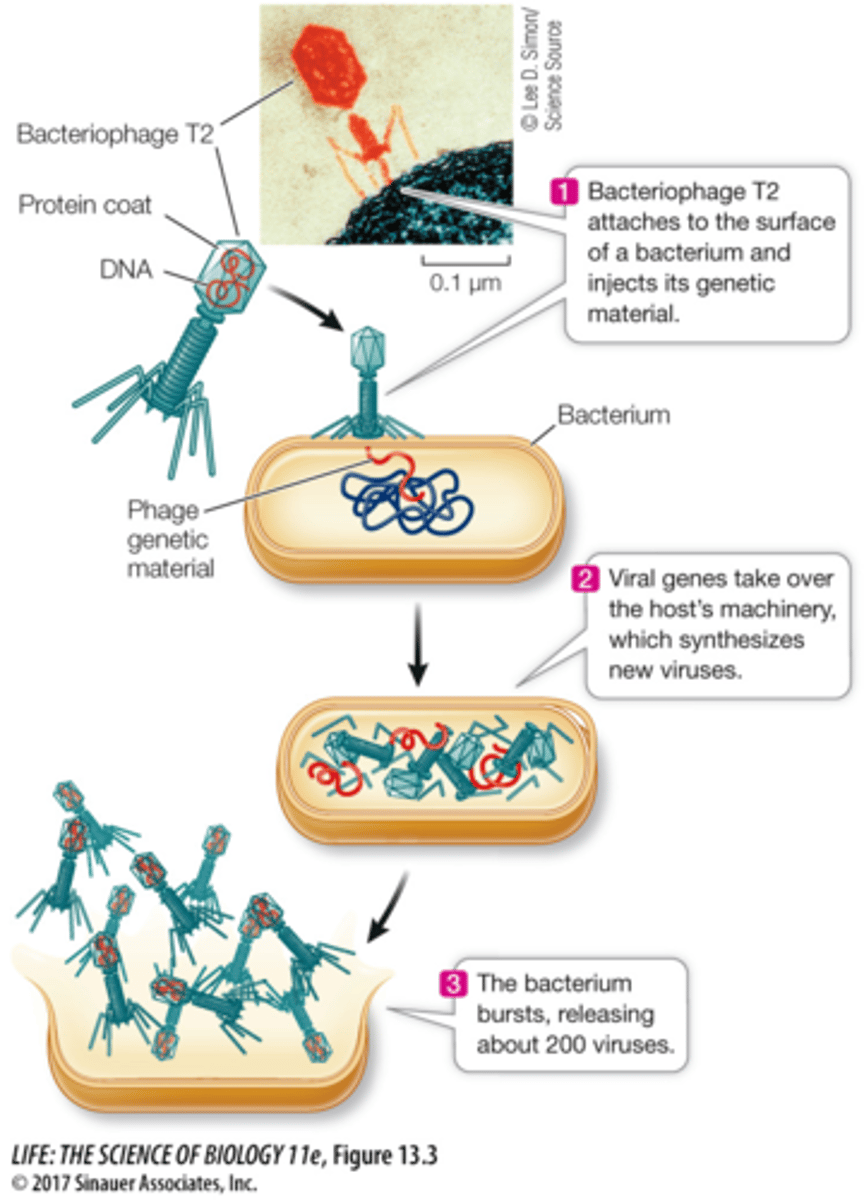
What was the Hershey-Chase experiment?
- Used Escherichia coli and bacteriophage T2 that infects i
- Used radioisotopes 32P and 35S to label DNA and protein in bacteriophage
- Demonstrated DNA enters bacterial cell during infection an directs viral reproduction
- Therefore, DNA, not protein, is the genetic material
Give reasons why many biochemists originally thought that protein was likely the genetic material.
- are major components of chromosomes
- very diverse and abundant in cells
- Lack of chemical diversity in DNA suggested it could not store extensive genetic information
Provide several examples of experimental evidence suggesting that DNA is the material of genetic inheritance.
transfection, Distribution of DNA, Eukaryotic DNA being functional in bacterial cells, Transgenic animals
What is transfection?
- E. coli cells take in viral DNA, and get infection just with the DNA
- Proves conclusively that viral DNA alone contains all necessary information for production of mature viruses
How does the distribution of DNA suggest that DNA is the genetic material?
- Close correlation between gametes and diploids in amount of DNA and number of chromosome sets
- No such correlation between gametes and diploids for proteins
How does Eukaryotic DNA being functional in bacterial cells suggest that DNA is the genetic material?
Segments of eukaryotic DNA corresponding to specific genes are isolated inserted into the bacterial DNA
- Bacteria expresses gene products from eukaryotic gene
How do transgenic animals support that DNA is the genetic material?
- Human DNA microinjected into fertilized mouse egg
-DNA encoded human β-globin gene
- Now present and expressed in mouse and transmitted to progeny
Some viruses have _______ as their genetic material, not DNA
RNA
Replication of the viral RNA is dependent on?
RNA replicase
What is reverse transcriptase?
an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of DNA from an RNA template in reverse transcription.
- used in retrovirus
Explain the composition of DNA and nucleotides.
DNA is a nucleic acid, as nucleotides are the monomer building blocks of nucleic acids
What do nucleotides consist of?
- Nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine)
- Pentose sugar
- Phosphate group
Which type of bond links nucleotides together to form a nucleic acid?
phosphodiester bonds
What type of bond forms between the complementary bases in two strands of DNA?
hydrogen bonds
What is the full name of all 5 nitrogenous bases?
- Adenine (A)
- Guanine (G)
- Cytosine (C)
- Thymine (T)
- Uracil (U)
What is the difference between purines and pyrimidines?
purines have two fused rings, with 9 nine carbons total, while pyrimidines have a six-member ring
Which bases are purines?
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
Which bases are pyrimidines?
Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and Uracil (U)
What is the difference between a nitrogenous base, a nucleoside, and a nucleotide?
- a nucleoside contains a nitrogenous base + pentose sugar
- a nitrogenous base is either a purine or pyridine that pairs
- a nucleotide has nitrogenous base + pentose sugar + phosphate(s)
What are Nucleoside Triphosphates (NTPs)?
Serve as precursor molecule during nucleic acid synthesis
- Energy released powers RNA and DNA synthesis
What does ATP and GTP stand for?
Adenosine triphosphate and guanine triphosphate
What is ATP used for?
energy "currency" for most endergonic cellular processes
What is GTP used for?
power reactions too, including translation
What is something ATP and GTP do together?
Large amount of energy involved in adding/removing terminal phosphate group
What evidence was used to elucidate the 3D structure of DNA?
X-ray diffraction: uses X-rays to reveal the atomic structure of molecules like DNA by producing a pattern of diffracted spots on a photographic plate
What does complementarity mean? (or complementary strands)
one nucleotide base in a strand will always pair with a specific partner in the opposite strand
What kind of bond is between Adenosine and Thymine?
double bond
What kind of bond is between Cytosine and Guanine?
triple bond
What did Watson and Crick propose?
semiconservative model of replication
What are the three classes of RNAs that function during gene expression?
mRNA, rRNA, tRNA
What are mRNAs?
Template for protein synthesis, carry genetic information from gene to ribosome
What are rRNAs?
Structural components of ribosomes for protein synthesis
What are tRNAs?
Carry amino acids for protein synthesis
What are some traditional non-coding RNAs in Eukaryotes?
RNA primers, Telomerase RNA, SnRNA, Antisense RNA, microRNA,and siRNA
What are RNA primers?
Short strands of RNA nucleotides bound to the template strand of DNA that act as a starting point for synthesis of the new DNA strand.
What is Telomerase RNA?
Serves as the template for the telomerase enzyme that extends the ends of chromosomes
What are SnRNAs?
small nuclear RNAs that aid in splicing mRNA
What is the function of Antisense RNA, microRNA, and siRNA?
Involved in gene regulation
What are some analytical techniques useful during DNA and RNA investigation?
- Absorption of UV light by DNA or RNA
- Denaturation and renaturation of nucleic acids
- Molecular hybridization
- FISH: Fluorescent in situ hybridization
- Electrophoresis of nucleic acids
Explain how the absorption of UV light helps investigation of DNA or RNA.
- nucleic acids absorb UV light strongly at 254-260 nanometers due to interaction between UV light and ring systems of the bases
- UV light is used to measure the concentration of DNA and RNA
- UV light is used in localization, isolation, and characterization
How does the denaturation and renaturation of nucleic acids help investigation of DNA or RNA?
DNA can denature due to heat or stress
How does molecular hybridization help the investigation of DNA or RNA?
via denaturation and renaturation of nucleic acids
How does FISH help the investigation of DNA or RNA?
Uses fluorescent probes to monitor hybridization, allows us to visualize specific sequences on a chromosome
What are probes?
nucleic acids that will hybridize only with specific chromosomal areas
How does electrophoresis help the investigation of RNA or DNA?
Separates DNA and RNA fragments by size
- Smaller fragments migrate through gel at faster rate than large fragments
Agarose gel restricts migration of ______ molecules more than it restricts ______ ones
larger, smaller
What does antiparallel mean?
The subunits of the sugar-phosphate backbones run in opposite directions of each other.
You should know that DNA has ___________.
directionality
What determines directionality (3' vs. 5' end)?
the free chemical groups at the ends of the sugar-phosphate backbone, specifically a phosphate group attached to a 5' carbon at the 5' end and a hydroxyl group attached to a 3' carbon at the 3' end
What are Chargaff's base pairing rules?
- Amount of A is proportional to T
- Amount of C is proportional to G
- Percentage of C + G does not necessarily equal percentage of A + T
Describe Watson and Crick's DNA model.
-Double helix
- Two anti-parallel strands connected by base pairing
- Stacked nitrogenous bases on the interior of the helix
- Phosphate-sugar backbone on the outside of helix
- Base paring rules: A-T and C-G
How is the base-pairing rule reflected in the data from Chargaff's experiment?
adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine in the DNA molecule, demonstrating a 1:1 ratio
What pieces of evidence allowed Watson and Crick to determine the base-pairing rules?
Chargaff's base pairing rules and Franklin's x-ray diffraction
How did Chargaff's rules and Franklin's X-ray diffraction help Watson and Crick determine the base pairing rules of DNA?
Chargaff's rules: amount of A is proportional to T, andamount of C is proportional to G
Franklin's X-ray diffraction image showed the width of the double helix was constant
- Only purine + pyrimidine would give constant width▪
Is Watson and Crick's 3D model of DNA (B-form DNA) the only 3D form in which DNA can exist?
no, DNA can exist as A-DNA, Z-DNA,
Describe how determining the 3D structure of DNA provided insight for the function of DNA.
- complementary base pairs create a perfect template for copying
- unwinding and separation ensures genetic fidelity from one cell generation to the next.
Briefly explain the semiconservative model of DNA replication.
During replication, the two strands of the helix unwind and separate. Each original (parent) strand then serves as a template for building a new, complementary (daughter) strand, creating two new DNA molecules, each containing one old and one new strand. This process ensures genetic fidelity from one cell generation to the next.
How do DNA and RNA differ?
- the sugar in RNA is ribose instead of deoxyribose
- RNA has uracil in place of thymine.
- RNA is a single strand of nucleotides, in contrast to the double-stranded structure of DNA
What are the major classes of RNA that participate in gene expression?
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
What is the function of microRNA?
downregulate gene expression