human body plan
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 1 - human body plan
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
what are the three anatomical planes?
horizontal (transverse) plane
midsaggita (median) plane
frontal (coronal) plane
define a plane
this is an imaginary division of a body/body part
midsagittal (median) plane
divides the body into EQUAL left and right parts
coronal
frontal plane, divides the body into posterior (front) and anterior (back) parts
transverse
horizontal plane, divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior ( lower) parts
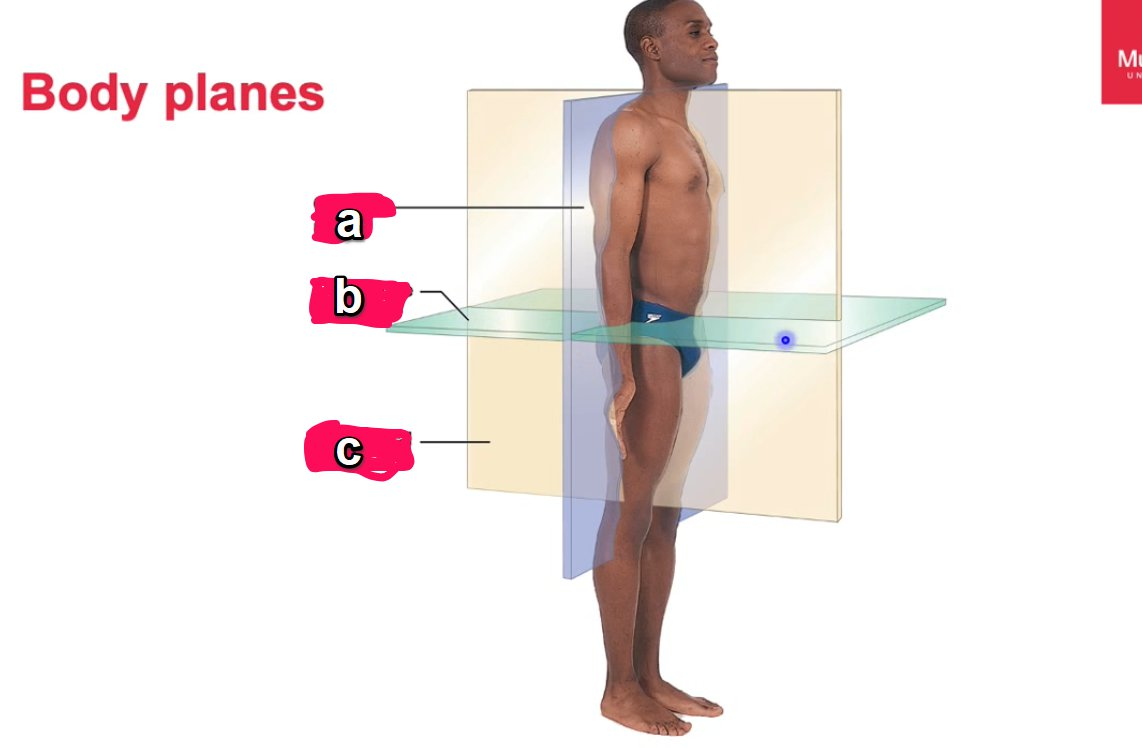
label the plane
a - midsaggital (median)
b- horizontal (transverse)
c- coronal (frontal)
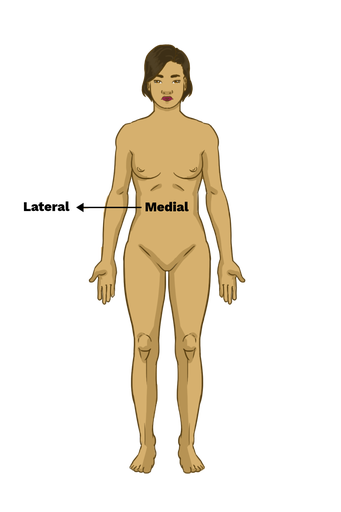
lateral
away from the mid-line
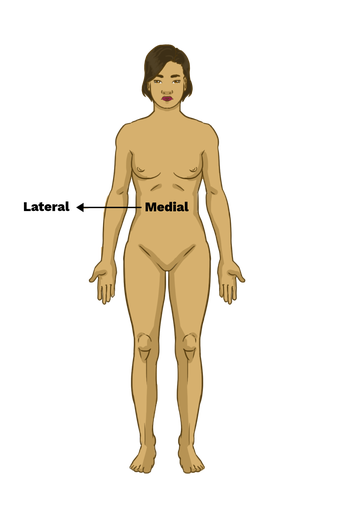
medial
close to the mid- line
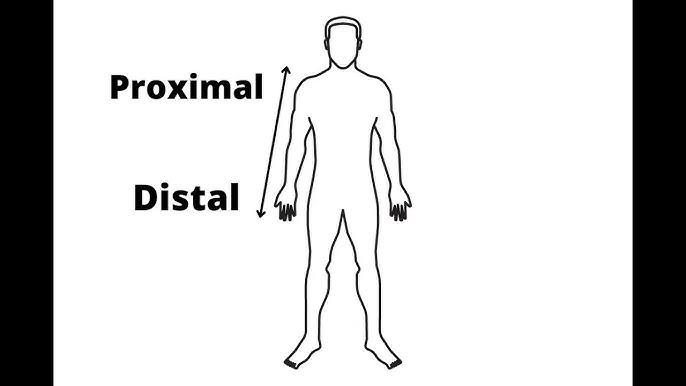
proximal
how close a limb is to the trunk
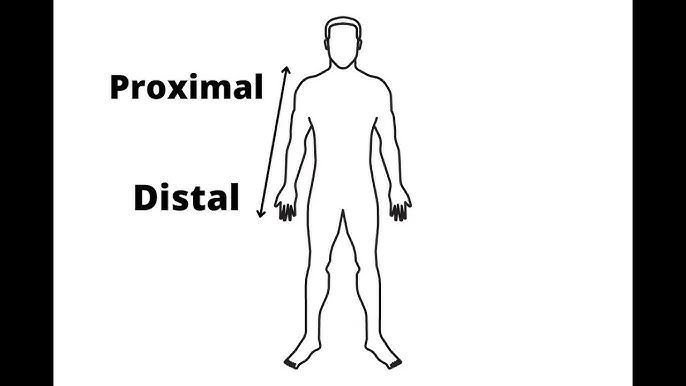
distal
how far a limb is from the trunk
superior
towards the top, closer to the head
inferior
towards the bottom, the feet
anterior
towards the front
posterior
towards the back of the body
dorsal
at the back side of the human body ( eg spine is in the dorsal side of body)
often used to describe body cavity
ventral
ventral is on the belly side of the human body
eg the umbilicus( navel, belly button) is on the ventral side of the body
caudal
at the rear or tail end ( so the abdomen is caudal to the head)
cranial
at the head end
the head is cranial to the trunk
deep
on the inside, underneath another strutcure
muscles are deep to the skin
superficial
on the outside
the external edge of the kidney is superficial to its internal structure
what are the four key principles of ethics
respect for human autonomy
benefience ( doing good)
non - maleficience ( avoiding harm )
justice and fairness in medical treatment
cephallic
head
deltoid
shoulder
digital / phalangeal
toes, fingers
patellar
kneecap
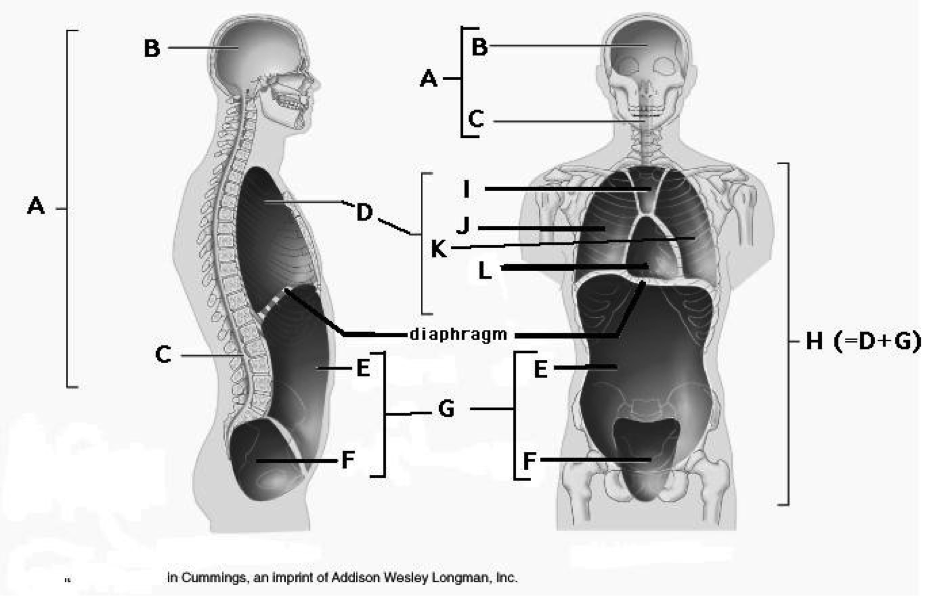
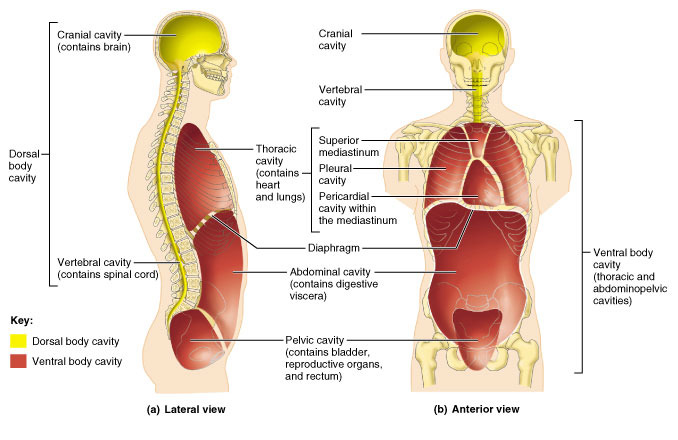
body cavities
superior body cavities
cranial cavity - formed by cranial bones
vertebral cavity - formed by vertebral column
inferior body cavities
thoracic : the superior cavity
abdominopelvic ; the inferior cavity, physcially seperated by diaphragm
superior body cavities
cranial - cranial bones
vertebral - vertebral colum
inferior body cavities
thoracic : the superior cavity
abdominopelvic : the inferior cavity
physically seperated by diaphragm
thoracic cavity
superior cavity
pericardial cavity
pleural
mediastinum
diaphragm
abdominopelvic cavity
the inferior cavity
physically separated by diaphragm
abdominal cavity
pelvic cavity
major organ systems & their associated functions
R - reproductive system
U - urinary system includes bladder, kidney, ureter
N - nervous system includes brain and spinal chord
M - muscular system
R - respiratory system - lungs, bronchi, trachea
S - skeletal system - bones
L - lymphatic system - lymph nodes, spleen
I - integumentary system - skin, hair and nails
D - digestive system - stomach, pancrease, liver
E - endocrine system - hypothalumus, glands
C - circulatory system - heart and blood vessels
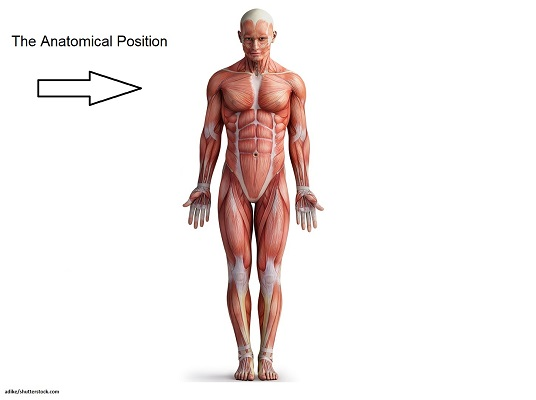
anatomic position characteristics
standing upright
palms facing forward, thumbs pointing away from body
feet parallel to floor
head level and looking forward
arms at side of the body
think of SAP
standing upright
arms at side of body
palms facing forward
dorsal
at the back side of the human body
ventral
at the belly side of the human body
caudal
at the rear/tail end
the forearm is — to the elbow
distal
the is — to the foot
proximal
the nose is —— to the ears
medial
thumb is —— to the pinky finger
lateral
the skin is —— to the muscles
superficial
the brain is —— to the spinal chord
superior
the wrist is —— to the fingers
proximal
the stomach is — to the diaphragm
inferior
the ribs are —— to the lungs
superficial
the fingers are —— to the elbow
distal
the shoulder is —— to the hand
proximal (torso)
eyes are —— to the mouth
superior
the toes are —— to the heel
distal
the liver is ——— to intestines
superior