Psychology Test #1
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Ann went to the pool for swimming practice. she jumped into the pool and found that the water was cold. however after spending time in the cold water, she no longer felt cold temperature this best represents…
Sensory Adaptation
The of Dreams is when the brain tries to make sense of random brain activity that occurs during sleep by combining the activity with memories
Activation Synthesis Theory
There are many ways of altering consciousness including the use of drugs for recreational purposes. The category of drugs that decreases the function of the nervous system and interfere with motor control, motor coordination, reaction time, and slurred speech are…
Depressants
Stacy has been struggling to fall asleep lately. no matter how early she goes to bed, she cannot fall asleep for hours. once she does fall asleep, she is only able to get a few hours of sleep before she must start her day. based on Stacy symptoms she most likely has…
Insommnia
Which of the following is NOT considered a stimulant?
Alcohol
Ryan smoked cannabis for the first time last month. Since then, he has smoked every other day and found that he needs to increase the amount he smokes to feel as high as he did before this is:
Drug intolerance
What is the main difference between frauds Interpretation of dreams and the activation synthesis hypothesis?
The activation synthesis hypothesis suggests that the dreams are the result of random brain signals that the brain is making sense of activity, whereas Fraud did NOT
witch of the following is true about sleep?
All of the above
According to humans and animals sleep to avoid Being hunted when predators are most active
adaptive theory
According to we must sleep in order to physically replenish chemicals and repair cell damage within the body
Restorative Theory
An experiment study two types of variables are used. one is a variable that is manipulated which is the . and the other variable of interest that is measured to see what effect the manipulation had on it. That is the .
independent variable ; dependant variable
I created a new job to treat migraines called the “migraine-be-gone”. I want to conduct an experiment study so that I can hopefully say my new drug causes migraines to go away. Participants in the experimental group will take the drug daily. What should I give participants in the control group?
Nothing or a sugar pill
For my experiment with “Migraine be gone” I need to make sure I use in order to maximize the likelihood that the experimental and control groups are similar before any treatment begins.
Random assignment
What is the difference between structuralism and functionalism?
Structuralism focuses on understanding the individual building blocks of the mind.
functionalism focuses on how the mind allows people to adapt work and play
Oscar wants to study how elementary school plays at recess. to do this he decides that he will hide somewhere on the playground and record his observation of the children. his methods are an example of
Naturalistic observation
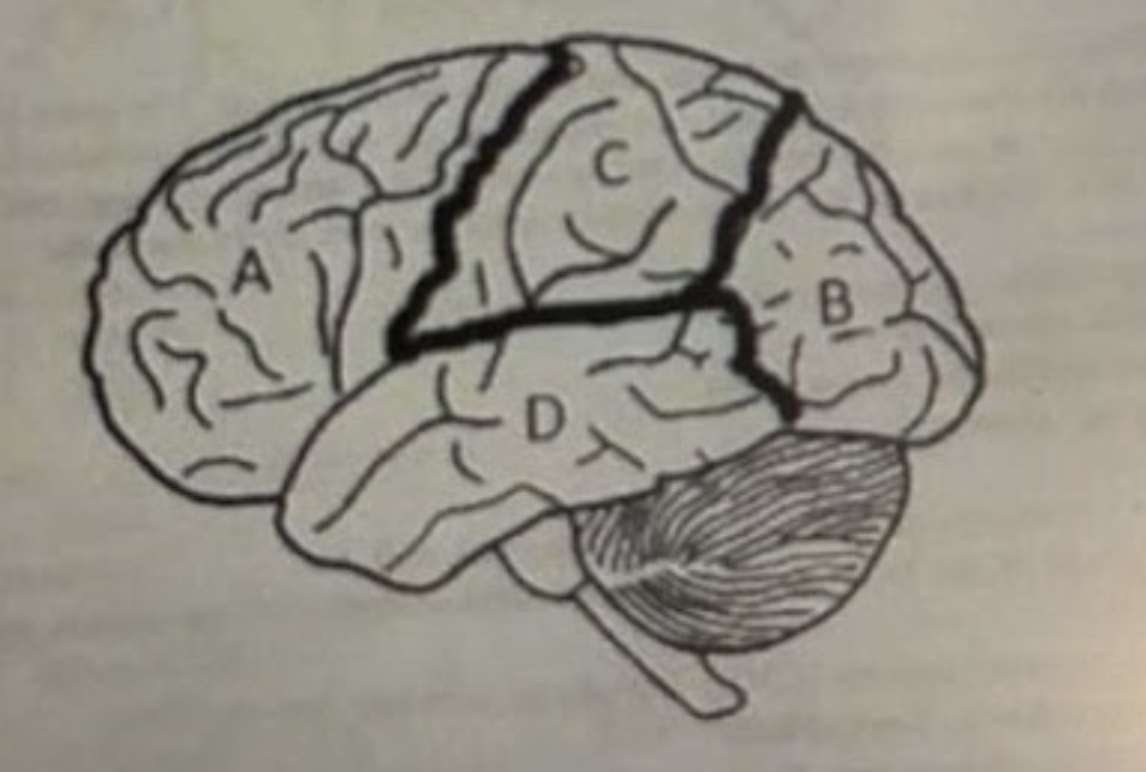
A is?
Frontal lobe
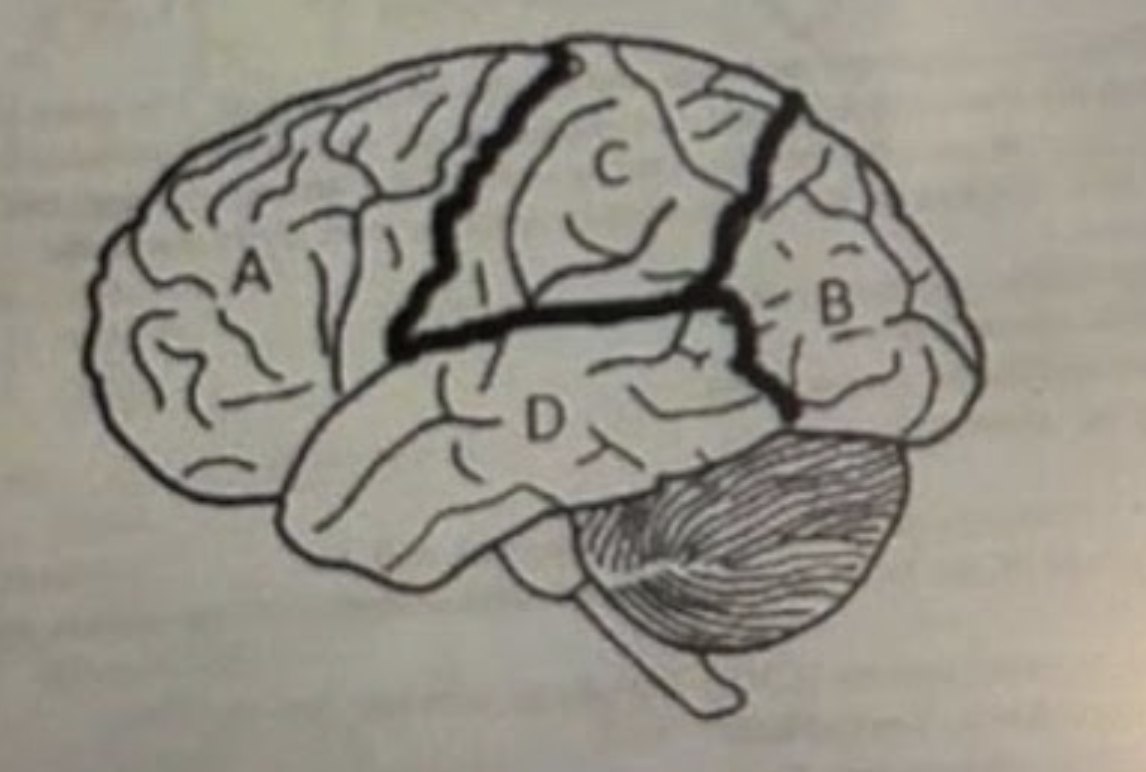
B is?
Occipital lobe
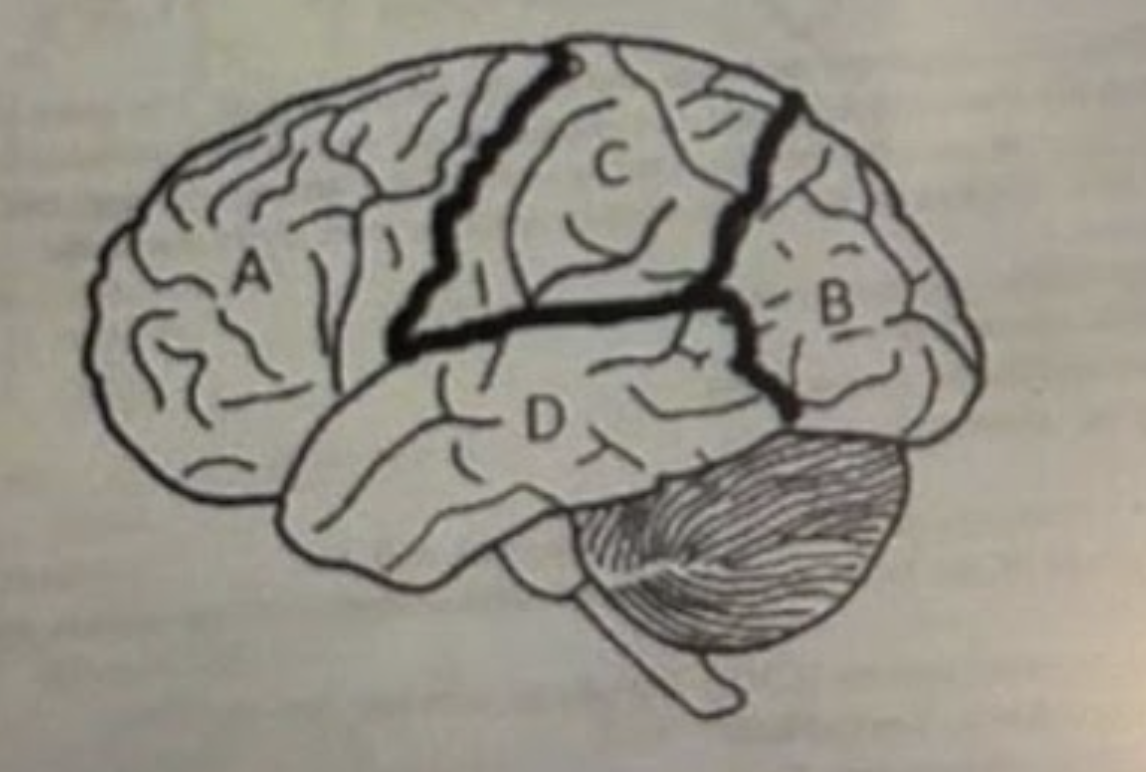
C is?
Parietal
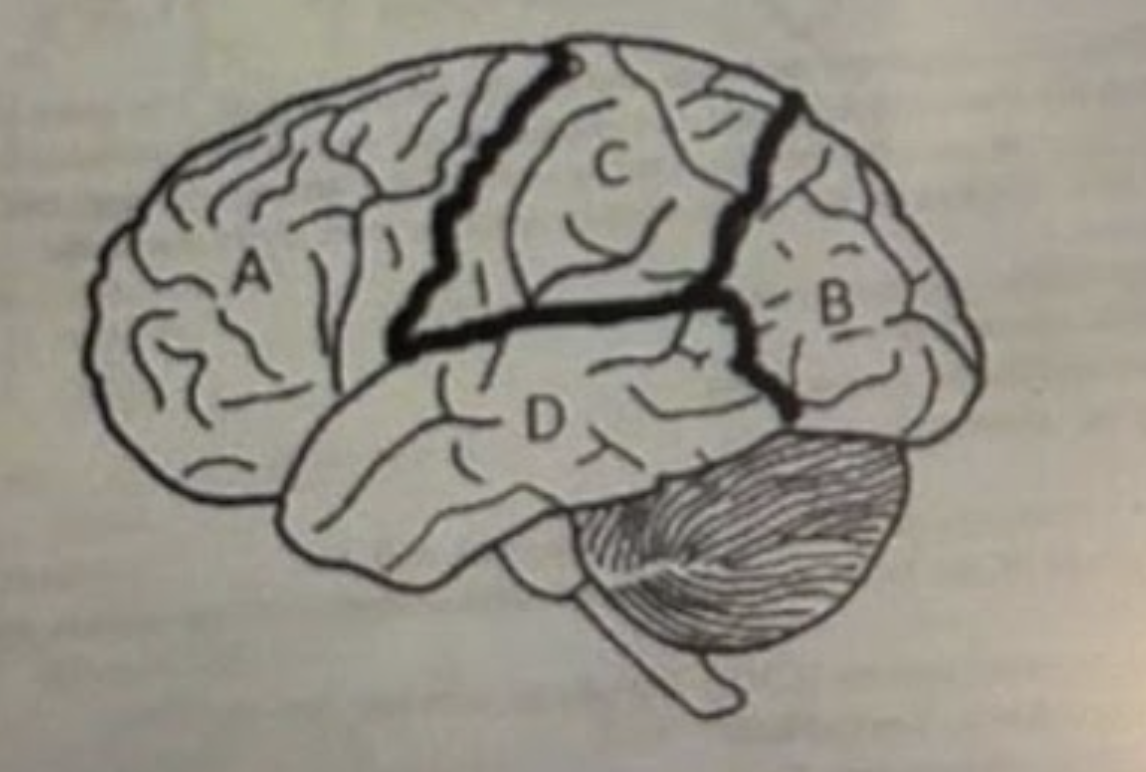
D is?
Temporal lobe
Which of the following methods of thought is characterized by looking at items in the environment as a “unorganized whole”
Gesalt
Which of the following sequences reflects the order in which a signal generally travels through neuron
Dendrite → Soma → Axon → terminal buttons
Dendrites
receive messages
Soma (cell body)
Integrates input
Myelin sheath:
insulates axon for faster conduction
Synapse:
gap between sending axon and receiving dendrite
terminal buttons:
release neurotransmitters
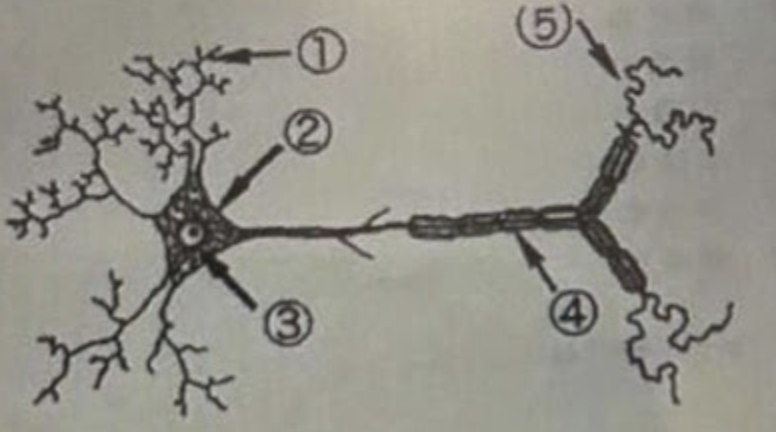
1 is the….
Dendrite
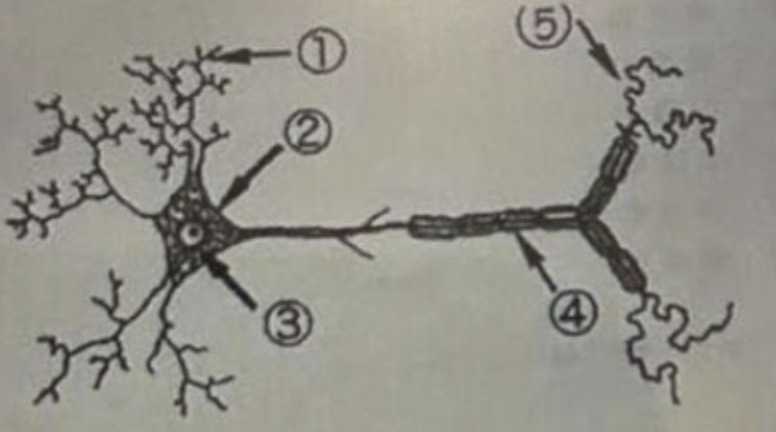
4 is the…..
Axon
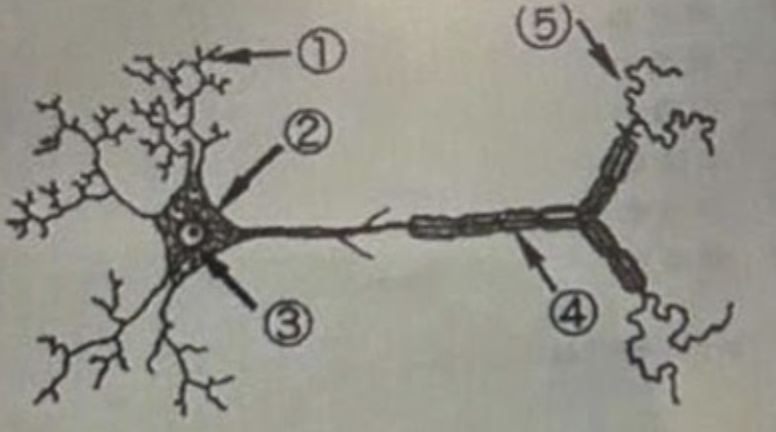
2 and 3 are pointing at the…..
Soma/cell body
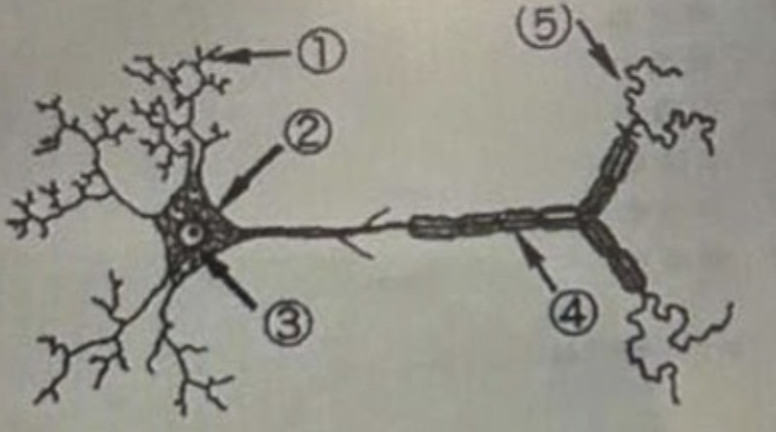
5 is the….
Terminal button
Axon
Passes messages away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands
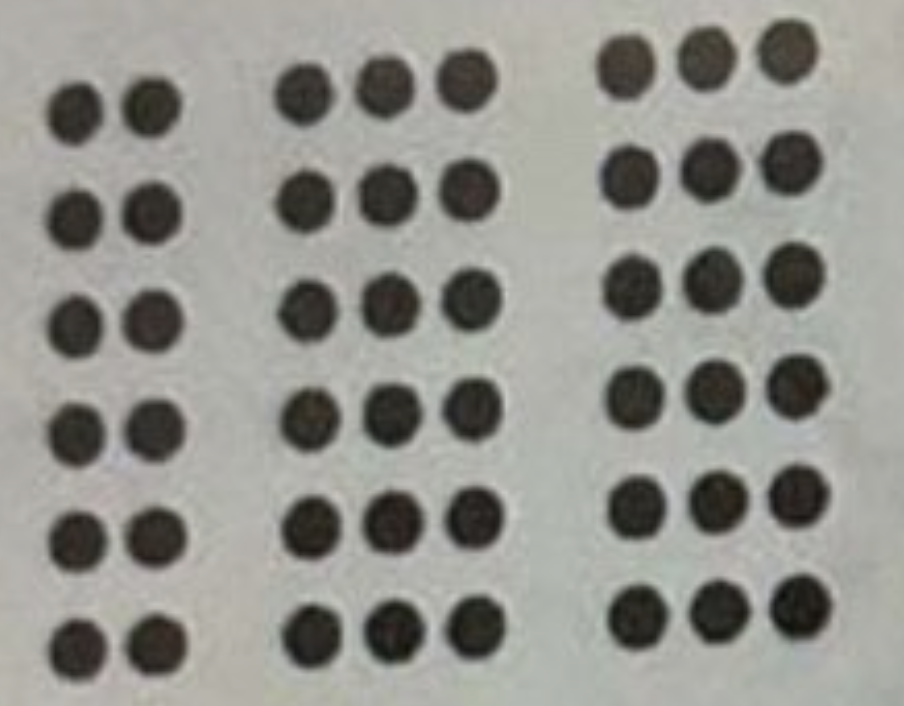

The image above best represents the Gestalt principle of…
Proximity
Amplitude
Loudness
Frequency
Pitch
are retinal cells that respond to low light and result in black and white perception, while are retinal cells that respond to higher levels of light and results in color perception
Rods ; Cones
Sam is driving on a snow covered road, and her car begins to slide. the quick behavioral response and the increased heart rate and respiration she experiences are most likely due to the nervous system. the feeling of relief and decrease in her heart rate and respiration once she has the car under control again are most likely due to the nervous system.
Sympathetic ; parasympathetic
The consist of the brain and spinal cord, the consist of the nerve cells outside of the brain and spinal cord (Also contains somatic and automatic nervous systems)
Central nervous system (CNS) ; Peripheral nervous system (PNS
In a neuron the captures the incoming chemical signal,
while the release the chemical signal.
dendrites ; terminal buttons
Structuralism
Mind only
Functionalism
Behavior + mind
Behaviorism
only behaviors
Gestalt
Undefined whole
Freud is known for what?
Subconscious/unconscious
Humanism
Stresses on human capacity for self-fulfillment, roles of consciousness, self-awareness, and decision making
Existentialism
Stresses on free choice and holds people responsible for the choices
Social Psychology
study of groups, social roles, and rules of social actions and relationship
Cultural Psychology
study of cultural norms, values, and expectations
Psychodynamic
Development of sense of self, motivation for social/interpersonal relationships
Behavioral
Classical and operant conditioning, concept of reinforcement, focus on observable behavior
Humanistic
The ability of the individual to direct and control his or her own life, free will, self-actualization
Cognitive
Perception, memory, intelligence, thought processes, problem solving, language, learning, the role of the brain and nervous system
Sociocultural
Relationship between social behavior and the contexts of family, social groups, and culture
Biopsychological
Influences of genetics, hormones, and the activity of the nervous system on human and animal behavior
Evolutionary
The biological bases for universal mental characteristics that are shared by all humans
Psychologist (PhD)
behavioral therapy, no meds
psychiatrist (MD)
meds
Humanism
Stresses on human capacity for self-fulfillment, roles of consciousness, self-awareness, and decision making
Existentialism
Stresses on free choice and holds people responsible for the choices
Social Psychology
study of groups, social roles, and rules of social actions and relationship
Cultural Psychology
study of cultural norms, values, and expectations
Psychodynamic
Development of sense of self, motivation for social/interpersonal relationships
Behavioral
Classical and operant conditioning, concept of reinforcement, focus on observable behavior
Humanistic
The ability of the individual to direct and control his or her own life, free will, self-actualization
Cognitive
Perception, memory, intelligence, thought processes, problem solving, language, learning, the role of the brain and nervous system
Sociocultural
Relationship between social behavior and the contexts of family, social groups, and culture
Biopsychological
Influences of genetics, hormones, and the activity of the nervous system on human and animal behavior
Evolutionary
The biological bases for universal mental characteristics that are shared by all humans
Psychologist
PhD: behavioral therapy, no meds
psychiatrist
MD
Experiment
A deliberate manipulation of a variable to see whether corresponding changes in behavior result, allowing the determination of cause-and-effect relationships
Operationalization
specific definition of a variable of interest that allows it to be directly measured
Independent variable
what is changed
Dependent variable
what I expect to change
Experimental group
who gets it
Control group
who doesn’t get it (placebo)
Afferent neurons
Neurons that transmit messages from sensory receptors to the spinal cord and brain.
- When you touch a hot stove these neurons tell your brain "this hurts"
Efferent neurons
neurons that transmit messages from the brain or spinal cord to muscles or glands, also called motor neurons
- When this hurts, you move your hand from the hot stove
Excitatory synapse
neurotransmitter that causes the receiving cell to fire
Inhibitory synapse: neurotransmitter that causes the receiving cell to stop firing