MEC320 - 2024-25 Paper Qs
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the physical meaning of the local derivative?
(a) The time rate of change following a moving fluid element.
(b) The time rate of change at a fixed point.
(c) The time rate of change due to the movement of the fluid element from one location to another in the flow field where the flow properties are spatially different.
(d) None of the above.
(b) The time rate of change at a fixed point.
Select the correct answer that mathematically describes a three-dimensional incompressible flow, steady state or transient.
a)\frac{\partial\rho}{\partial t}+\left[\frac{\partial u}{\partial x}+\frac{\partial v}{\partial y}+\frac{\partial w}{\partial z}\right]=0
b)\frac{\partial u}{\partial x}+\frac{\partial v}{\partial y}+\frac{\partial w}{\partial z}=0
c)\frac{\partial u_i}{\partial x_i}=0,\quad i=1,2
d)\frac{\partial u}{\partial x}+\frac{\partial v}{\partial y}=0
b)\frac{\partial u}{\partial x}+\frac{\partial v}{\partial y}+\frac{\partial w}{\partial z}=0
What is the Stokes relationship?
(a) Relationship between inertial and viscous forces.
(b) Relationship between surface and volumetric forces.
(c) Relationship between viscous stresses, and velocity gradients.
(d) Relationship between pressure and viscosity.
(c) Relationship between viscous stresses, and velocity gradients.
Consider the flow of an incompressible fluid between two infinite horizontal parallel plates placed at y=0 and y=H. The plates are fixed and the flow is driven by a constant pressure gradient in the streamwise direction − 𝑑𝑝/𝑑𝑥 = 𝐺 > 0. The laminar velocity profile inside the channel is given by 𝑢(𝑦) = 𝐺/2𝜇 𝑦(𝐻 − 𝑦). What is the correct expression for the shear stress (𝜏) at the centerline?
a)\tau=\mu\frac{GH}{2}
b)\tau=-\frac{GH}{2\mu}
c)\tau=\frac{GH}{2\mu}
d)\tau=0
d)\tau=0
What is the definition of 𝑢 +?
a) The ratio of the friction velocity to velocity normal to the wall
b) The ratio of velocity normal to the wall to the friction velocity
c) The ratio of the friction velocity to velocity parallel to the wall
d) The ratio of velocity parallel to the wall to the friction velocity
d) The ratio of velocity parallel to the wall to the friction velocity
What is Reynolds stress?
a) Stress due to velocity fluctuations
b) Tangential component of pressure
c) Stress due to pressure fluctuations
d) Normal component of viscosity
a) Stress due to velocity fluctuations
What do k and ε stand for?
a) Turbulent kinetic energy and its dissipation rate per unit mass
b) Turbulent kinetic energy and turbulent diffusivity
c) Turbulent diffusivity and its dissipation rate per unit mass
d) Turbulent kinetic energy and mass transfer
a) Turbulent kinetic energy and its dissipation rate per unit mass
Express the turbulence velocity scale in terms of k and ε.
a)\quad\epsilon^{1/2}
b)\quad\left(\frac{\epsilon}{k}\right)^{1/2}
c)\quad k^{1/2}
d)\quad\left(\frac{k}{\epsilon}\right)^{1/2}
c)\quad k^{1/2}
Let Cμ be a dimensionless constant and ρ be the density of the flow. Express the dynamic eddy viscosity in terms of turbulence kinetic energy (k) and a turbulence time scale (𝜏).
a)\quad\frac{\rho C_{\mu}k^2}{\tau}
b)\quad\frac{\rho C_{\mu}k}{\tau}
c)\quad\rho C_{\mu}k\tau
d)\quad\frac{\rho C_{\mu}\tau^2}{k}
c)\quad\rho C_{\mu}k\tau
The Reynolds stress turbulence model is particularly useful if the flow is:
a) Separated from the surface
b) Dominated by swirl
c) Three-dimensional
d) Unsteady
b) Dominated by swirl
Select the incorrect statement.
a) The low-Reynolds number model requires no wall function.
b) The low-Reynolds number model is for low-Reynold number flow only.
c) The low-Reynolds number model requires 𝑦 + < 1.
d) The low-Reynolds number model considers viscous effect near the wall.
b) The low-Reynolds number model is for low-Reynold number flow only.
Which of these is an advantage of the Finite Difference Method over the Finite Volume Method?
a) Conservativeness
b) Higher-order
c) Stability
d) Complex problems
b) Higher-order
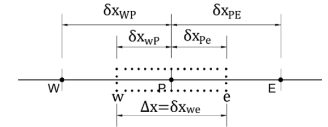
Consider the following stencil.
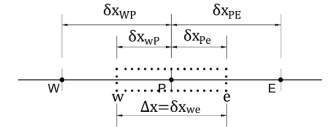
The discretized form of (𝑑𝜙/𝑑𝑥)𝑒 using the central differencing scheme is:
a)\quad\frac{\phi_{P}+\phi_{E}}{\delta x_{PE}}
b)\quad\frac{\phi_{E}-\phi_{P}}{2}
c)\quad\frac{\phi_{E}-\phi_{P}}{\delta x_{PE}}
d)\quad\frac{\phi_{P}+\phi_{E}}{2}
c)\quad\frac{\phi_{E}-\phi_{P}}{\delta x_{PE}}
The numerical convection schemes are often upwind biased for_________.
a) Higher accuracy
b) Better stability
c) Low numerical diffusion
d) Ease of calculation
b) Better stability
The number of discretized equations is equal to the number of __________.
a) Discretized internal cells
b) Boundary conditions
c) Unknowns
d) Boundary-side elements
a) Discretized internal cells
The CFL number should normally be kept
a) >1
b) <1
c) >10
d) <10
b) <1
The SIMPLE algorithm is a ____________.
a) Weighted average method
b) Predictor-corrector method
c) Euler method
d) Newton method
b) Predictor-corrector method
CFD packages solve the algebraic equations of flow using ____________ method.
a) Direct
b) Analytical
c) Trial and error
d) Iterative
d) Iterative
The aim of the mesh independence study is to understand the
a) Effect of turbulence model
b) Convergence of iteration
c) Effect of mesh resolution
d) Effect of convection schemes
c) Effect of mesh resolution
A solution is ideally converged if _________.
a) the results match with the exact solution
b) the results for two consecutive iterations are the same
c) the residuals fall below some pre-set criterion
d) the results for different boundary conditions are the same
c) the residuals fall below some pre-set criterion