Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Sensory Neurons
Neurons that deliver information to the CNS.
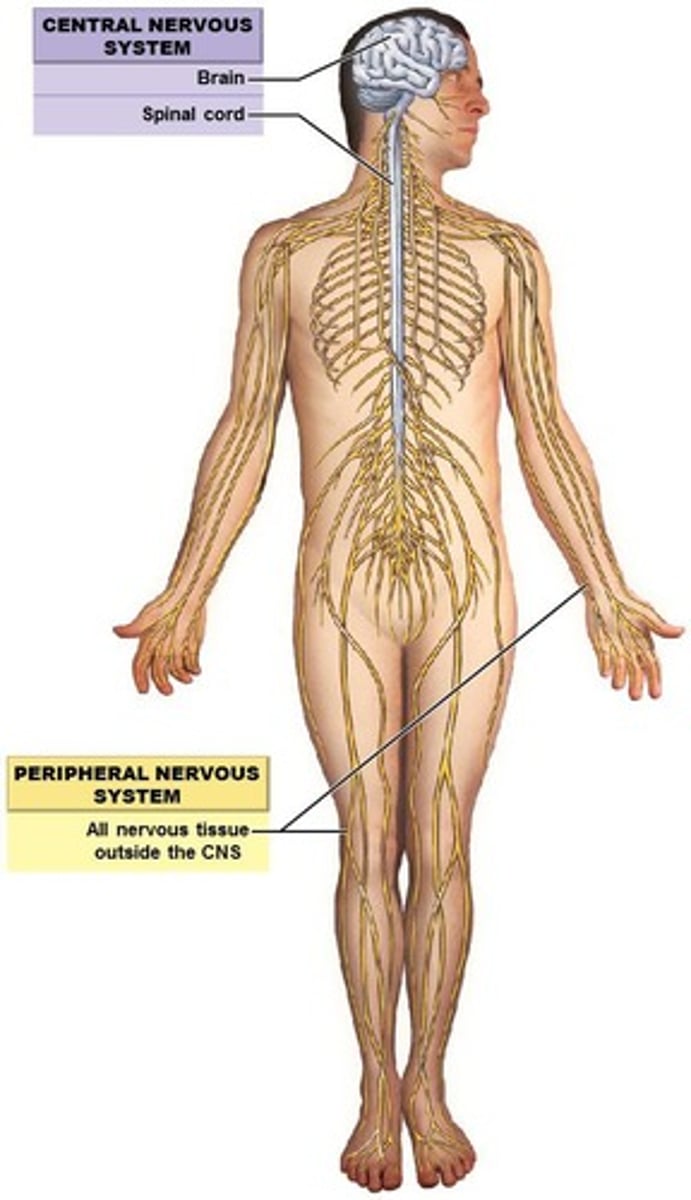
Motor Neurons
Neurons that cause the body to respond in various ways.
Ascending Tract
Sensory tract that delivers information to the brain.
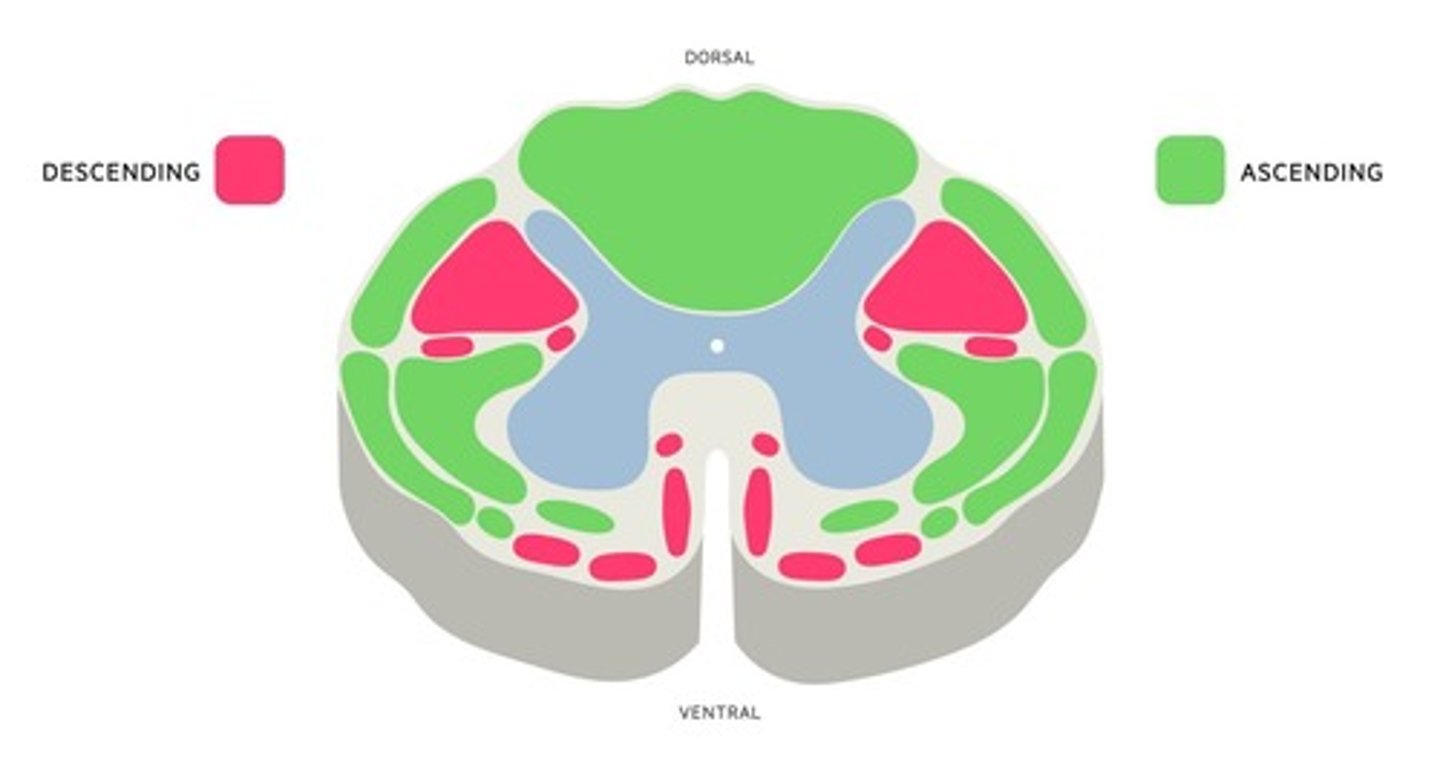
Descending Tract
Motor tract that delivers information to the periphery.
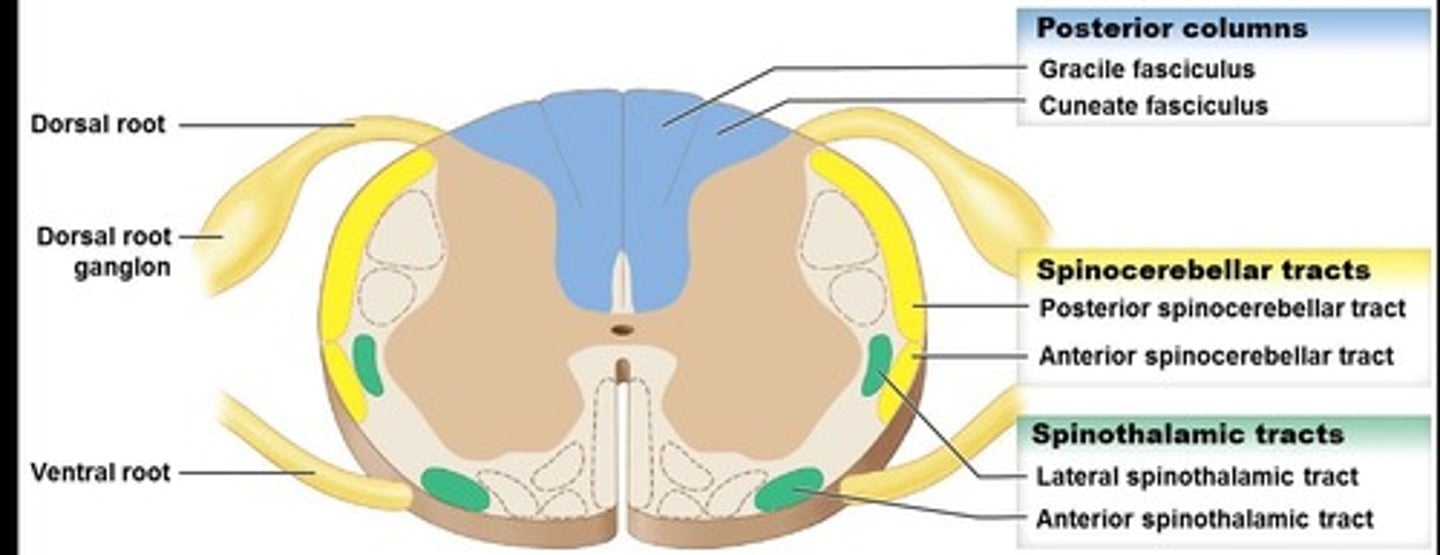
Spinocerebellar Tract
Origin is spinal cord and destination is cerebellum.
Spinothalamic Tract
Origin is spinal cord and destination is the thalamus.
Corticospinal Tract
Origin is cerebral cortex and destination is spinal cord.
Vestibulospinal Tract
Origin is vestibular nuclei and destination is spinal cord.
Posterior Column
One of the three major sensory tracts that transmits information to the CNS.
Gracile Fasciculus
Transmits information to the cerebrum from areas inferior to T6.
Cuneate Fasciculus
Transmits information to the cerebrum from areas superior to T6.
Sensory Homunculus
A sensory map representing the body in the brain.
Lateral Spinothalamic Tract
Transmits pain and temperature sensations.
Anterior Spinothalamic Tract
Transmits crude touch and pressure sensations.
Posterior Spinocerebellar Tract
Involved in proprioception.
Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract
Involved in proprioception.
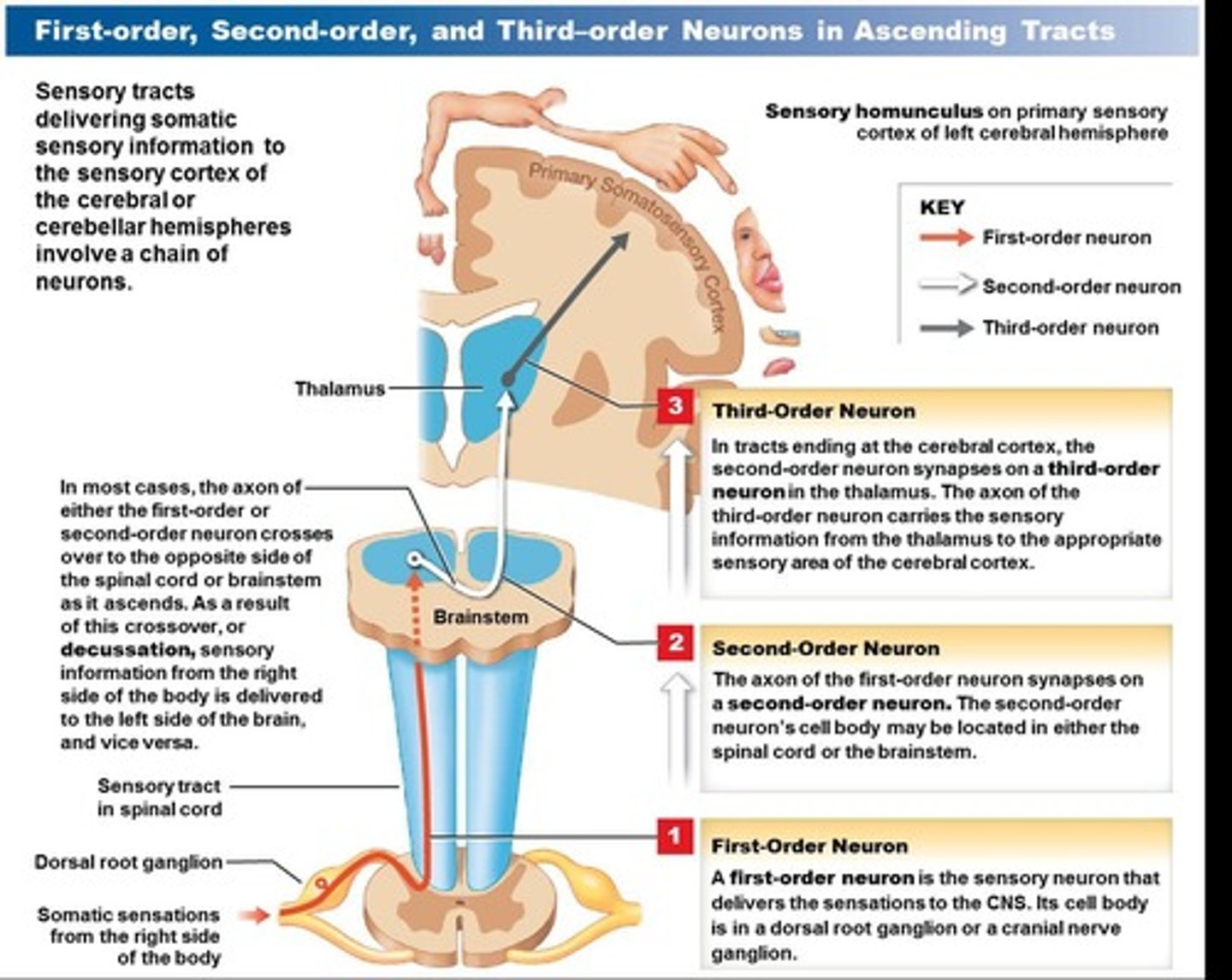
First-Order Neurons
Neurons that transmit sensory information from the periphery to the CNS.
Second-Order Neurons
Neurons that transmit sensory information from the spinal cord to the thalamus.
Third-Order Neurons
Neurons that transmit sensory information from the thalamus to the cerebral cortex.
Decussation
The crossing of nerve fibers from one side of the CNS to the other.
Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus
Final destination for the gracile fasciculus in the thalamus.
Axons of second-order neurons
Axons that join the medial lemniscus.
Dorsal root ganglia of lower body
Ganglia where axons enter the CNS in dorsal roots and ascend within the gracile fasciculus.
Gracile nucleus of medulla oblongata
Nucleus where axons decussate before entering the medial lemniscus.
Cuneate fasciculus
A structure that carries sensory information from the upper body.
Ventral posterolateral nucleus of thalamus
Nucleus in the thalamus that processes sensory information.
Primary somatosensory cortex
Cortex on the side opposite the stimulus that processes sensory input.
Proprioception, fine touch, pressure, and vibration
Sensory modalities from levels at or superior to T6.
Dorsal root ganglia
Ganglia of upper body; axons enter CNS in dorsal roots and ascend within cuneate fasciculus.
Cuneate nucleus
Located in the medulla oblongata; axons decussate before entering medial lemniscus.
Lateral spinothalamic tracts
Transmits pain and temperature sensations.
Ventral posterolateral nucleus
Final destination for lateral spinothalamic tracts.
Dorsal root ganglia (first-order neurons)
Location of neuron cell bodies for lateral spinothalamic tracts; axons enter CNS in dorsal roots and enter posterior horn.
Anterior spinothalamic tracts
Transmits crude touch and pressure sensations.
Primary somatosensory cortex
Final destination for sensations from both lateral and anterior spinothalamic tracts on side opposite stimulus.
Posterior spinocerebellar tracts
Transmits proprioception sensations; not present at site of decussation.
Cerebellar cortex
Final destination for posterior spinocerebellar tracts on side of stimulus.
Anterior spinocerebellar tracts
Transmits proprioception sensations; axons enter anterior spinocerebellar tract on same or opposite side.
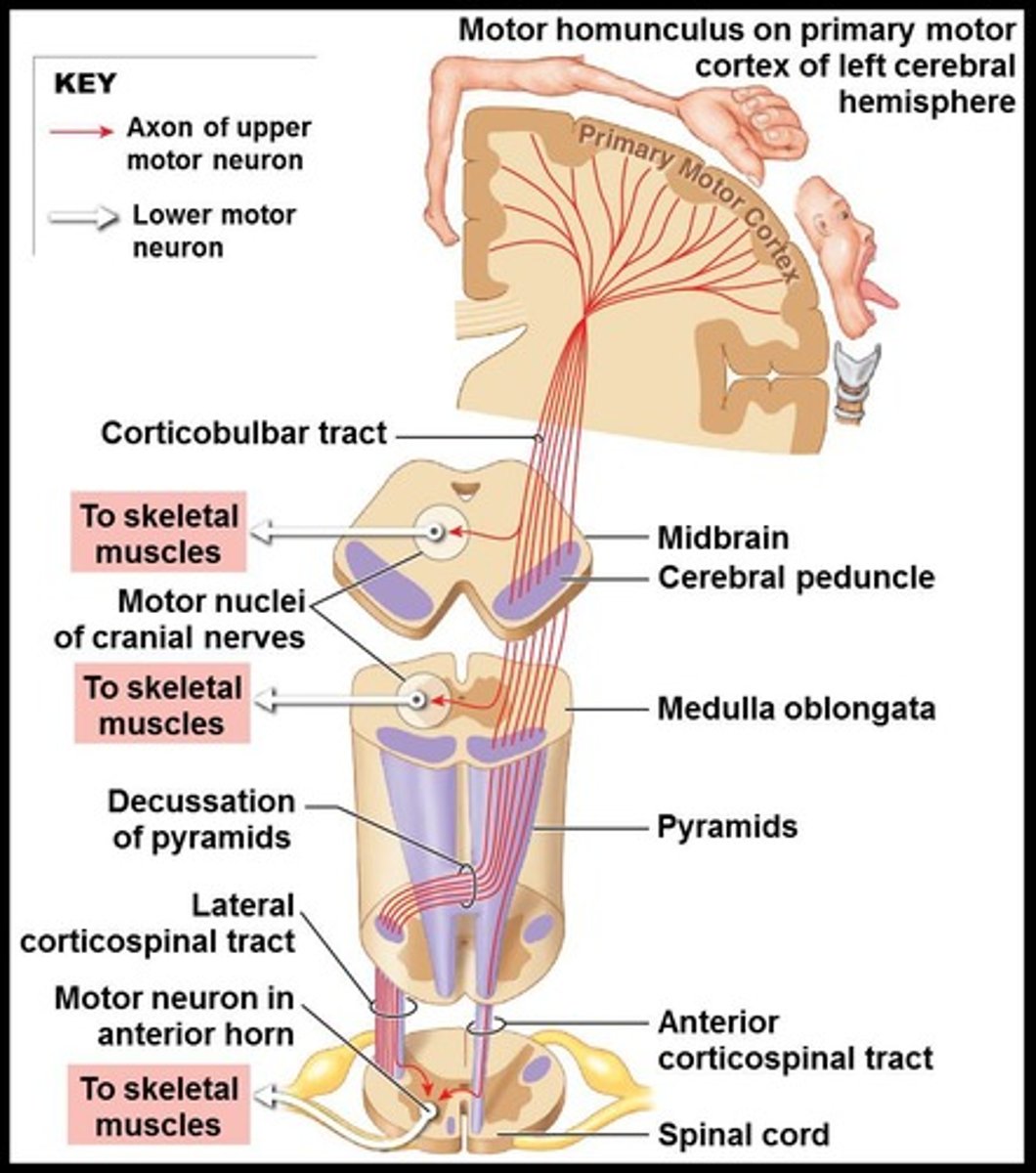
Corticospinal tracts
Consist of three pairs of descending tracts that control skeletal muscles.
Corticobulbar tracts
Provide conscious control over eye, jaw, and face muscles.
Lateral corticospinal tracts
Provide conscious control over skeletal muscles; decussate in the pyramids of the medulla oblongata.
Anterior corticospinal tracts
Provide conscious control over skeletal muscles; decussate at the level of the lower motor neurons.
Motor Homunculus
A diagrammatic representation of control over the primary motor cortex.
Vestibulospinal tracts
Send information from the inner ear to monitor position of the head.
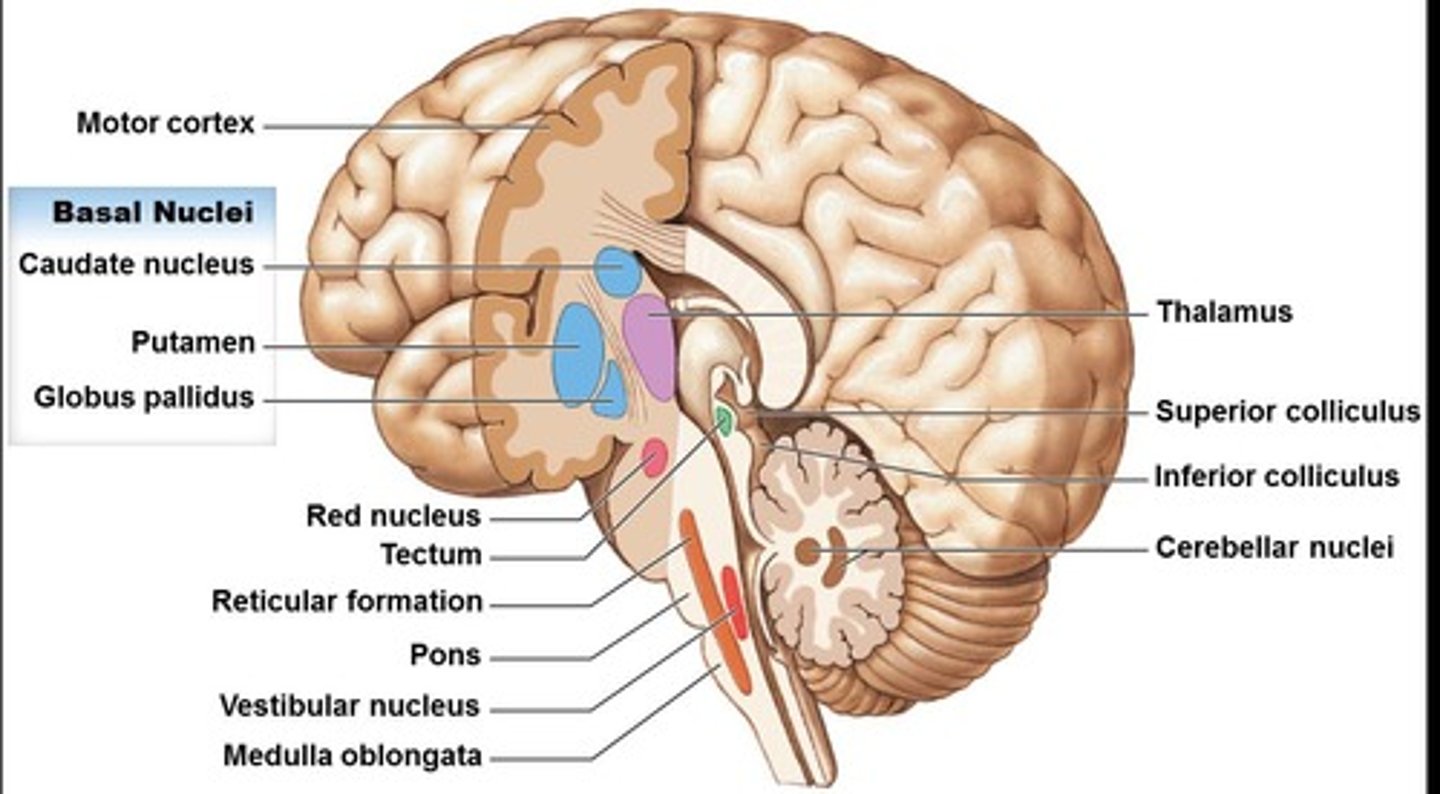
Tectospinal tracts
Send information to the head, neck, and upper limbs in response to bright lights and sudden movements.
Superior colliculi
Receive visual information.
Inferior colliculi
Receive auditory information.
Medial reticulospinal tracts
Send information to cause eye movements and activate respiratory muscles.
Rubrospinal tracts
Send information to the flexor and extensor muscles.
Corticobulbar tracts (upper motor neuron location)
Located in the primary motor cortex (cerebral hemisphere).
Lateral corticospinal tracts (upper motor neuron location)
Located in the primary motor cortex (cerebral hemisphere).
Anterior corticospinal tracts (upper motor neuron location)
Located in the primary motor cortex (cerebral hemisphere).
First-order neuron
The cell body of which sensory neuron may be located in either the spinal cord or the brainstem.
Second-order neuron
The cell body of which sensory neuron may be located in either the spinal cord or the brainstem.
Third-order neuron
The cell body of which sensory neuron may be located in either the spinal cord or the brainstem.