1.3 market failure
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
market failure
exists whenever a free market left to its own devices, fails to deliver economics efficiency.
what does normal interaction of supply and demand lead to:
producing or consuming too much of some goods
producing or consuming too few of some goods
or even failing to produce some goods that are needed by society
3 cause of market failure
public goods
externailities
information failure - merit and demerit goods
public goods
goods that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous
left to its own devices market may not supply these goods at all
non-excludable
once the good is provided for one consumer its impossible to stop other consumers benefiting from it
non-rivalrous
as more and more people consume the product, the benefit to those already consuming the product are not diminished
examples of public goods
streetlights, lighthouses, park benches
free rider principle
market may fail to produce public goods because of this
if one consumer pays for the public good others benefit therefore firms are unable to make a profit and so they must be provided from the government
private costs
costs to individual
private benefits
benefit to individual
external costs
costs imposed on a 3rd party
external benefits
benefits imposed on 3rd party
full social benefits
private benefits + external benefits
full social costs
private costs + external costs
economic efficiency / pareto optimiality
social costs = social benefits
externalities
imposed on 3rd parties outside of the economic transaction
negative externalities
costs imposed on 3rd parties
positive externalities
benefits imposed on 3rd parties
what does a negative externality mean in a free market
too much of the good will be produced
i.e we need to reduce the amount
not economically efficient
what does a positive externality mean in a free market
too little of the good is produced
i.e we need to increase the amount
not economically efficient
PMB
Private marginal benefit
SMB
Social marginal benefit
SMC
Social marginal costs
PMC
Private marginal costs
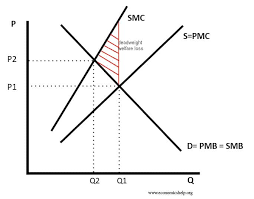
negative production externality graph
assumed there is no external benefits therefore PMB=SMB
product has many negative externalities, but if we see if left to its own devices (Q1) there is under-pricing and over-production
therefore if we include external costs we go to SMC which is at a higher price and a lower production equilibrium.
and the triangle represents deadweight welfare loss
gradients aren’t same because as more products there is an even bigger increase in external costs
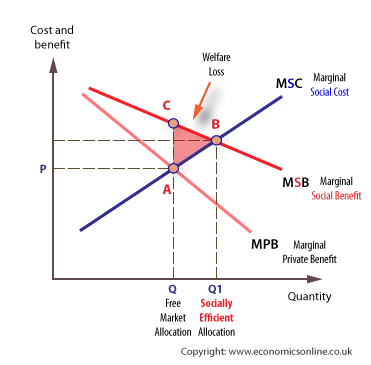
positive consumption externalities
assumed there is no external costs therefore PMC=SMC
product has many positive externalities, but if we see if left to its own devices (Q) there is under-production
therefore if we include external benefits we go to SMB which is at a higher price and a higher production equilibrium.
and the triangle represents welfare gain
gradients aren’t same because as more products there is an even bigger increase in external benefits
symmetric information
when buyers and sellers have potential access to the same information
assymetric information
when 1 party has superior knowledge compared to another in which they have the advantage
what leads to information gaps
most advertising
why do information gaps lead to market failure in a free market
misallocation of resources because people do not buy things that maximise welfare
e.g. drugs - young people dont see long term effects
merit goods
goods which are underconsumed because of either lack of awarness of positive externalities or information gaps.
demerit goods
Demerit goods are goods which are overconsumed because of either lack of awarness of positive externalities negative externalities or information gaps.