Receptors
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 3: Tuesday, September 9th - Thursday, September 11th
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
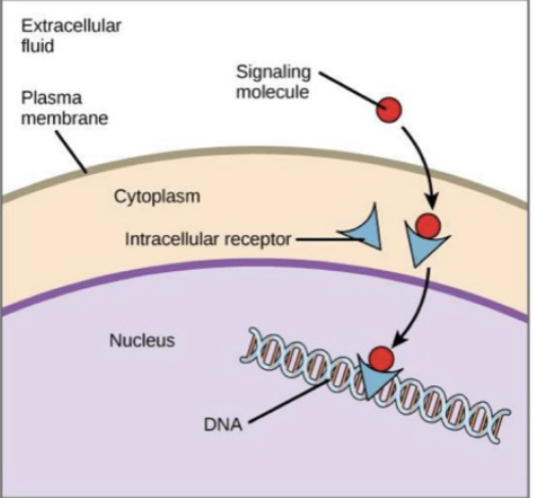
these receptors are inside the cell; non-polar (fat soluble) hormones bind here
intracellular receptors
these receptors are on the membrane and always need secondary messengers; polar hormones (water soluble) bind here
transmembrane receptors
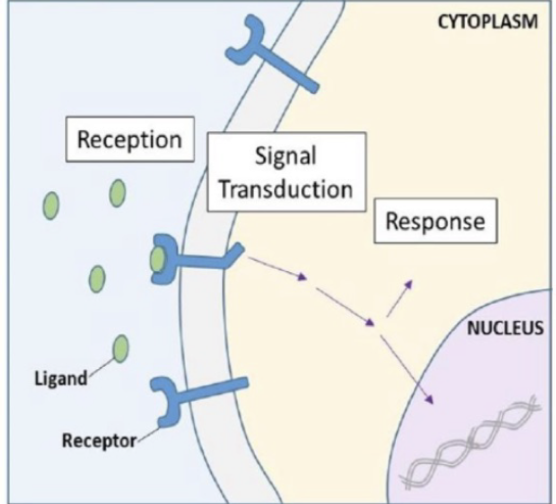
this process is involved in transmembrane receptors and consists of the conversion of hormone mesage into cellular respinse by cahnging cell biochemistry
signal transduction
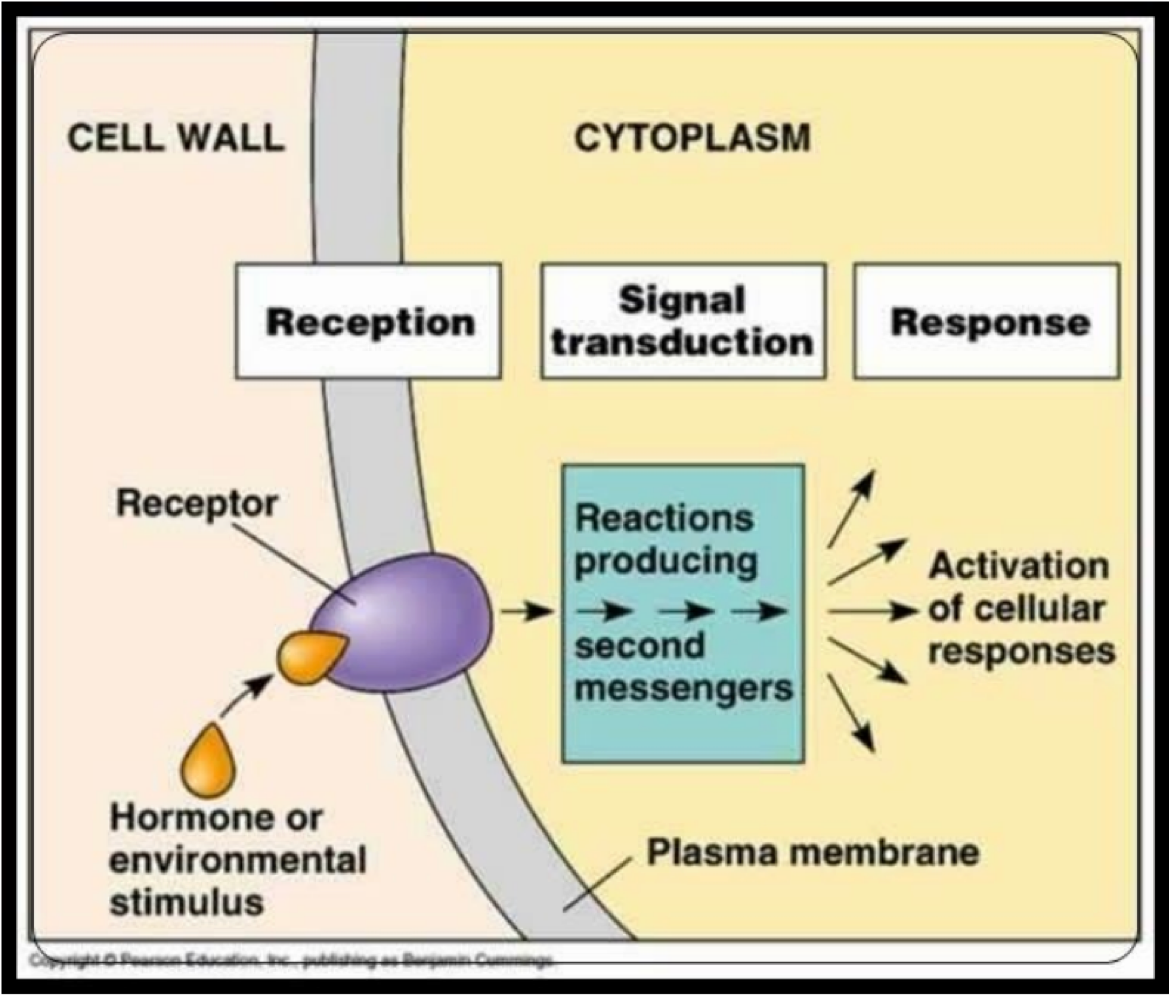
these receptors are transmembrane and open or close channels (sodium-potassium pump)
ionotropic receptors
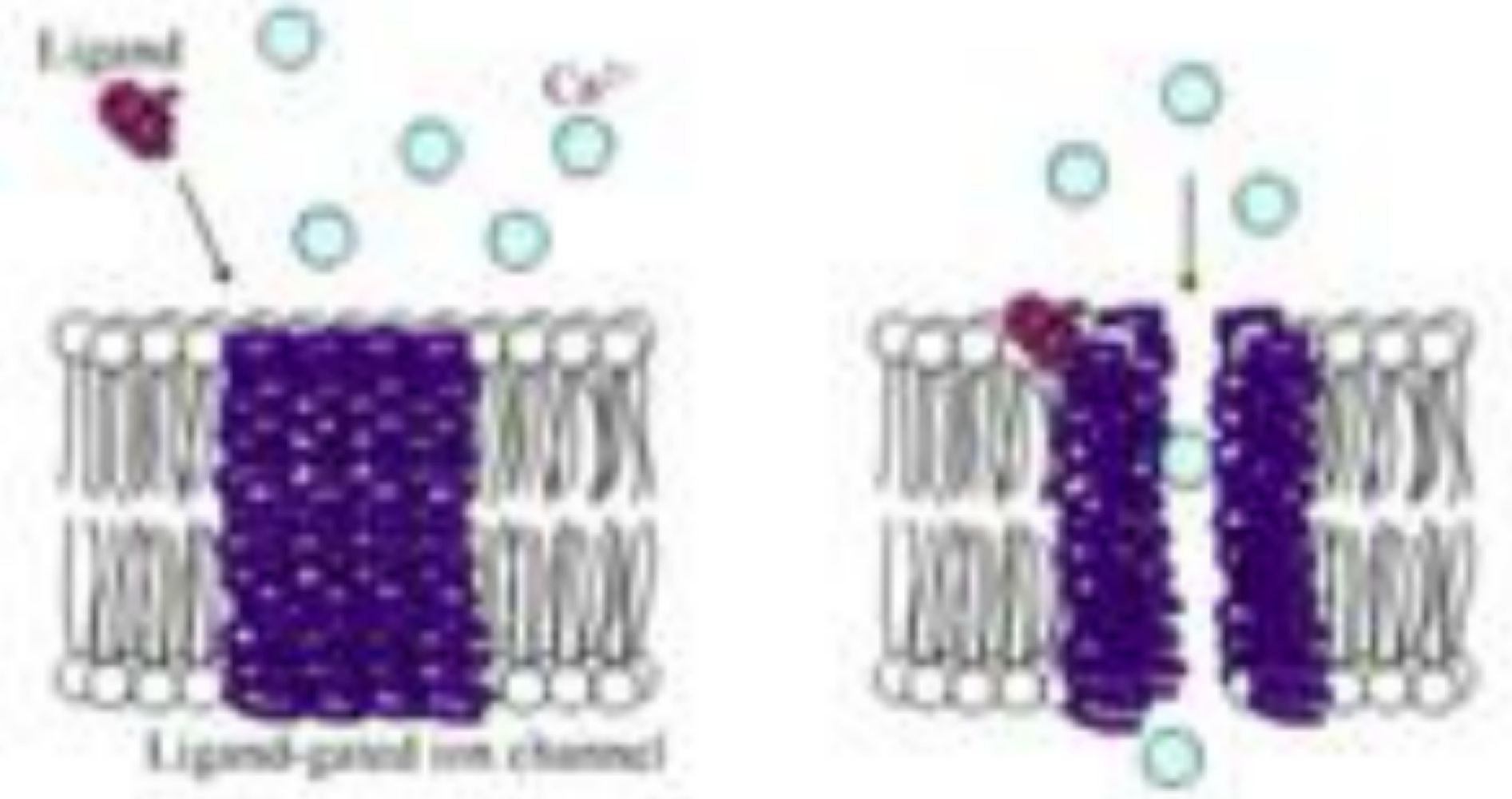
true or false: in the ECF, there are a lot of sodium ions, but in the ICF, there are a lot of potassium ions (both cations)
true
true or false: in the ECF, there are a lot of hydrogen phosphate ions (HPO42-), but in the ICF, there are a lot of calcium ions (both anions)
false. in the ECF, there are a lot of calcium ions, but in the ICF, there are a lot of hydrogen phosphate ions (HPO42-)
these receptors can be intracellular or transmembrane (with or without enzymes), and initiate signaling mathways within the cell
metabotropic receptors
these receptors have enzymes in side (guanylyl cyclase, insulin)
intrinsic enzyme transmembrane receptors
these receptors have enzymes attached (g-protein)
enzyme-coupled transmembrane receptors
true or false: receptors are proteins/glycoproteins, located in the membrane, cytosol, or nucleus, and are categorized base don their derived-from gene
true
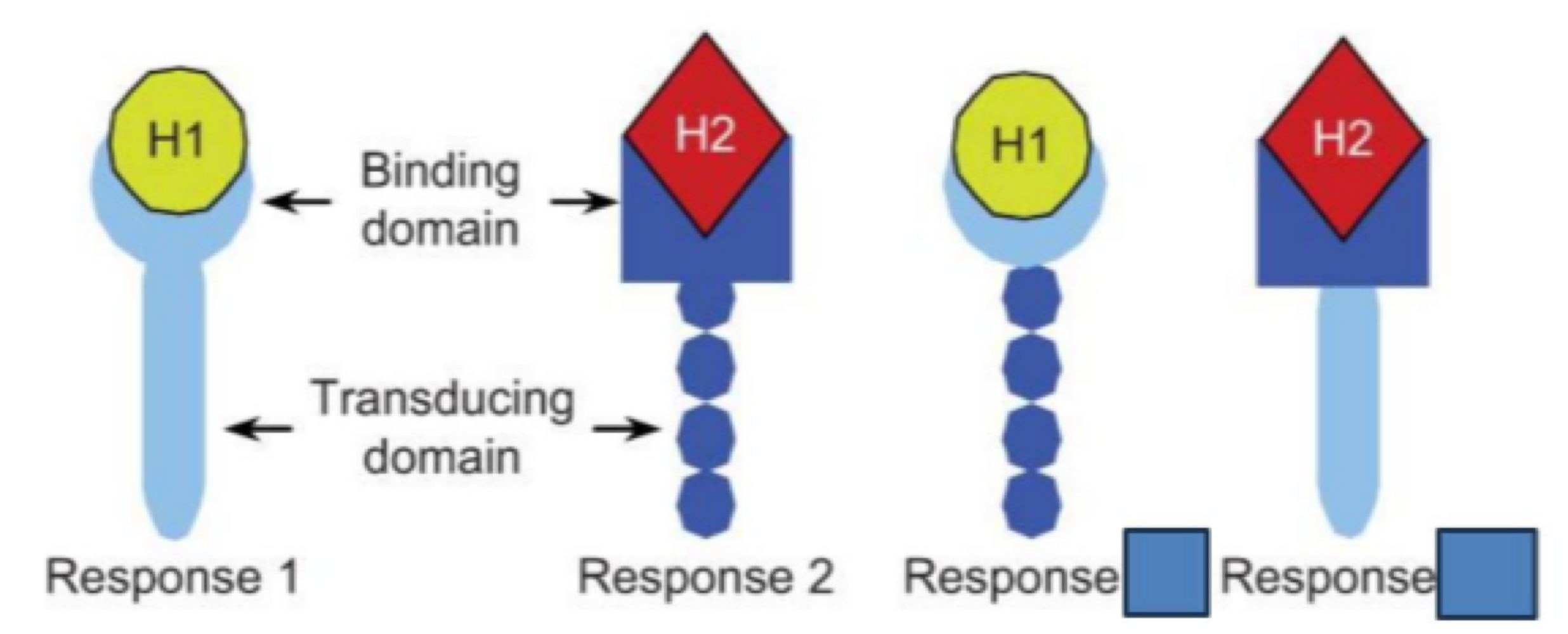
the _______ is where the hormone binds to the receptor
binding site
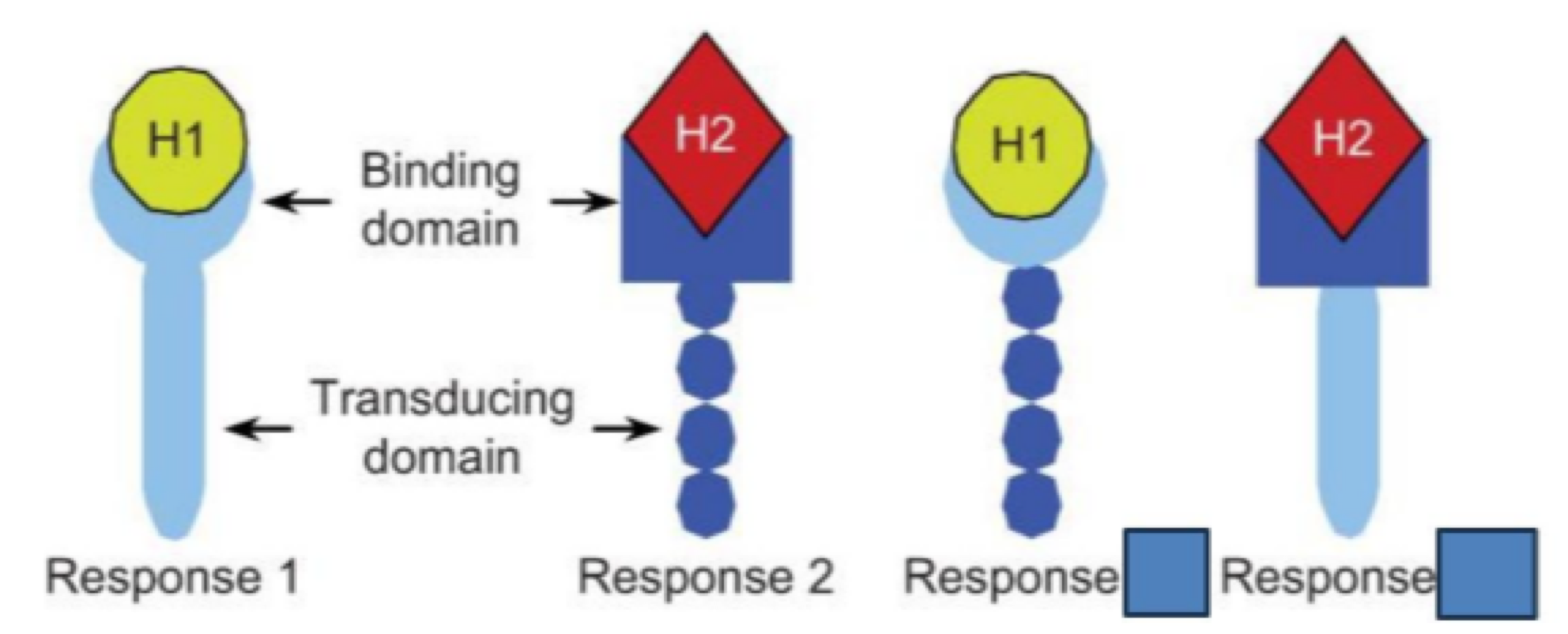
the _______ is where the response is created on a receptor
transducing domain
true or false: fat soluble steroids binding to intracellular receptors results in enzyme production/changes in enzyme production rate
false. fat soluble steroids binding to intracellular receptors results in protein production/changes in protein production rate
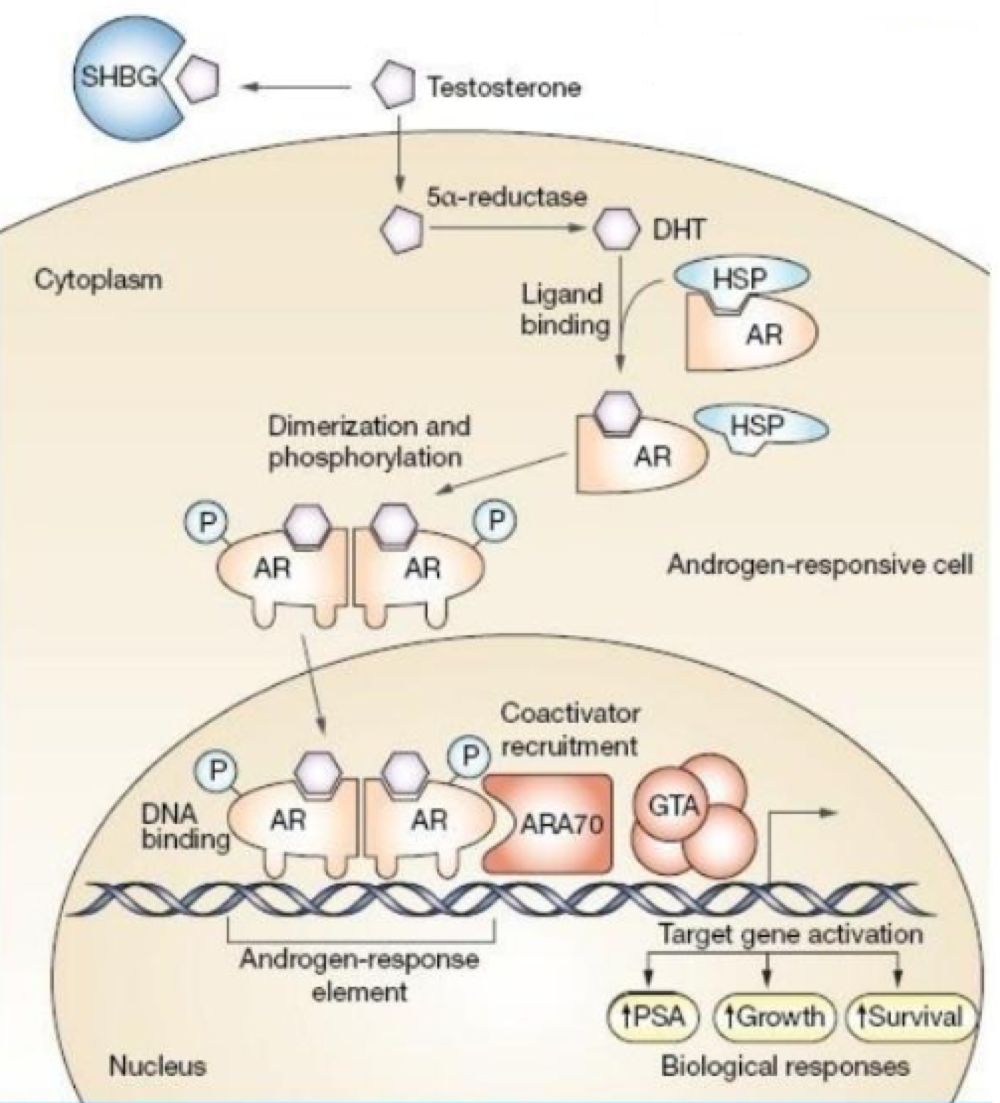
true or false: adding a phosphate to a steroid hormone activates it
true
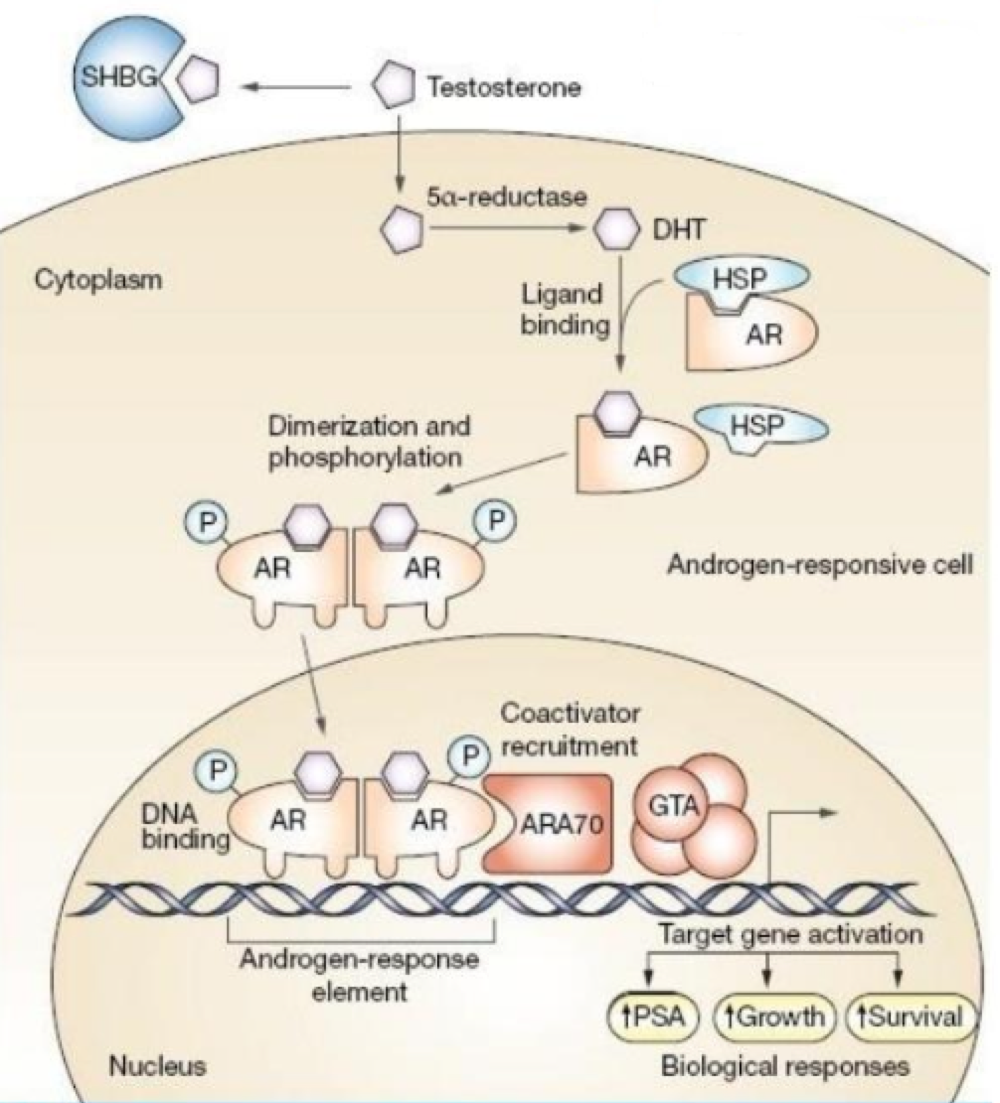
_______ activates proteins, and _______ deactivates them
kinase, phosphokinase
intracellular receptors are _______. if they’re separated, they dont’t work
dimers
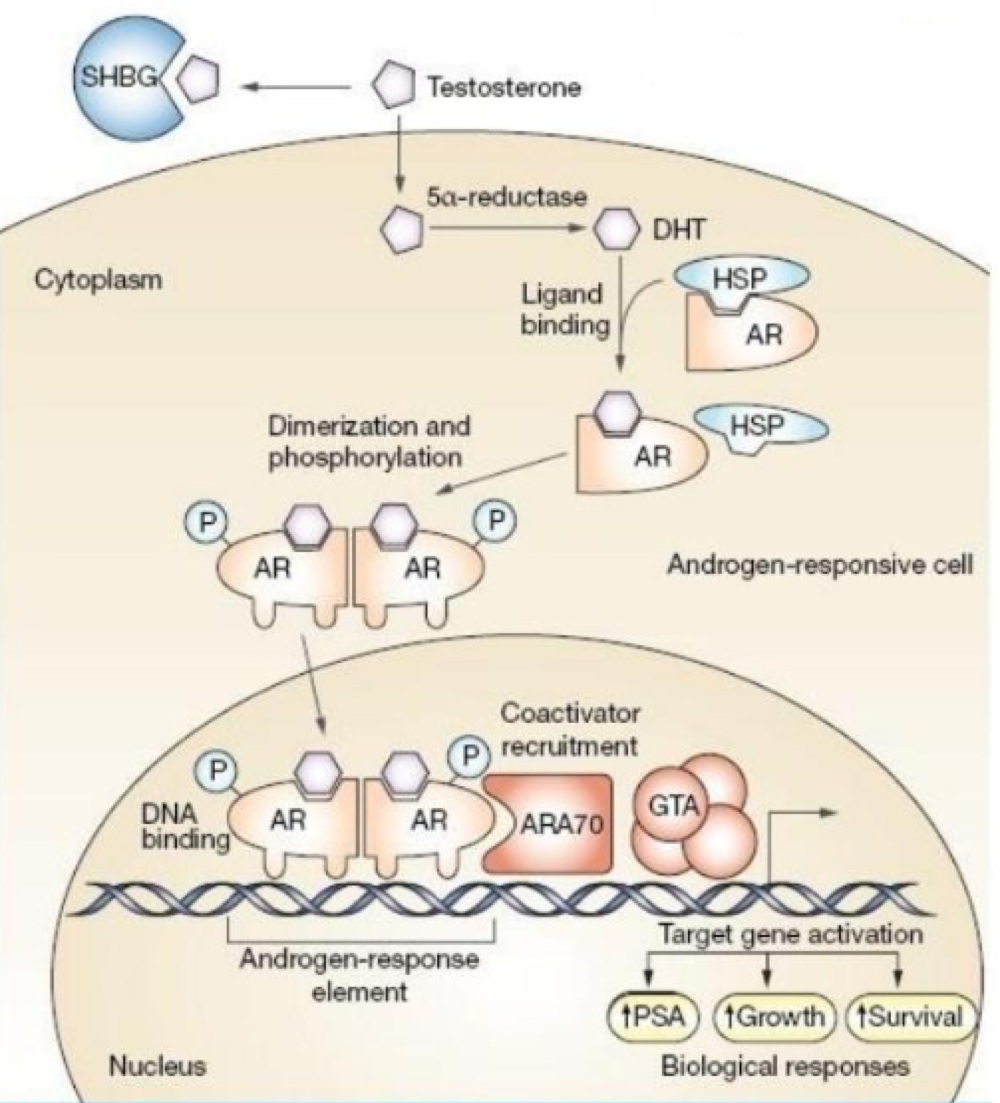
receptor conformation changes stimulates the complex to bind to _______ on DNA, which are specific sequences that stimulate/repress activity of transcription factors
hormone receptor elements (HREs)
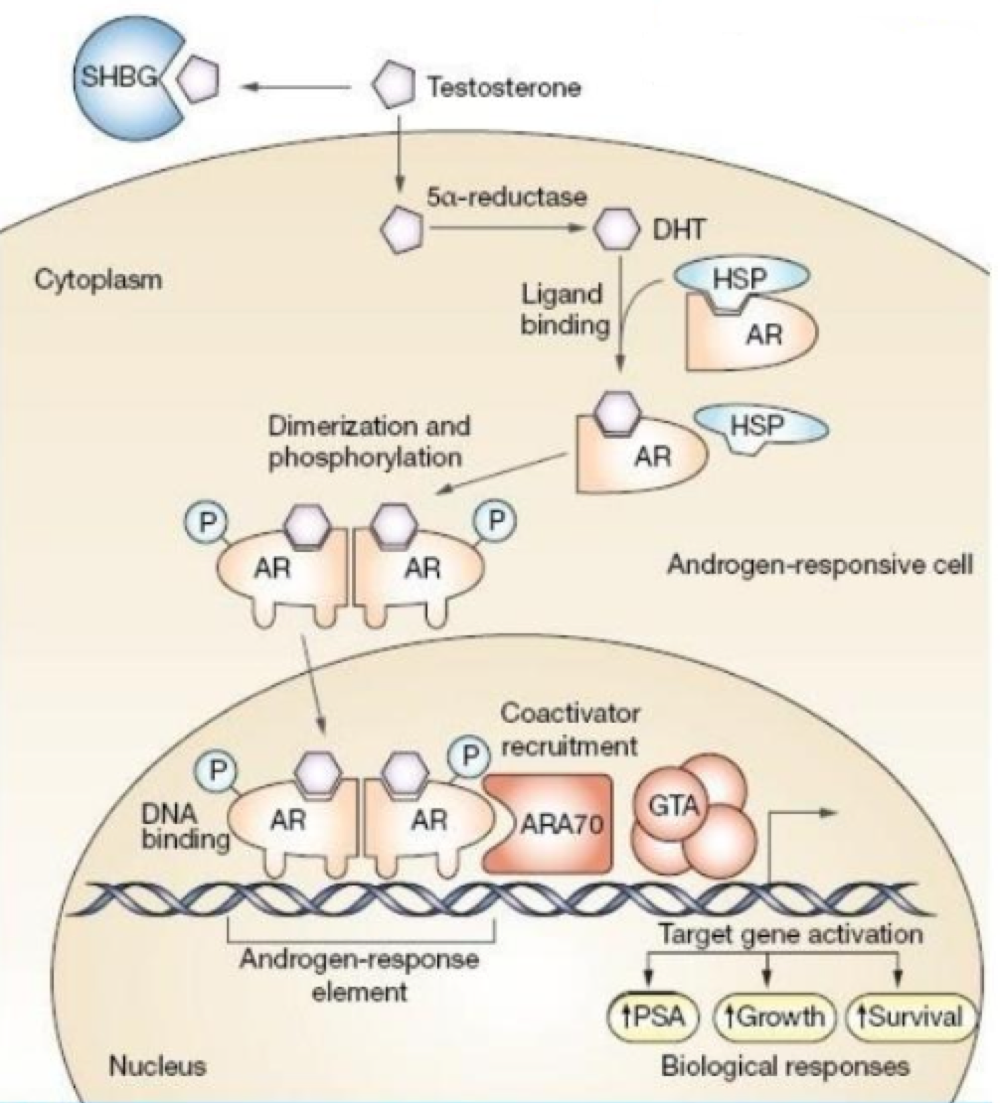
true or false: thyroid/vitamin D hormones are permanently detached to HREs on DNA, regardless if the hormone is present.
true
For thyroid/vitamin D hormone receptors, nuclear proteins attache to receptors to prevent DNA damage because _______
ligands are absent
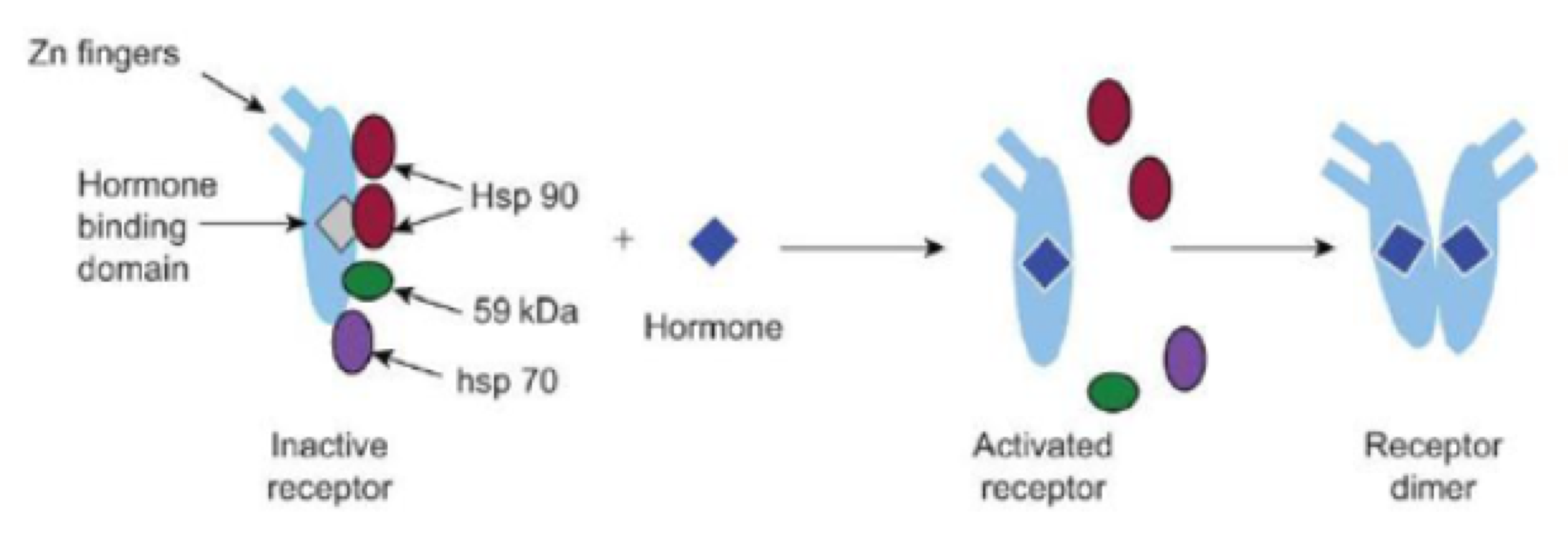
For thyroid/vitamin D hormone receptors, nuclear proteins which with other proteins so silent genes are expressed because _______
ligands are present
For thyroid/vitamin D hormone receptors, hormones dissociate from the receptor, are inactivated, then diffuse into ECF because_______
hormone levels declined
_______ initiate signaling pathways that changes gene expression or cell bio chemistry
secondary messengers
_______ receptors have single proteins germs and seven stretches of 25 amino acids
G-protein
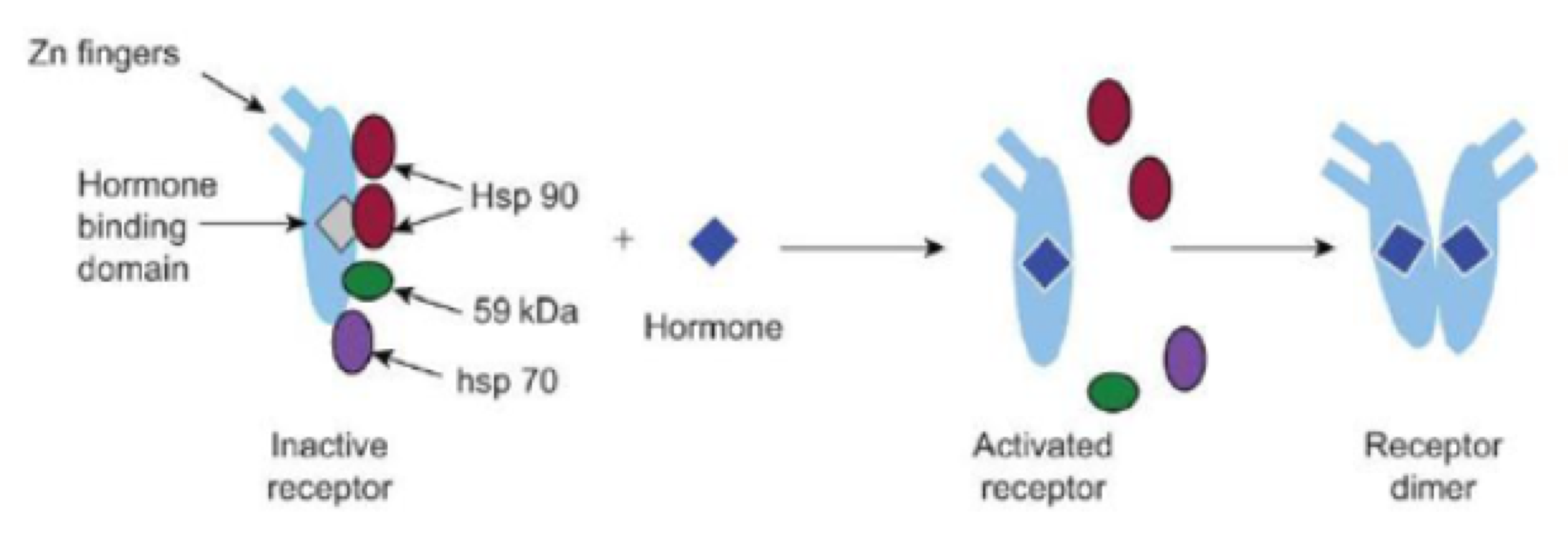
G-protein subunits are _______, _______, and _______; all bind to and activate ion channels
alpha, beta, and gamma
Gas proteins stimulate _______ to catalyze ATP → cAMP
adenylyl cyclase
Gai proteins _______ adenylyl cyclase
inhibit
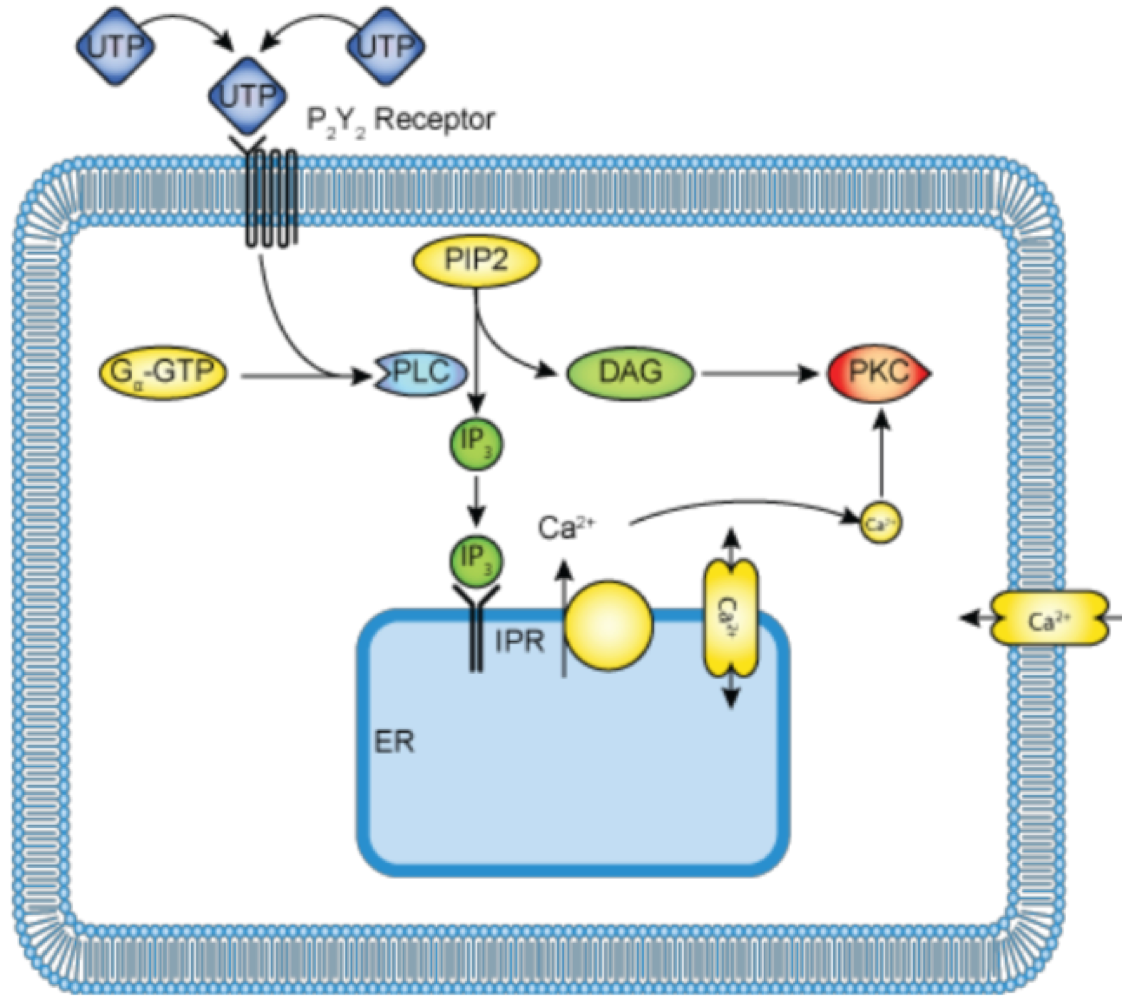
Gaq stimulates _______
phospholipase C
Ga12 binds to _______ nucleotide exchangee factors
guanine
G-protein alpha subunit is GTPase, and catalyzes _______ to make _______
guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to guanosine triphosphase (GTP)
_______ is a G-protein second messenger that activates protein kinase A (PKA)
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
_______ and _______ are G-protein second messengers that activate protein kinase C (PKC) and calcium
DAG and IP3
_______ is a G-protein second messenger that activates cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase so guanylyl cyclase converts GTP → GMP
cyclic GMP
_______ are G-protein second messengers that activate calmodulin kinase
calcium-calmodulin
true or false: kinases activate enzymes/ion channels/transcription factors and add a phosphate group (PO43-) to proteins for biochemical reactions/protein synthesis
true
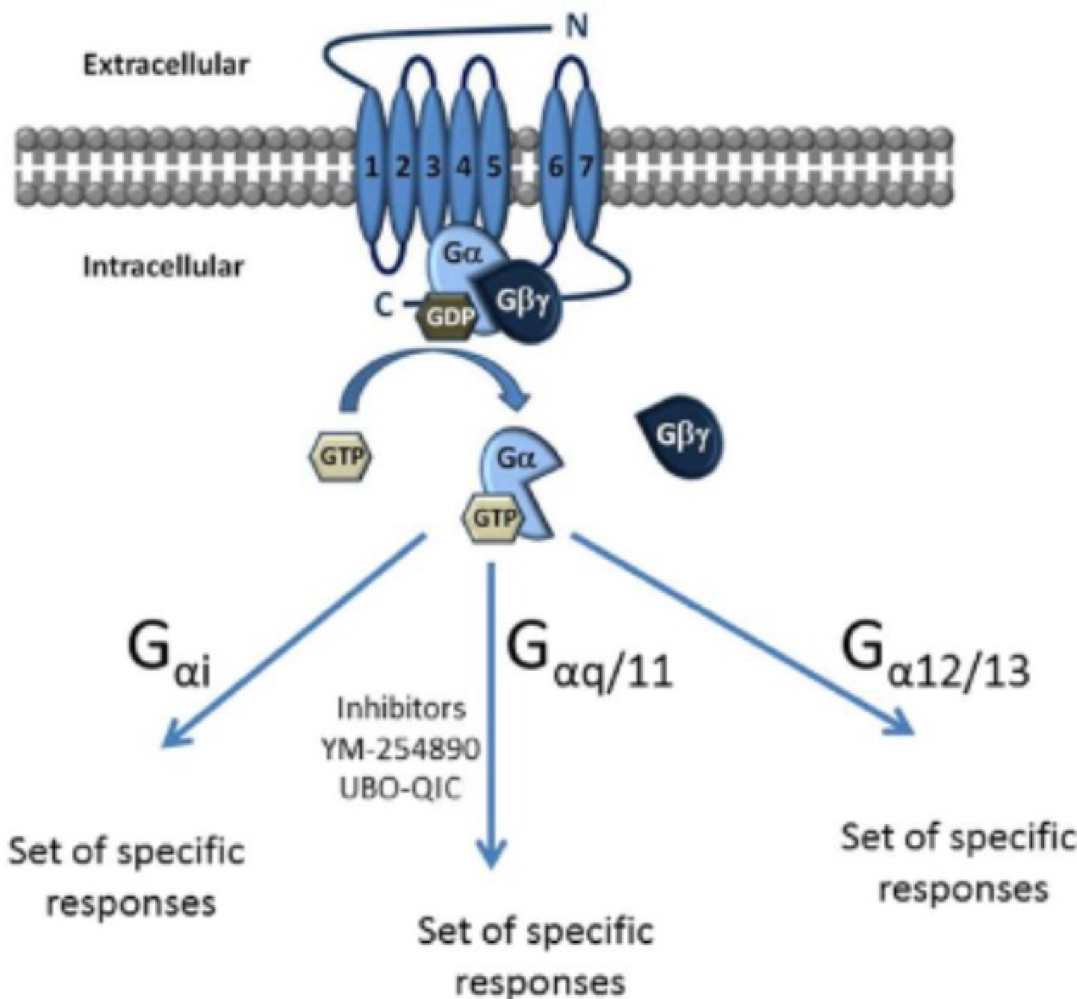
_______ is one of the major ways growth factors communicate with cells
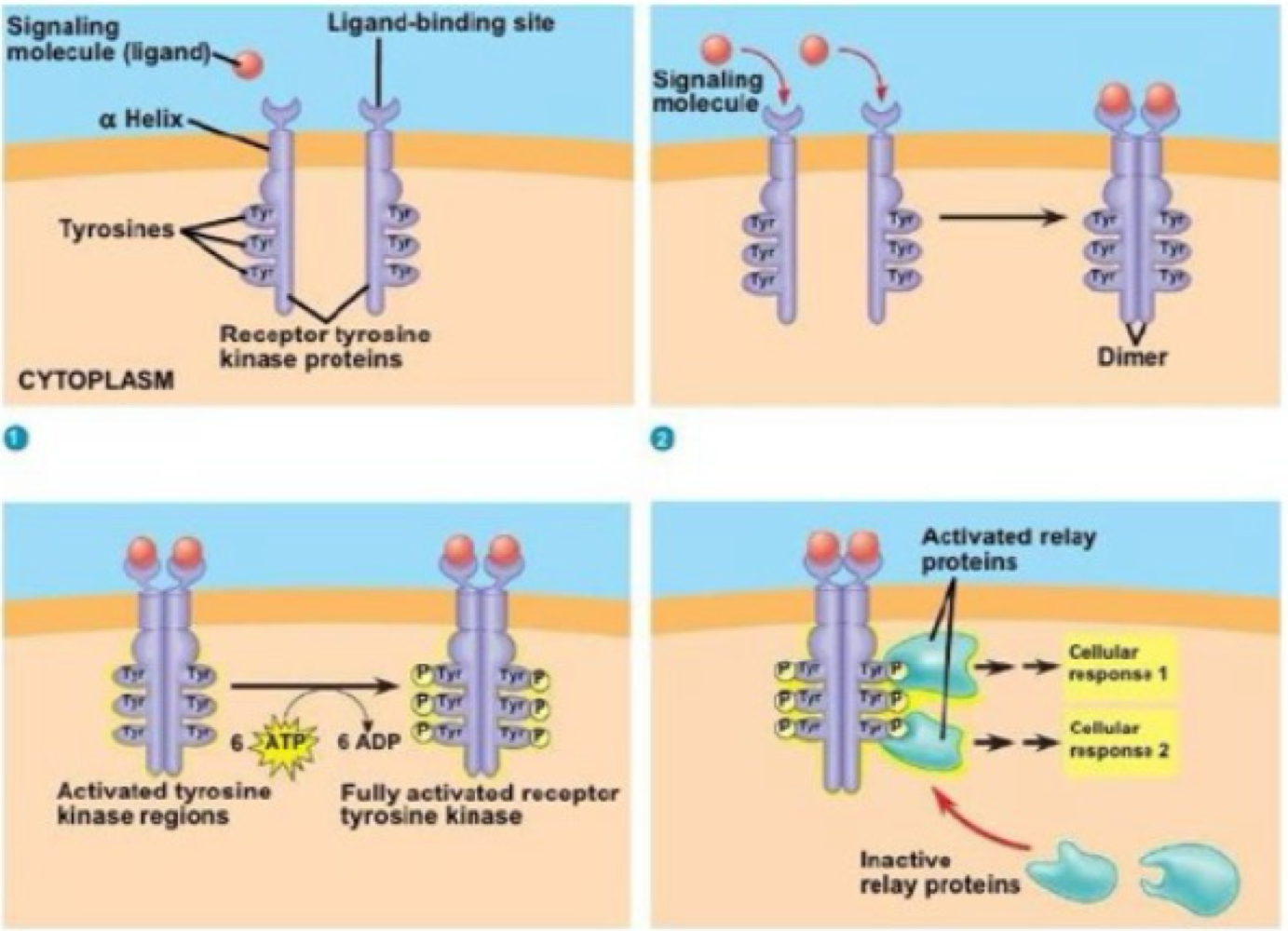
tyrosine kinase signaling
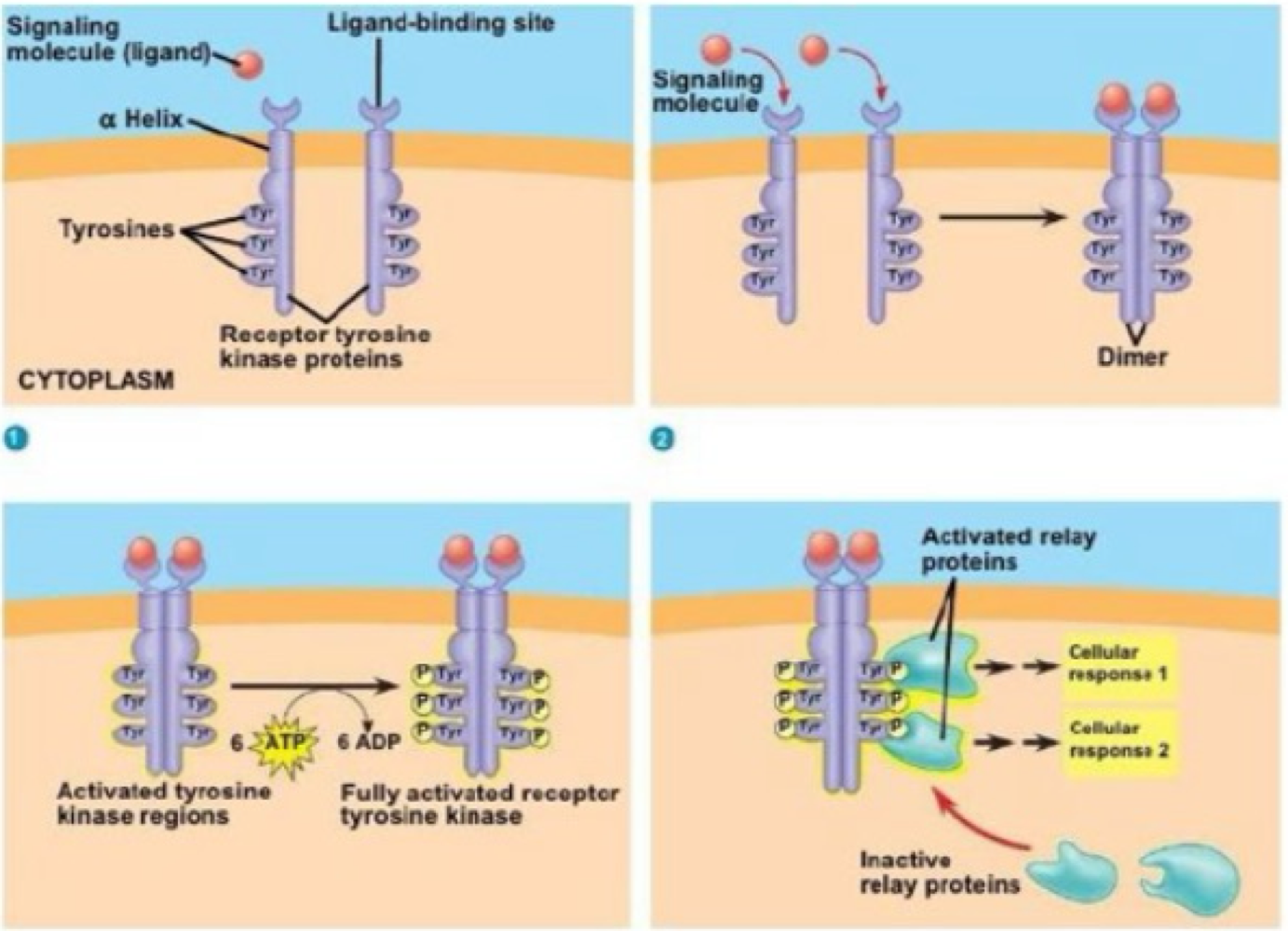
true or false: during tyrosine kinase signaling, receptors gain phosphorus from proteins to add to tyrosine that binds to them
false. during tyrosine kinase signaling, receptors autophosphorylize their own tyrosine
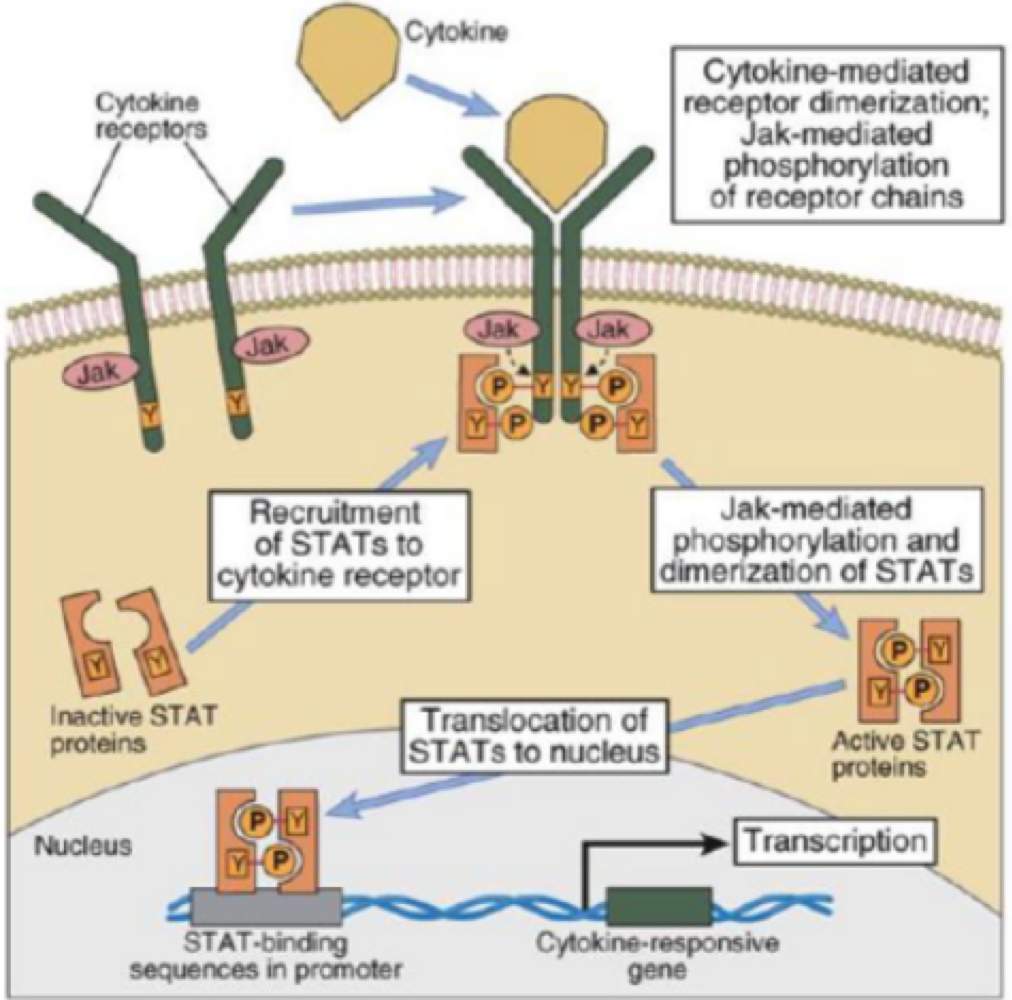
_______ is a special type of tyrosine kinase signaling used mostly by cytokines
JAK/STAT pathway
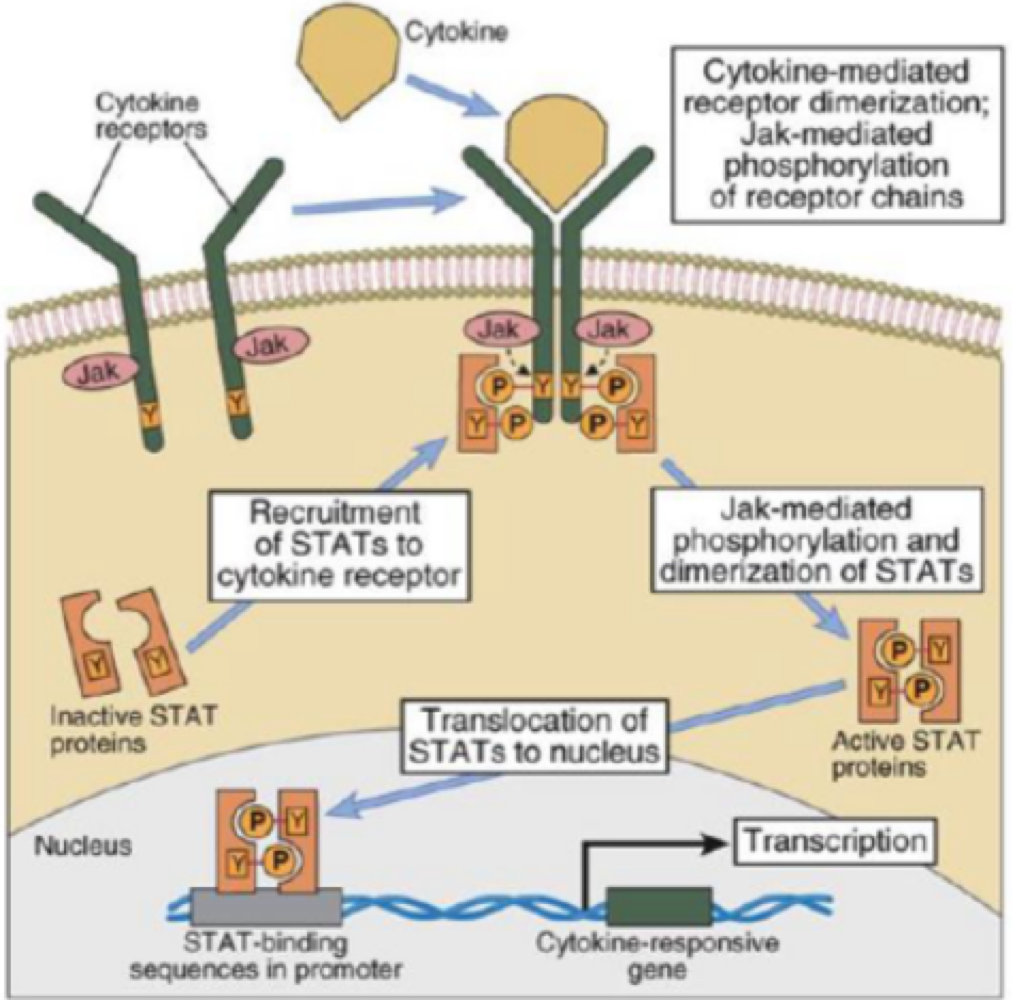
true or false: Janus kinase are a type of proteins that phosphorylate the dimer receptors cytokine binds to
true
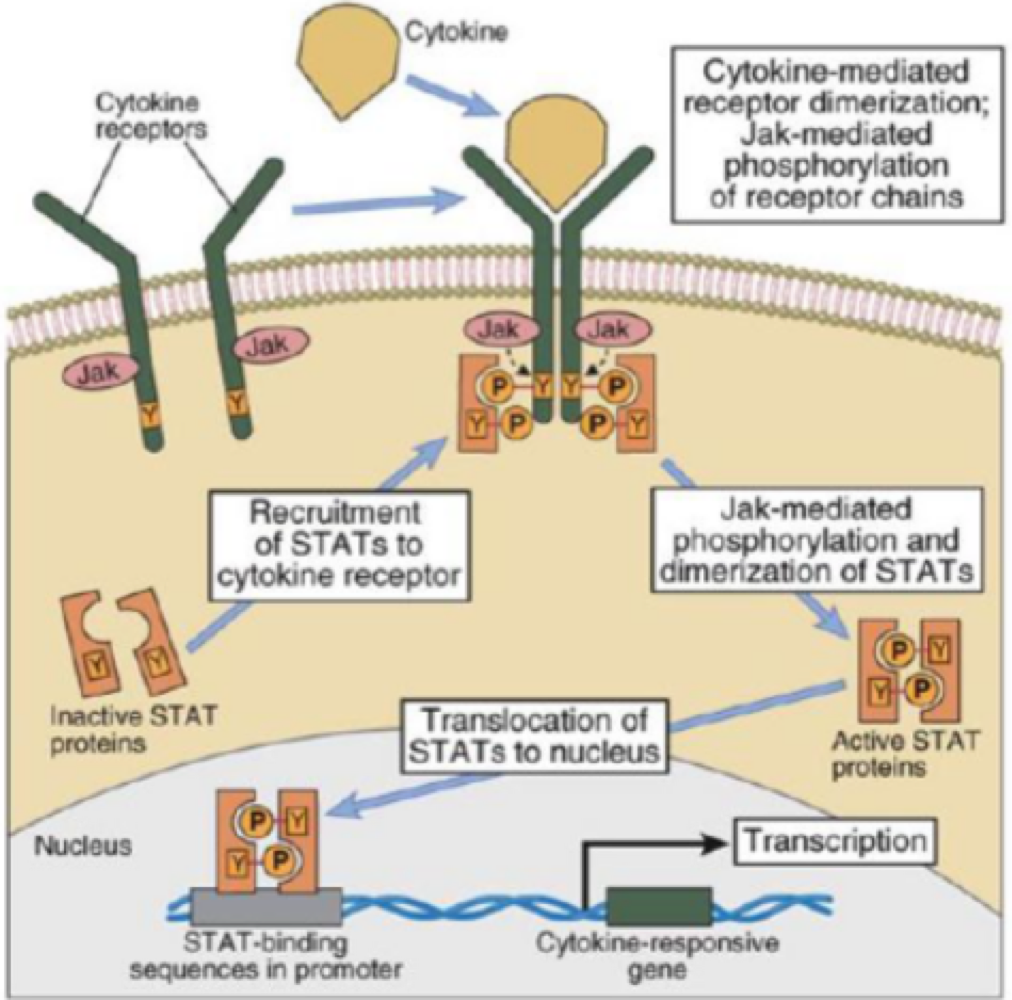
true or false: signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) are phosphorylated by JAKS, dimerize, then move into the nucleus to turn on gene transcription
true