DNA Electrophoresis: BIO 105
1/5
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
DNA Characteristics
all organisms have the same 4 DNA bases: GCAT
the order in which the bases are put together are what makes individuals different
with the exception of identical twins, each individual in the population has a unique sequence of bases
Genetic Fingerprinting (slide 1)
DNA can be cut with special enzymes termed endonuclease or restriction enzymes
recognize specific sequences of nucleotides and cut the DNA at these sites
evolved in bacterial cells as a defense against bacteriophages (bacterial viruses)
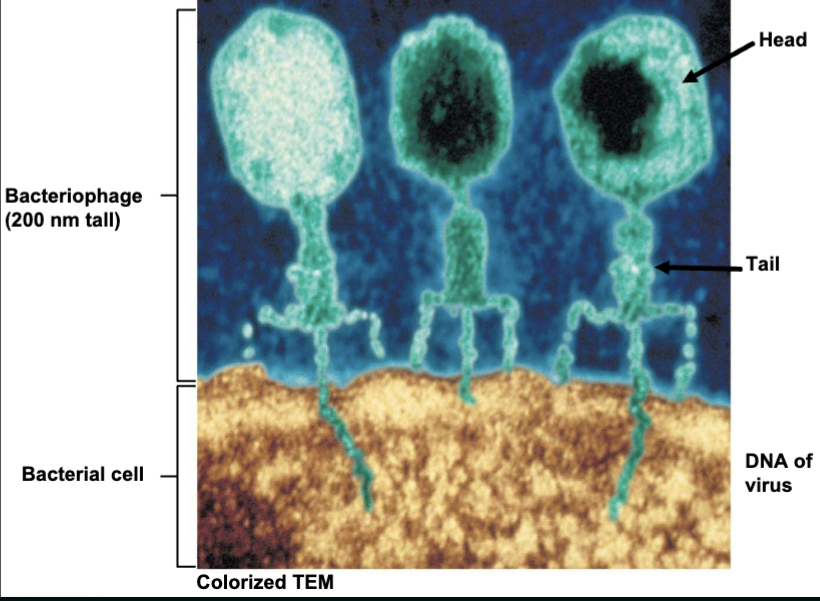
Genetic Fingerprinting (slide 2)
since their discovery in 1962, hundreds of RE have been identified and isolated from bacterial cells
these RE are extremely specific and work by recognizing short nucleotide sequences in DNA molecules
termed Recognition Sequences
aka Substrate
once these sequences are detected, the RE cuts the DNA at this point
Genetic Fingerprinting (slide 3)
For example, EcoR1 cuts at the following recognition sequence:
CTAGATCCGTG|AATTCTATACGGCCTATAG
GATCTAGGCACTTA|AGATATGCCGGATATC
EcoR1 will cut the DNA every time the above
recognition sequence is detectedsince everyone has a unique sequence of bases,
the number of restriction sites will differ from
person to person
Genetic Fingerprinting (slides 4-6)
ex: Suppose Travis has 4 restriction sites, EcoR1 will cult Joe’s DNA 4 times
5 fragments result from the action of EcoR1 when applied to Joe’s DNA
ex: Suppose Taylor’s DNA has 3 restriction sites for EcoR1, EcoR1 will cut Jane’s DNA in three separate places
4 DNA segments will result
So, EcoR1 cuts Travis’s DNA into 5 segments and Taylor’s DNA into 4 segments
Genetic Fingerprinting (slide 7)
These fragments can now be separated from one
another using ELECTROPHORESIS
- DNA electrophoresis utilizes an agarose gel and a
voltage current to separate the cut DNA fragments
from one another
- The DNA samples are placed into the agarose gel
(a medium in which the DNA fragments will travel)
and the voltage current separates the fragments
since every individual has a unique sequence of bases in their DNA, a unique banding pattern will be generated by electrophoresis for each individual
= genetic fingerprinting