International Marketing Session 1
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
MARKETING:Definition
Marketing – performance of business activities designed to plan, price, promote, and direct the flow of a company’s goods and services to consumers or users for a profit
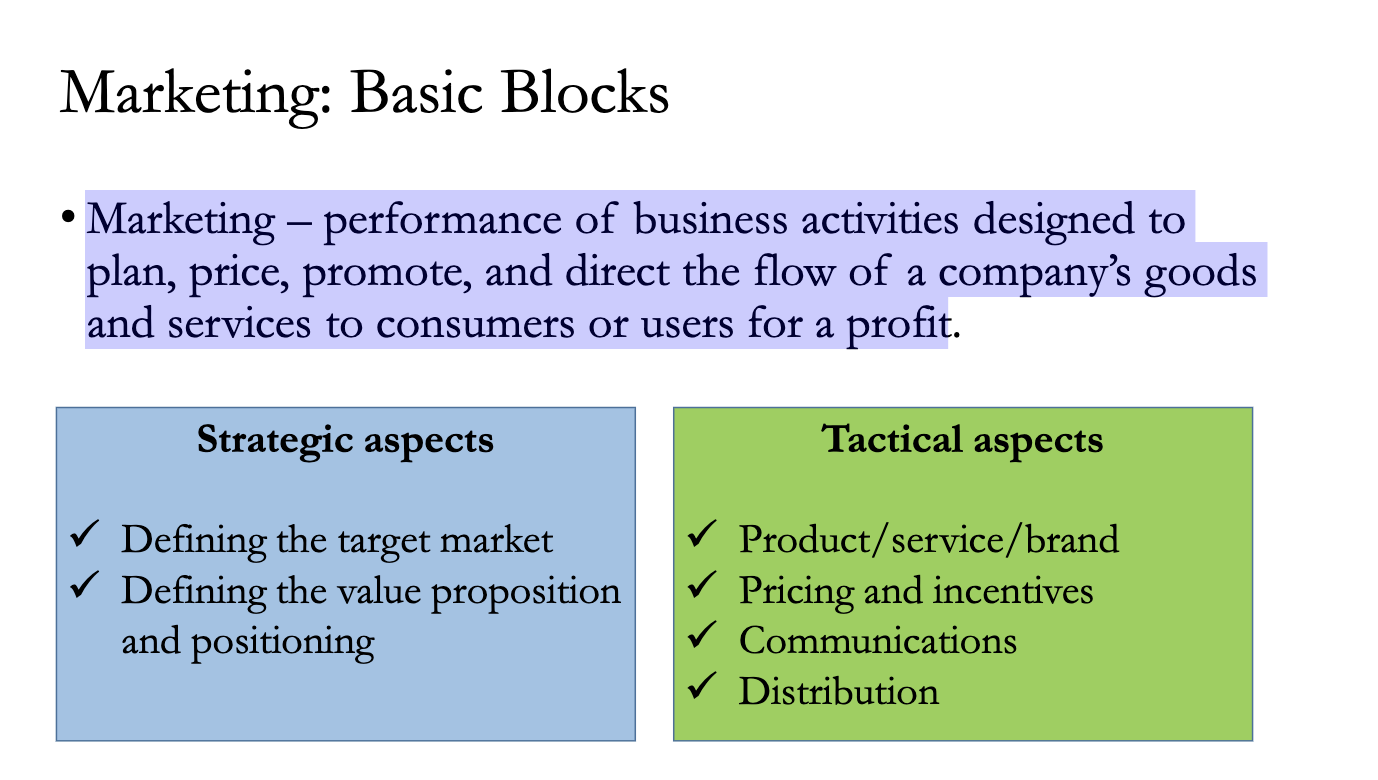
Marketing Strategy: 5C’s of the Target Market
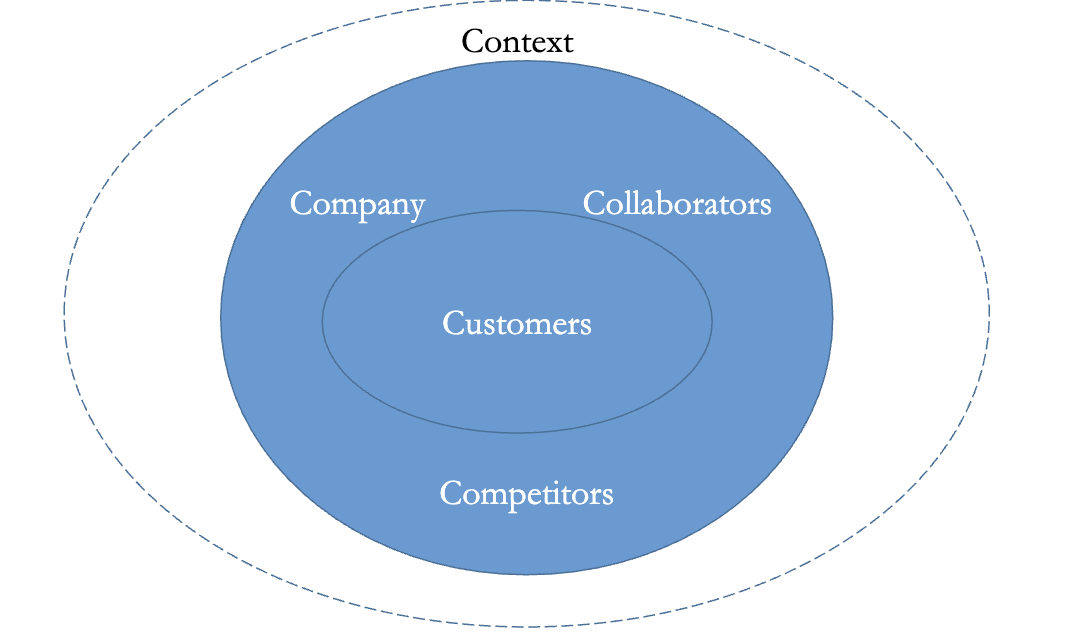
The lecture introduces a core framework for defining a "Target Market" called the 5C’s. You can visualize this as a circle with layers.
1. Context (The Outer Layer) This is the environment the company operates in. It includes factors largely outside the company's control.
Sociocultural: Trends, values, religion, and lifestyles.
Example: More women joining the workforce led to fewer home-cooked meals, increasing the demand for food delivery.
Technological: New skills, processes, and tools.
Example: Smartphone usage rates and internet infrastructure are critical for app-based businesses like Dodo Pizza.
Regulatory: Laws, taxes, import tariffs, and safety regulations.
Example: Food safety laws or data protection regulations (GDPR).
Economic: Inflation, interest rates, and economic growth.
Physical: Climate, location, and natural resources.
2. Company This refers to the organization itself—its product portfolio, resources, and internal value.
Case Study: Dodo Pizza. It is a Russian pizza delivery franchise founded in 2011 that uses technology (its own app and website) to drive 90% of its delivery orders.
3. Collaborators These are the partners who help the business function.
Example: For Dodo Pizza, this includes their franchisees (partners who open independent stores).
4. Competitors Who are you fighting for market share?
Example: In the slides, Dodo Pizza is compared against competitors like "Doner 42" and other pizzerias.
5. Customers (The Core) These are the people buying the product. A key part of marketing is understanding that customers in different countries may have different profiles.
Example (Russia vs. UK):
Russian Customers: Price-sensitive, low trust in delivery, and less tech-savvy.
UK Customers: Value-conscious (willing to pay for quality), tech-savvy, and experienced with international food.
The Value Proposition
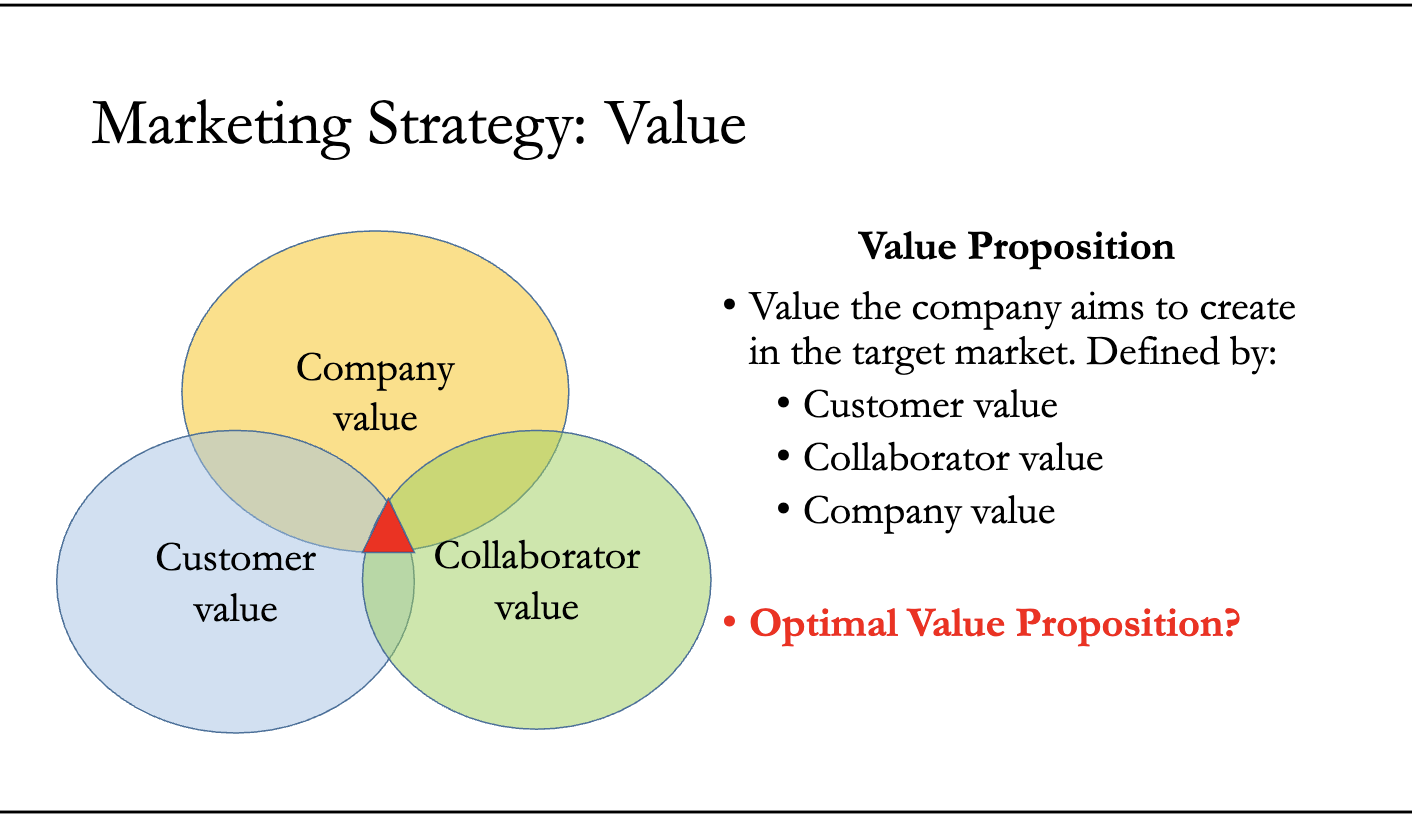
Why does the business exist? The Value Proposition is the "sweet spot" where three types of value overlap.

Customer Value: Why should a person spend money on your product instead of a competitor's?.
Collaborator Value: Why should a partner (like a franchisee) choose your brand instead of opening their own independent store?.
Company Value: Why should the company invest its limited money and engineering time into this specific product rather than a different one?.
Key Concept: The goal is to achieve an Optimal Value Proposition where all three areas are satisfied
International Marketing = Marketing?


This leads us to Global vs. Multinational Strategy
Global vs. Multinational Strategy
ADAPTATION VS. UNIVERSALISM
The lecture contrasts two major ways to approach international business, heavily referencing Theodore Levitt's famous 1983 theory.
1. The Global Corporation (Standardization)
Philosophy: Treats the entire world (or major regions) as a single entity. It sells the same thing, the same way, everywhere.
Benefits: Standardization leads to lower costs and lower prices for consumers.
Levitt’s View: He believed companies should concentrate on what everyone wants (reliability, low price) rather than worrying about small local preferences.
Classic Quote: Henry Ford said of the Model T car: "Any customer can have a car painted any colour that he wants so long as it is black".
2. The Multinational Corporation (Adaptation)
Philosophy: Recognizes differences between countries and adjusts products and practices for each one.
Downside: This leads to higher relative costs and prices.
Reality Check
Even "Global" brands usually adapt.
McDonald's: Customizes sandwiches for different countries.
Louis Vuitton: Adjusts prices and products for Japan.

Interbrand: Global Brand Measures

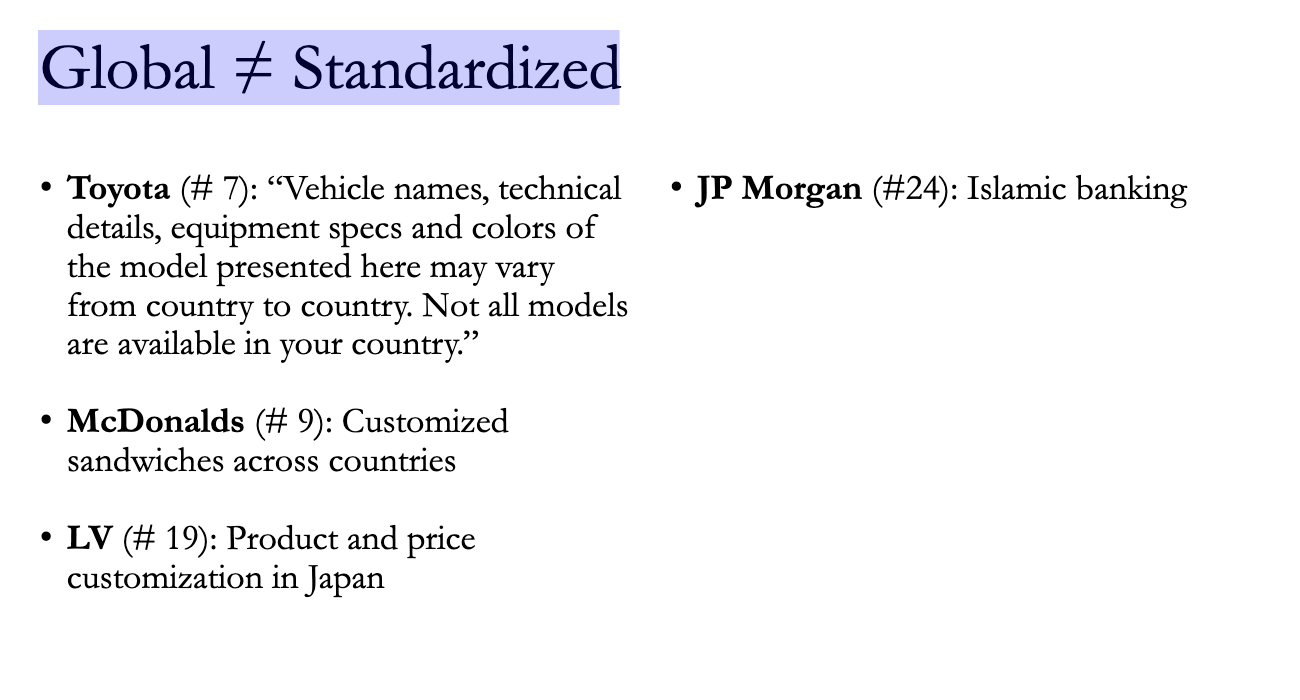
Global ≠ Standardized
Reality Check
Even "Global" brands usually adapt.
McDonald's: Customizes sandwiches for different countries.
Louis Vuitton: Adjusts prices and products for Japan.
BUT ARE MARKETS AND CONSUMERS THAT DIFFERENT?

CULTURAL UNIVERSALS
A major question in the course is: Are consumers different everywhere, or are we basically the same?.

To study this, researchers use two types of constructs:
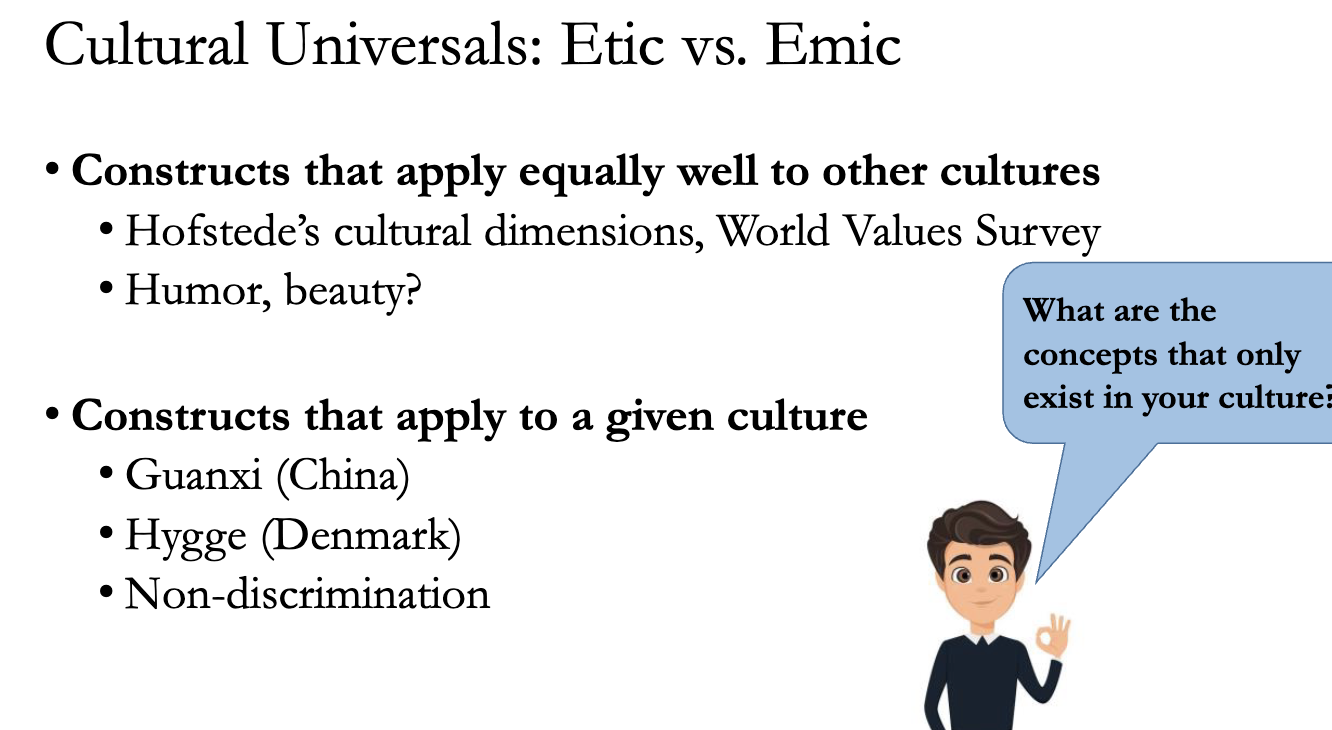
1. Etic Constructs (Universals)
These apply equally well to all cultures.
Examples:
Fairness: The slides show a study with monkeys who get angry when paid unequally (cucumber vs. grape), suggesting a biological, universal sense of fairness.
Price Hikes: Humans universally dislike "unfair" price gouging, such as the Daraprim drug price hike from $13.50 to $750.
Quality Signals: A study by Dawar and Parker (1994) found that across 38 countries, consumers universally use Brand Name, Price, and Physical Appearance to judge quality.
2. Emic Constructs (Culture-Specific)
These only apply to a specific culture and don't translate well.
Examples:
Guanxi: A Chinese concept of networks/relationships.
Hygge: A Danish concept of coziness.

Self reflection questions Session 1

Here are the refined and comprehensive answers to all 10 self-check questions. I have polished your existing good answers to match the lecture terminology perfectly and provided full explanations for the ones you were unsure about.
1. Market Definition: The 5C's Model
Answer: The 5C's are Context, Company, Collaborators, Competitors, and Customers .
Refinement:
Context: The outer ring representing the macro-environment (factors outside the company's control).
The Core: The other four (Company, Collaborators, Competitors, Customers) sit inside the context and interact directly.
2. Examples of the 5C's (Using Apple)
Answer:
Context: The global shift toward remote work and digital nomadism (Sociocultural/Technological).
Company: Apple Inc., with its strong brand equity, iOS ecosystem, and internal R&D capabilities.
Collaborators: App Store developers (crucial partners), authorized service providers, and Foxconn (manufacturers).
Competitors: Samsung (hardware), Google (OS), and increasingly services like Spotify.
Customers: Users seeking status, privacy, and ecosystem integration; includes distinct segments like creative professionals vs. casual users.
3. Factors Defining Market CONTEXT
Answer: The context is defined by five factors: Sociocultural, Technological, Regulatory, Economic, and Physical .
4. Examples of Context Factors (Using Apple)
Answer:
Sociocultural: The trend of "status" consumption in developing markets; lifestyle shifts requiring portable health monitoring (Apple Watch).
Technological: The rise of AI and 5G infrastructure needed to support new iPhone features.
Regulatory: The EU "Common Charger Directive" forcing the switch to USB-C; data privacy laws (GDPR) affecting how Apple tracks users.
Economic: Global inflation and recession fears reducing disposable income for luxury tech products.
Physical: Supply chain reliance on rare earth minerals; climate change driving the need for "Carbon Neutral" branding.
5. What is the "Optimal Value Proposition"?
Answer: The Optimal Value Proposition is the intersection where Customer Value, Company Value, and Collaborator Value overlap.
Refinement: It is the "sweet spot" where the company creates value for the customer (they want to buy it) and the collaborator (they want to partner), while still capturing value for itself (profit/growth) .
6. How to assess if a Value Proposition is optimal?
Answer: You assess it by checking for conflicts or imbalances between the three stakeholders.
The Assessment Test:
Customer Check: Is the product better than the competition? (If no, customers won't buy) .
Collaborator Check: Do partners (franchisees/retailers) make a fair profit? (If no, they will quit or underperform, like the "Uber China" drivers or Dodo franchisees) .
Company Check: Is it profitable and sustainable for us? (If no, the business fails) .
Conclusion: If the answer to all three is "Yes," it is optimal. If satisfying the customer bankrupts the collaborator, it is not optimal.
7. Levitt's Theory: Strengths, Weaknesses, and Applicability
Answer:
The Theory: Theodore Levitt (1983) argued that technology is driving the world toward a "converging commonality." He believed global companies should standardize products to achieve low costs and low prices, which everyone wants.
Strengths:
Economies of Scale: Mass production lowers unit costs.
Lower Prices: Standardized products are cheaper for consumers.
Global Branding: Creates a consistent worldwide image.
Weaknesses:
Cultural Blindness: Assumes consumers only care about price and quality, ignoring cultural preferences (e.g., taste in food).
Alienation: Consumers may reject generic global products in favor of local ones that fit their specific needs better.
When it Holds: Likely to hold for industrial products (steel, chemicals) or technology (iPhone, microchips) where usage is universal.
When it Fails: Less likely to hold for food, fashion, or cultural services, where local taste dominates (e.g., McDonald's adapting menus).
8. What are Emic and Etic constructs?
Answer:
Etic Constructs: Concepts that are universal. They apply equally well to all cultures and are often used in cross-sectional comparisons.
Emic Constructs: Concepts that are culture-specific. They exist only within a specific culture and do not translate well to others.
9. Examples of Emic and Etic constructs
Answer:
Etic (Universal):
Fairness Norms: Humans (and even monkeys!) universally dislike unequal treatment.
Quality Signals: Across 38 countries, consumers universally use Brand Name, Price, and Physical Appearance to judge quality.
Emic (Specific):
Guanxi (China): A specific system of social networks and influential relationships.
Hygge (Denmark): A specific sense of coziness and wellbeing.
10. Weaknesses of the Cultural Universals Study (Dawar and Parker)
Answer: While the study found universal behaviors, the design had specific flaws that might make the world look more similar than it really is:
Sampling Bias (The "Global Elite"): They only surveyed people who were "young, mobile, affluent, and educated". A rich student in London is naturally very similar to a rich student in Mumbai. This ignores the vast differences between the general/rural populations of those countries.
Product Category Bias: They tested "Technology products" (electronics). Tech is inherently more standardized. If they had tested food or traditional clothing, they likely would have found fewer universals.
Grouping Bias: The study grouped vastly different countries into broad clusters (e.g., placing China, Hong Kong, Singapore, and South Africa into one "Other" group). This generalizes results and hides distinct cultural differences within those groups