China_Korea_Japan
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
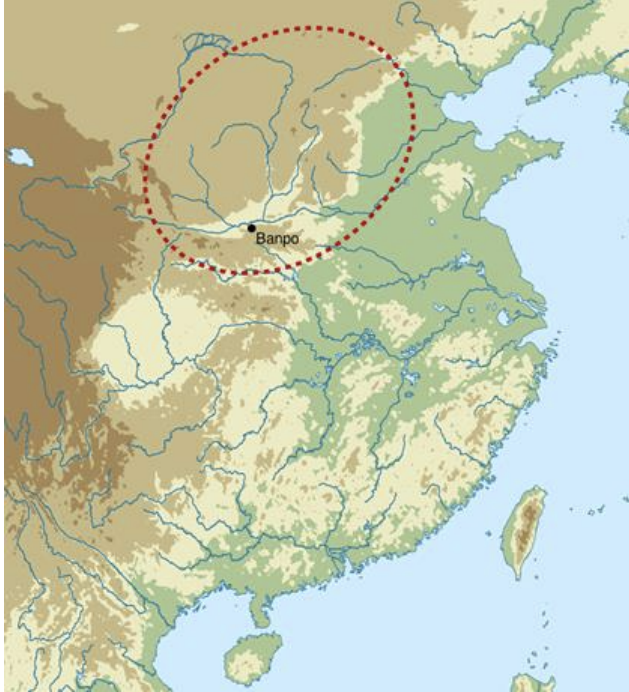
Banpo, China, ca. 4600-3500 BCE
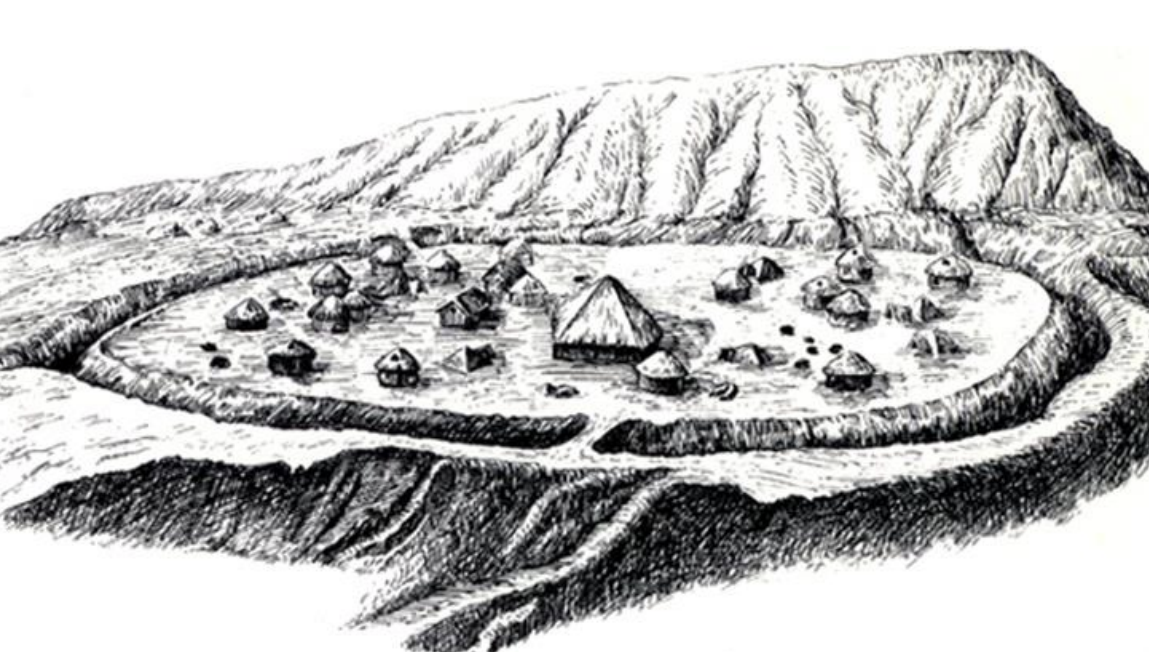
Banpo, China, ca. 4600-3500 BCE
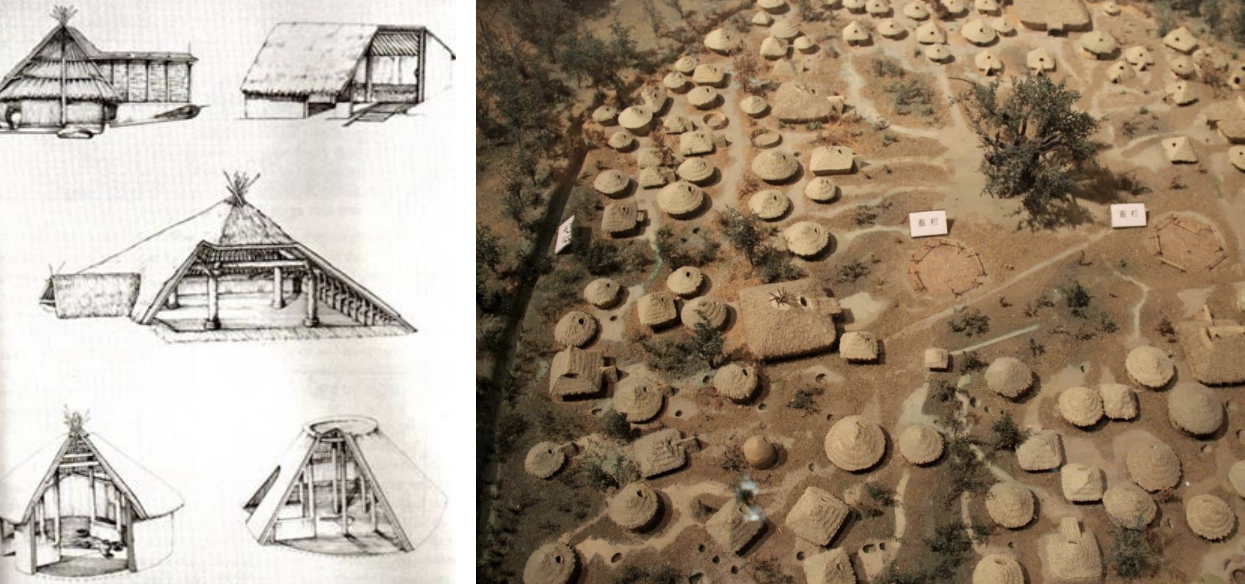

Left Yangshao dwellings (Banpo) and (Jiangzhai), China, ca. 4600-3500 BCE

Oracle Bone, China, ca. 1500-1200 BCE
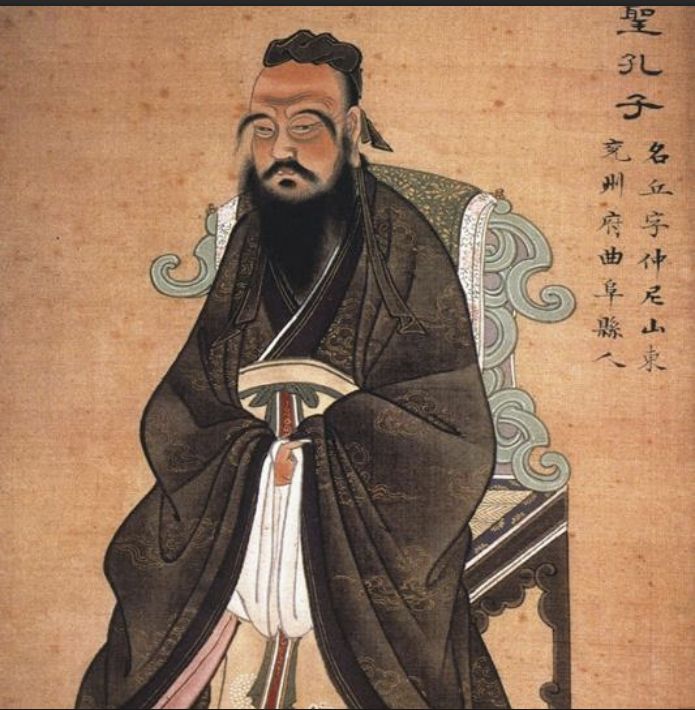

Confucius, ca. 551-473 BCE
Confucianism
social and ethical philosophy situated around benevolence and authorial respect

Laozi (Loa-Tzu/Lao-Tze), ca. 6th-4th century BCE
Taoism
anti-authoritarianism, harmony with nature, yin and yang duality

Kao Gong Ji, China, ca. 400 BCE
Li
measurement 9 ______ =4.5km (Chinese mile)
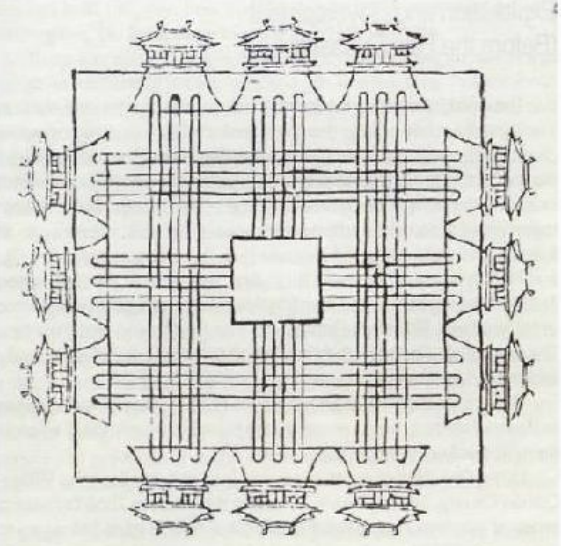
Wangcheng (Ruler’s City), 1676
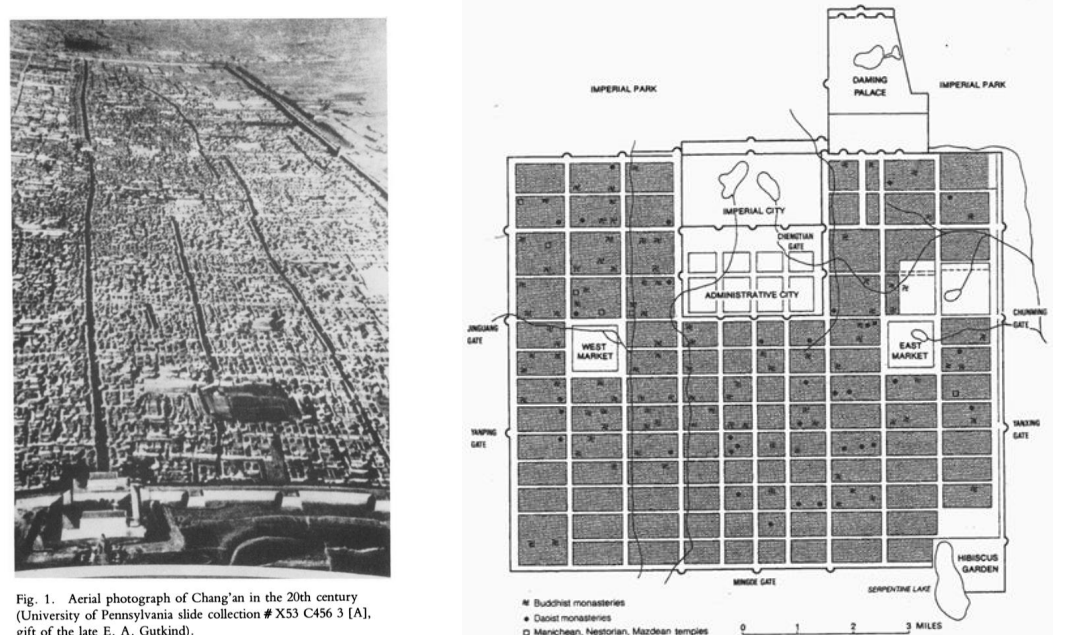
Chang’an, China, 582-904 CE
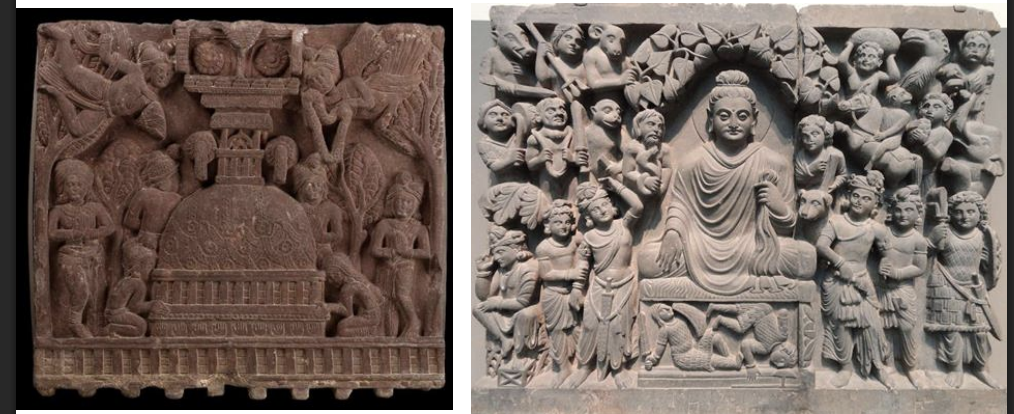

Representations of Buddha (Siddhartha Gautama), 1st century BCE and 2nd century CE
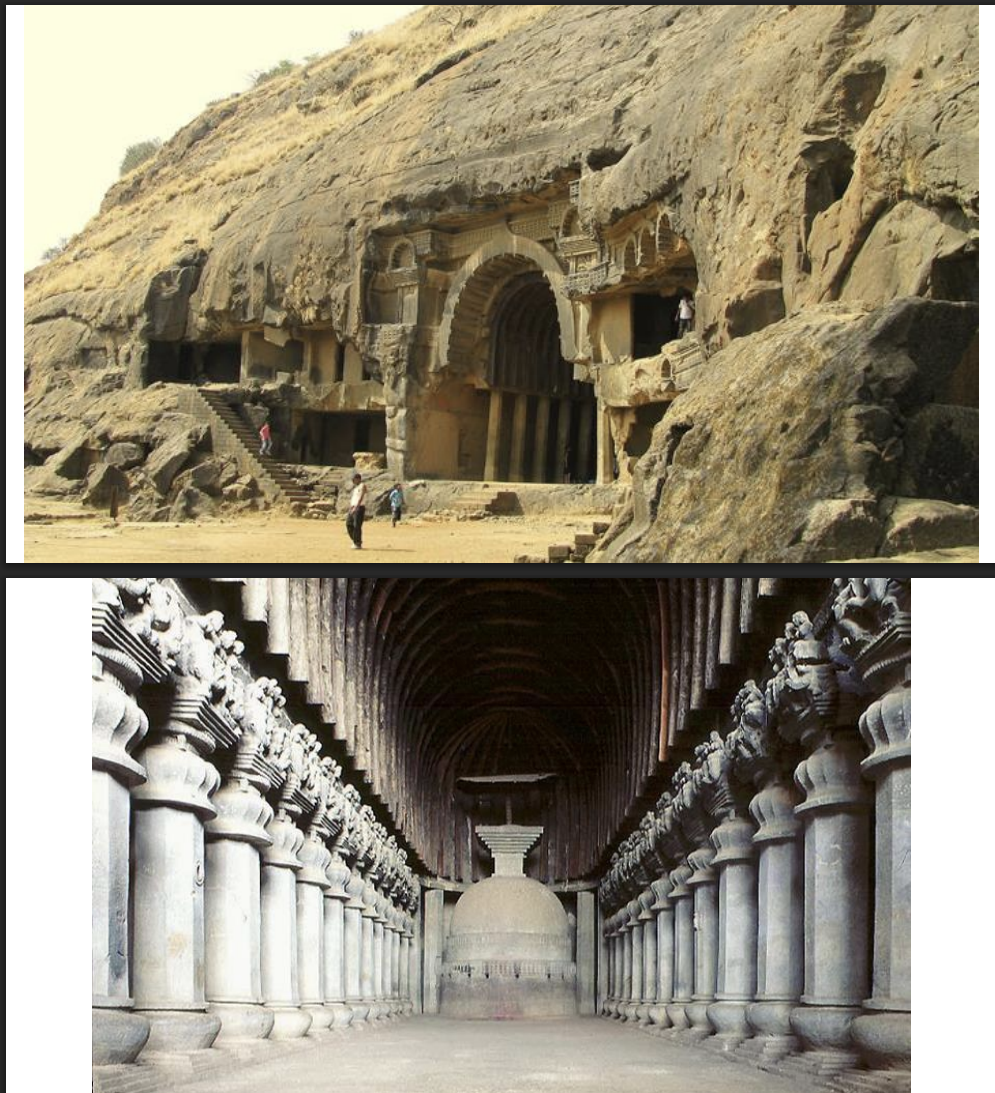

Cave Temple, Karli, ca. 100 BCE

Yungang Grottoes, China, ca. 400 CE
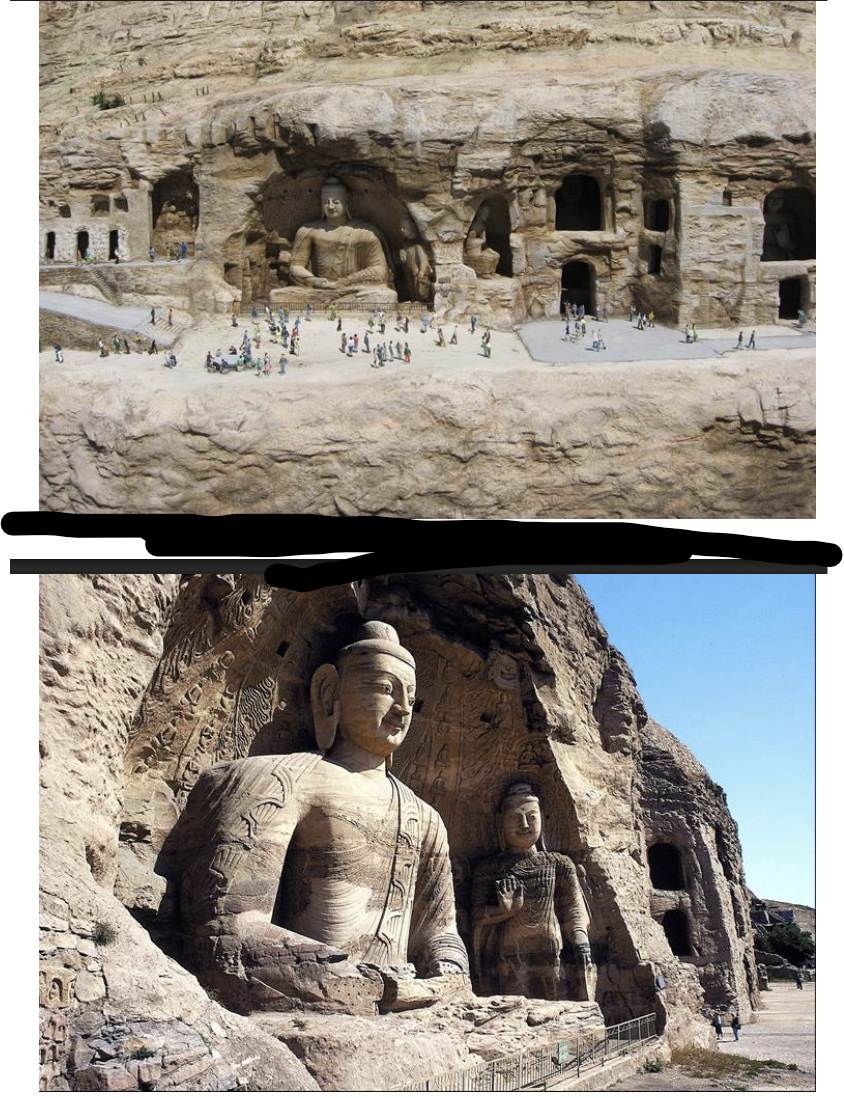

Yungang Grottoes, China, ca. 400-500 CE
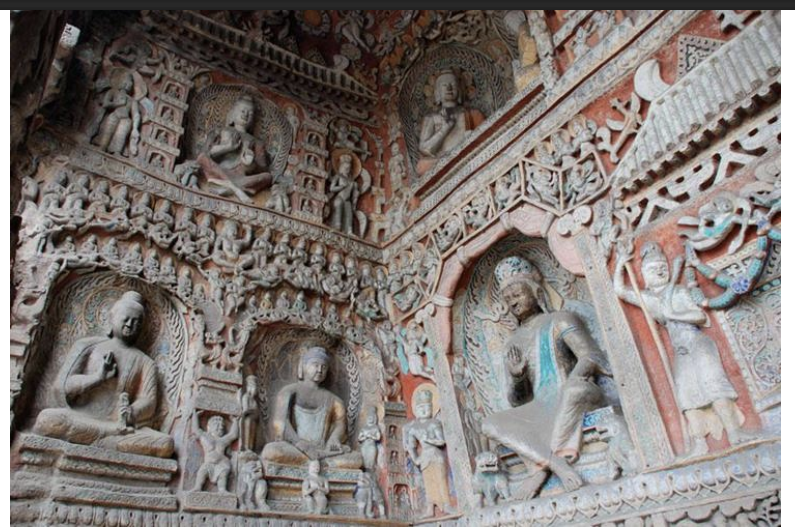

Yungang Grottoes, China, ca. 400-500 CE
Pagoda
Is a type of spiritual, monumental and high tech architecture of the period from the late Eastern Han (25-220 CE) until the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911 CE) in China. The Pagoda is a storeyed tower, and each story is a separate building consisting of all structural components.

Painted pottery model of a fortified manor, mid-Eastern Han. Excavated in 1993 at Jiaozuo, Henan province. Height: 192cm (main building).

Glazed pottery model of a courtyard house, Eastern Han. Excavated in 1969 at Leitai, Wuwei, Gansu. Height: 105cm.
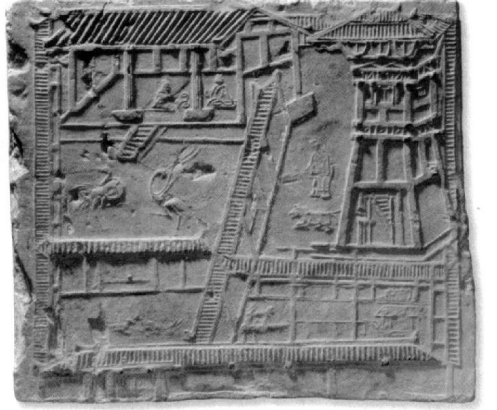
Pictorial brick, Han dynasty. Excavated in Chendu, Sichuan. province. 48x41cm.
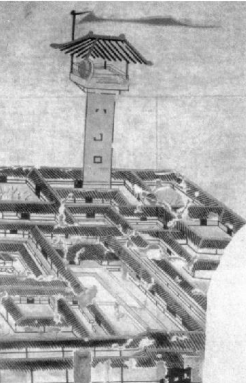
Watchtower depicted in the wall painting of a Han tomb, ad 176, at An'ping, Hebei province.

Model of waterside pavilion with figures, Eastern Han. Excavated at Songwanhe, Xichuan. Height: 53cm, Diameter 43ст.

Pavilion tower, 2d half of Eastern Han. Excavated in 1987 from no. 4 tomь, Liujiaqu, Sanmenxia. Height: 107cm, Diameter 45cm.

Pavilion tower with its basin lost, late Eastern Han. Collected in 1954 at Niunuzhong, Huiyang. Height: 144cm, Width: 43cmт, Length: 47ст.
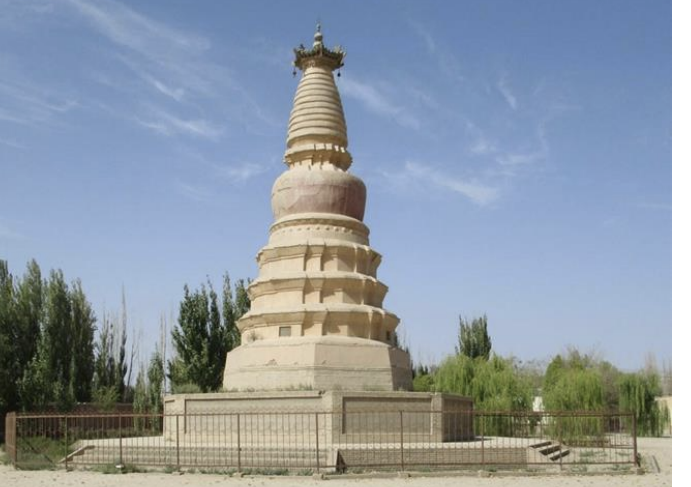

White Horse Pagoda, China, 384 CE
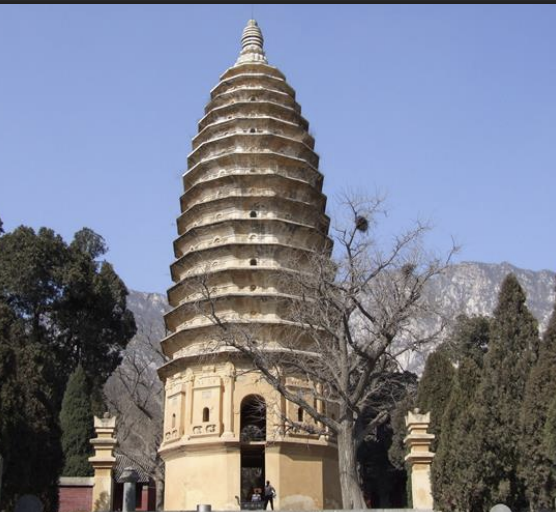

Songyue Pagoda, China, 523 CE

Fogong Pagoda, China, 1056 CE
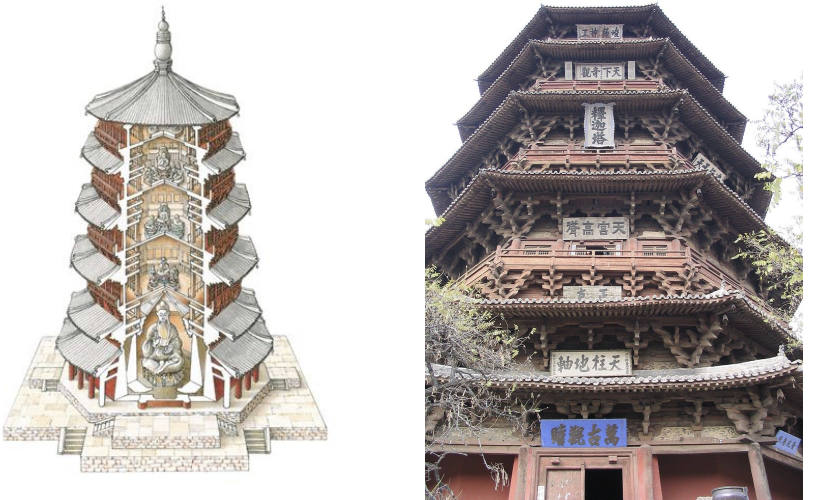

Fogong Pagoda, China, 1056 CE

The Tang Code
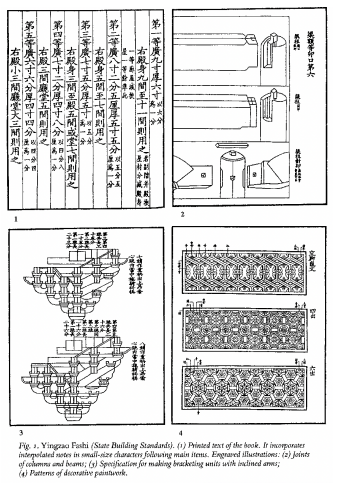
examples of pages from Yingzao Fashi (“State Building Standards”), 1103 CE

Jørn Utzon's 1925 edition of Yingzao fashi, bought in Beijing in 1958. The Utzon Archives, Aalborg University Library.
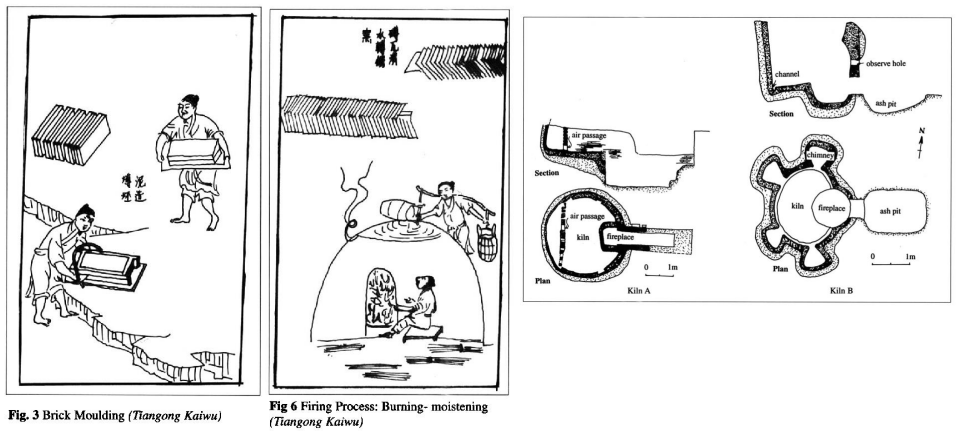
Illustrations included in Qinghua Guo, "Tile and Brick Making in China: a Study of the "Yingzao Fashi”
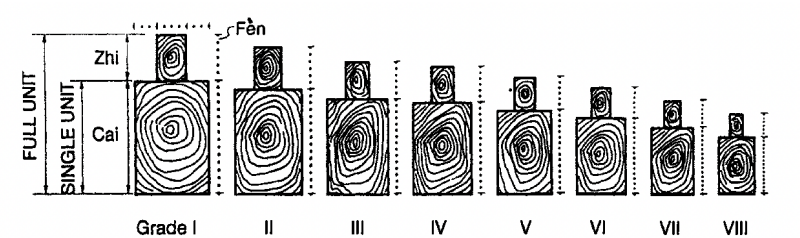
Cai-fen system (grading system of timber elements)
jian
space between columns
duogong
cap and block system; network of wooden joinery or interlocking brackets that distribute weight of horizontal beam to vertical
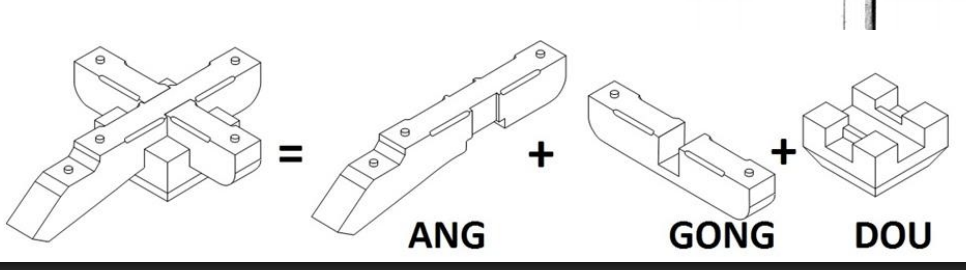
duogong
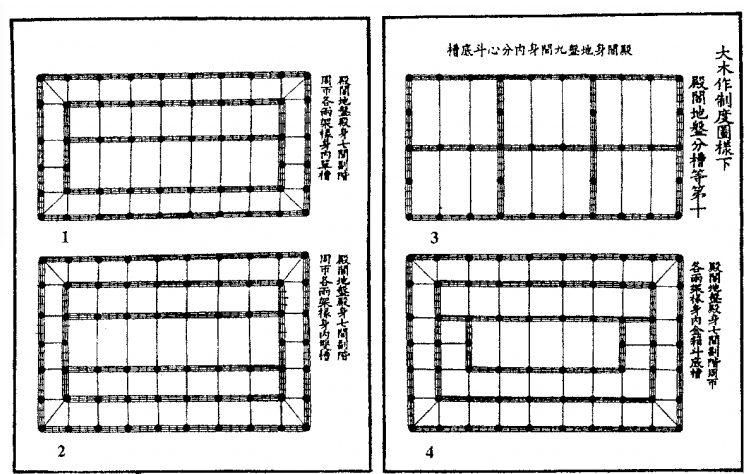
Inner structural arrangements of palace-type buildings: (1) single cao; (2) double; (3) cruciform; (4) rectangular.
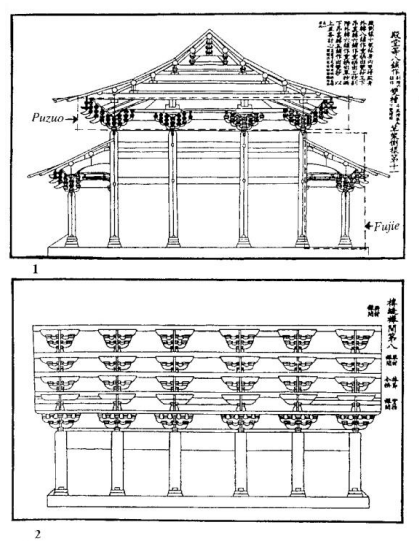
Palace-type building: (1) Transverse framework; (2) Longitudinal framework.
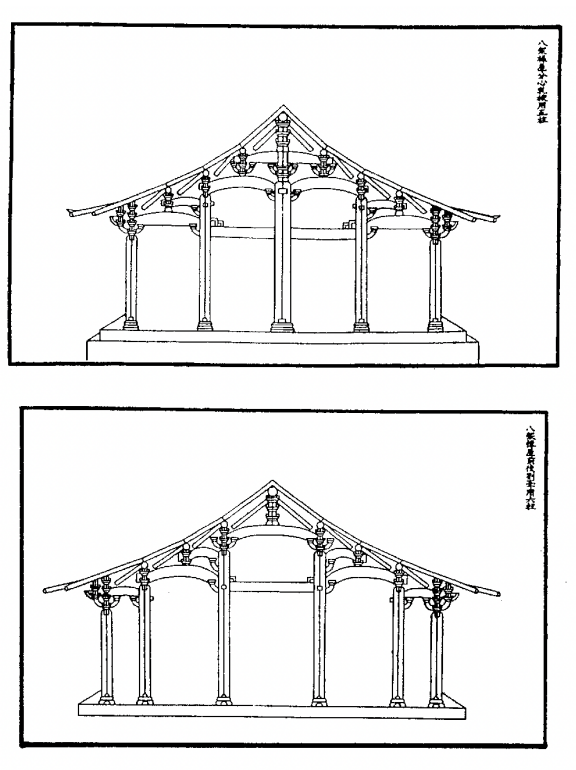
Mansion-type buildings. A total of 18 different patterns are specified in the Yingzao Fashi.
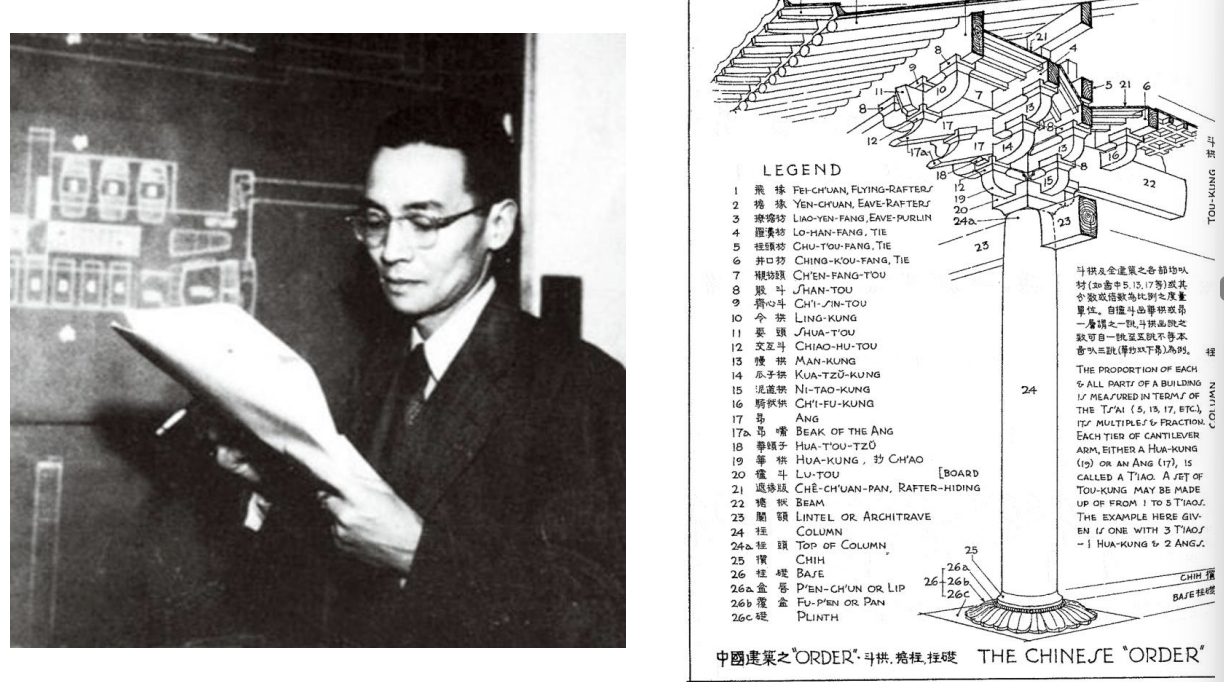
Liang Sicheng proposed Architectural Order
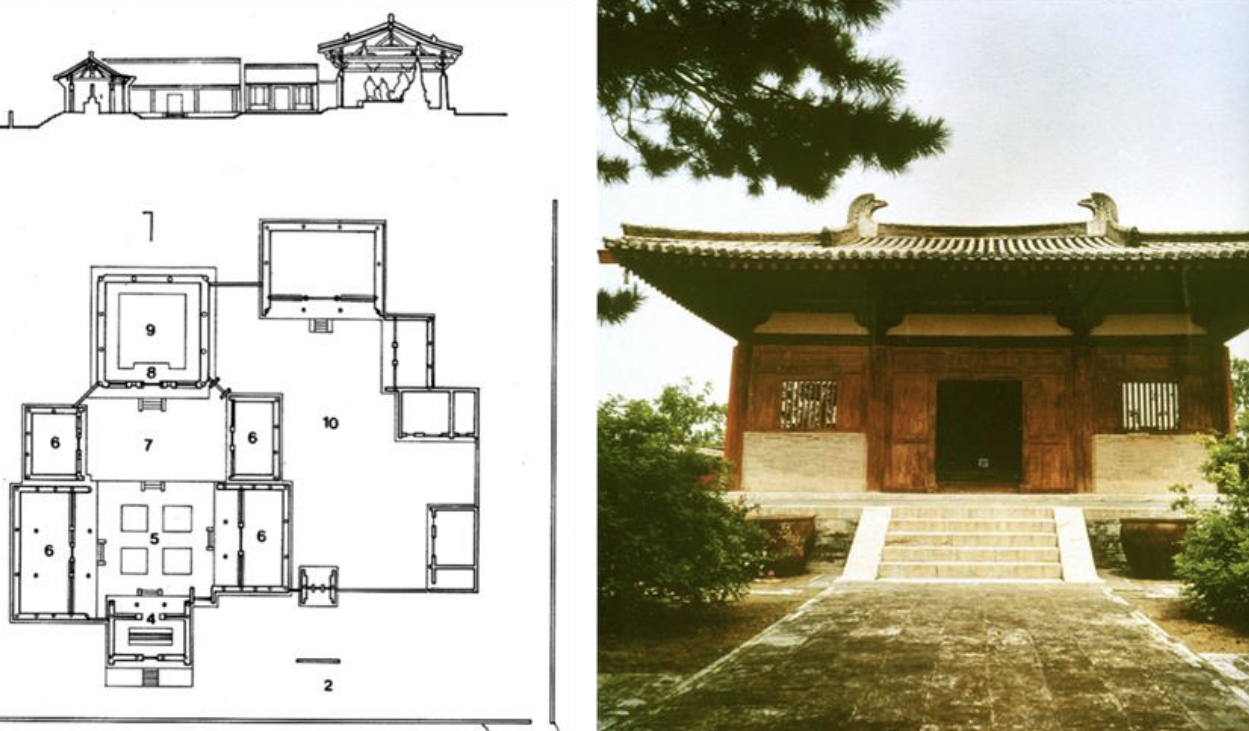
Nanchan Temple, China, 782 CE
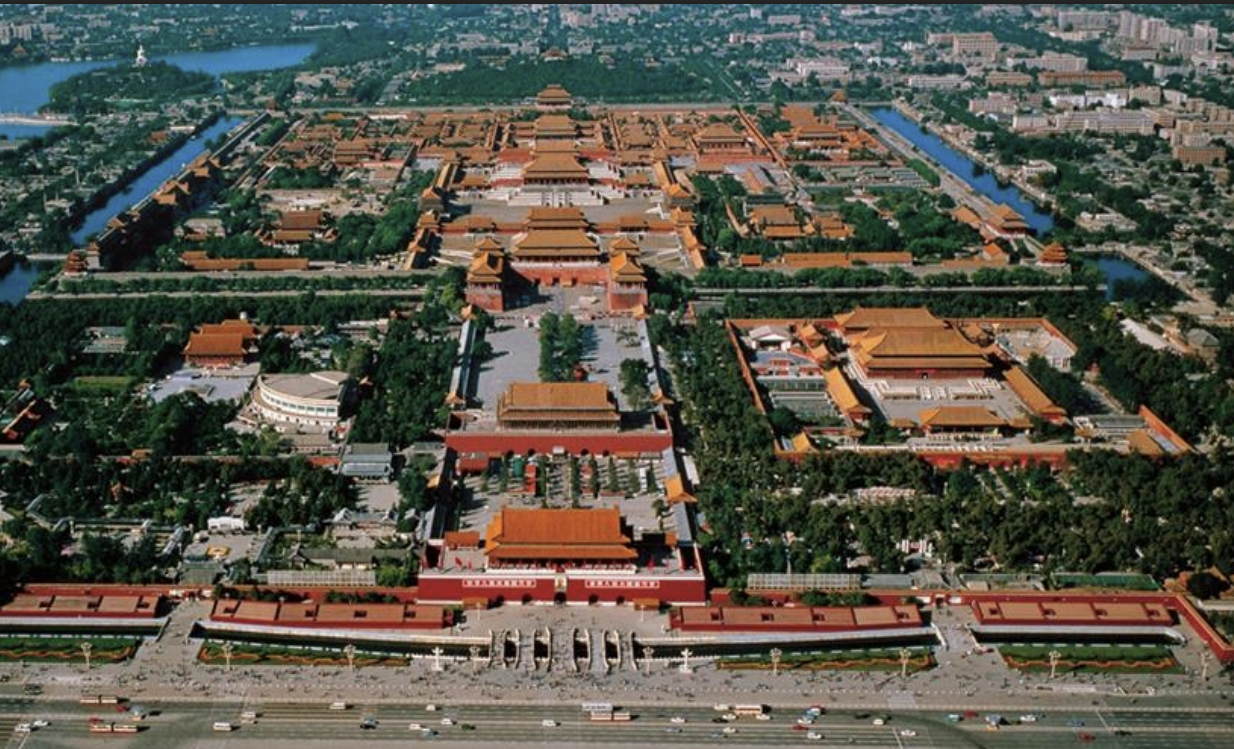

Forbidden City, China, 1406-1420 CE
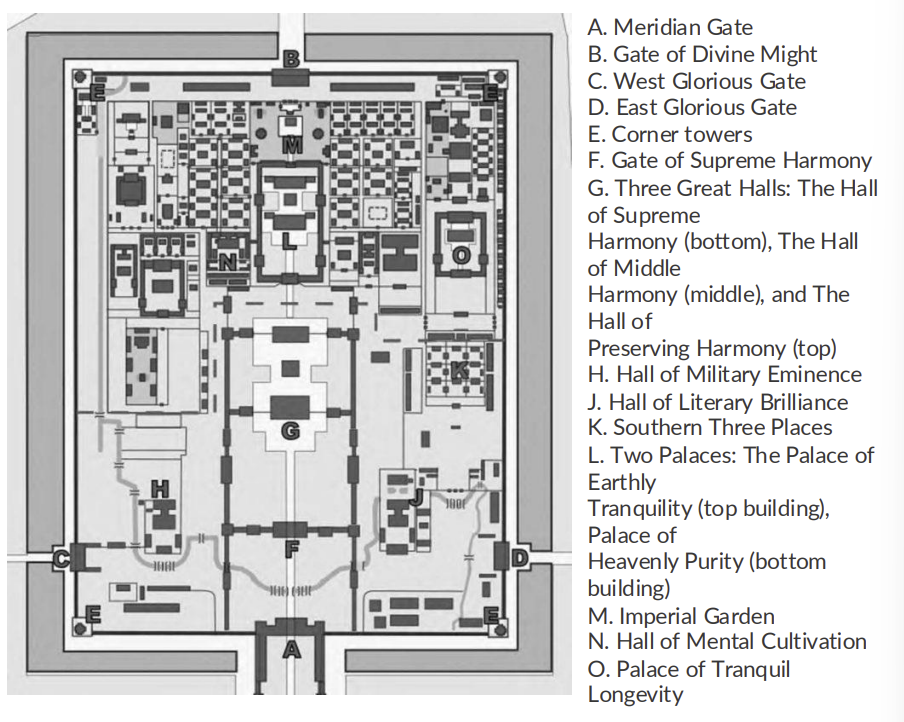
Forbidden City, China, 1406-1420 CE
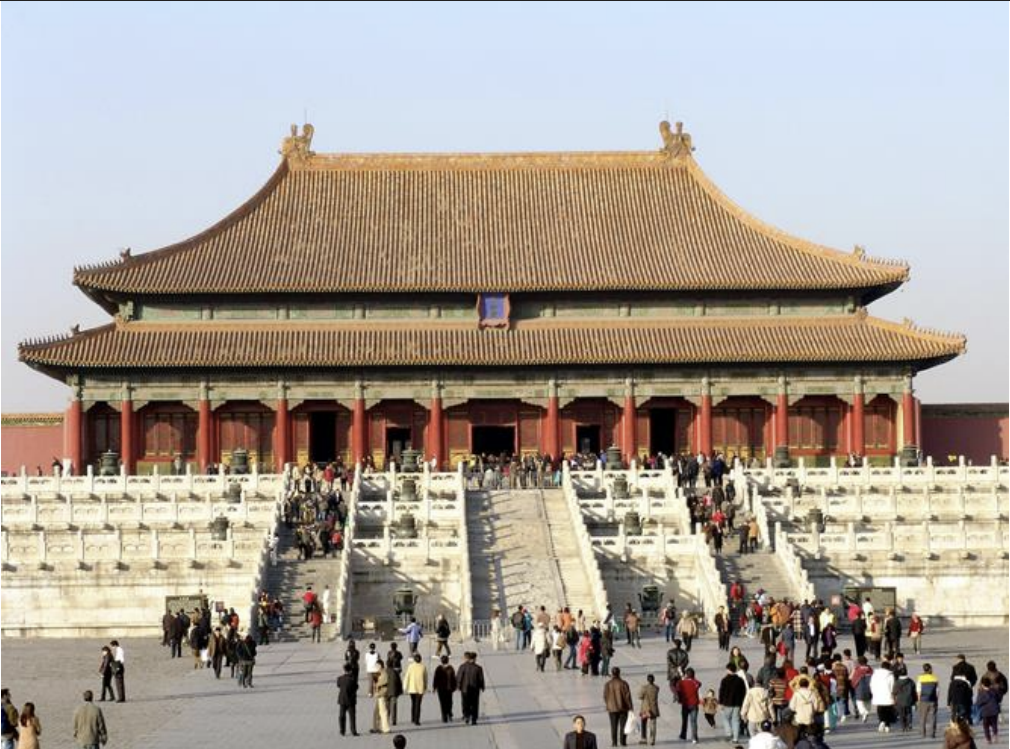

Hall of Supreme Harmony, Forbidden City, China, 1406-1420 CE
“Wu Xing”
Elemental concept of the world relating to fire, water, wood, earth, metal (the five Elements)
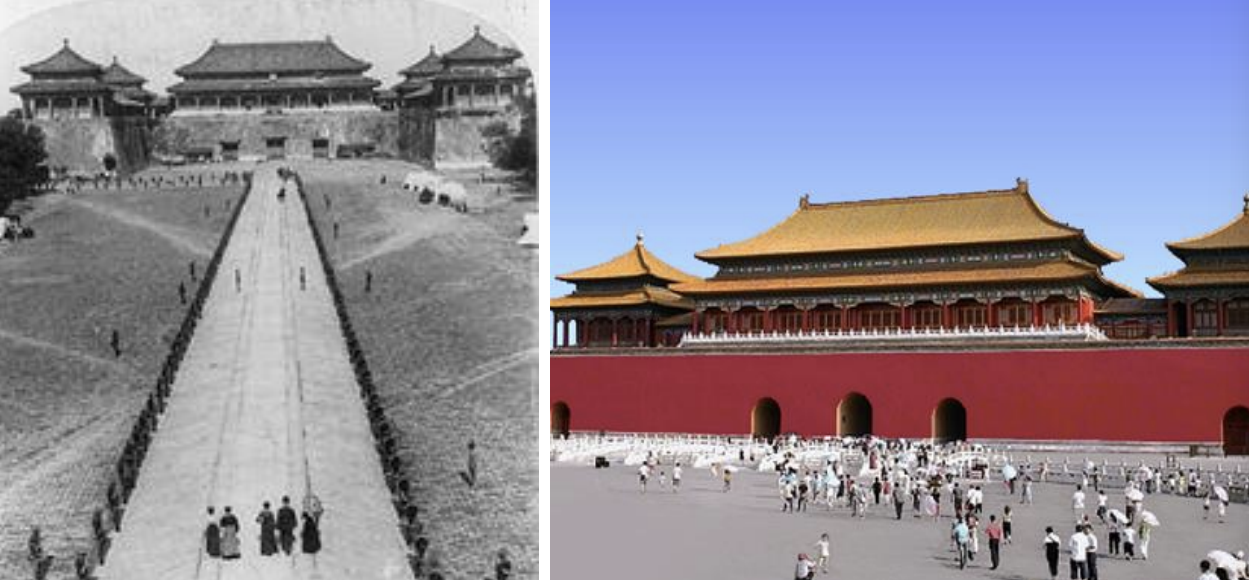

Forbidden City, China, 1406-1420 CE
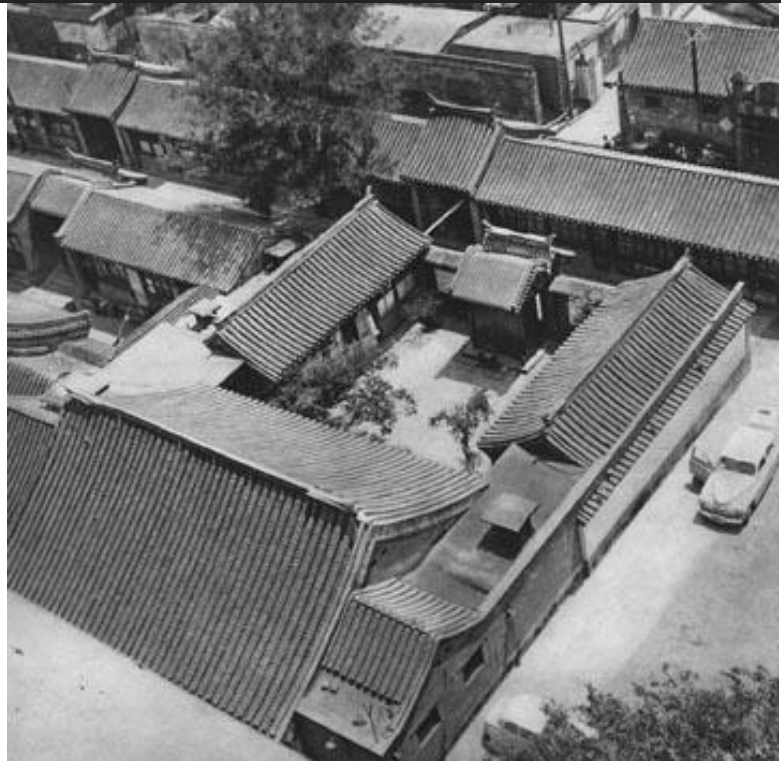

Common house type, Siheyuan
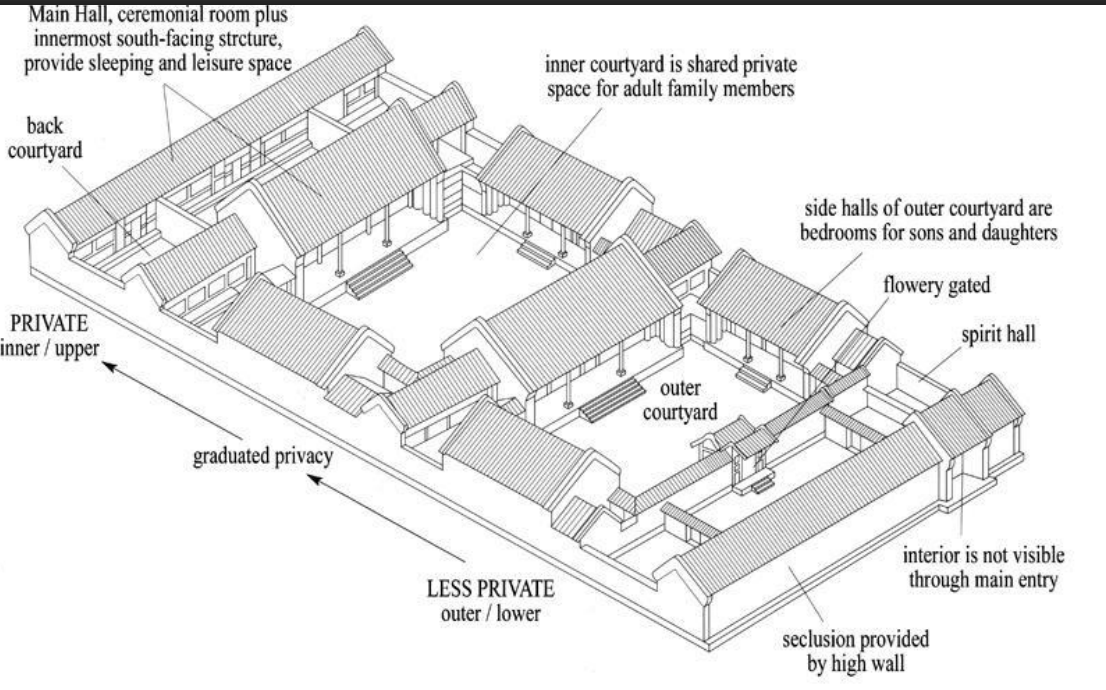
Common house type, Siheyuan
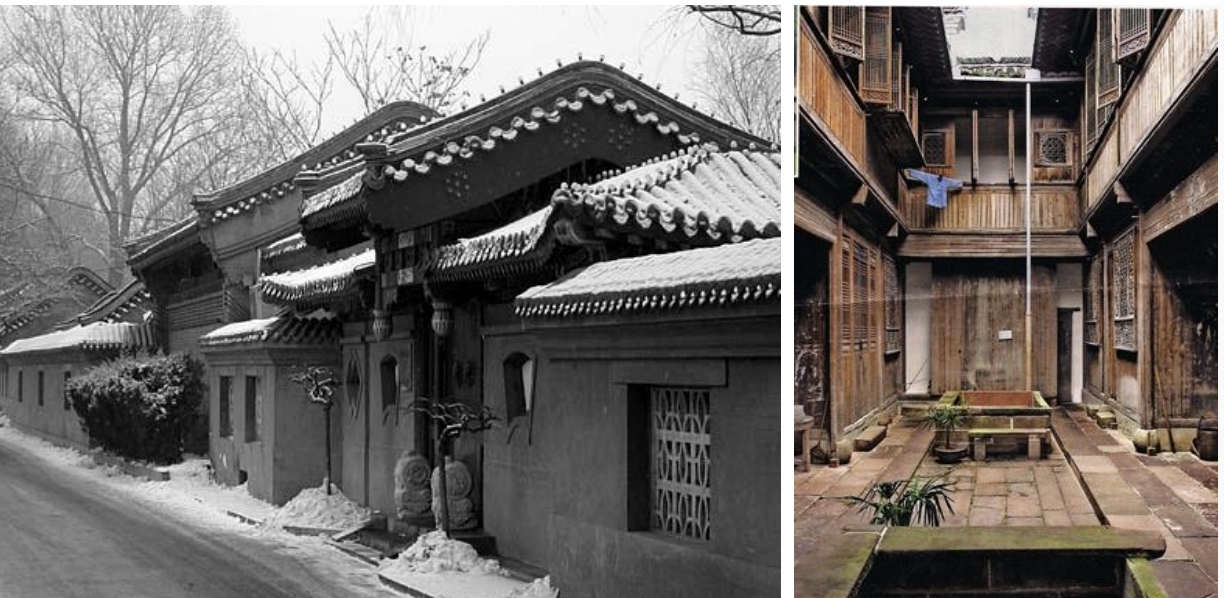

Common house type, Siheyuan
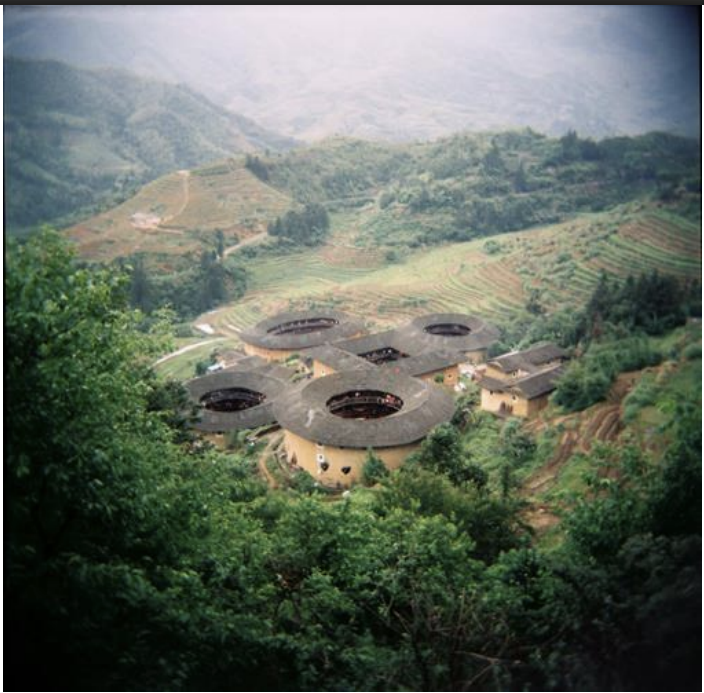

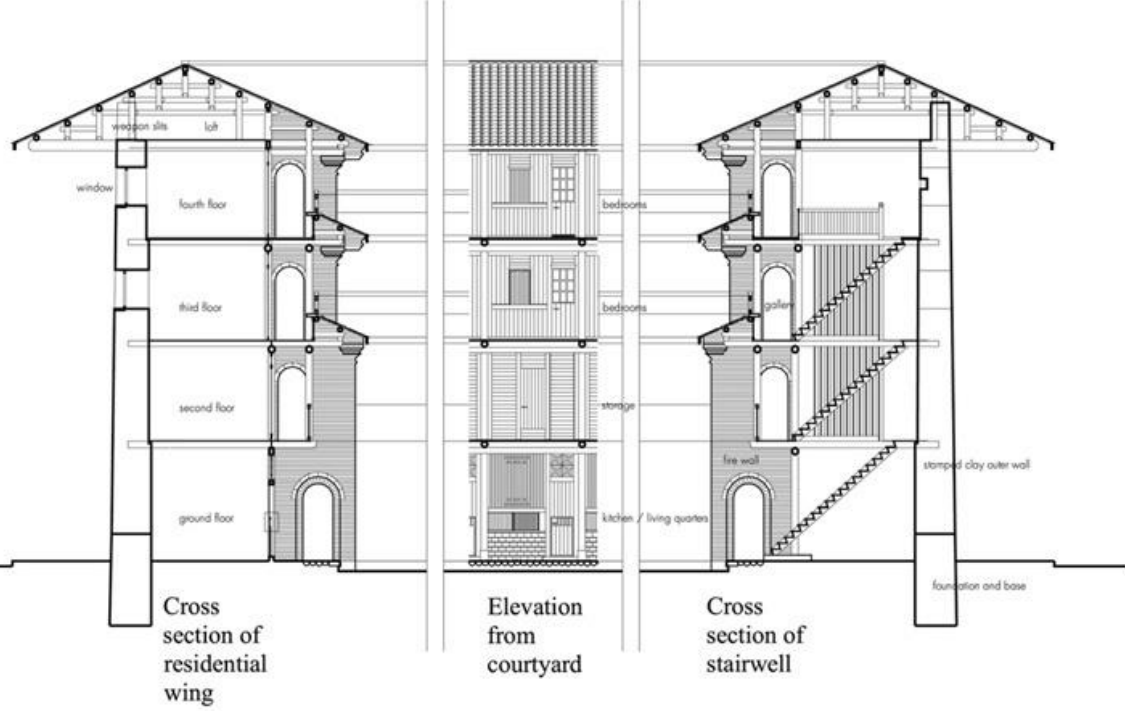
Tulou, China, ca. 1100 CE - present
tulou
communal residence, usually of a circular configuration surrounding a central shrine; literally “earthen building”
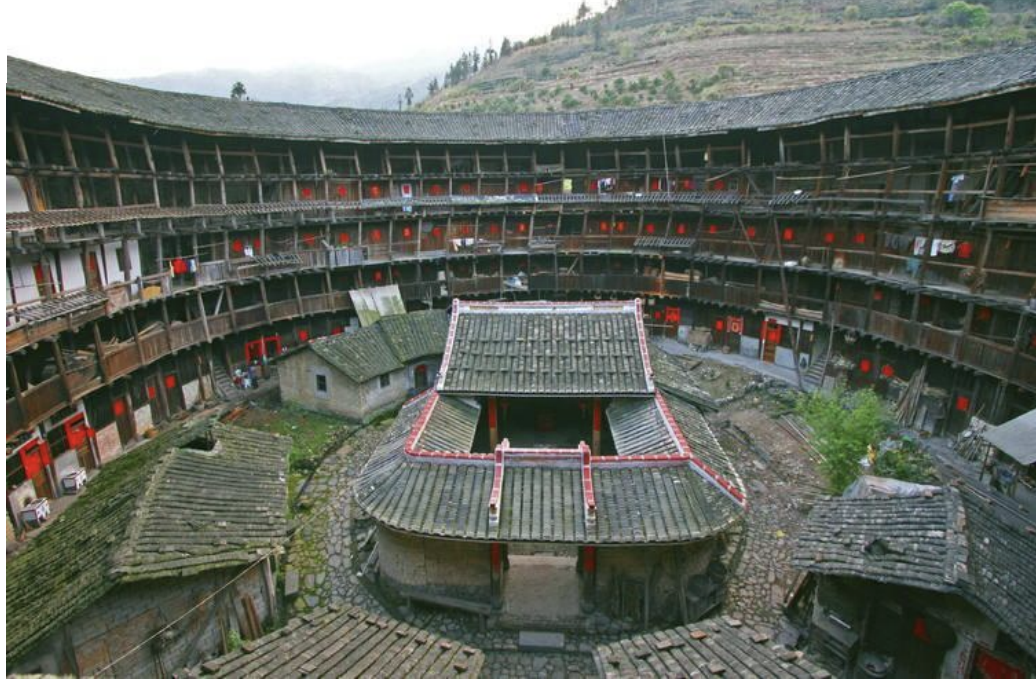

Tulou, China, ca. 1100 CE - present
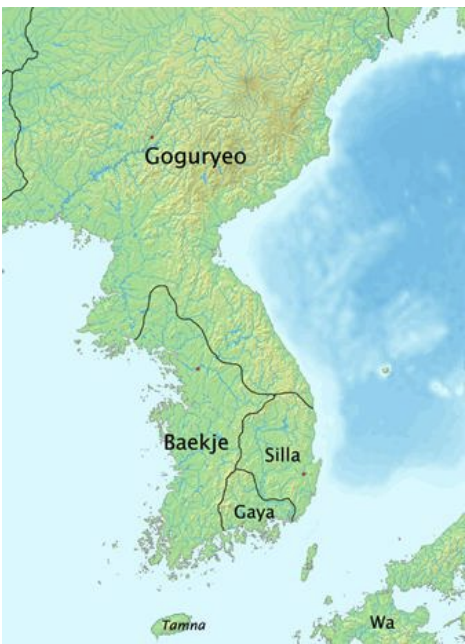
Baekje Kingdom, 18-660 CE
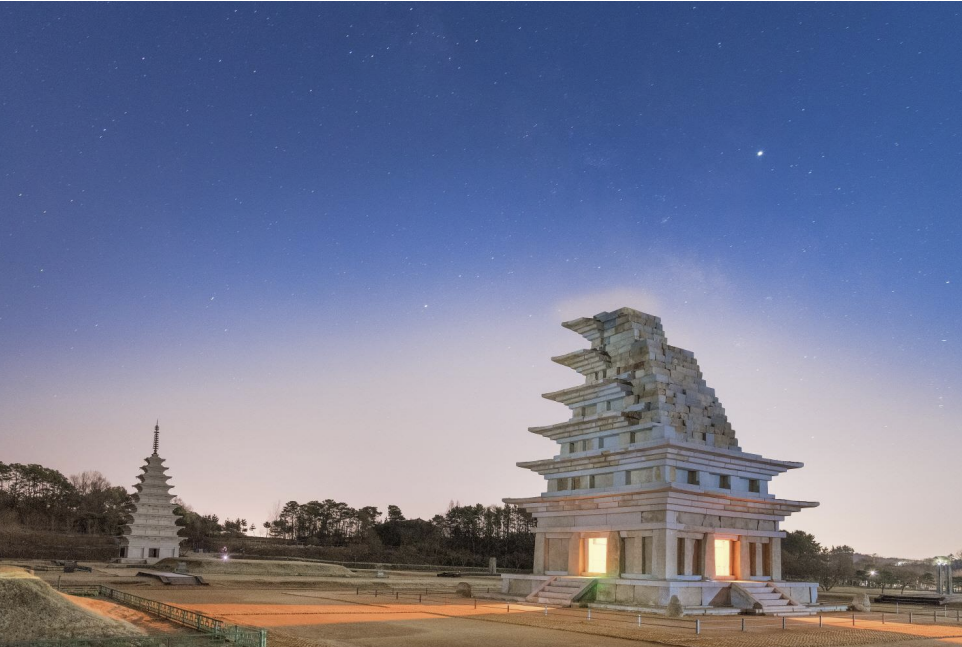

Mireuksa, Korea, ca. 602 CE
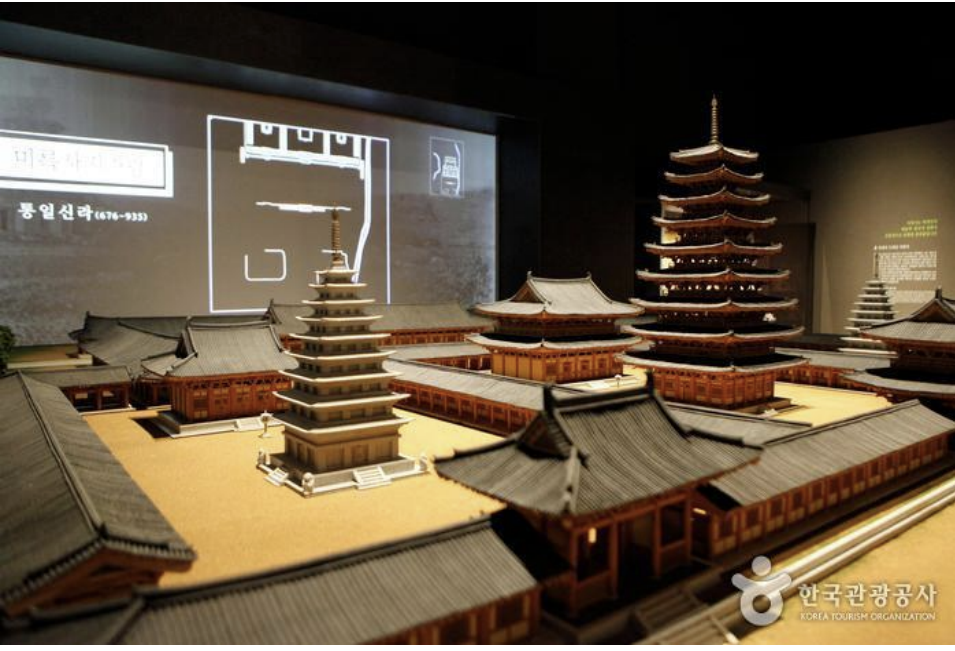

A model of Mireuksa Temple found inside the Iksan National Museum
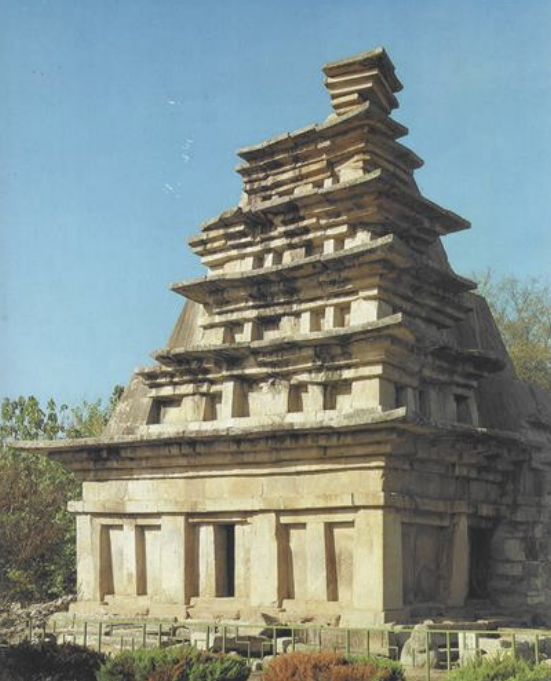

Stone Pagoda, Mireuksa, Korea, ca. 602 CE
Joseon dynasty (1392–1910)
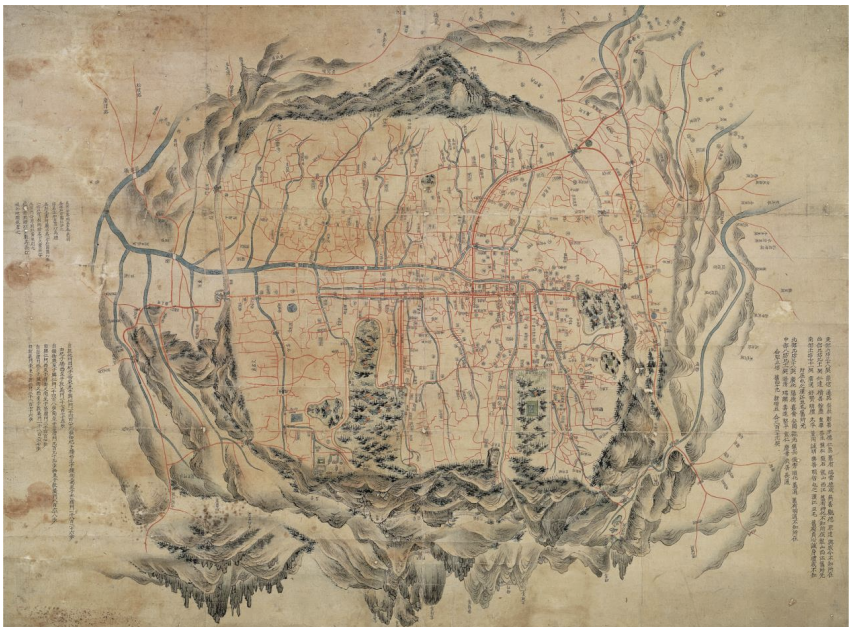
Map of Seoul (ca. late 18th c)
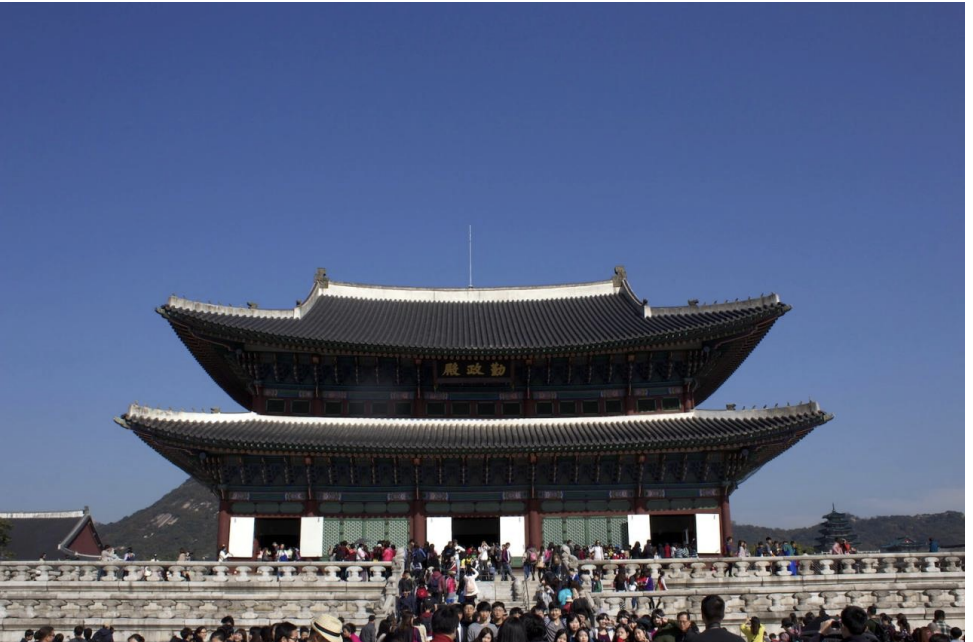

Gyeongbokgung, or Gyeongbok Palace ca. 1395CE
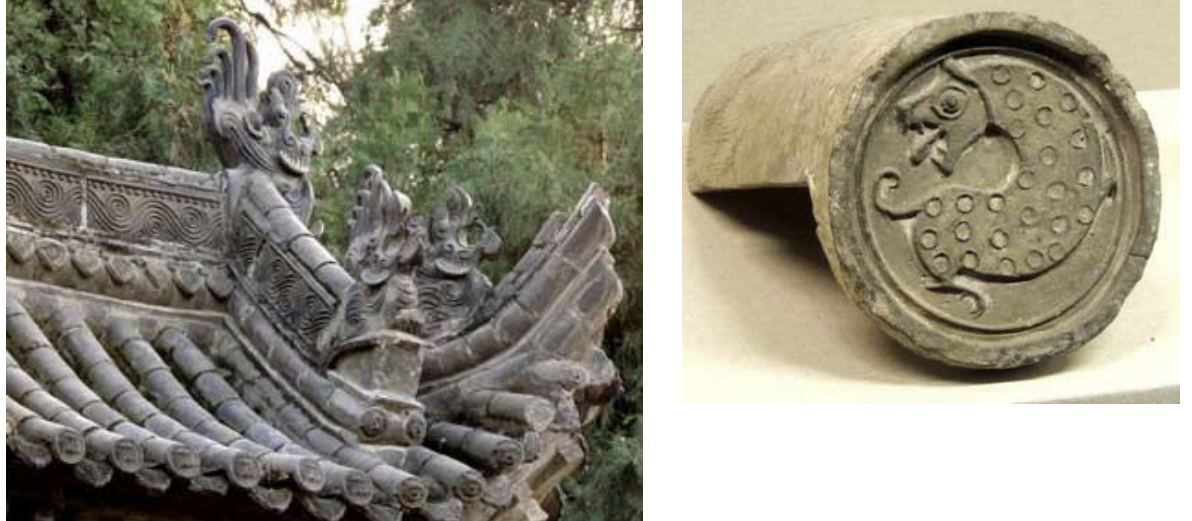

Tile-End: a particular piece of tile that is placed over the last tile in each line of tiles on the traditional Chinese roof."
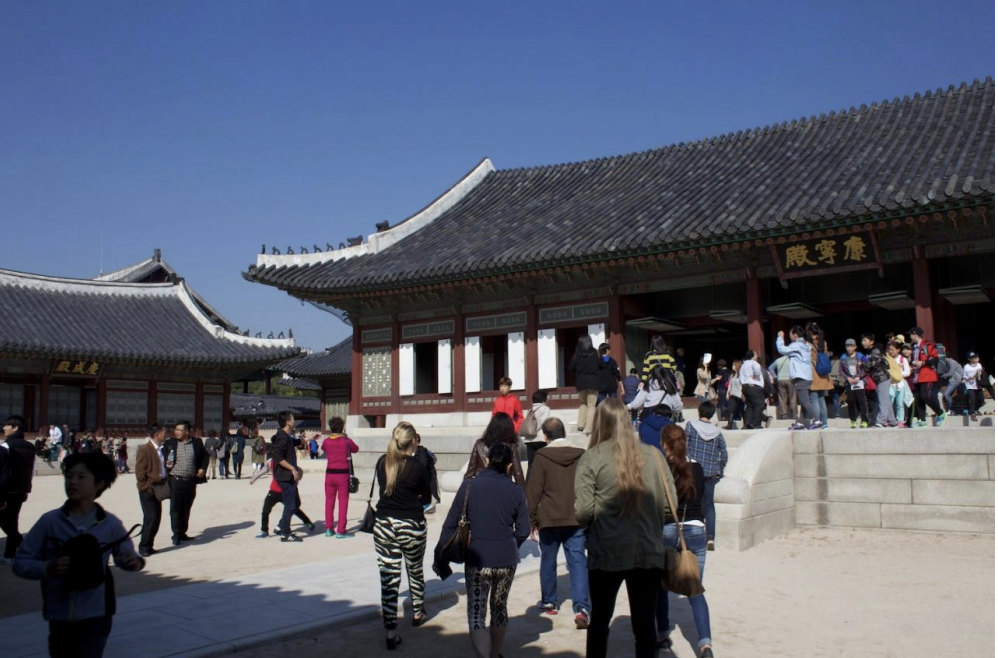

Gyeongbokgung, or Gyeongbok Palace ca. 1395CE
Tile End
A particular piece of tile that is placed over the last tile in each line of tiles on the traditional Chinese roof."
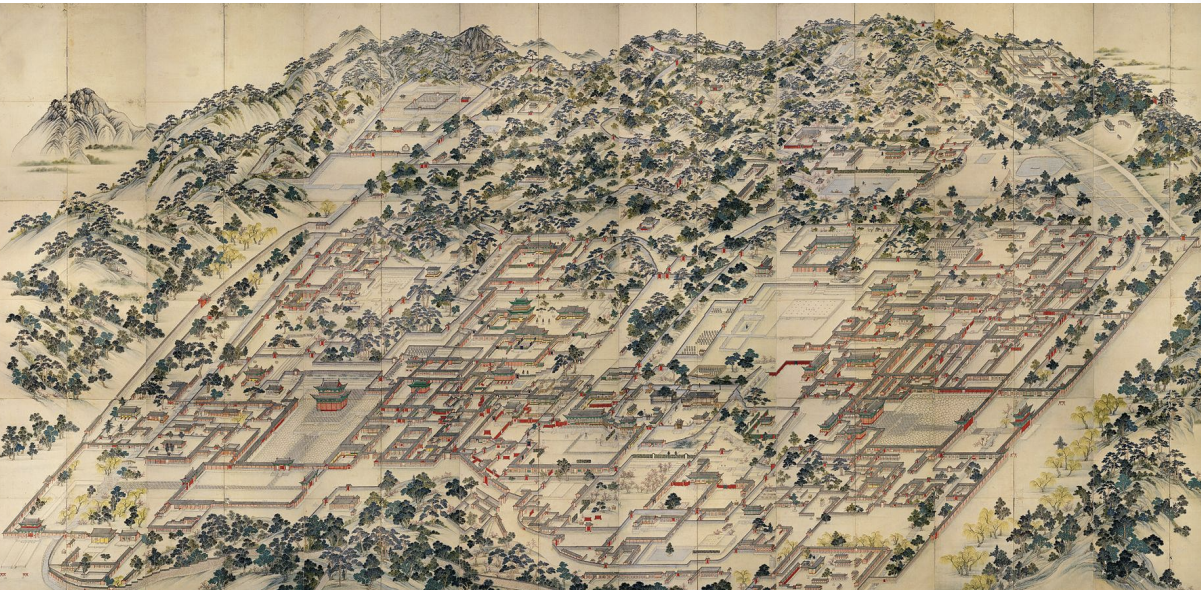
Donggwoldo painting Changdeokgung Palace Complex, Painted c. 1830.
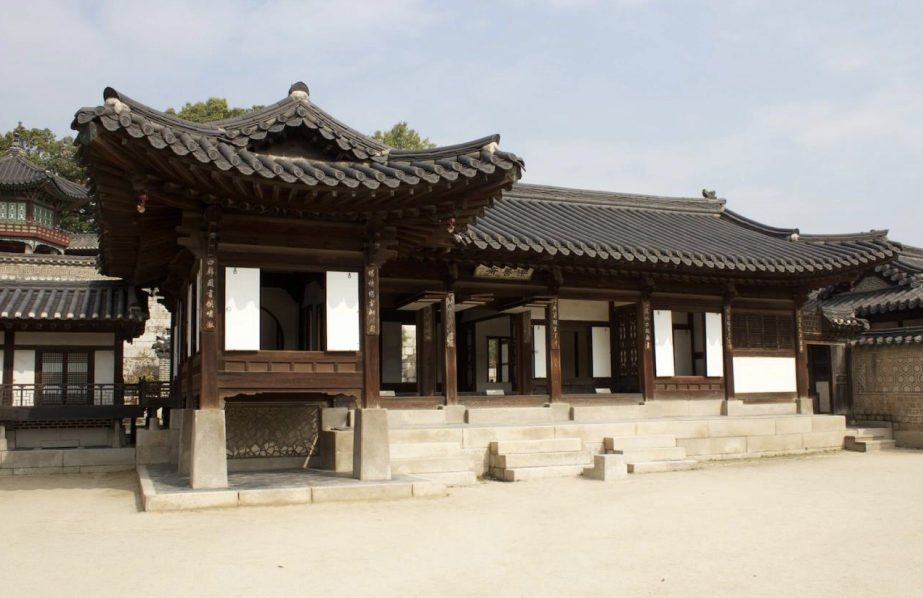

Changdeokgung Palace Complex, Seoul, Korea, 1405 and 1412 CE
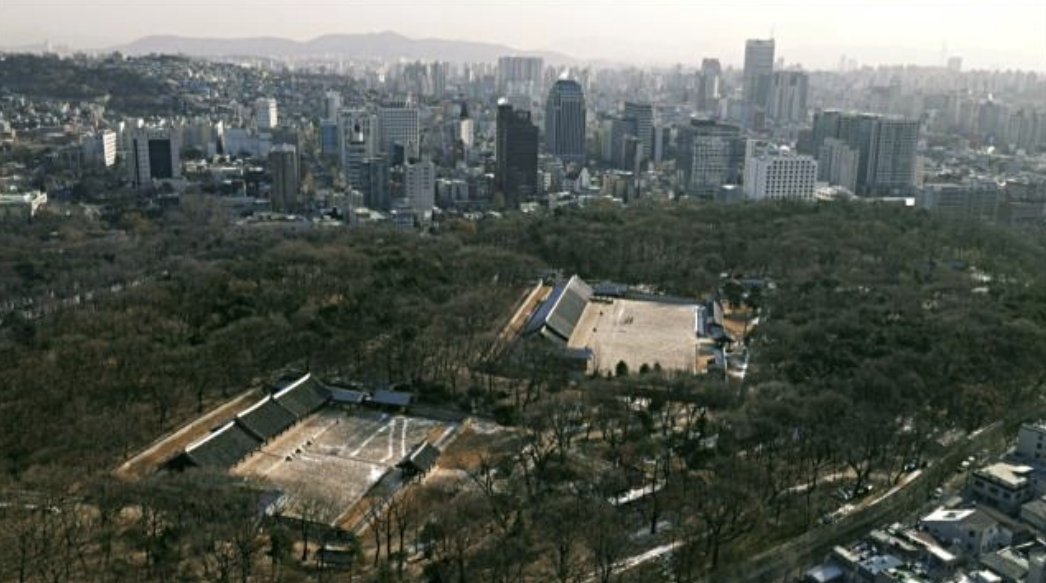

Jongmyo Shrine, Korea, 1395-1836 CE
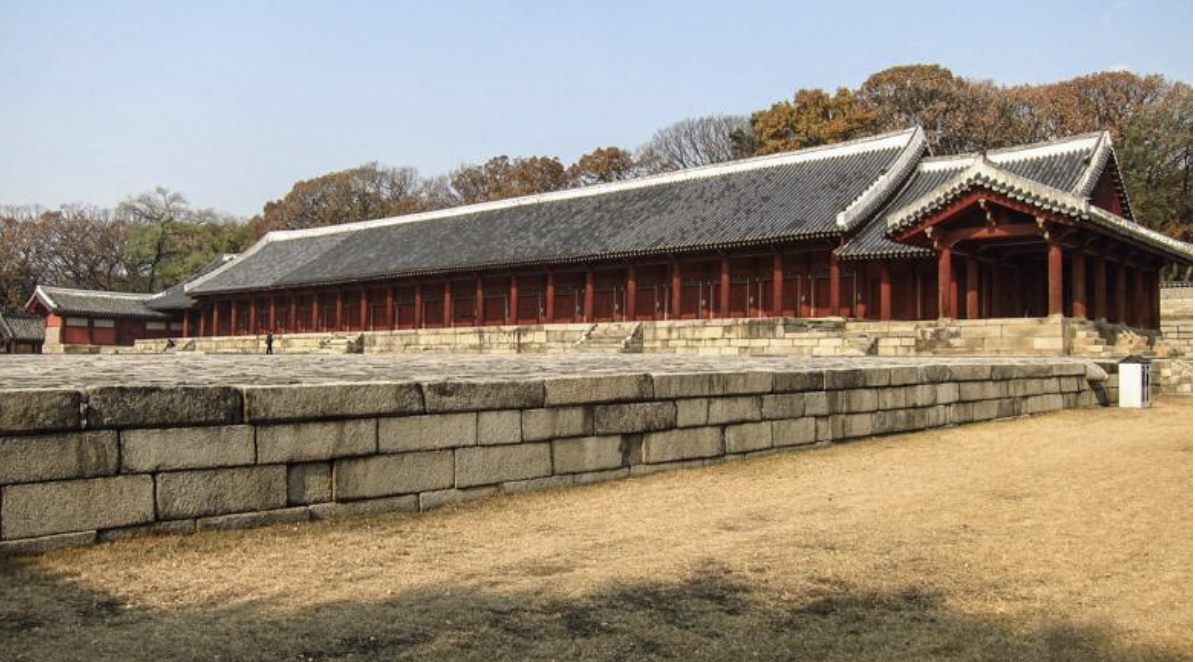

Main Hall, Jongmyo Shrine, Korea, 1395-1836 CE
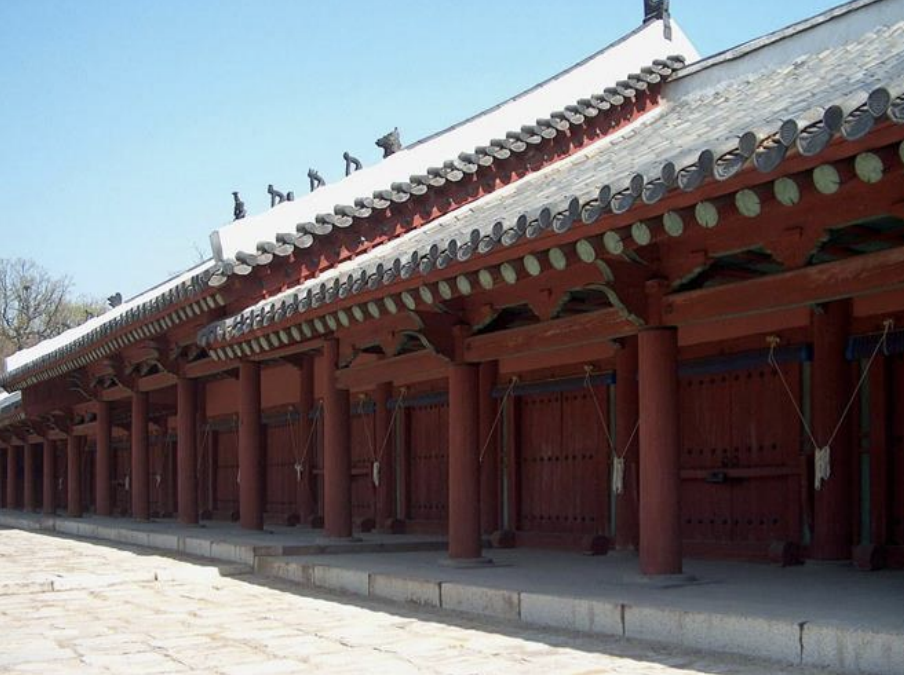

Jongmyo Shrine, Korea, 1395-1836 CE
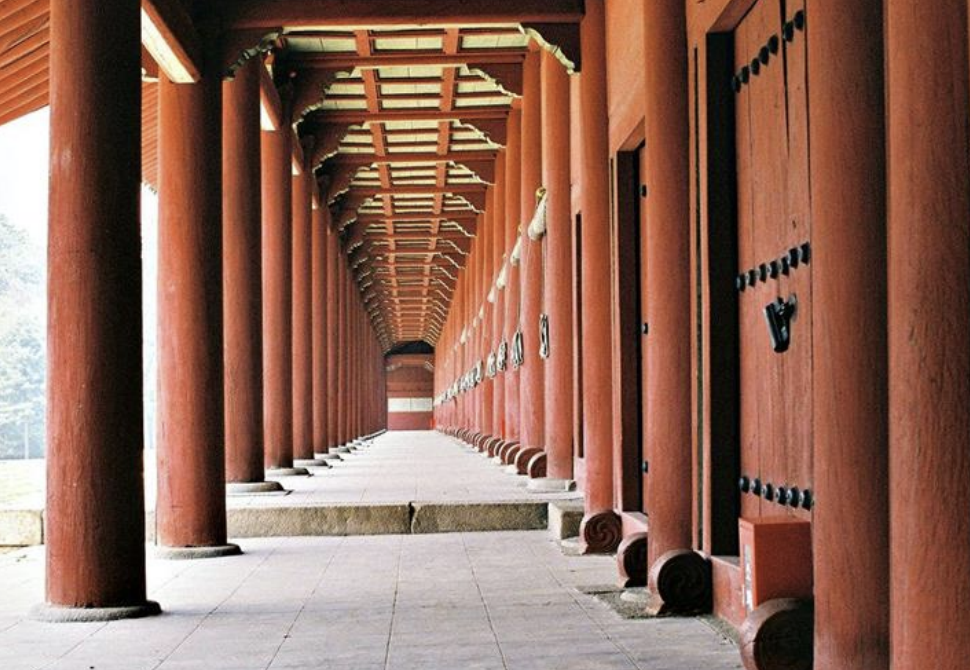

Jongmyo Shrine, Korea, 1395-1836 CE
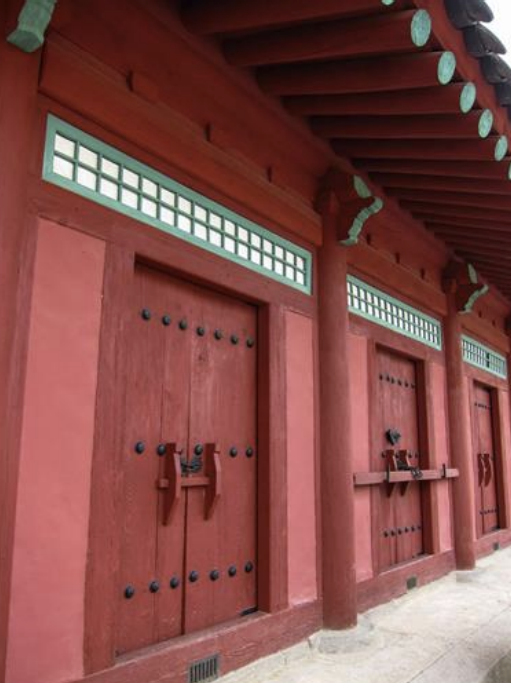

Jongmyo Shrine, Korea, 1395-1836 CE
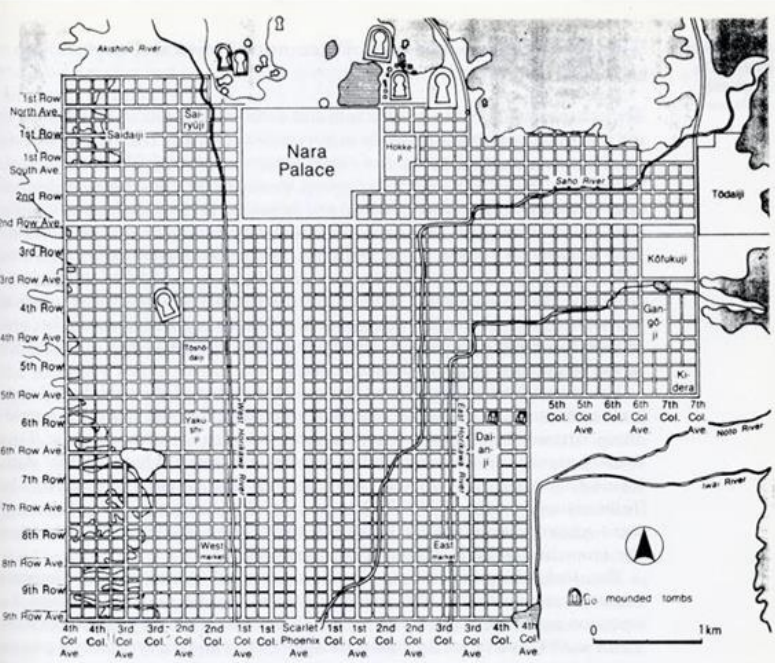
Nara, Japan, ca. 710 CE
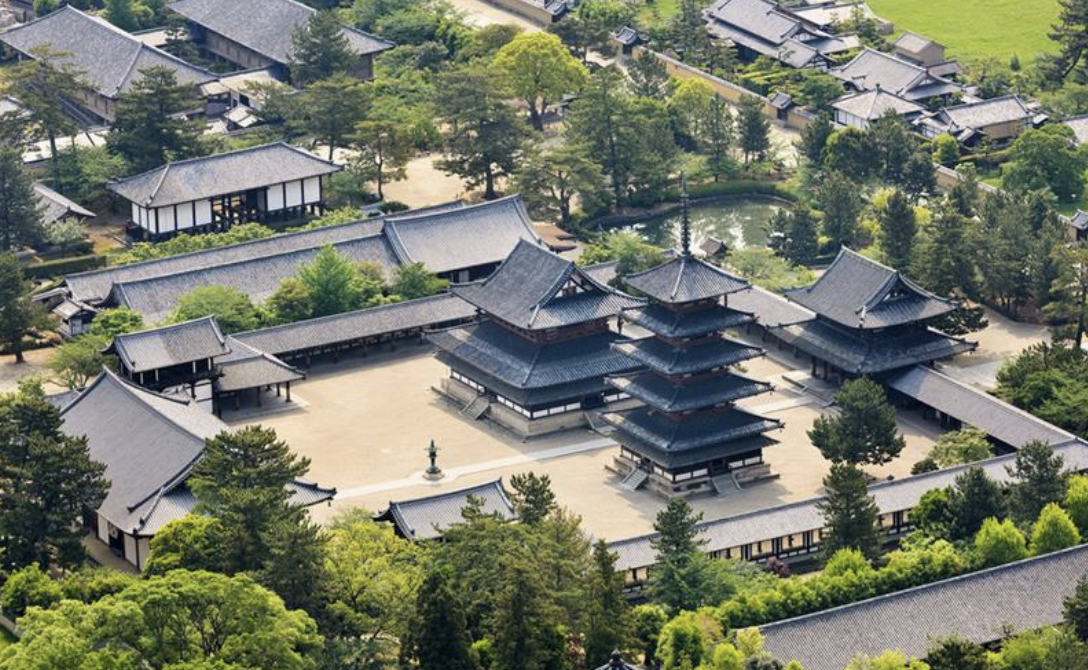

Hōryū-ji, Japan, 607-714 CE
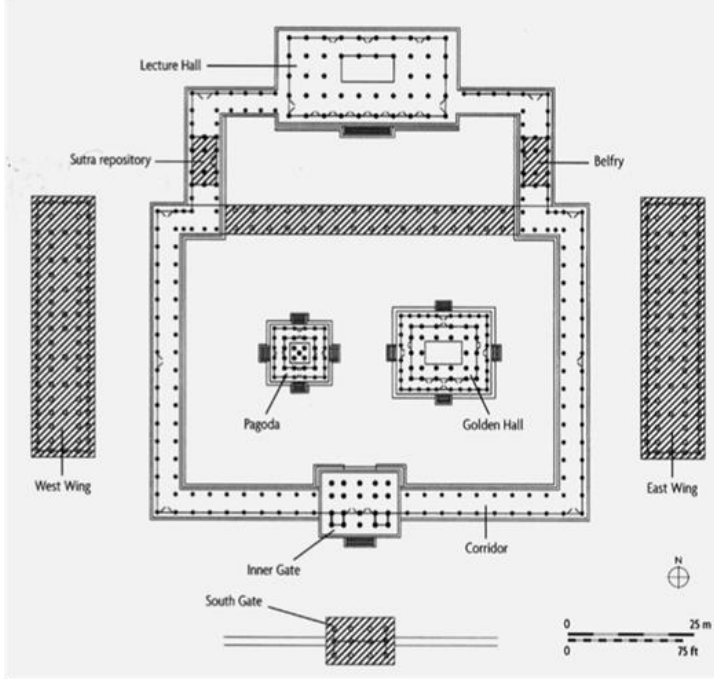
Hōryū-ji, Japan, 607-714 CE
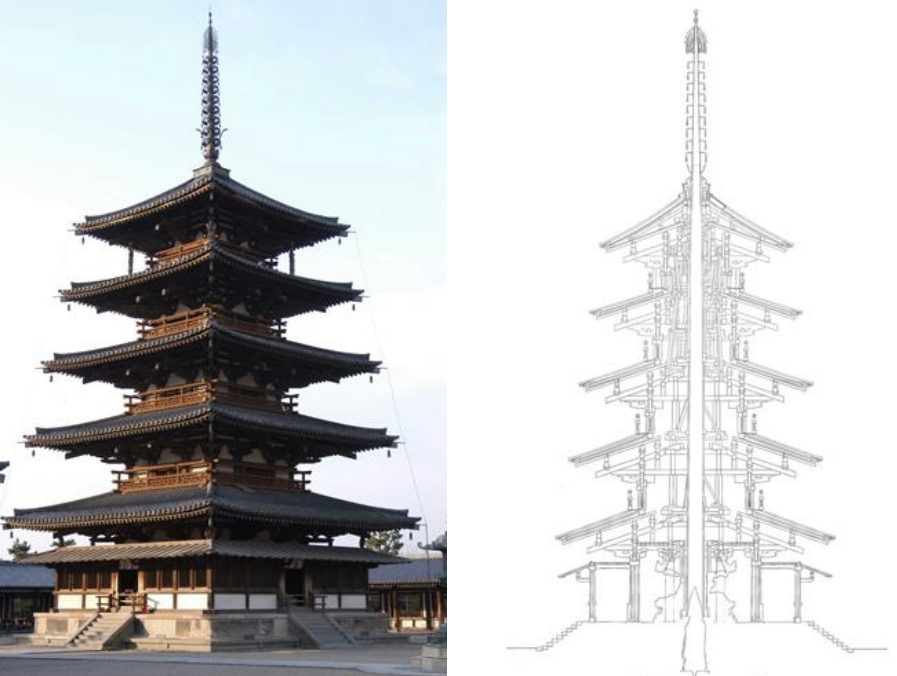

Hōryū-ji, Japan, 607-714 CE
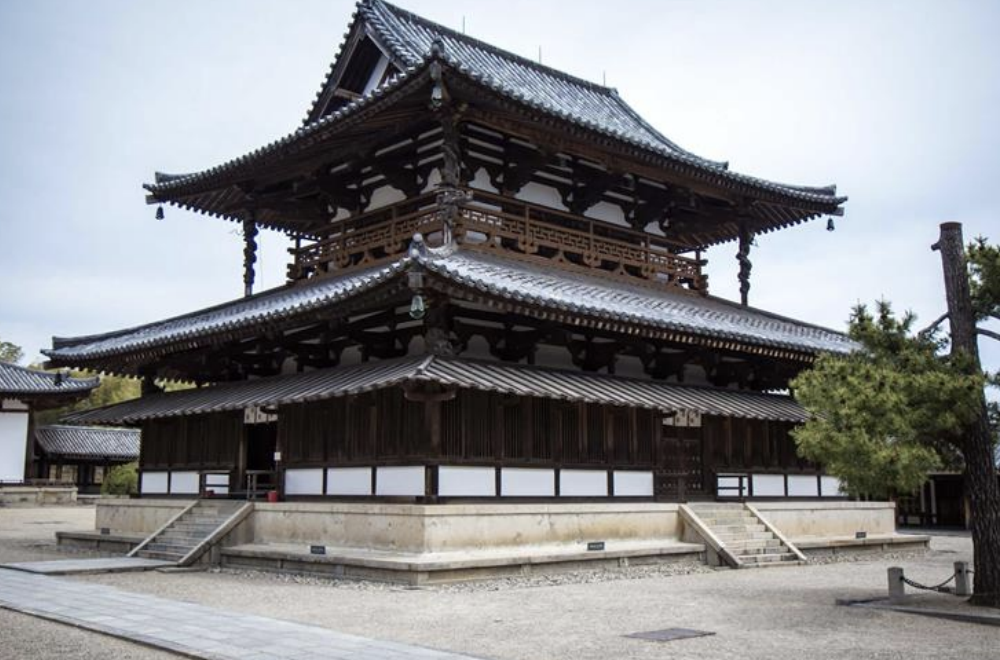

Hōryū-ji, Japan, 607-714 CE
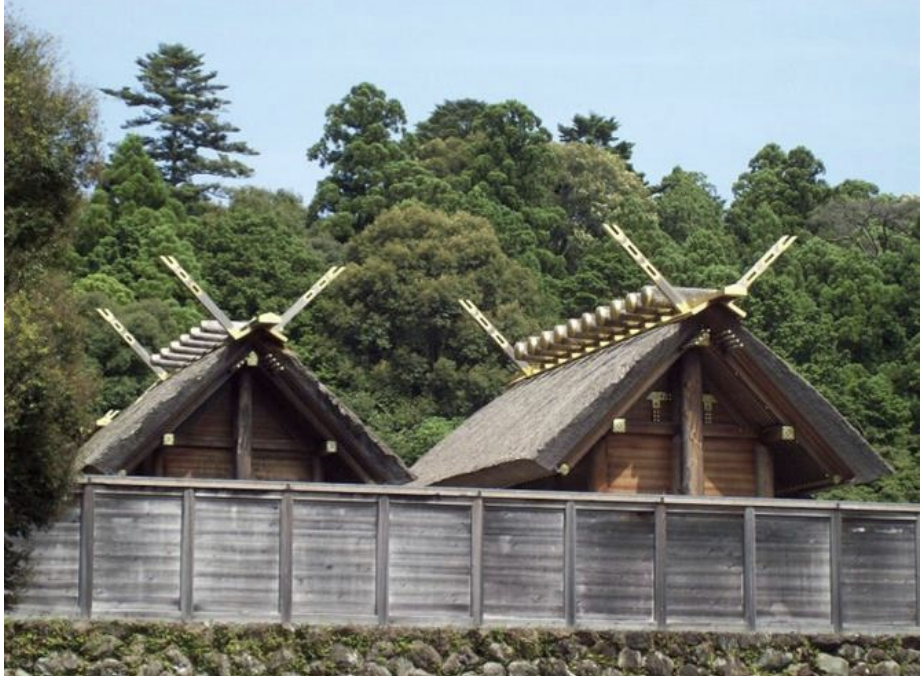

Ise Shrine, Japan, 690 CE - present
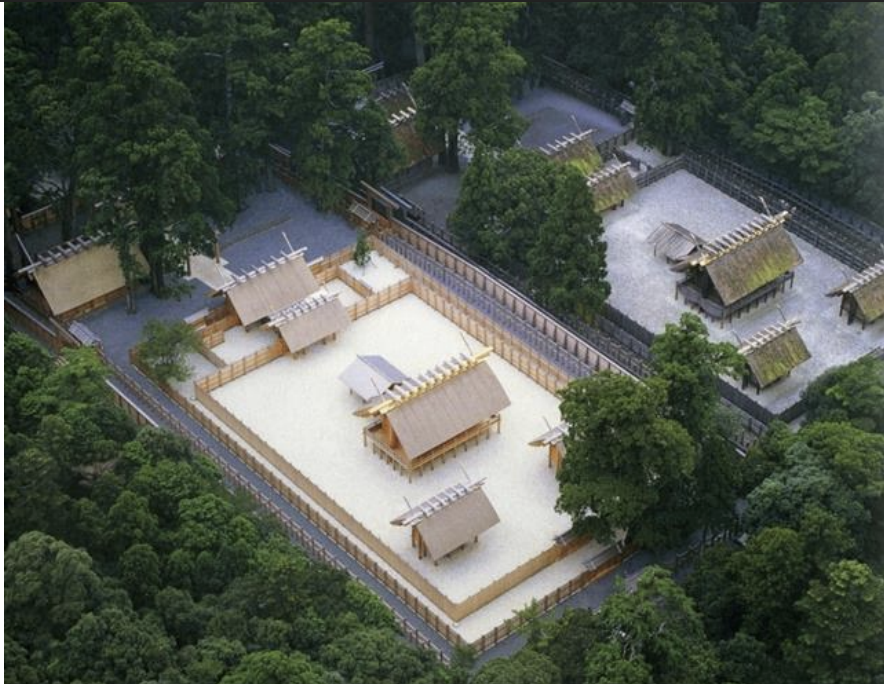

Naiku, Ise Shrine, Japan, 690 CE - present
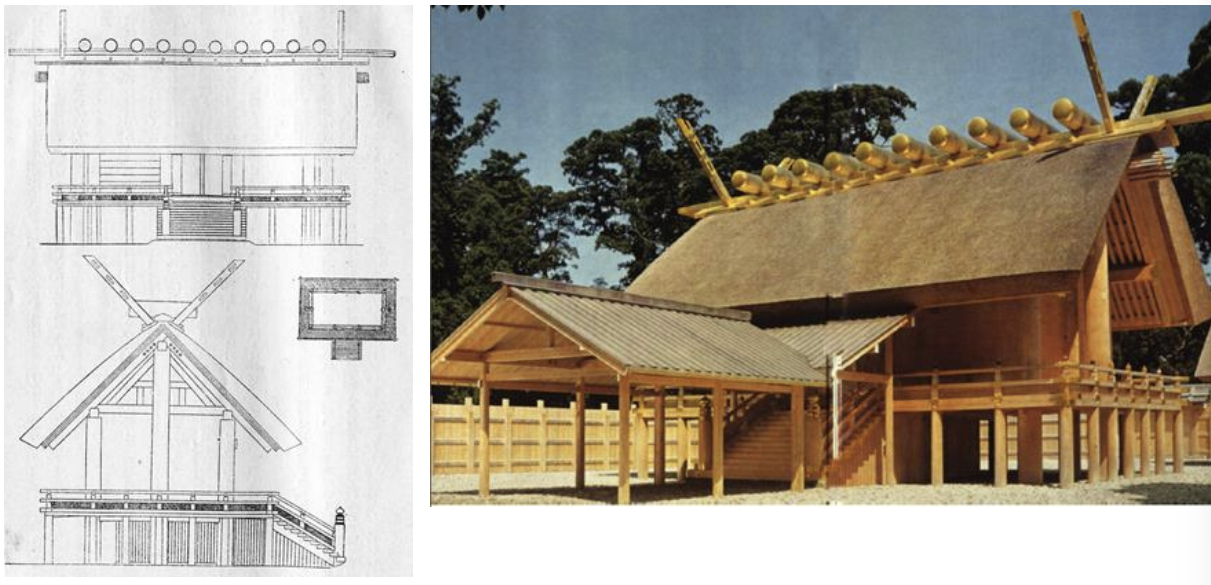
Ise Shrine, Japan, 690 CE - present
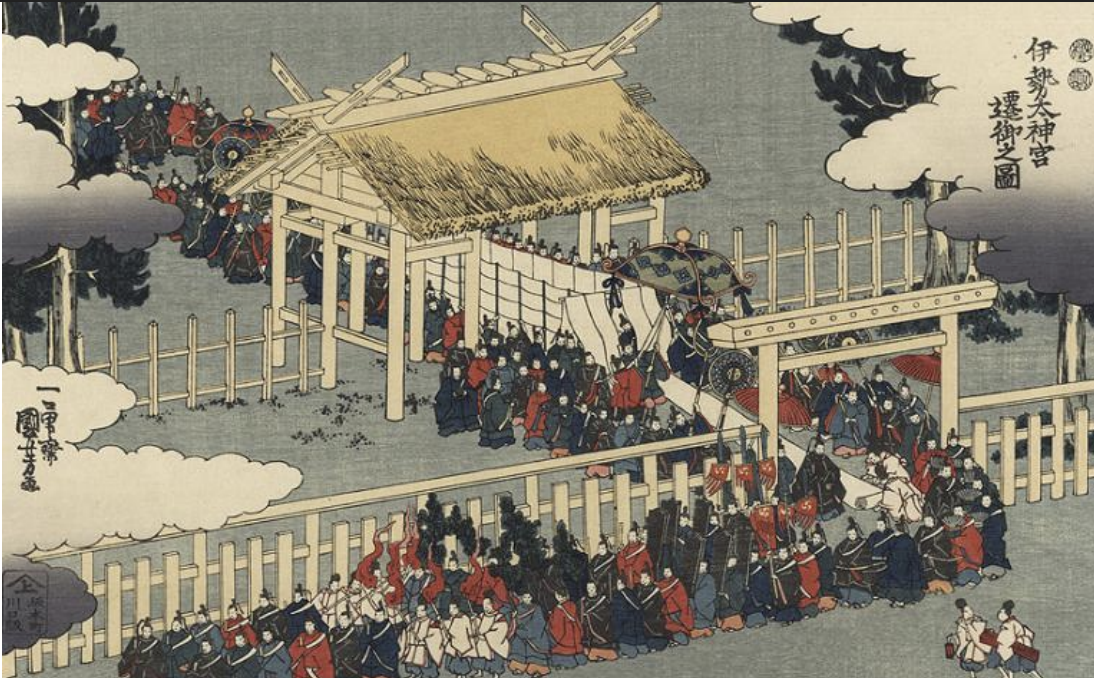

Shikinen sengu at Ise Shrine, Japan, 690 CE - present
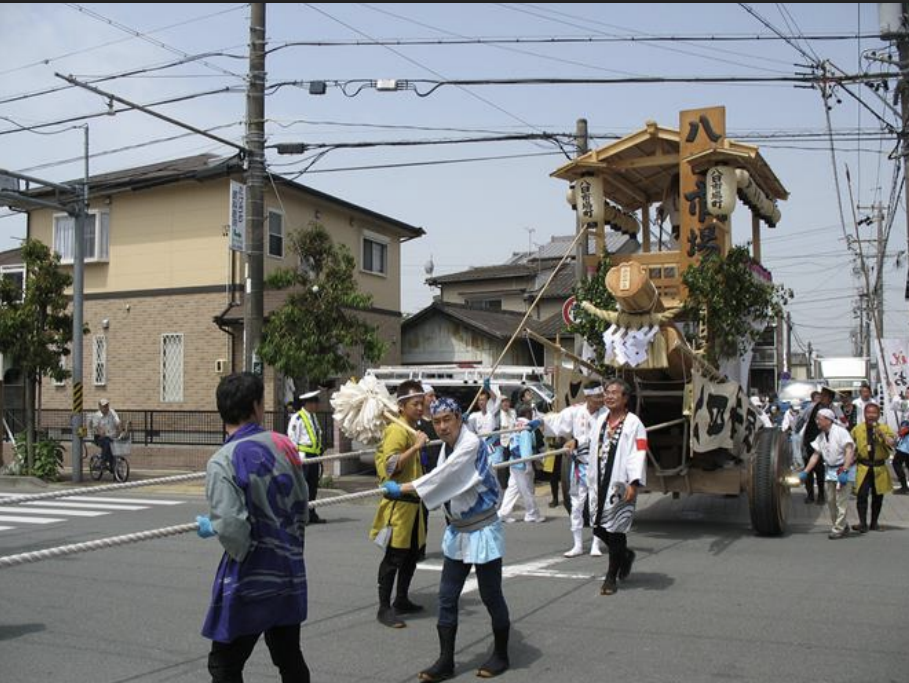

Ise Shrine, Japan, 690 CE - present