unit 4
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
republicanism government
Wanted to build a republic
gov. in which citizens ruled through their elected/appointed representatives
representation came from states
popular sovereignty
wanted to create gov. using this principle
gov. was created by and subject to the will of the people (white men) through their elected representatives
land ordinance of 1785 and northwest ordinance of 1787
gov. did not have the power to tax so they needed to make money by selling land west of the appalachian mountains
passed these ordinances to make it easier to buy land for settlers
problems with trade
too many foreign goods on the market
americans are not contributing to their own economy
foreign gov. found loopholes in trade laws
problems with diplomacy
conducting negotiations between nations
weak diplomatic relationships with british and spanish
british are not leaving forts
territory disputes with spain
loyalists still live in the US
recession of 1780s
major costs of building a new nation on top of war dept
state and nation gov need money from people that don’t have it themselves
causes a big economic slowdown (recession)
shays rebellion
wealthy elites put heavy taxes on people in order to get the money they invested in the war back
higher state taxes put a strain on farmers and poor people
farmers did not like the heavy taxes that were put on them because they could not pay it
they already did not have money from the war but now they are forced to pay taxes for the war
if they did not pay they would go to jail and or lose property (lose the right to vote)
farmers found this very unfair because they felt they fought for a representative gov. but were not getting one
state government powers under the AOC
given all powers that are not given to congress
has 2-7 representatives but 1 vote in congress
cannot wage war or make an international alliance
collect taxes
committee of states will be given power to run the USA when congress cannot at that moment
national government powers under the AOC
declare war
regulate currency
negotiate foreign affairs (treaties)
command army
borrow money from states
9/13 states have to approve to pass anything
weaknesses of AOC
cannot pass anything without 9/13 states agreeing (supermajority, very hard)
congress cannot tax
congress cannot regulate trade (only foreign, not between states)
no national court
only 1 vote per state (unfair)
only 1 branch of gov.
cannot enforce anything, congress can only as and hope states will do it, if one state does not want to congress cannot force it
in order to amend they need 13/13 states vote, nearly impossible
strengths of AOC
states had equal representation
successful northwest ordinance/expansion of country
made some treaties with other countries
gave power to states and not all of it to congress
can amend this document but have to reach unanimous vote
federalism
dividing the powers equally among state and national governments
philadelphia constitutional convention
There were 55 delegates there and their original mission was to amend the Articles of Confederation (They soon realized they could not amend the document because it was too hard to so they threw it out and started from scratch)
enumerate powers for congress
Congress has the power to collect taxes, pay debts, borrow money; regulate commerce; coin money; establish post offices; protect patents and copyrights; establish lower courts; declare war; and raise and support an Army and Navy.
Also established the elastic clause
national government powers under the constitution
Maintain military, declare war, establish postal system, weights and measure system, protect copyright patents, coin money, make treaties, etc
state powers under constitution
Establish local governments, set up schools, regulate state commerce, make regulations for marriage, regulate corporations, etc
Do all the rest as long as does not violate nation gov laws
shared powers
Collect taxes, regulate interstate commerce, regulate banks, borrow money, provide for general welfare, punish criminals, etc
big vs small states
Large states- congress should have 2 houses, delegates should be assigned according to population
Small states- congress should have one house, each state would have one vote
north vs south states
North– enslaves people should no be counted when deciding number of delegates but should be counted when levying taxes
South- enslaves people should be counted when determining number of representative but should not be counted when levying taxes
virginia plan, new jersey plan and great compromise
Virginia plan- gov would have 2 houses, both houses would assign according to population
NJ plan- legislature would have 1 house, each state would get 1 vote
Great compromise- 2 houses, senate would give equal representation and HOR would have representation according to population
3/5 compromise
In order to compromise for southern states with a majority of their population consisting of slaves, the ⅗ compromise counted enslaved people as ⅗ of a person rather than a whole person.
slave trade clause
Federal government could not regulate how many people (enslaved people) were imported into the country until 20 years later
powers and duties of each branch
Checks and balances were created to ensure that no one branch has all the powers
- ex. President can veto a law made by congress and supreme court can rule it unconstitutional
Judicial- court system, interpret laws
Legislative- congress, make and establish laws
Executive- president, enforce the laws
amending constitution
Many different ways to amend constitutions, make it difficult but not impossible
We have 27 amendments (first 10 are the bill of rights)
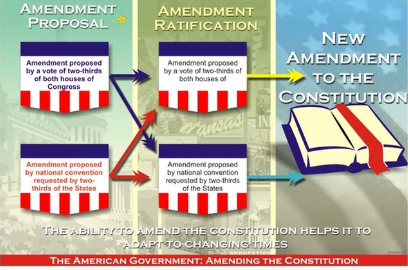
impeachment
Accuse federal official of a wrongdoing (treason, bribery, high crimes and misdemeanors, and abuse of power)
Only the House of representatives has the power to do this, but the senate will hold all the trials
⅔ vote of the senators is required to impeach
Only if congress is impeaching president or vice president the chief justice of the supreme court acts as a trial judge
power of the purse
Congress has the right to spend public money where they see fit
electoral college
How the president is elected
Each state has a representative that chooses (mostly based off popular vote) what way their states want to vote and that person will win all of the states votes
538 electors (100 from senate, 435 from HOR, and 3 from D.C.) person has to win 270 votes to win
bill of rights
It was created because the Anti-Federalists would not ratify the constitution if the BOR was not added

federalist vs anti-federalists
federalists- the federalists promised to include a Bill of Rights which would guarantee fundamental rights
anti-federalists-the Anti-Federalists would agree and ratify if the Bill of Rights were promised
commerce clause
Gives congress ability to regulate trade and commerce inside states and foreingly
Restricts states from impairing interstate commerce, makes sure states don't take advantage of other states, equal opportunities
necessary and proper clause (elastic clause)
Allows congress to make laws or act where the constitution doesn't give authority, within reason
Implied power
full faith and credit clause
States must honor the laws and judgements of other states
Protects conflict among states and ensures peoples rights
supremacy clause
Establishes that federal laws takes precedence over state laws and state constitutions
It is a check on state power
guarantee clause
Requires US to guarantee every state republicanism and government protection from foreign invasion and domestic violence
loos and strict interpretation of constitution
loose- flexible reading of the constitution, giving considerable weight to modern values and social consequences and precedents
strict-literal reading of the constitution, relying more on the original text or the intent of the framers