C1.3 Photosynthesis
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
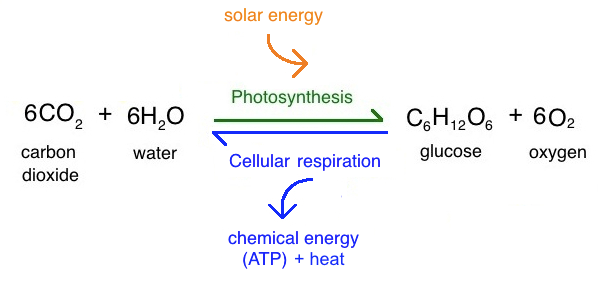
Relationship between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
They are reversible to each other essentially
Pigments
globular protein
located in thylakoid membrane
membrane of the chloroplast
proteins embedded in the thylakoid bilayer
found in clusters (photosystems)
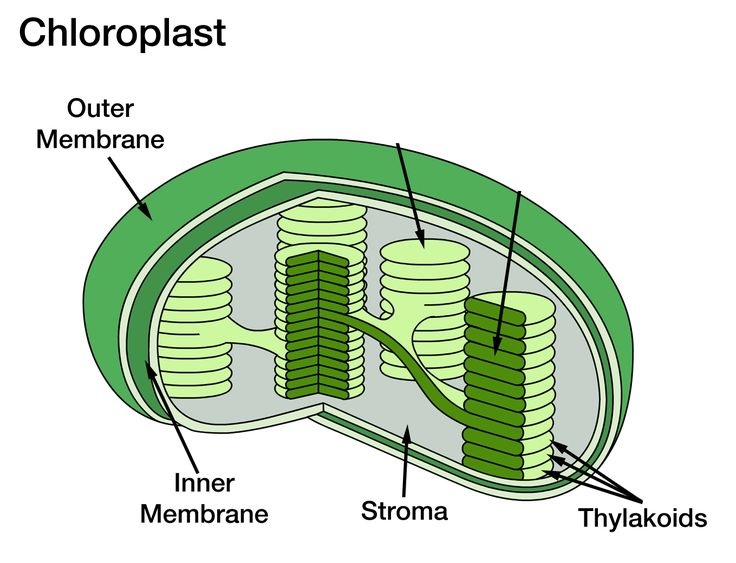
Draw and Label a Chloroplast
Thylakoids
Double bilayer membrane
Stroma
Chlorophyll
Two Types:
Chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll B
The difference between them is that they each absorb and reflect different lengths of light and have different chemical structures
Four Types of Pigments
Chlorophyll
Betalains
Anthocymanins
Carotenoids
They are all measured by wavelength (nanometer)
400-700 nm is visible light
Why does a tree change color?
Due to change in temperature of the proteins, which get denatured/degraded
The highest absorbed color means
it is the lowest reflected, or not that color
The lowest absorbed color means
it is the highest reflected, or that color
Organisms that can perform photosynthesis
Green plants (excludes plants underwater)
Phytoplankton (Protist)
Cyanobacteria
Why can organisms perform photosynthesis?
They have special type of cells aka photosynthetic cells that contain chloroplasts
Step One in Thylakoid Membrane
Chlorophyll in photosystem 2 absorbs sunlight
The electrons get excited
They leave into the electron transport chain
Which carries them to photosystem 1
Step Two in Thylakoid Membrane
These electrons should be replaced by breaking down H2O into
O
H2
e-
The process is called photolysis
Step Three in Thylakoid Membrane
The protons (H ion) will move from high concentration (inside the thylakoid) to low concentration (in the stoma) by a protein channel called ATP Synthase
Step Four in Thylakoid Membrane
ATP Synthase makes ATP by adding 3H+ to an ADP
Step Five in Thylakoid Membrane
NADP+ will bind 2e- and 1H+ to form NADPH
ATP is a
energy carrier and used in light independent reactions too
NADPH is an
electron carrier and used in light independent reactions too
Phase One of the Calvin Cycle: Carbon Fixation
5-Carbon (RubP) + 1CO2 → 6 Carbon
6 Carbon made into 2 3-carbon molecules
Phase Two of the Calvin Cycle: Reduction
2 3-Carbon Molecules → Reduced 2 3-Carbon Molecules (1)
then into 6 3-Carbon Molecule and one leaves for glucose
ATP → ADP (2)
NADPH → NADPH+ (3)
3 Products
Phase Three of the Calvin Cycle: Regeneration of RubP
5 of 3-carbon → 5 RubP
How many times does the Calvin Cycle has to happen to create glucose?
Twice because glucose is the product right before phase 3