C4.2 transfers of energy and matter
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
how energy enters systems
light
how energy leaves systems
heat
open system
allows matter to go in and out
closed system
matter doesnt leave or enter system
earth system type
closed
systems theory
explains how systems interact with each other and their environment and predict what would happen if sth in or around a system is changed
laws that ecosystems obey
law of conservation of mass
law of thermodynamics
producers
photosynthetic organisms, transform water and air into food
flow of energy through a food chain
process of passing energy from one organism to another through feeding
what x→z indicates
x is eaten by z
food chain
linear set of connections from producers to consumers with only one species at each trophic level
food web
more complete picture since multiple producers may be eaten by one consumer
decomposers
saprotrophs and detritivores, break down non living food sources
adaptations of decomposers
digestive enzymes that convert organic matter into a more usable form, eg proteins turned into ammonia nh3, nitrogen in turn converted into NO3 nitrates by bacteria (minotaur beetle)
humus
rich black layer of soil
autotrophs
capable of producing their own organic molecules as a source of food
photoautotrophs
use light energy from the sun combined with inorganic molecules to obtain chemical energy in form of carbon compound such as glucose
carbon fixation
ability to convert inorganic co2 into organic molecules useful for energy and growth
chemoautotrophs
capable of using inorganic molecules such as co2 or H2S as an energy source for building more complex useable molecules
egs photoautotrophs
cyanobacteria
clover
algae
pine trees
chemoautotrophs
sulfur oxidising bacteria
nitrogen oxidising bacteria
iron oxidising bacteria
heterotroph examples
zooplankton
sheep
insects
fish
what heterotrophs do with food
digest proteins into amino acids, lipids into fatty acids, and dna and rna into nucleic acids
process of integrating nutrients into usable substances in the tissue of the body
assimilation
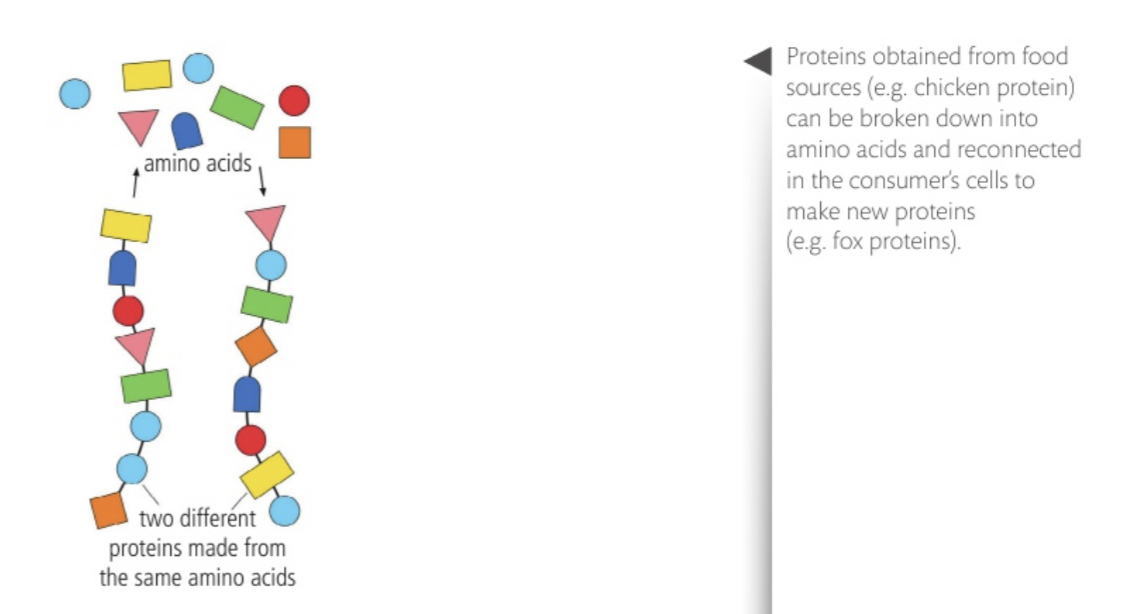
what heterotrophs do with sugar etc
oxidise it
trophic level use
indicate how many organisms the energy in the system has flowed through
first trophic level
producers
second trophic level
primary consumers
problems with food web representation
cant show trophic levels very well
pyramid of energy use
show how much and how fast energy flows from one trophic level to the next in a community
units pyramid of energy
energy per unit area per unit time, ie kJ per m² per year (kj m^-2 yr^-1)
whats impossible in energy pyramid
have a higher trophic level wider than lower trophic level because organisms cant produce energy only transfer it inefficiently

how much percent energy is used from the previous step
10-20%
reasons why not all the energy present can be used
not all of organism is ingested, some is discarded as waste
not everything swallowed can be digested and use, eg seeds in animal feces
some organisms die without being eaten by organism from next trophic lvl
considerable heat loss from celllular respiration at all trophic levels, especially endotherms

why heat energy = lost isnt a problem
sunlight
number of trophic levels
up to six, but most have four
what limits amount of trophic levels
hm energy enter the ecosystem
biomass of trophic level
estimate of the mass of all organisms on that level
biomass
dry weight of an organism, because actual mass contains a lot of water
unit for biomass
gram per metre squared per year (g/m^-2/yr^-1)
what influences biomass
amount of sunlight reaching photosynthetic producers = sunnier parts of the world can produce more biomass eg phytoplankton near equator vs no
why biomass decreases up trophic levels
subsequent levels have continuing appetite for energy
cooler biomes
lower biomass ergo can support less organisms
biome
large community of plants and animals; tend to cover wide expanses, often on continental scale
primary production
biomass generated by activity of producers such as photosynthetic organisms when they fix carbon and make carbon compounds that can be used as a food source. measured in gm^-2y^-1
eg of molecule lost from accumulated biomass
co2 during celllular respiration, waste product excretion such as urea
what isnt necessarily passed on to next trophic level
both biomass and energy
secondary production
conversion of one carbon molecule into another within a consumer eg glucose to lipids
biosphere
all places where life is found
lithosphere
all places where rocks are found
what produces methane
microbes such as archaea, especially important in digestive tracts of mammals as they significantly contribute to climate change
net producer vs consumer of carbon
carbon source vs carbon sink
importance of fire
burns away fallen branches, gives way for renewed growth, plus some seeds can only germinate when exposed to fire eg pinus contorta
peat
heterogenuous mixture, minimum 30% biomass
keeling curve
shows avg trend and seasonal changes of co2 concentration which are due to photosyhtetic organisms activity
elements important for life that are cycled and passed through the food chain
hydrogen oxygen calcium potassium sodium iron phosphorus etc. when organisms die, these are either passed on to the next trophic level or to detritivores and decomposers