Sam's NSCI 175 Exam Review - Units 1 and 2
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Reductionist Approach
Breaking apart a complex phenomenon into fundamental parts to make analysis easier
Molecular (Level of Analysis)
The Nervous System is composed of a multitude of molecules; Studies molecules associated with the nervous system e.g. Dopamine (a neurotransmitter), Glucose, Sodium Ions
Cellular (Level of Analysis)
How all present molecules work together to give neurons their special properties
Systems (Level of Analysis)
Having a group of neurons that work together/share a common function e.g. visual and motor system (sensory systems)
Behavioral (Level of Analysis)
How neural systems work together to produce integrated behaviors → things that we can observe e.g. movement
Cognitive (Level of Analysis)
Understand the neural mechanisms that are responsible for higher levels of human mental activity e.g. attention, consciousness, learning
Difference between molecular and cellular level of analysis
Is it a neuron or is it a part of a neuron
Four Essential Steps in Scientific Process
Observation, Replication, Interpretation, Verification
Observation
Carefully watching experiments and making sense of results (typical scientific method)
Replication
Seeing if the original result happened by chance by repeating the original proces
Interpretation
After finding that it didn’t happen by chance, you find meaning by using what’s already published
Verification
Other scientists in different locations under potentially different circumstances are able to replicate your experiment. This is where scientific fact is established
Explain why the progress of science is often slow
Depends on how the controls are set
Within Subject Experiment
the control group is the same set of subjects tested before an alteration
Between Subject Experiments
The experimental control is compared to a separate control group that has been treated identically except for experimental manipulation
Independent vs Dependent Variables
Manipulated vs Measured
Why do we use animals in neuroscience
We use animals to mdoel human brains because they are very similar
Animal Rights
Terminate the use of animals for human purposes including research because they have the same moral and legal rights as humans
Animal Welfare
Aims to ensure that animals are treated well through “institutional animal care and use committees” which are federally required
Which animal model would be best suited for a cognitive neuroscience experiment?
A primate would be best suited because they are the closest to human subjects
Reticular Theory (Golgi)
Neurons are continuously connected and information spreads through the neuron similar to a cell - nerve net as the basic unit of the CNS
Neuron Doctrine (Cajal)
Neurons communicate through direct contact - each neuron is an individual cell
How did Golgi and Cajal get their data?
Golgi Stains - staining neurons within brain tissue
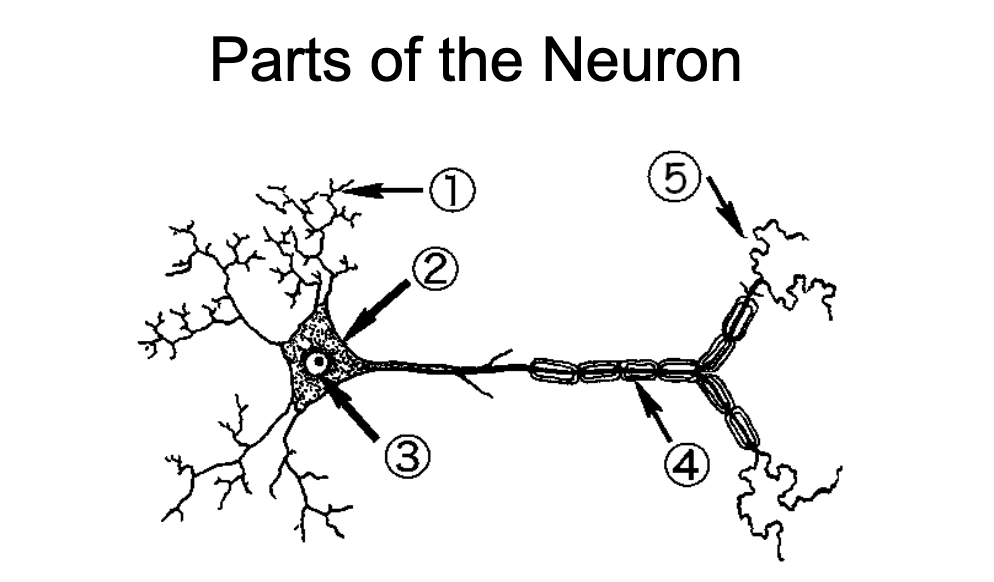
1
Dendrites - Neurite specialized to receive inputs from other neurons
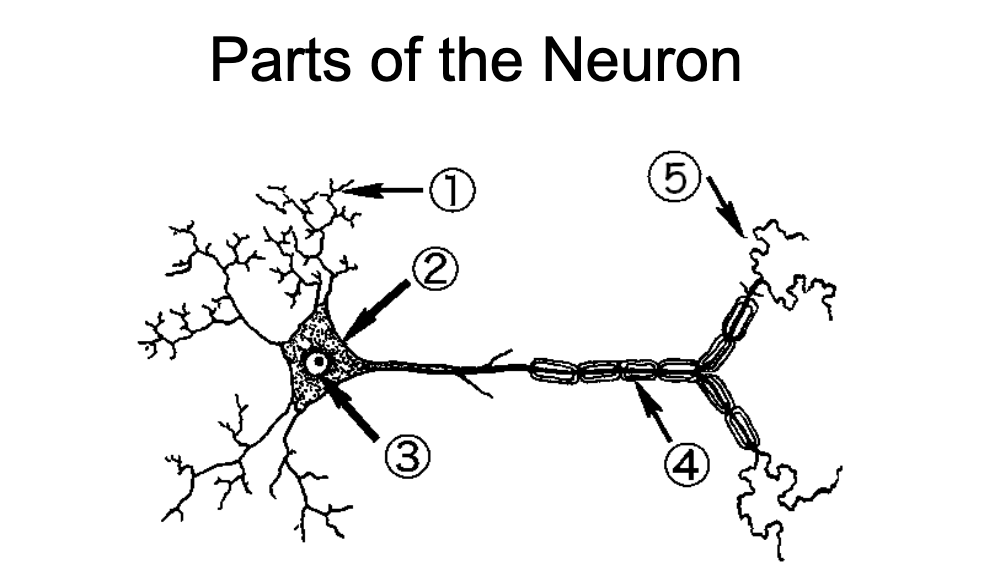
2
Soma - region of the neuron that contains the nuclear and other organelles
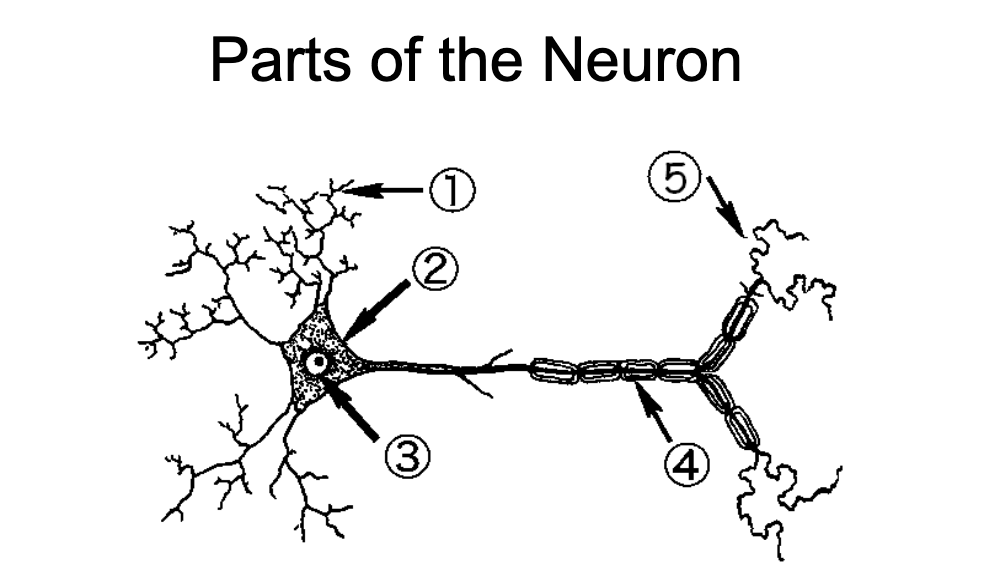
3
Nucleus - spherical center of the neuron
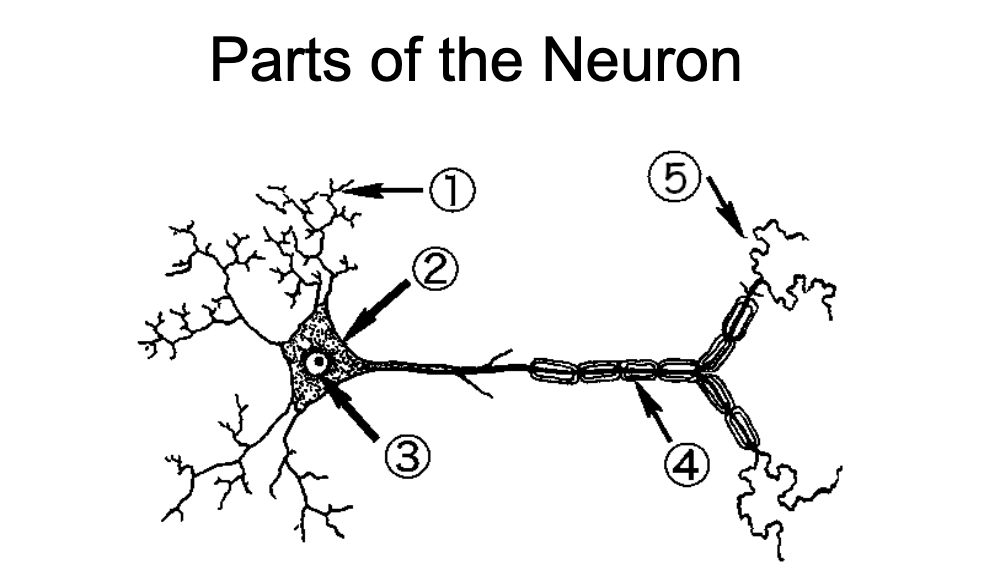
4
Nodes of Ranvier/Myelin Sheaths - wrap around axons and insulate them to speed up propagation of action potentials
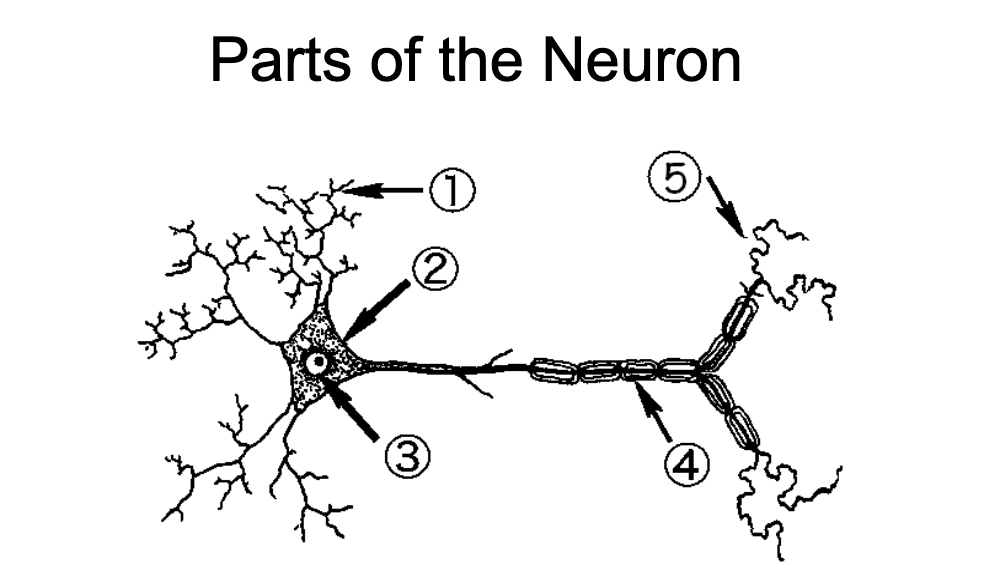
5
Axon Terminal - End region of the axon and usual site of synaptic contact with another cell
Axon/Presynaptic Terminal
Neurite specialized to conduct nerve impluses aka action potentials. Synaptic vesicles are present and neurotransmitters are released
Synpase
the location in which neuronal communication happens
How are neurons specialized for communication?
Synaptic clefts bind to receptors; postsynaptic dendrites receive information from contact with axon terminals; many terminals but only 1 axon
How can neurons be classified?
Structure, Connections, and Gene Expression (what neurotransmitter)
3 Types of Neuron Structure - Depend on number of Neurites
(Sensory)Unipolar, (Motor) Bipolar, (Inter) Multipolar
Sensory Neurons
Have connections with sensory surfaces allowing them to convert external stimuli into internal electric impulses
Motor Neurons
Connect with muscles to transmit the synpase
Types of Glial Cells
Schwann Cell, Oligodendrocyte, Microglia, Ependymal Cells, Astrocyte
Schwann Cell
Found in the PNS, they myelinate singular segments
Oligodendrocyte
Myelinate multiple segments in the CNS
Microglial Cell
Triggers inflammation and removes debris left by dying neurons - can change their morphology
Ependymal Cell
Direct cell migration during development
Astrocyte - The most numerous glia
Fill up the spaces between neurons and are associated with neurite growth - regulate chemical content
Glia outnumber neurons in the brain, but neurons are the focus why?
Neither can function without the other and we don’t know which is more common
Nissl Staining
Distinguishing Neurons and Glia
Golgi Staining
Stains neurons entirely, but is selective for some neurons
Immunohistochemistry
Stain the protein of a receptor using an antibody
In Situ Hybridization
Targets mRNA with radioactive coloring
Neurons vs Glia
Neurons are responsible for unique functions, like sensing/communicating/commanding and Glia contribute to brain function by insulating/supporting/nourishing