Lecture 3 - Somatic polyploidy
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Counting Chromosomes
what do c + n represent?
c = amount of DNA in a gamete (# of base pairs)
n = # of chromosomes in a gamete
What is an exception to diploidy in cells in normal adults?
Sex chromosomes
XY
What are 2 organisms mentioned in class that are Diploid
Humans: 2n = 36
Drosophila: 2n = 8
Define Euploid vs. aneuploid
Euploid = Normal # of chromosomes
Aneuploid = Abnormal # of chromosomes
What does Polyploidy mean?
Adults have more than 2 of each chromosome
triploid, tetraploid, hexaploid + octoploid
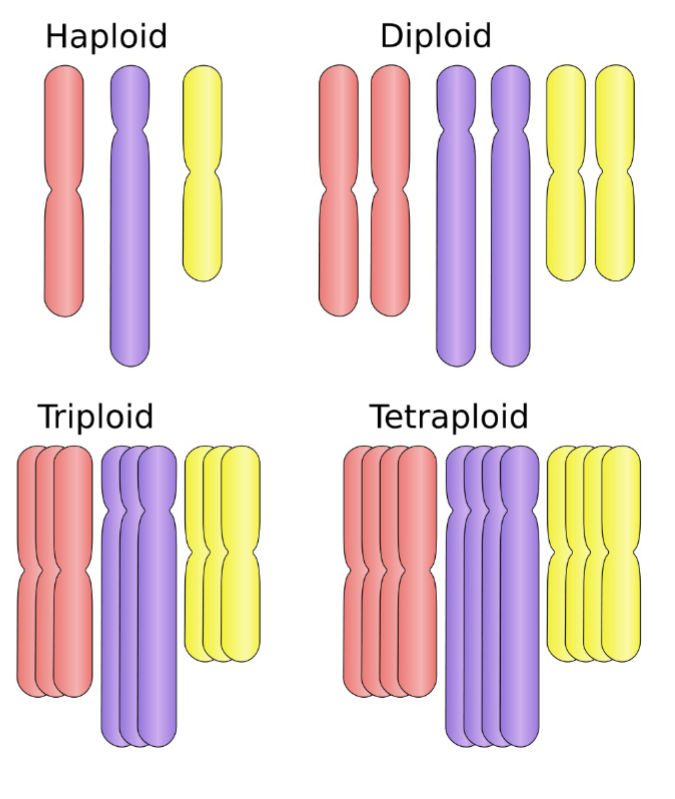
What are 2 examples of polyploidy covered in class?
Banana = triploid
Durum (pasta wheat) = Tetraploid
both are germline polyploids
****Define Germline polyploid
ALL cells (both gametes + somatic) have extra chromosomes
******Define somatic polyploidy
SOME cells are polyploid in an otherwise DIPLOID organism
What are 2 pros + 1 con of polyploid cells?
Pros:
Larger
Export more proteins
Cons:
Can’t reproduce (in most cases)
********What are 4 possible mechanisms that result in Somatic polyploidy?
Cell fusion
Skip cytokinesis
Skip Telophase + cytokinesis
Skip mitosis + cytokinesis
Mechanism #1: Cell fusion
diagram of process
Example given in class
Type of cell that results
Type of cell resulting = MULTINUCLEATED
eg. Human skeletal muscle cells
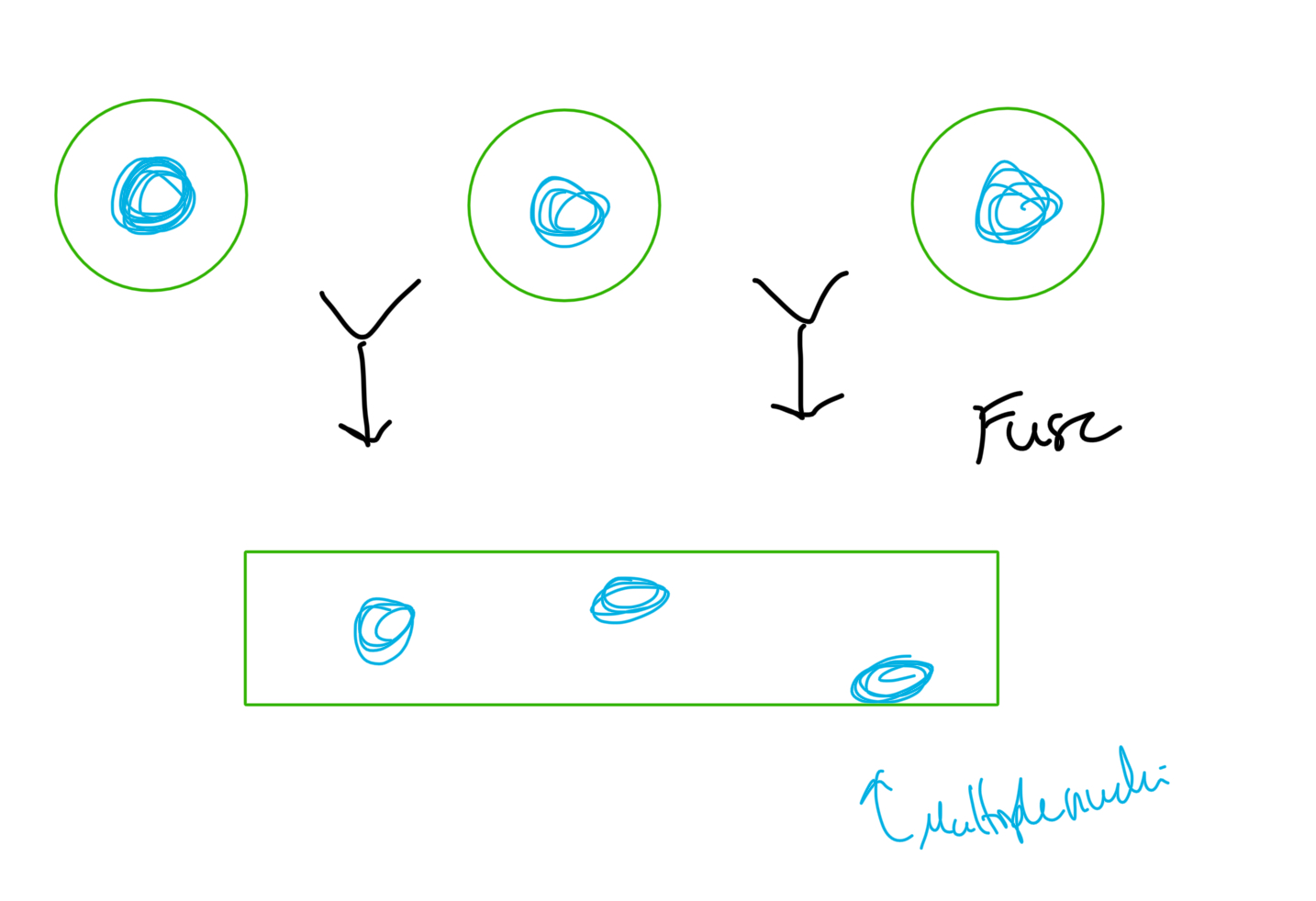
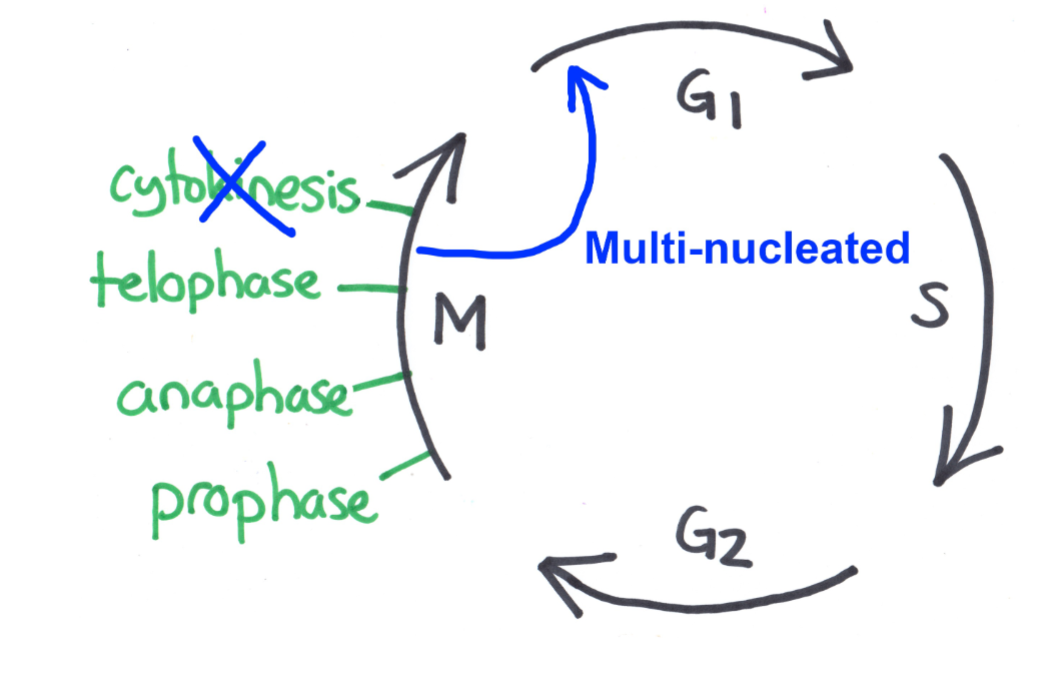
Mechanism #2: Skip cytokinesis
diagram of process
Example given in class
Type of cell that results
Type of cell resulting = MULTINUCLEATED
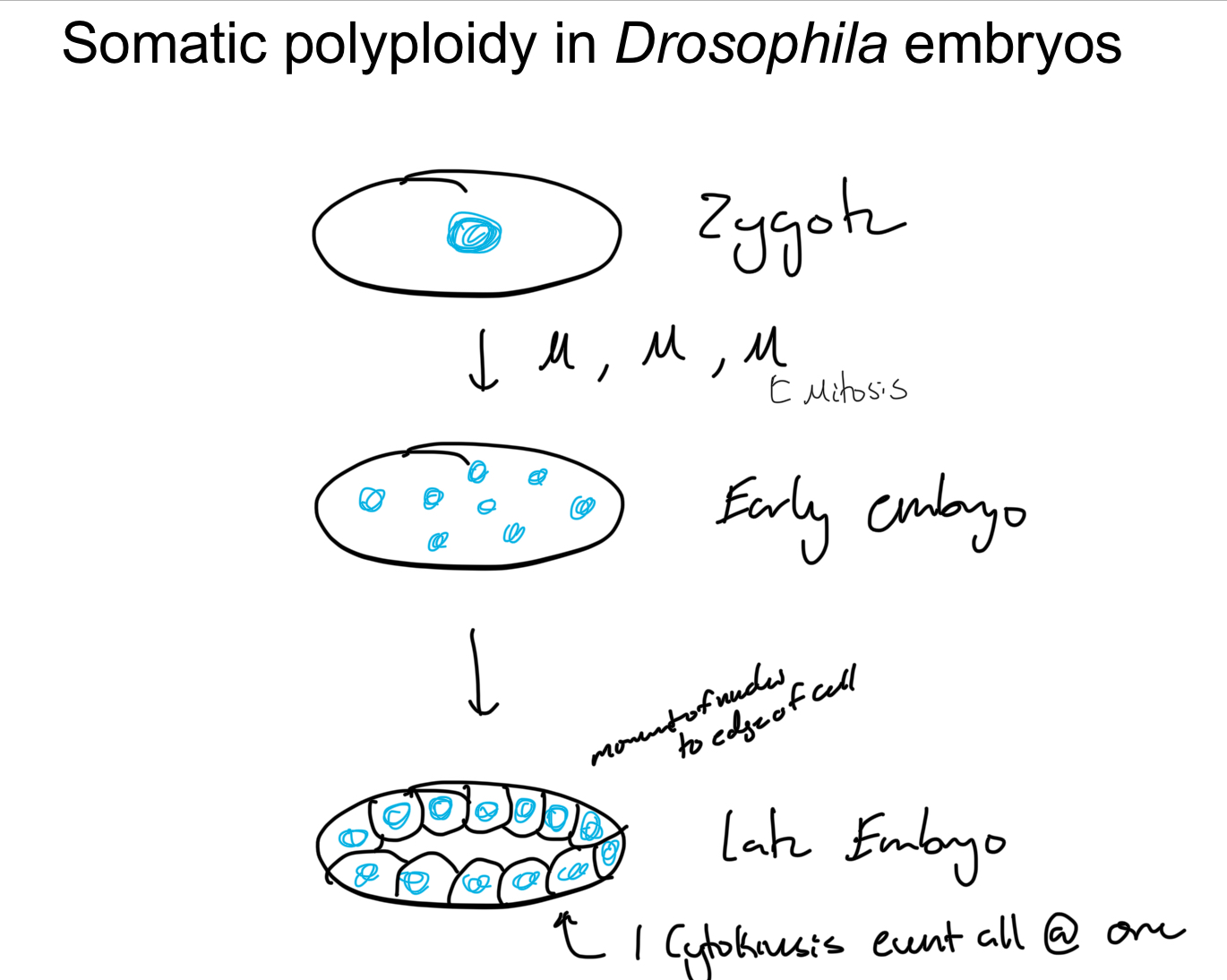
eg. Drosophila Embryos
use somatic polyploidy to speed up embryogenesis (egg needs to become larvae ASAP = larvae temp. somatic polyploid)
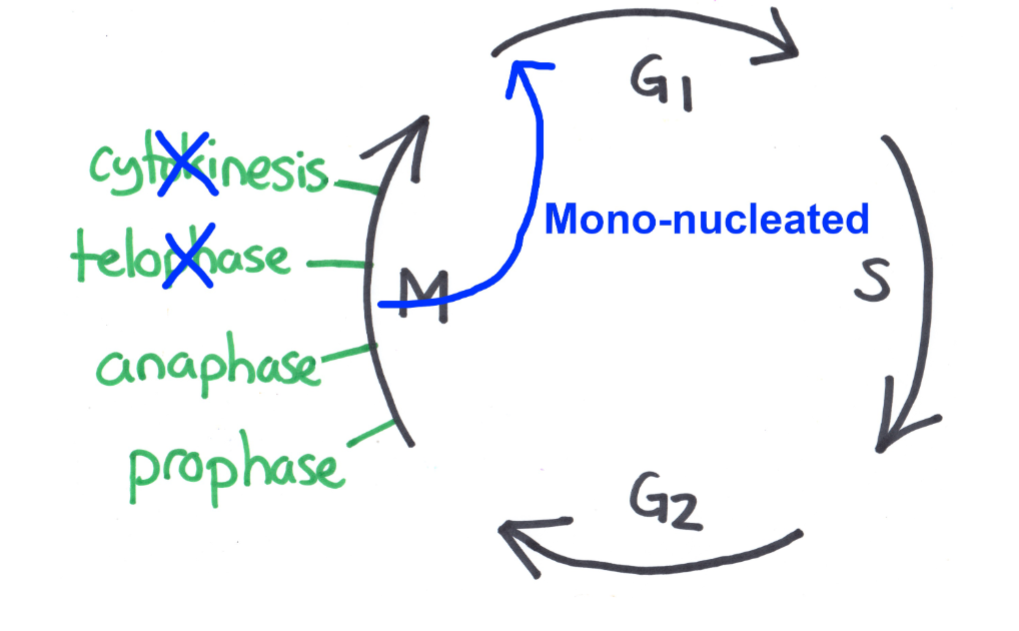
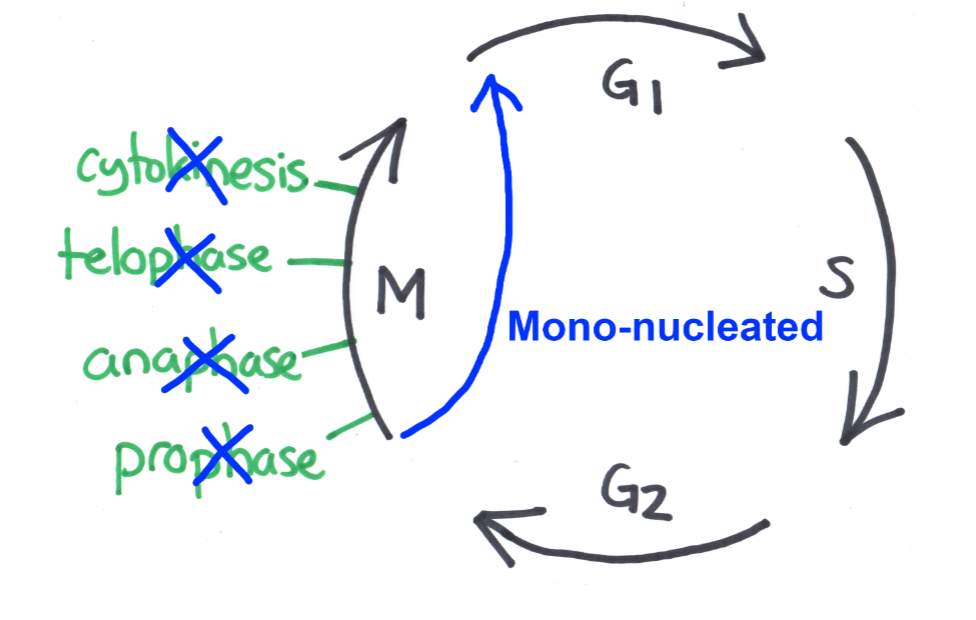
Mechanism #3: Skip telophase + cytokinesis
diagram of process
Examples given in class
Type of cell that results
Type of cell resulting = MONO-nucleated
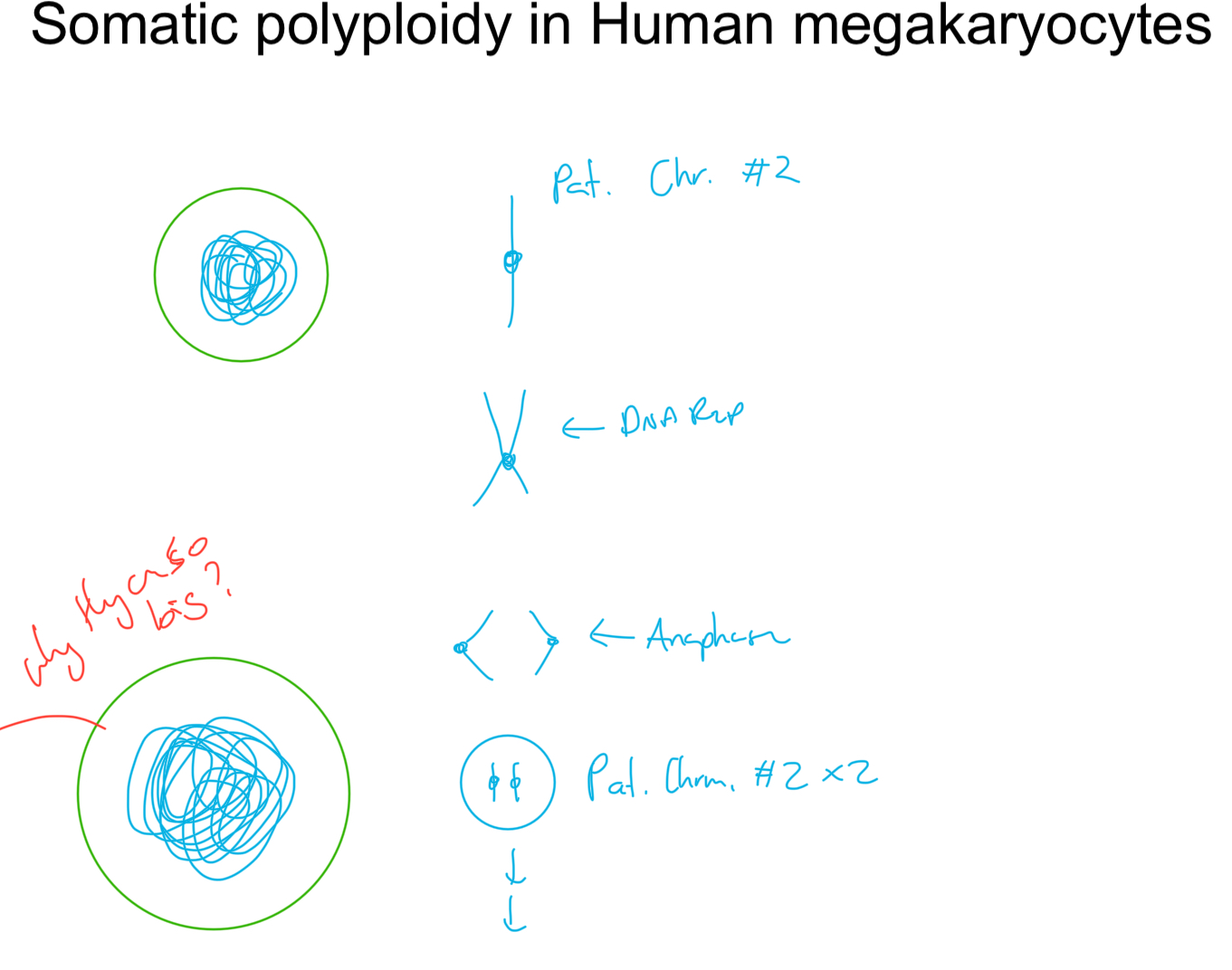
eg. Human MEGAKARYOCYTE WBC
use somatic polyploidy to get large “Giant nucleus cell”
Purpose = PLATELETS
RBC + Nucleus?
Expel the nucleus during maturation = NO NUCLEUS
why?
Without nucleus = smaller + more flexible = can get through capillaries
Mechanism #4: Skip Mitosis + cytokinesis
diagram of process
Examples given in class
Type of cell that results
Type of cell resulting = MONO-nucleated
eg. Drosophila larvae ORGANS
Larvae have both larval organs: don’t need to reproduce = POLYPLOID
And future adult organs (imaginal discs): Must reprod = DIPLOID
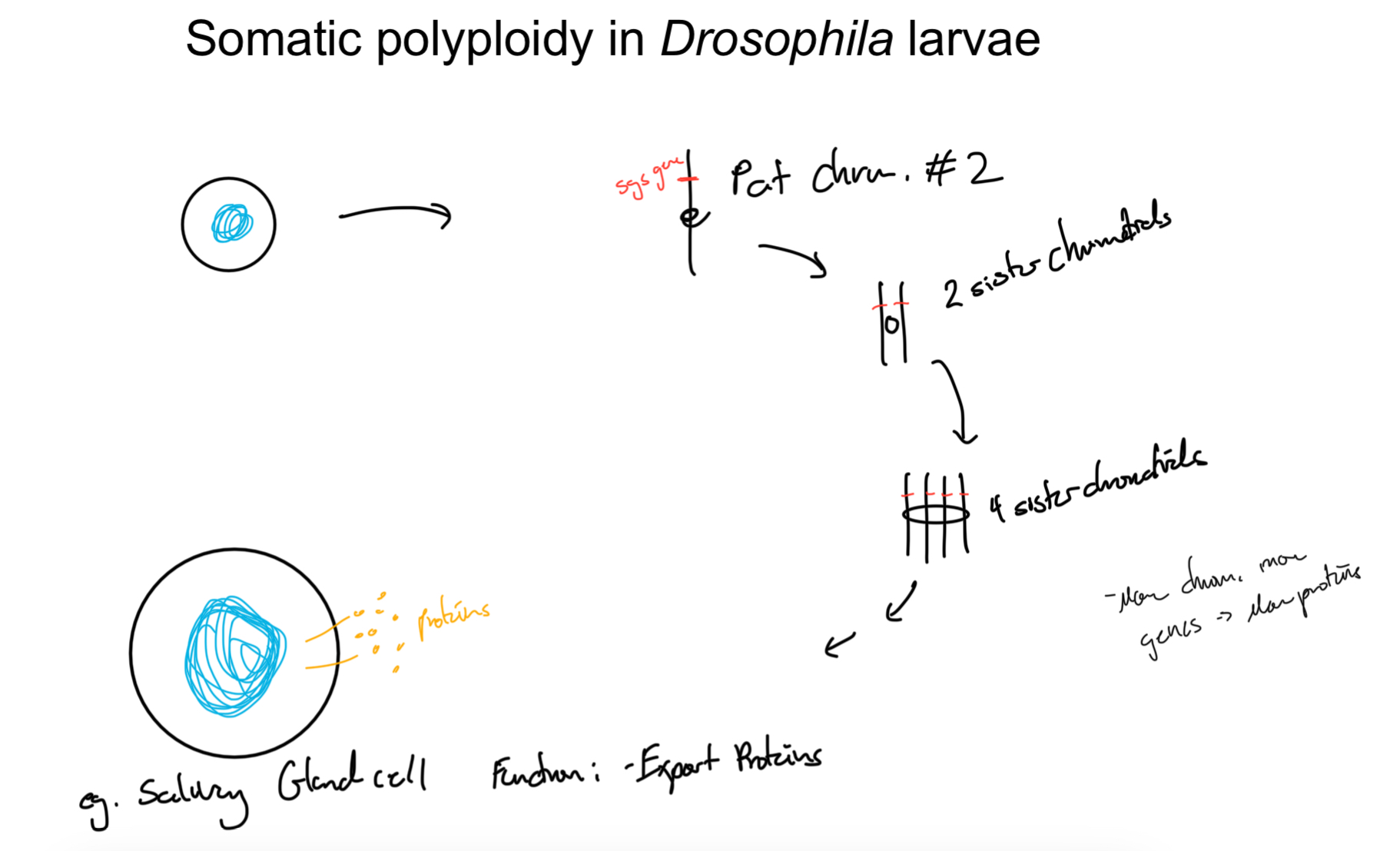
The example of Drosophila larvae somatic polyploidy covered in class
Infodump
What cell
Function/purpose
Salivary gland = Massive (1 giant nucleus)
Why so large?
To make more proteins (Salivary glue proteins) made by Sgs gene
salivary glue proteins = cover entire larvae to make it sticky + stick to surfaces to pupate

E
