Reproduction Topic #4 Puberty
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Puberty
_____ is defined as the aquisition of reproductive competenece that occurs over time.
NOT A BIG EVENT
Puberty is ______
Hypothalamus
Puberty is defendent on the ________ production of GnRH at appropriate frequency and quantities to stimulate production of FSH and LH
Gamete Production
Puberty
Required for _________
Estrogen
Puberty
Differs between male and female - responses to _______
Nutrition, Season, Social Cues, Genetics
Puberty
Presynaptic neurons to transmit information to GnRH neurons.
These neurons are influenced by:
__________ (influence hypothalamus)
Female
The hypothalamus is inherently _______
Testosterone
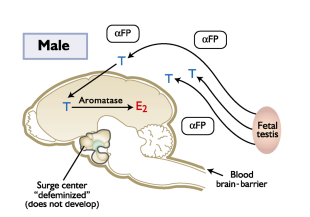
During male embryonic development __________ defeminizes the hypothalamus and eliminates the GnRH surge center → Males don’t need surges of testosterone
Estradiol
Testosterone defeminizes the hypothalamus, but it must first be converted to _________.
Estrogen
The female fetal brain is protected from _______
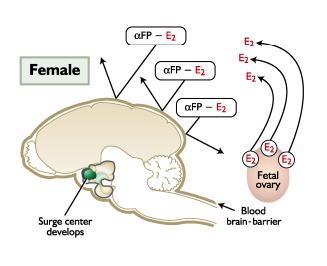
Blood-Brain Barrier
FEMALE
Fetal estrogen does not cross____________
Estrogen travels to the brain binded to alpha-feto proteins that prevents the estrogen from entering the brain.
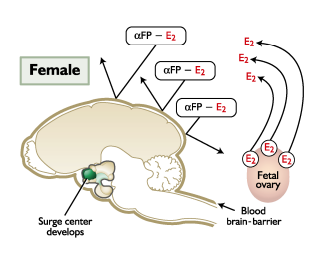
GnRH
FEMALE
The lack of estrogen in the brain is permissive to ____ and surge center development
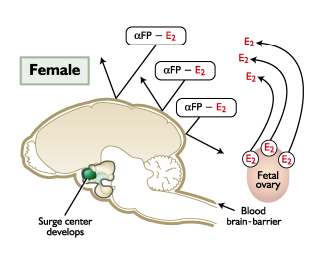
Defeminizes
MALE
Fetal testosterone _______ the hypothalamus
Estradiol
MALE
Testosterone crosses the blood brain barrier and is converted to ______
Lead to NO DEVELOPMENT of GnRH surge center (defeminization)

Female Hypothalamus
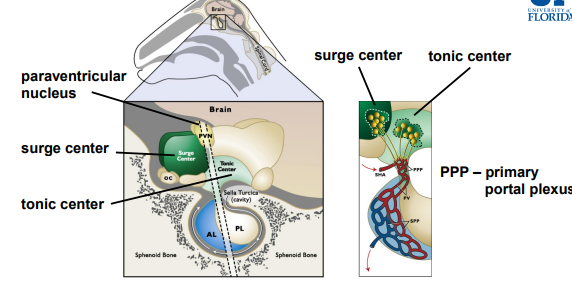
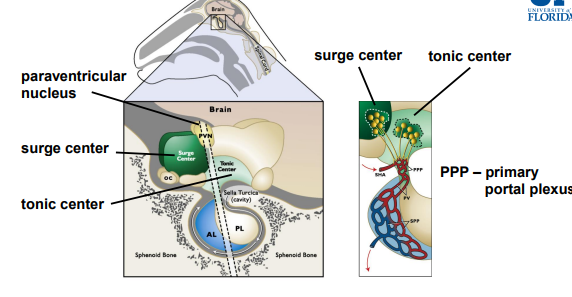
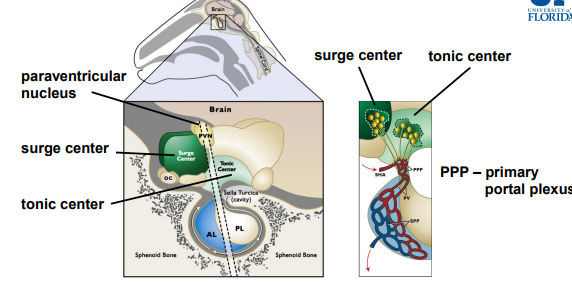
The surge center is specific to the ________
Males don’t have surges, stable production
If males do not have a surge center, how do you think GnRH and LH secretions differ in males and females?
Spikes
Surge center: responsible for GnRH ______ (+ve, -ve feedback)
Basal
Tonic center: responsible for ____GnRH secretion.
Surge Center
The tonic center regulates the _____
Surge
After puberty, LH does not ____ in the male
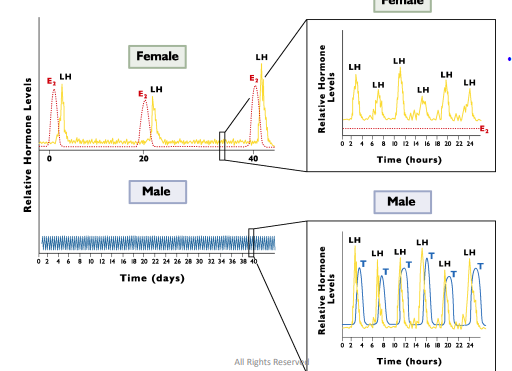
Males have low amplitude and predictable LH surges
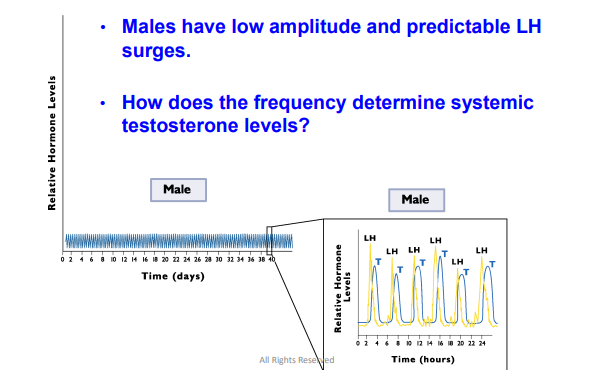
High amplitude or basal
LH can be _________ in the female
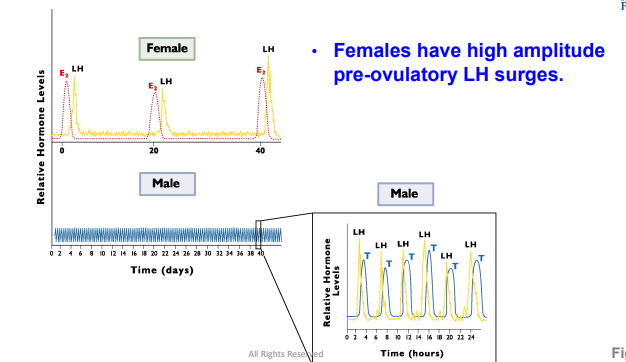
Pre-Ovulatory
Females have high amplitude ______ LH surges
Ovulation
Females also have basal pulsatile epides between ______
Pregnancy
Definitions of Puberty
FEMALE
Age at which a female can support _____
Ovulation
Definitions of Puberty
FEMALE
Age at first _______ - How do we know if ovulation has occured → ultrasound
Estrus
Definitions of Puberty
FEMALE
Age at first _____ (heat) - usually 1st behavioral estrus
Female becomes sexually receptive
Sexually receptivity DOES NOT always indicate ovualtion
The one being mounted
In this photo the animal that in heat is

Mounting and Erection
Definitions of Puberty
MALE
Age when behavioral traits first expressed
________- behaviors that precede sexual maturity

Ejaculation
Definitions of Puberty
MALE
Age at first _____
Coordination of nerves, muscles, seminal fluids
Substantially preceds ability to produce enough sperm for fertilization
Spermatozoa
Definitions of Puberty
MALE
Age when ejaculation contains threshold _______ for fertilization
Species differenes
Bull: > 50 × 10^6 sperm/mL w/10% motility
Body Size (threshold) and Enviornment and/or social cues?
What two factors impact hypothalamic GnRH neurons?
________
________
Body Size (threshold)
Factors Impacting Hypothalamic GnRH Neurons
_____
Fat Deposition (Increased fat will each puberty faster)
Enviornment and/or social cues
Factors Impacting Hypothalamic GnRH Neurons
________
Season of partutition
Photoperiod onset of puberty (sunlight exposure)
Presenece of opposite sex
Denisty of animals of the same sex
Genetics- breed specific
Genetics
Onset of Puberty
________________
Early maturing breeds have earlier onset of puberty than late maturing breeds
Cattle: Angua < Charolais, Braham
Maternal Breeds
Onset of Puberty
_______ reach puberty earlier than meat type breeeds
Cattle: Holstein < Charolais
Swine: White Landrace < Yorkshire
GnRH
The major limiting factor for onset of puberty is _____ secretion

LH Spike
The hypothalamus must secrete enough GnRH to induce an ______ → Ovulation

gradually with age
GnRh release increase __________ (male and female)
Exogenous GnRH
GnRH
Female: Prepubertal pituitary and ovaries respond to ____________ - mechanics (neurons) are already in place!
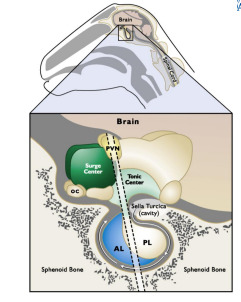
Can regulate the surge center
Female: Remember the tonic center regulates the pulse frequency in GnRH and this the surge center … so the tonic center must also reach a functional state so that it ________
Low amplitude and low frequency
GnRH neurons release __________________ of GnRH
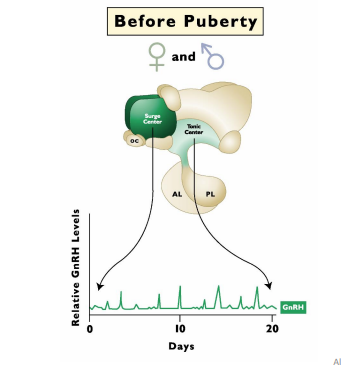
Minimial Follicular Growth
GnRH Neurons (Female)
Low Estrogen means there is a lack of surge center stimulation (GnRH secretion) → the tonic center has a high sensitivity to negative feedback of E2 before puberty and this the surge center cannot respond.
LH Pulse Frequency is Low
Low estrogen is due to ________________
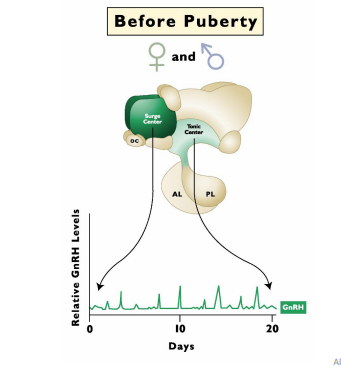
Puberty
GnRH secretion changes after _____

Surge Center
GnRH secretion and puberty (Female)
With age estrogen increases to reach the minimum threshold to activate the __________. (Tonic center activates to secrete GnRH from surge center)
Thus: LH/FSH increases
Follicle Development increases
Positive Feedback on estrogen to INCREASE GnRH surge center
LH SURGE causes ovualtion
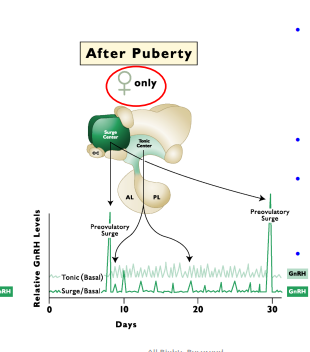
Surge
Onset of Puberty in the Female
The female surge center can respond to estrogen even at birth. So the sensitivity of the _______ to Estrogen never really changes. However, the sensitivity to negative feedback in the tonic center decreases with age and TRIGGERS PUBERTY
Estrogen
Onset of Puberty Female
The surge center responds to positive feedback of ______
Cannot Respond
Onset of Puberty Female
The tonic center has a high sensitivity to negative feedback of Estrogen before puberty, and thus the surge center ________
Tonic center has to be active before surge center → regulates
yes
LH frequency increases with GnRH secretions, look at Graph
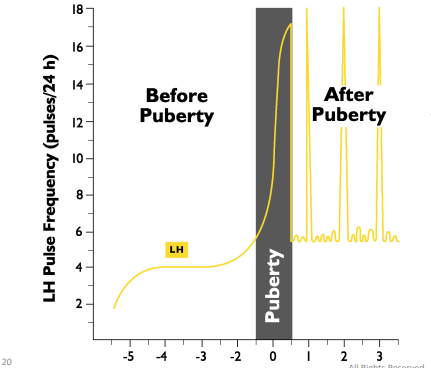
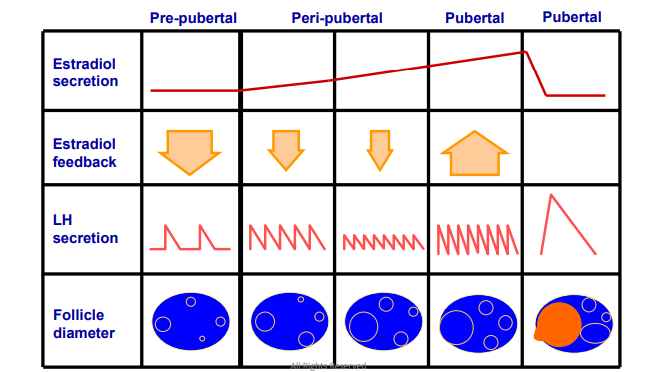
as ovarian follciles get bigger → producing more Estrogen
Endocrine and Ovarain Changes with Puberty (look at notes)
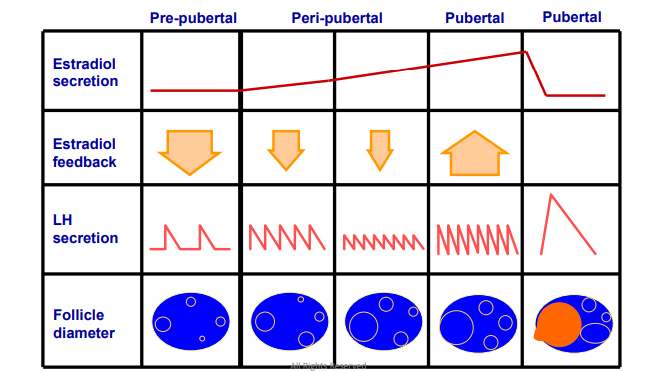
Hypothalamus Defeminization
Males do not have a surge center due to _________ before or after birth.
Negative Feedback
MALE
How does the male hypothalamus respond to GnRH sensitivity?
Densensitized
MALE
Estrogen and Testosterone from prepubertal males causes negative feedback on GnRH secretion
As puberty increases the GnRH become ________ to the Testosterone and Estrogen resulting in Increased GnRH → LH & FSH secretion (gradual process)
Testes develop and produce more sperm and testosterone
Slighty Faster
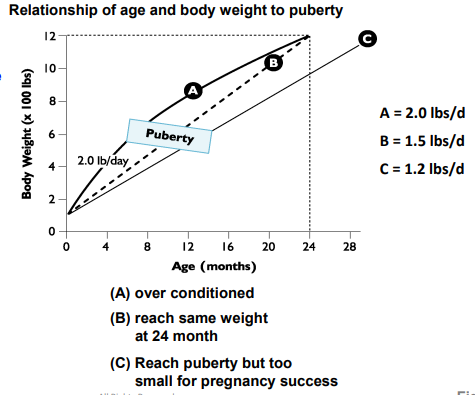
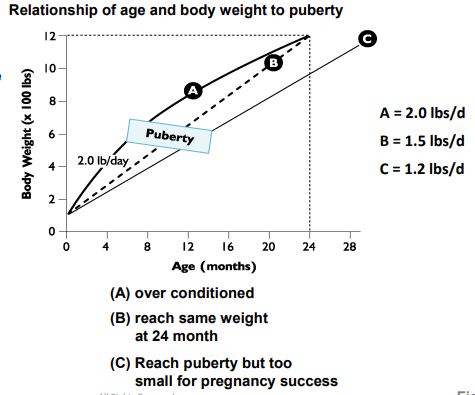
Overfed animals may reach puberty ______
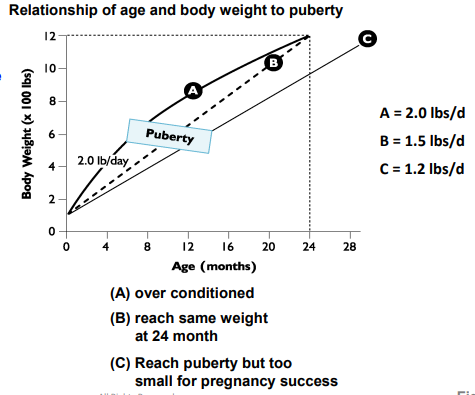
Correlated
Metabolic Factors that regulate the onset of puberty
Free fatty acids and glucose are ______ (proportional) to GnRH concentrations
Thus, Overfed animals may reach puberty slightly faster
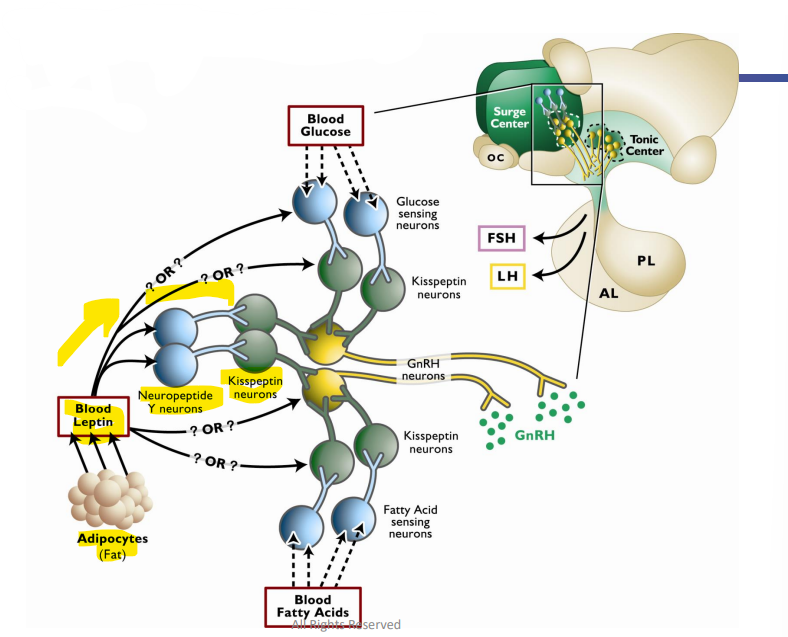
Leptin
Metabolic Factors that Regulate the Onset of Puberty
__________: hormone secreted by adipocytes (fat) with receptors on the pituitary
Increase in fat → Increase in Leptin → Increase on pituitary → Increase in Gonadotropins
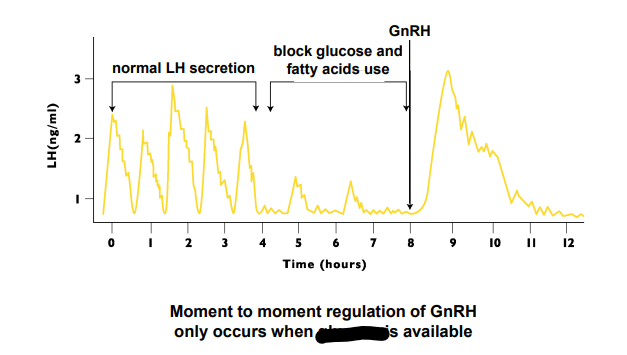
Glucose
Moment to Moment regulation of GnRH only occurs when ____ is availiable
GnRH neurons to produce GnRH
Metabolic Factors and Onset of Puberty
Glucose → Fuels Glucose Sensing Neurons → Innervates Kisseptin Neurons → Innervate ____________
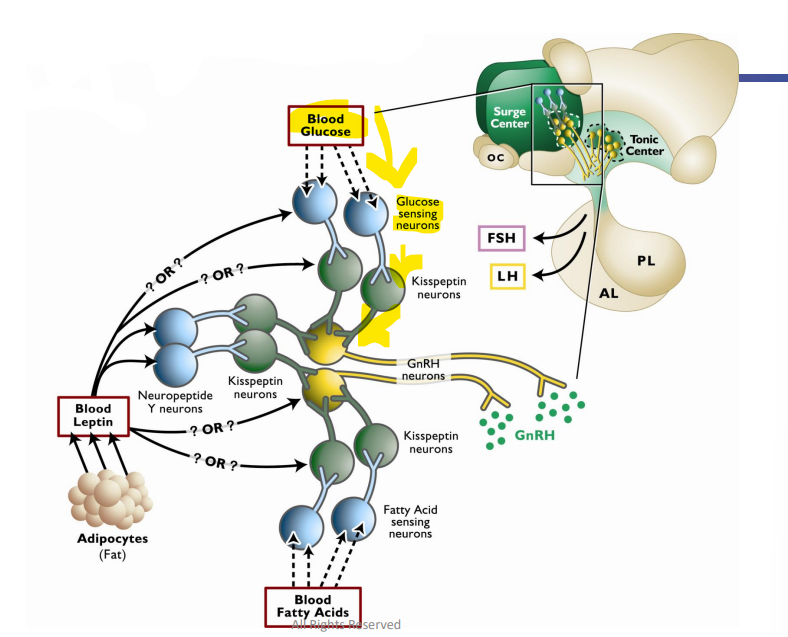
GnRH neurons to produce GnRH
Metabolic Factors and Onset of Puberty
Aipocytes (Fat) → Forms Blood Leptin → Innervates Neuropeptide Y Neurons → Innervates Kisspeptin Neurons → Innervate _______
GnRH neurons to produce GnRH
Metabolic Factors and Onset of Puberty
Adipose Fatty Acids → Innervate Fatty Acid Sensing Neurons → Innervate Kisspeptin Neurons → Innervate ______GnRH neurons to produce GnRH
Regulate
KIsspeptin Neurons ______ GnRH Secretion
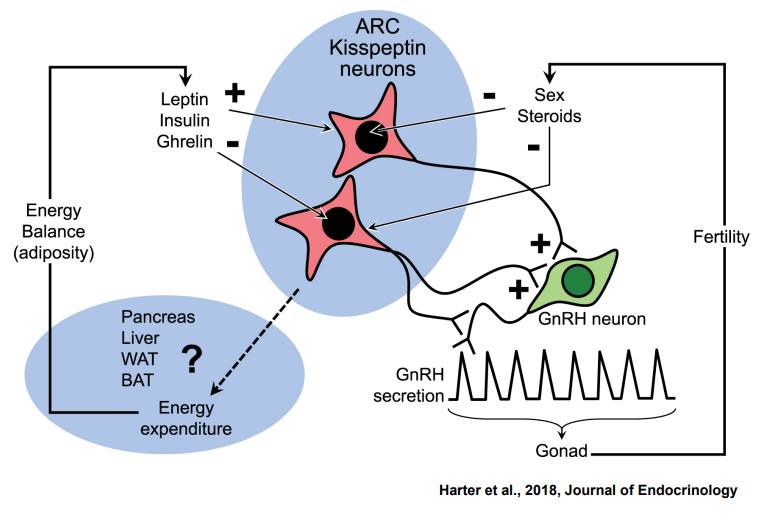
Regulate Puberty
Enviornmental and Social Conditions that _______
Season of Birth
Social Cues from Males
Size of Social Group

Hasten
Social cues ____ the onset of puberty in some livestock

Olfactory Recognition of Pheromones in Urine
Social Cues that Hasten the Onset of Puberty
___________________ (Rat, Ewe, Sow, and Possibly Cow)
Pheremones: volatile chemical compounds secreted by the body that are detected by olfactory system in some species - CAN STIMULATE GnRH

External Factor
Social Cues Hastening Onset of Puberty
_______
Opitic and Olfactory Neurons
Act on hypothalamus to increase GnRH
Season of Birth
Social Cues Hastening Onset of Puberty
__________ particularly in seasonal breeders like sheep and horse
Present in rams but not bulls
Bitch: minimal seasonal effects on puberty
Queen: increased photoperiod (more light) hastens onset of puberty
Fall
Season of Birth
Short-Day Breeders = ______
Spring
Season of Birth
Long-Day Breeders = ____
All external stimuli
Despite social cues, puberty onset cannot be achieved without a threshold metabolic status to initiate hypothalamic (T and E2) responsiveneess to ______
Puberty
The month of birth influences the age of _____ in sheep
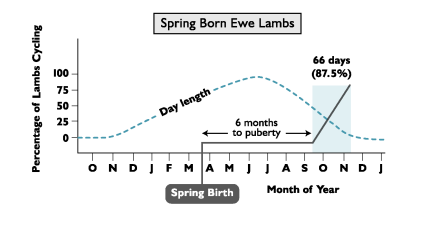
Faster
Sheep born in the spring reach puberty ______ than those born in the Fall
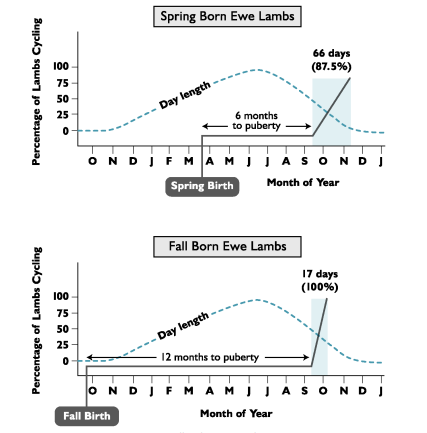
Puberty
Social Cues in Swine
_________ dictated by number of gilts in a pen and exposure to intact males
(not even physical contact → fence line exposure similar to physical contact)
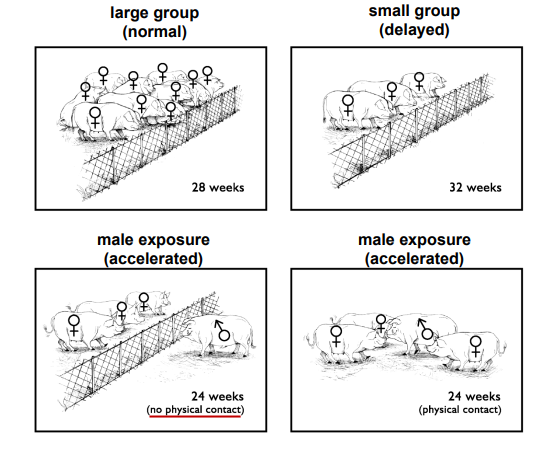
Delayed Puberty
Social Cues in Swine
Gilts housed in small groups experienced _________
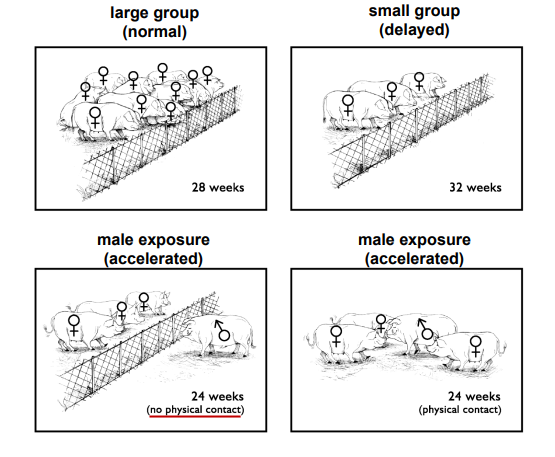
FASTER
Social Cues in Swine
Gilts exposed to males will enter puberty ____ THAN LARGE OR SMALL GROUPS OF GILTS WITH NO EXPOSURE
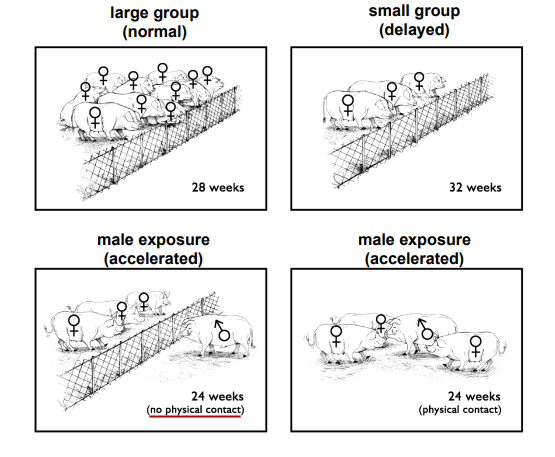
Accelerate
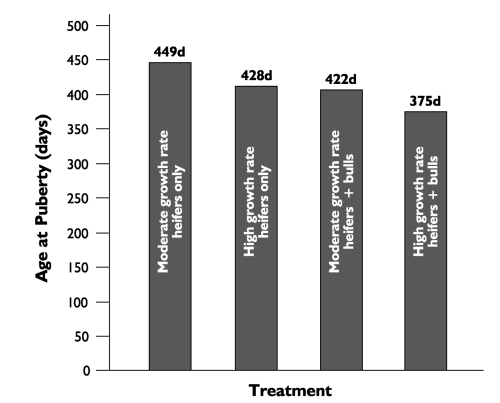
Bulls ____ the onset of puberty in heifers