module 5—nervous system
1/419
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
420 Terms
Neurons are masses of…
nerve cells that transmit information (functional unit of the system)
Cell body definition
contains the nucleus and other cell organelles
Dendrite definition
shorter, more numerous, receive information
Axon definition
single long fibers, conducts information away from the cell
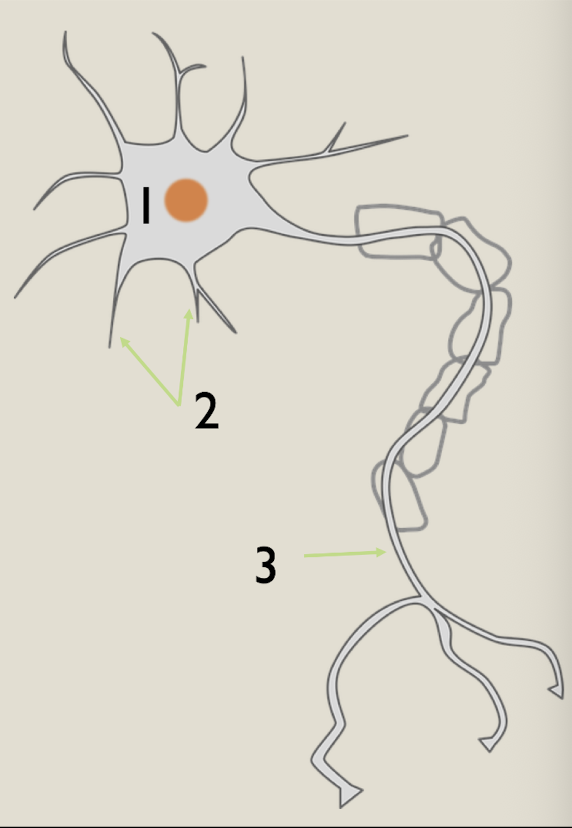
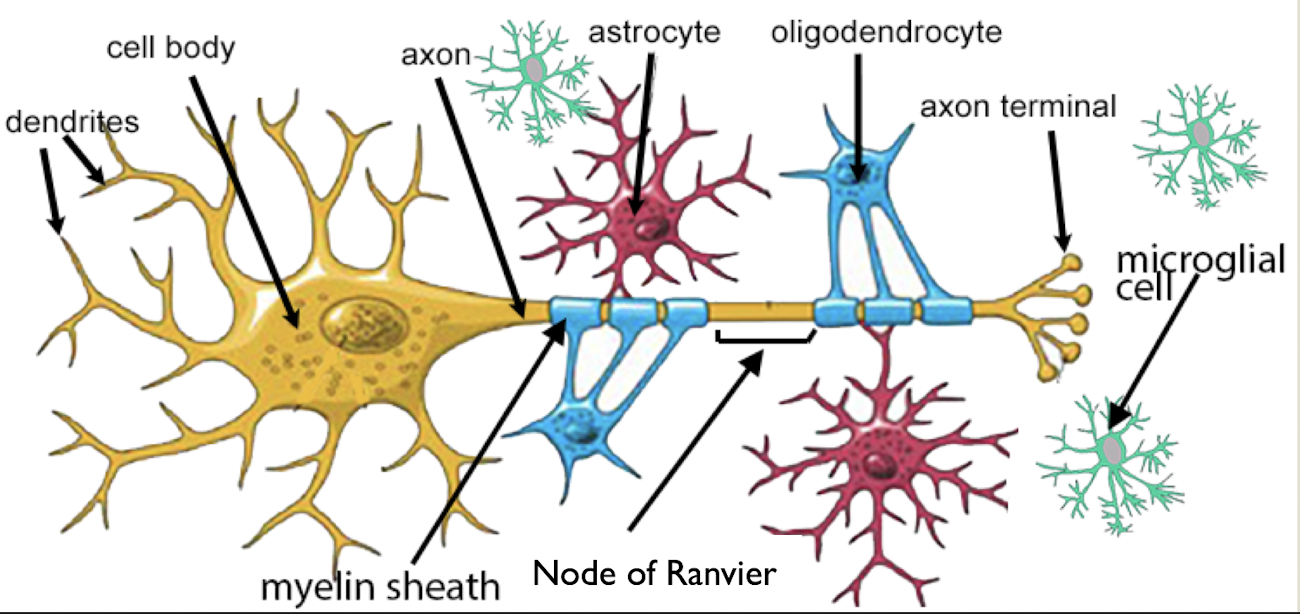
Label 1, 2, and 3
cell body
dendrites
axons
The central nervous system (CNS) includes the…
brain
spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes the…
nerves throughout the body
How many pairs of spinal nerves
31
How many pairs of cranial nerves
12
What is the overall function of the nervous system
coordinate the body’s systems by receiving and sending information
maintaining homeostasis
What does the sensory/afferent input do
gathers info from receptors in the body
What does the integrative system do
determines where information is sent
What does the motor/efferent output do
responds to signals
restores homeostasis
The peripheral nervous system is made up of the…
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
enteric nervous system
The somatic nervous system involves the…
skeletal
Is the somatic nervous system voluntary or involuntary
voluntary
The autonomic nervous system involves the…
smooth muscles, glands
Is the autonomic nervous system voluntary or involuntary
involuntary
The enteric nervous system is responsible for controlling the…
smooth muscle and glandular tissue in the digestive system
What nervous system is a large part of the PNS, and is not dependent on the CNS?
enteric nervous system
It is valid to consider the enteric system to be a part of the autonomic system because…
the neural structures that make up the enteric system are a component of the autonomic output that regulates digestion
What does the brain perceive and process?
senesory stimuli (somatic/autonomic)
The brain (CNS) executes the…
voluntary motor responses (somatic)
The brain (CNS) regulates…
homeostatic mechanisms (autonomic)
The nerve (PNS) are…
fibers of sensory and motor neurons (somatic/autonomic)
The digestive tract (ENS) is located in the…
digestive tract
The digestive tract (ENS) is responsible for…
autonomous functions and can operate independently of the brain and spinal cord
The spinal cord (CNS) initiates…
reflexes from the ventral horn (somatic) and lateral horn (autonomic) gray matter
The spinal cord (CNS) gives rise to pathways for…
sensory and motor functions between periphery and brain (somatic/autonomic)
The ganglia (PNS) receive…
sensory stimuli by dorsal root and cranial ganglia (somatic/autonomic)
The ganglia (PNS) relay…
visceral motor responses by autonomic ganglia (autonomic)
What are the two branches of the autonomic nervous system?
parasympathetic and sympathetic
Which branch of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for rest and digest?
parasympathetic
What branch of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for fight or flight?
sympathetic
What happens during an autonomic conflict?
is the simultaneous activation of parasympathetic and sympathetic autonomic inputs
causes thing like arrythmias
What happens to the eyes in the parasympathetic branch?
pupils constrict
What happens to the salivary glands in the parasympathetic branch?
stimulates salivation
What happens to the heart in the parasympathetic branch?
heartbeat slows
What happens to the lungs in the parasympathetic branch?
bronchi constrict
What happens to the stomach in the parasympathetic branch?
stimulates digestion
What happens to the liver in the parasympathetic branch?
stimulates bile release
What happens to the intestines in the parasympathetic branch?
stimulates peristalsis and secretion
What happens to the bladder in the parasympathetic branch?
bladder contracts
What happens to the eyes in the sympathetic branch?
pupils dilate
What happens to the salivary glands in the sympathetic branch?
inhibition of salivation
What happens to the heart in the sympathetic branch?
heartbeat accelerates
What happens to the lungs in the sympathetic branch?
bronchi dilate
What happens to the stomach in the sympathetic branch?
inhibition of digestion
What happens to the liver in the sympathetic branch?
stimulates glucose release
What happens to the kidneys in the sympathetic branch?
stimulates epinephrine and norepinephrine release
What happens to the intestines in the sympathetic branch?
inhibition of peristalsis and secretion
What happens to the bladder in the sympathetic branch?
bladder relaxes
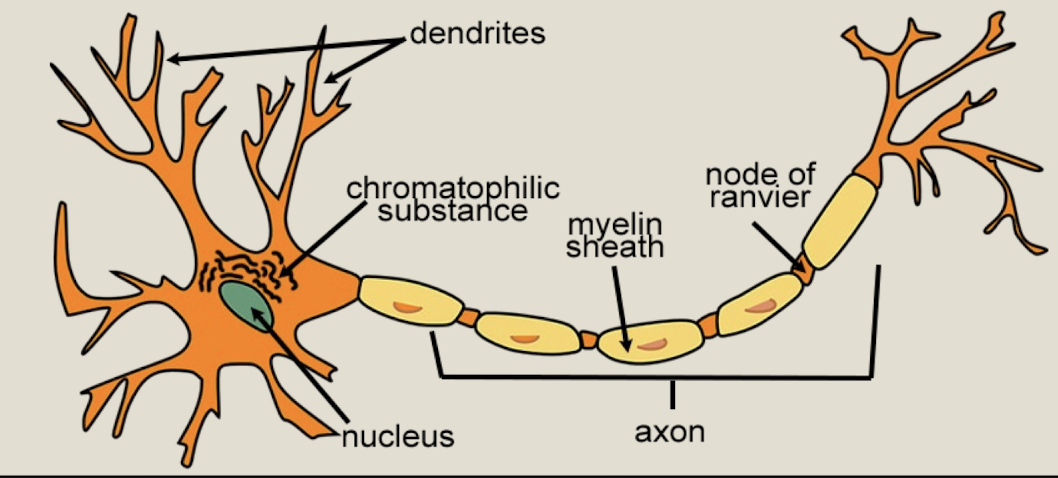
What is the chromatophilic substance (rough ER) in a neuron?
transport system
What does the myelin do in a neuron?
is insulation surrounding axons
What are nodes of Ranvier?
gaps in the insulation
If there is no myelin around the axon, what happens to signals?
they jump
Neurofibrils definition
fibers within the axon
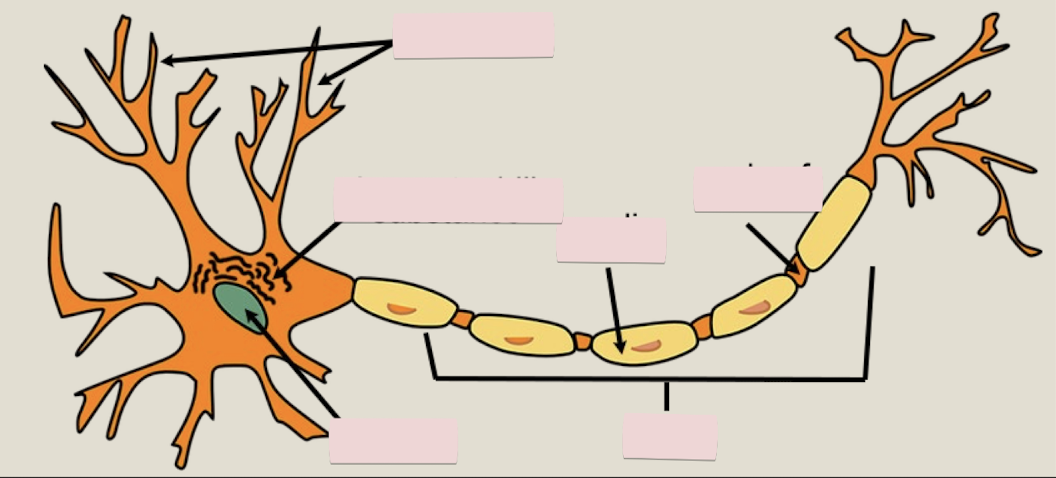
Label the figure
Glial cells definition
supporting cells
The function of the glial cells
directed at helping neurons complete their function for communication
The name glia comes from the Greek word that means…
“glue”
The glia in the CNS are…
astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
microglia
ependymal cell
The glia in the PNS are…
satellite cells
schwann cells
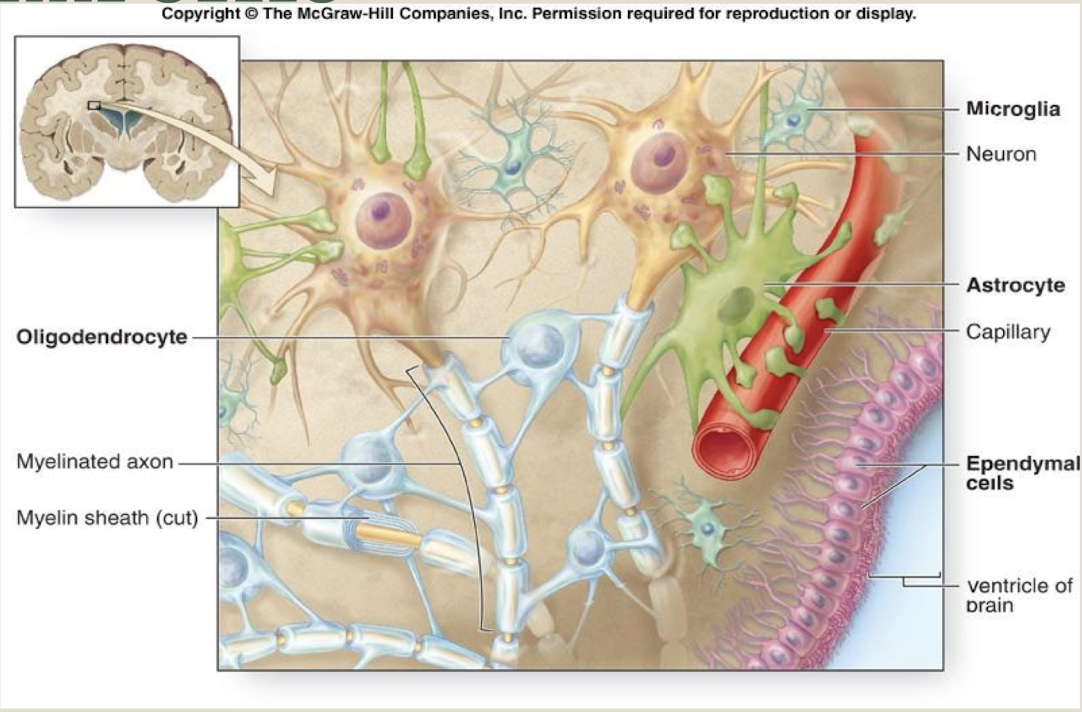
Location and function of astrocytes
CNS
support
Location and function of oligodendrocytes
CNS
insulation, myelination
Location and function of microglia
CNS
immune surveillance and phagocytosis
Location and function of ependymal cell
CNS
creating CSF
Location and function of satellite cells
PNS
support
Location and function of schwann cells
PNS
insulation, myelination
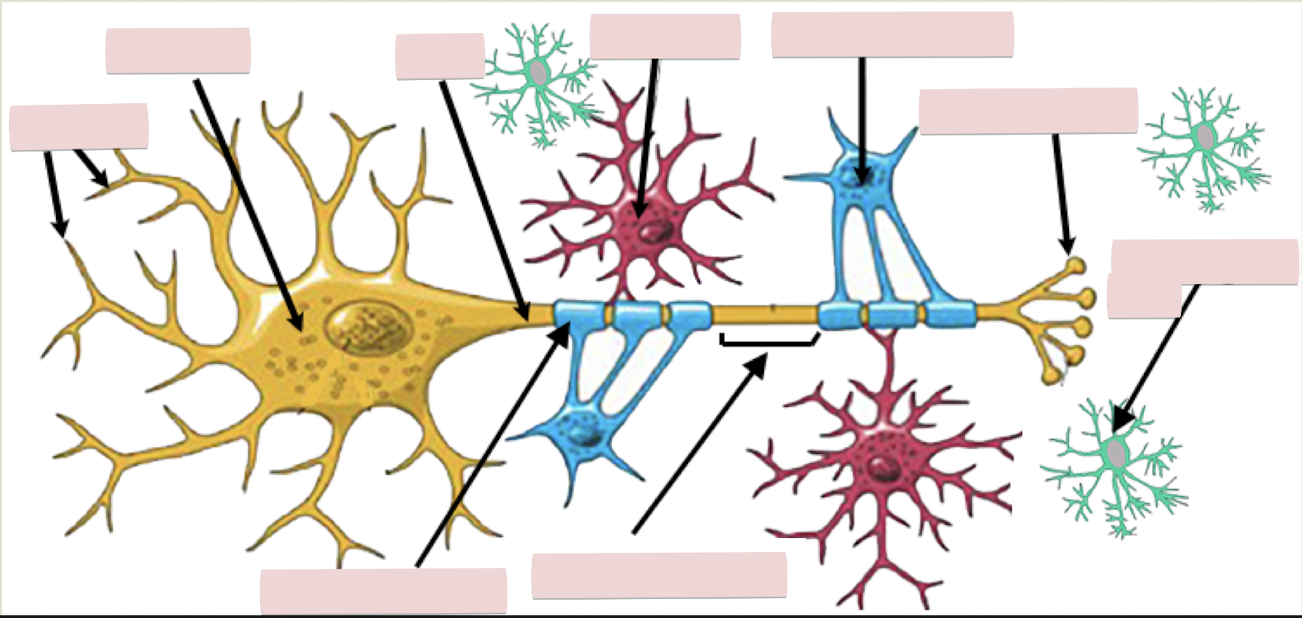
Label the figure
Astrocytes connect…
blood vessels to neurons
Astro means…
star
Astrocytes have many…
processes extending from their main cell body
The processes on astrocytes extend to interact with…
neurons
vessels
connective tissue covering the CNS
Astrocytes maintain the concentration of chemicals in the extracellular space by…
removing excess signaling molecules
reacting to tissue damage by brining in a blood supply
Astrocytes contribute to the…
blood brain barrier (BBB)
Very little substances can pass through the BBB by diffusion, why?
it has tight junctions
Most substances that want to cross the wall of a blood vessel into the CNS must do so through…
active transport
Substances that need to pass through the BBB
glucose
amino acids
water
gases and ions
Oligodendrocytes definition
make myelin sheath that provides insulation around the axons
Name breakdown of oligodendrocyte
oligodendrocyte = “cell of a few branches”
oligo- = “few”
dendro- = “branches”
-cyte = “cell”
How do oligodendrocytes form myelin?
the few processes that extend from the cell will reach out and surround the axon to insulate it with myelin
One oligodendrocyte can provide myelin for…
multiple axon segments
Can an oligodendrocyte provide myelin for the same axon or for separate axons?
same and separate!
Microglial cells definition
immune function, digest debris, kills bacteria
Microglial cells are ______ than most of the other glial cells
smaller
Microglial cells may originate as…
macrophages
When do microglial cells become part of the CNS…
during early development
What is the function of microglial cells
related to what macrophages do in the rest of the body
When macrophages encounter diseased or damaged cells in the rest of the body they…
ingest and digest those cells or the pathogens that cause disease
Ependymal cells definition
forms membranes around tissue
Ependymal cells form the lining of the…
ventricular system in the brain
Ependymal cells are in direct contact with the…
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Ependymal cells line each…
ventricle in the brain
The relation of the BBB and ependymal cells
considered a component of the BBB
a place where the BBB breaks down
How are ependymal cells similar to epithelial cells
make a single layer of cells with littel intracellular space
tight connections between adjacent cells
Ependymal cells have cilia on their apical surface to…
help move the CSF through the ventricular space
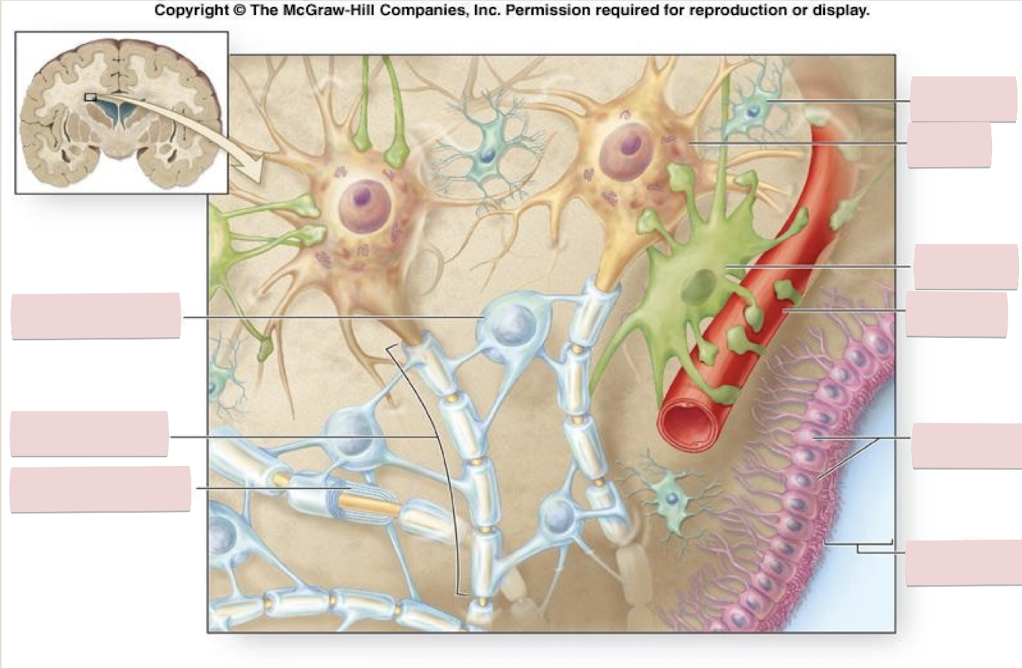
Where are satelliete cells found
in sensory and autonomic ganglia in the PNS
Satellite cells surround (satellite) the…
cell bodies of neurons