NURS 201: Unit 1 - Global Health and the Social Determinants of Health
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Health
- An ideal state of optimal well being toward which all individuals could strive to
- Applies to all persons, sick or well
- Broad in perspective
Global Health
- An area of study, research and practice that places a priority on improving health and achieving health equity in health for all people world wide
- The optimal well-being of all humans from an individual and collective perspective
Global health refers to the ____ not their ____
Scope, location
3 Factors that Global Health Encompasses
- Prevention
- Treatment
- Care
Global Burden of Disease
A metric that quantifies the health of the population at many levels
Communicable Diseases
Infectious diseases
Non-Communicable Diseases
Chronic diseases
Global Violence
Various forms of violence impacting health outcomes
Gender Equality
People of all genders enjoying the same rights and opportunities in all aspects of their lives
Intersectionality
The interconnected nature of social categorizations such as race, class, and gender as they apply to a given individual or group
Health Disparity
A statistically significant difference in health indicators that persists over time
Healthcare Disparity
A difference in access to healthcare by different groups
9 Indicators of Health Disparities
- Burden of disease
- Mortality rate
- Infant mortality rate
- Morbidity rate
- Life expectancy
- Birth rate
- Total fertility rate
- Disability
- Nutritional status
Burden of Disease
- The impact of a health problem in an area measured by financial cost, mortality, morbidity, or other indicators
- Helps to measure the impact of health interventions
Mortality Rate
The number of deaths in a population, scaled to the size of that population (expressed in units of death/1000 people)
Infant Mortality Rate
- The number of death of infants/1000 live births
- Indicator of a country's level of health/development
Morbidity Rate
- The number of individuals in poor health during a given time or number who currently have that disease, scaled to the size of that population
- Takes into account the state of poor health, degree/severity of a health condition, and total number of cases in a particular population and point in time, regardless of cause
Life Expectancy
- The average number of years of life remaining at a given age or average life span or average length of survival in a specific population
- The most important measure of health
Birth Rate
The number of childbirths/100 000 people/year
Total Fertility Rate
The average number of children born to each woman over the course of her life
Disability
Lack of ability relative to a standard
Nutritional Status
A factor influenced by diet, levels of nutrients in the body, and ability to maintain normal metabolic integrity
Globalization
- A process resulting from a combination of forces that is increasing the flow of information, goods, capital, and people across political and geographical boundaries
- Relates to the increased interconnectedness and interdependence of people and countries
3 Ways that that Globalization Impacts Health
- Spread of disease
- New health problems
- Lifestyle influences
CNA's Position Statement Towards Health
- Health is a global issue
- Health is a human right
- Registered nurses have the responsibility and right to seek out inequalities
6 Roles in Global Health
- Governments
- Non-governmental and voluntary organizations
- Nursing organizations
- Registered nurses
- Communities
- Individuals
Role of Governments in Global Health
- Protect public interests
- Advocacy
- Policy
- Knowledge sharing
Role of Non-Governmental and Voluntary Organizations in Global Health
- Advocacy
- Advancement in research and policy
- Service providers
Role of Nursing Organizations in Global Health
- International partnerships
- Advocacy
- Education of members
- Response to international health issues
Role of Registered Nurses in Global Health
- Raising awareness
- Advocacy
- Educators
- Research
Role of Communities in Global Health
- Determining priorities
- Determining approaches to address health issues
Role of Individuals in Global Health
- Informing themselves
- Being responsible for others
4 Examples where Nurses may Experience the Impact of Global Health in their Work
- Clients
- Organizations
- Work colleagues
- Employment
2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
- A document adopted by world leaders that came into force on January 1, 2017, and outlines the 17 sustainable development goals
- Overall goal is to fight inequality, end all forms of poverty, and address climate change for all people of the world
17 Sustainable Development Goals
- No poverty
- Zero hunger and food security
- Healthy well-being for all ages
- Quality education
- Gender equality
- Access to water and sanitation
- Affordable and clean energy
- Decent work and economic growth
- Resilient infrastructure and sustainable industrialization
- Reduced inequality within/among countries
- Inclusive/safe/resilient/sustainable cities
- Sustainable consumption and production patterns
- Maintain the environment
- Promote peace, justice, and strong institutions
- Revitalize global partnerships for sustainable development
Equality
The state of being equal

Equity
The state of being fair

Health Inequity
Differences in health that are unfair, unjust, unavoidable, and are often a result of a power dynamic
Downstream Thinking
A way of thinking that blames the individual as the source of the problem
Upstream Thinking
A broader way of thinking that acknowledges that their are SDOHs that affects a person's overall well-being
LaLonde Report 1974
An important report that emphasized the importance of a biopscychosocial model over a biological model of health (Ex. SDOHs)
Determinants of Health
The broad range of personal, social, economic, and environmental factors that determine individual and population health
Social Determinants of Health (SDOH)
- The conditions in which people are born, grow,
live, work and age
- Shaped by the distribution of money,
power and resources at global, national and local levels
- Determines what resources a person has to achieve their goals
- Determines health or lack thereof
- Impacts individual choice
12 Main Determinants of Health
- Income and social status
- Social supports and coping skills
- Education and literacy
- Employment and working conditions
- Childhood experiences
- Physical environment
- Healthy behaviours
- Biology and genetic endowment
- Access to health services
- gender
- Culture
- Race/racism
Food Security
The access to adequate quality and quantities of food
Food Insecurity
A state of being without reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable and nutritious food
3 Types of Food Insecurity
- Marginal
- Moderate
- Severe
Marginal Food Insecurity
Type of food insecurity in which people have limited choice in food items or worry about running out of food
Moderate Food Insecurity
Type of food insecurity in which people have uncertain access to food impacting the quality and or quantity of food
Severe Food Insecurity
Type of food insecurity in which people run out of food, with 1 or more days without food
Neoliberalism
A concept relating to how some nations are wealthier, and therefore, healthier than others
Institutional Racism
Differential access to goods, services, and opportunities of society by race
Systematic Racism
Racism that is embedded in the laws, regulations, policies, and practices of a society or an organization
Colonization is _____ and not ______
Contemporary, historical
3 Main Types of Social Determinants of Indigenous People's Health
- Root
- Core
- Stem
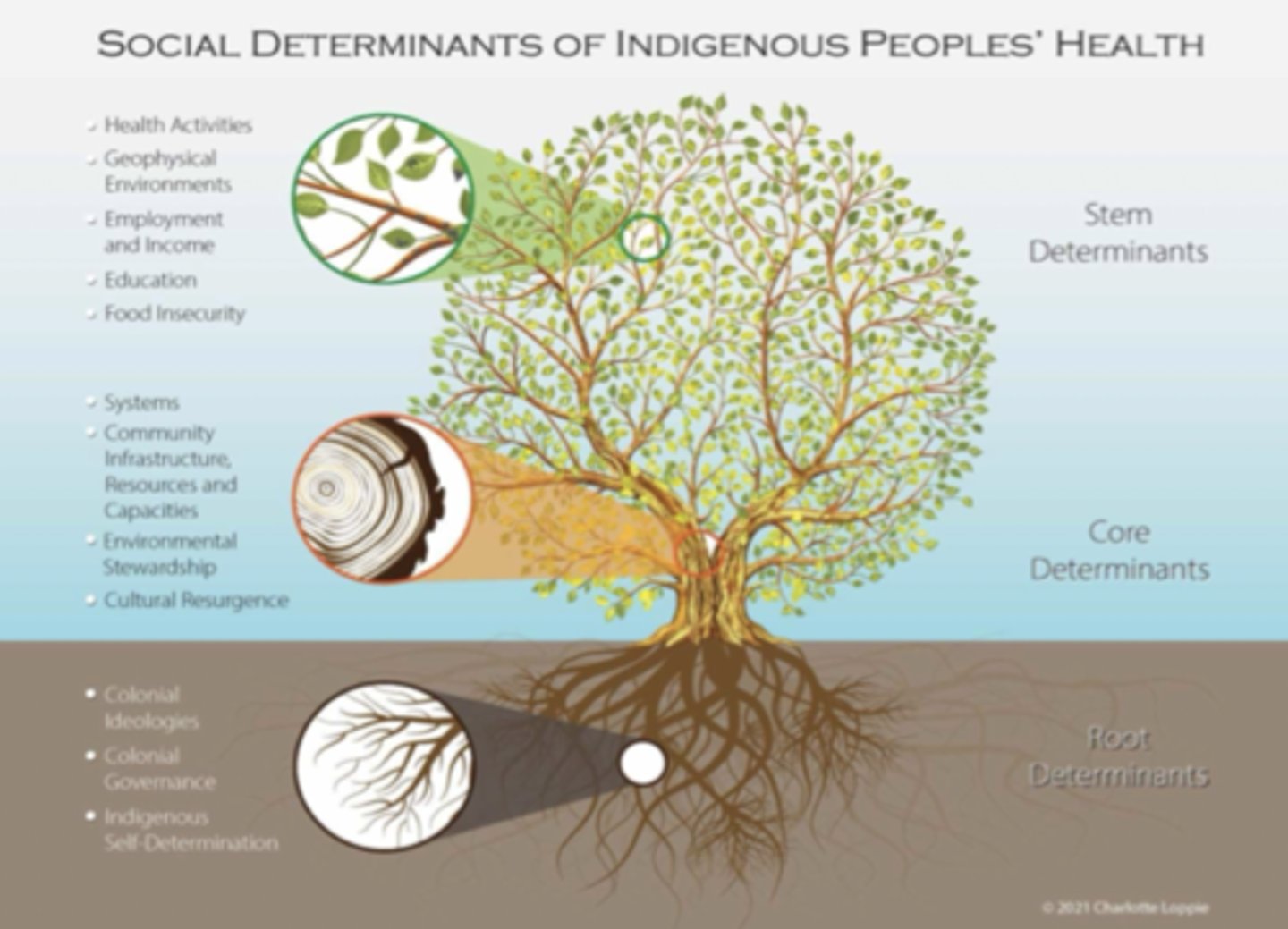
Root (Structural) Determinants
- Determinants that are deeply embedded ideological and political foundations that shape all other determinants
- Has the most profound influence
- Ex.) Colonialism

Core Determinants
- Determinants that represent infrastructure and systems responsible for the allocation of resources, supports, and engagement of individuals and communities
- Ex.) Education, health, justice, social welfare

Stem Determinants
- Determinants that have a more direct impact on the health of individuals
- Often the primary focus
- Ex.) Education/training, employment, social supports, resources

3 Areas of Focus in Addressing Indigenous Health Inequities
- Adopt a structural approach
- Community strength-based approach
- Acknowledge the positive determinants of health Indigenous people hold
Community
- A group of people who live, learn, work, and play in an environment at a given time
- May be defined by geopolitical boundaries, common interests, goals, beliefs, and cultures
Health Literacy
The skills that enable individuals to obtain, understand, and use information to make decisions, and take actions that will have an impact on health status