Hematopoiesis & Homeostasis
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
cell membrane consists of
lipid bilayer - semi-permeable
hydrophobic HC tail
transmembrane proteins
nucleus
contains nucleolus which produces cell’s ribosomes → ribosomes transported to cell cytoplasm for protein synthesis
cytoplasm
place for protein synthesis, growth, motility, phagocytosis
organelles include
mitochondrion
ribosomes
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi appartus
lysosomes
flow of genetic info in a cell
DNA replication/synthesis (nucleus)
transcription: RNA synthesis (nucleus)
translation: RNA → protein (in cytoplasm)
protein degradation: 2 methods
to maintain homeostasis
lysosome system
ubiquitin proteasome system
tissue homeostasis
mitotic cell division → differentiation → apoptosis
proto-oncogenes
human genes w potential to cause cancer ie cell proliferation growth factors
mutations in these genes → tumor
growth factors
growth factor receptors
signal-transduction proteins
transcription factors
→ activate oncogenes
cell-cycle control proteins → tumor suppressors
DNA repair proteins
pro- or anti-apoptotic proteins
hematopoiesis is
the process that replaces circulating rbc
depends of precursor cells in BM
controlled by cytokines
development of blood cells
3 weeks: formation of blood islands from yolk sac
6 weeks: liver = hematopoietic (HP) organ
6-8 weeks: spleen (until 8th month)
12-weeks: bone marrow (life long)
normal BM composition
60% granulocytes & precursors
20% erythroid precursors
10% lymphocytes, monocytes
10% unID’d or disintegrated cells
bone marrow consists of mainly _ cells
neutrophils??
hematopoietic precursor cells
stem: 0.5%, totipotent
progenitor: 3%, multipotent
maturing: 95%, unipotent (committed)
hematopoiesis chart
cytokine signaling pathways
caspase → apoptosis
Bcl2 = cell death repressor
myeloid maturation
mitotic:
myeloblast
promyelocyte (primary granules)
myelocyte (secondary granules)
post-mitotic:
metamyelocyte
band
segmented neutrophil
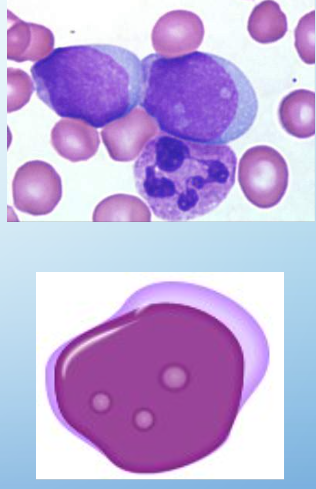
myeloblasts
size: 8-13 um
2% nucleated cells in BM
CP: basophilic (free ribosomes), no prominent granules
NC: undifferentiated (fine chromatin, sieve-like), round to ovoid
cell division: yes
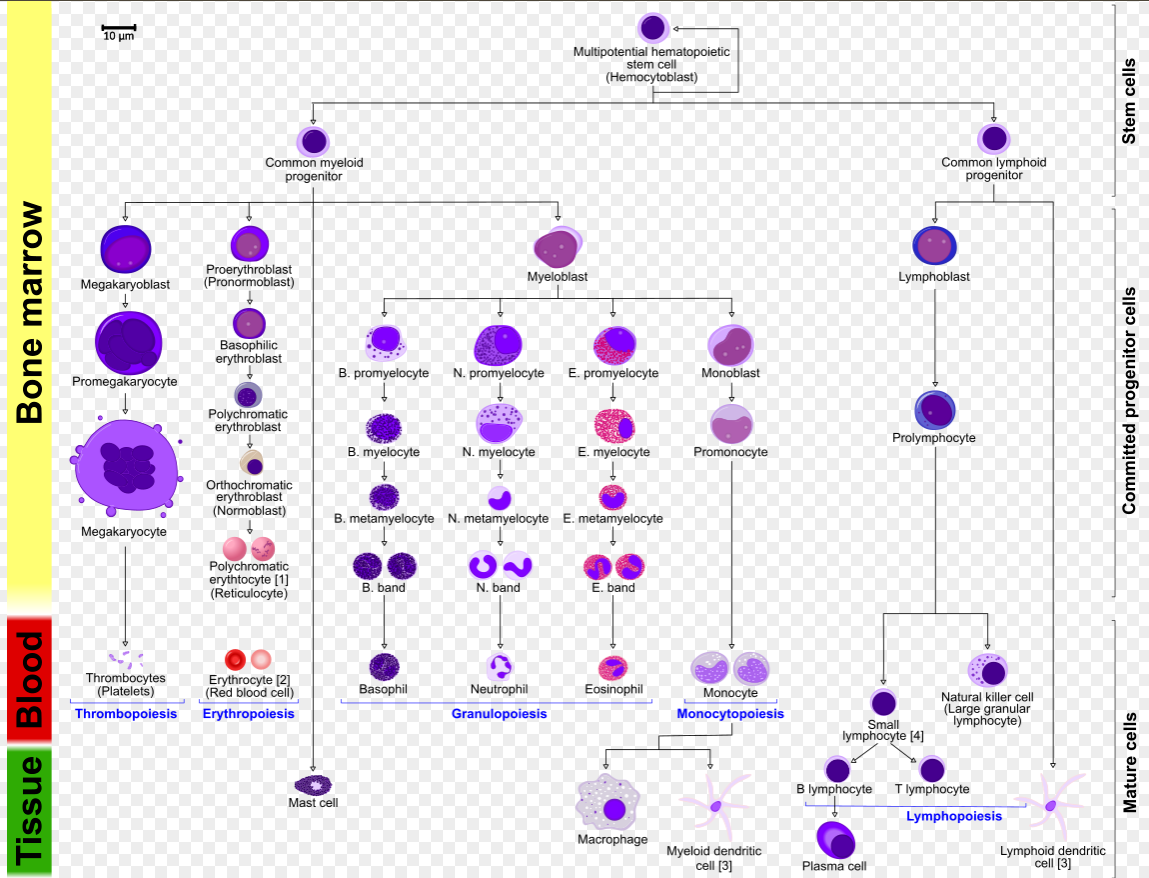
promyelocytes
5% of nuc’d cells in BM
size: 20 um
CP: deep blue, azurophilic granules, well developed golgi
NC: prominent nucleoli, occasionally indented, round-ovoid
cell div: yes
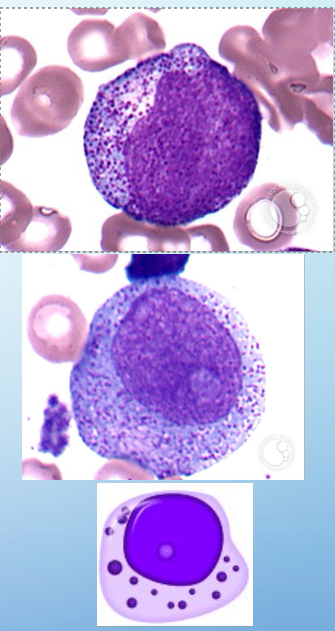
myelocytes
5-20% of nuc’d cells in BM
CP: specific granules, dec in basophilia
NC: ovoid, irregular shape, nucleoli disappear, dense/compact chromatin
cell div: yes
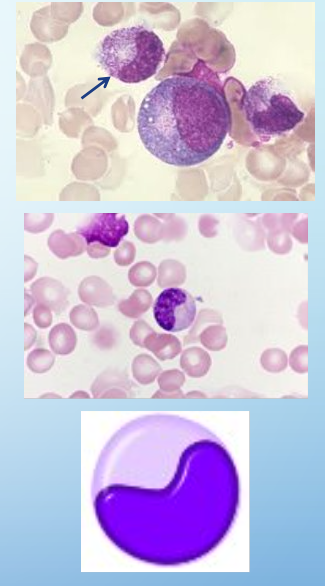
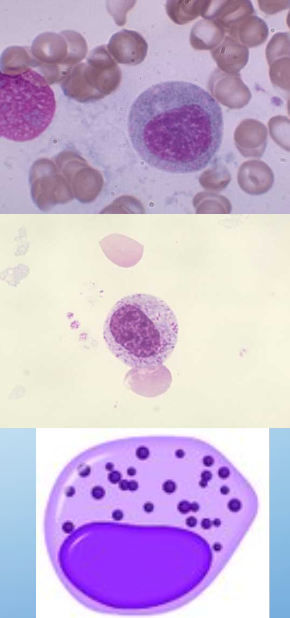
metamyelocytes
20% of nuc’d cells in BM
size: 10-18um (slightly larger than mature neutrophil)
CP: prominent secondary granules
NC: slightly indented, kidney-shaped (less than 50% indentation), dense chromatin, no nucleolus
cell div: NO
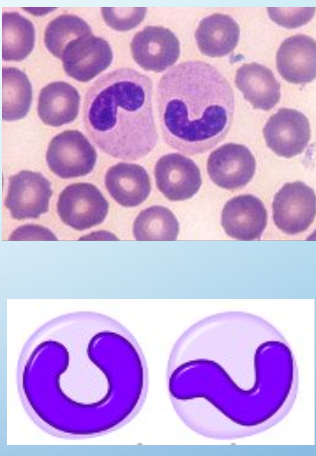
bands
NC: curved w no lobes (>50% indentation)
3-5% of wbc’s in adults
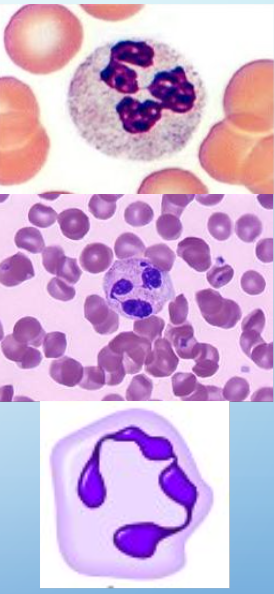
neutrophils
secondary granules stain neutral pink by H&E
bright red = eosinophil
dark blue = basophil
NC: 3-5 lobes
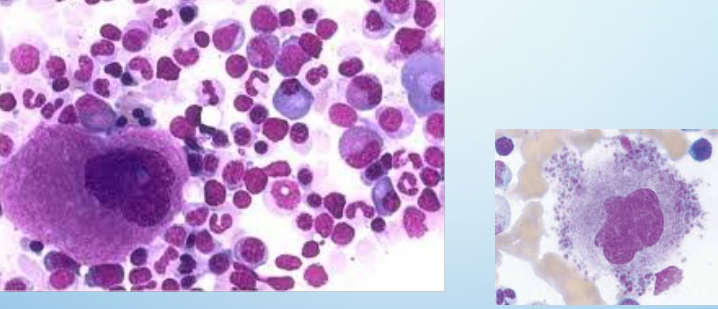
megakaryocytes
biggest cell in BM
produce plt
erythroids development
basophilic erythroblasts
polychromatophilic erythroblast
normoblast
reticulocyte (immature rbc released into bloodstream)
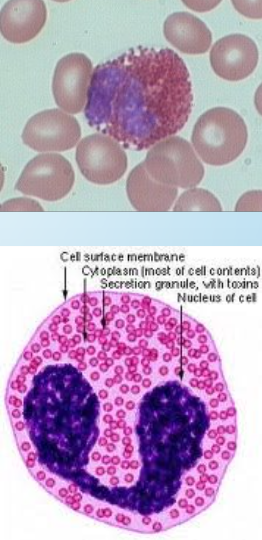
eosinophils
size: 12-15um
NC: 2-3 lobes
0-6%
large bright pink-orange granules
granule contains:
rhomboid crystals by EM
major basic protein which is toxic to some parasites
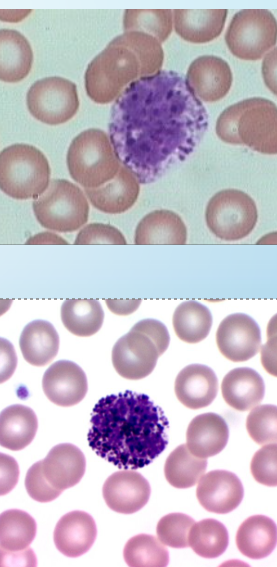
basophils
size: 12-15um
NC: 2-3 lobes
0.5-1%
purple-black, often large coarse irregular granules which may obscure the NC
granules contain:
heparin
histamine
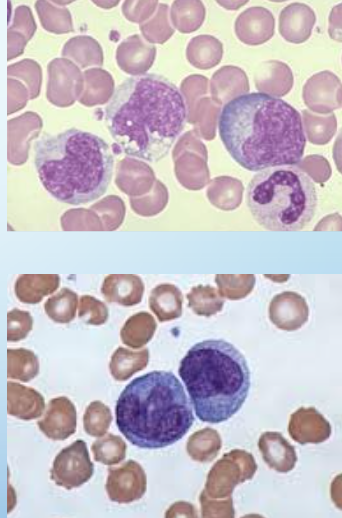
monocytes
largest cell in blood: 12-20um
NC: irregular, folded, or lobated w reticular chromatin
0-10%
abundant blue-gray, sometimes pale-pink CP
generally indistinct granules
CP vacuoles often seen
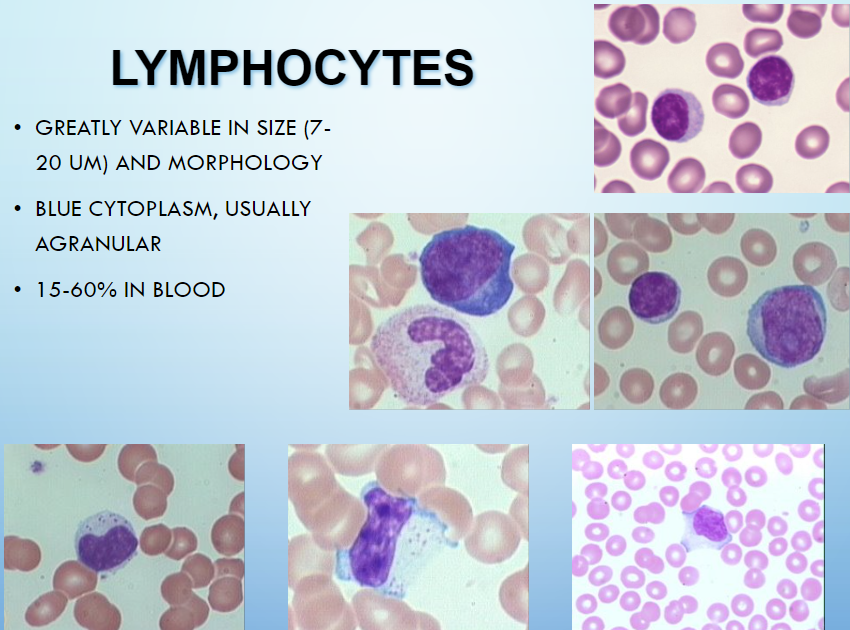
lymphocytes
greatly variable in size: 7-20um & morphology
blue CP, usually agranular
15-60% in blood
hugs rbc, thin rim of CP
plasma cells
in BM
eccentric NC
wbc normal counts (ANC - absolute neutrophil count)
ANC = (absolute polys + absolute bands)*1000
polys = seg neutrophils
normal >=1500 cells/mm3
mild neutropenia >= 1000-1499/mm3
moderate >=500-999/mm3
severe <500/mm3
rbc lifespan
120 days
plt lifespan
10 days
granulocyte lifespan
9 hours in circulation
days in tissue
lymphocyte lifespan
variable (hours to years) in circulation
weeks to years in tissues
rbc size variability = anisocytosis
mean cell volume (MCV) [fL/cell]
microcytes: MCV <80
iron-defic anemia
thalassemias
macrocytes: MCV >100
vit B12 or folate defic
liver dz
normocytic: MCV 80-100 (76-96)
rbc Hgb content
hypochromia = inc area of central pallor (>1/3 of diameter) directly due to dec amount of Hgb
iron-defic anemia
thalessemia
hyperchromia → spherocytes
rbc shape
poikilocytosis = various shapes
microcytic rbc
pyridoxine defic
thal
iron defic anemia
chronic dz anemia
sideroblastic anemia
macrocytic rbc
vit B12 or folate defic
liver dz
MDS
chemotherapy (methotrexate)
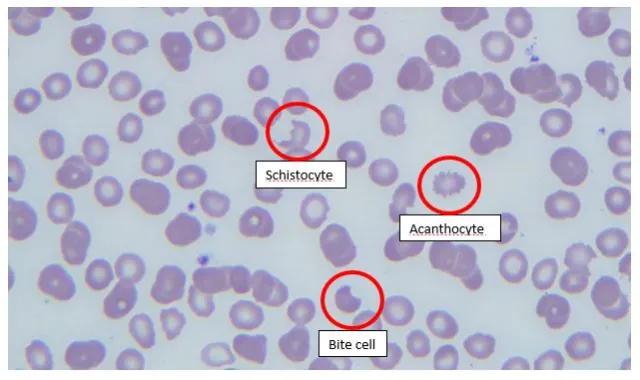
spurr cells rbc (acanthocyte)
abetalipoproteinemia
liver dz
McLeod blood group phenotype
post-splenectomy
etc
Burr cell rbc (echinocyte)
artificat
uremia
liver dz
etc
schistocyte
microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
mechanical valve induced
bite cell rbc
G6PD defic
unstable Hgb disorders
oxidative drugs
elliptocyte
hereditary elliptocytosis
severe iron defic anemia
spherocyte
hereditary spherocytosis
autoimmune hemolytic anemia
stomatocyte
hereditary stomatocytosis
liver dz
target cell rbc
thal
hemoglobinopathies
post-splenectomy
liver dz
artifact
sickle cell rbc
Hgb SS dz
Hgb SC dz
Hgb SD dz
S-beta thal
teardrop rbc
myelofibrosis
underlying marrow process/infiltrate
Hgb C crystals
Hgb C dz
Hgb SC dz
red cell agglutinate
cold autoimmune hemolytic anemia
paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria
IgM assoc’d lymphoma
multiple myeloma
rouleaux
chronic liver dz
malignant lymphoma
multiple myeloma
chronic inflammatory dz
caused by circulating abnormal proteins: monoclonal immunoglobulin/paraprotein in lymphoma/myeloma
marked hyperfibrinogenemia
reversible w dilution
do not affect automated CBC parameters
unlike rbc aggregates from immune phenomena
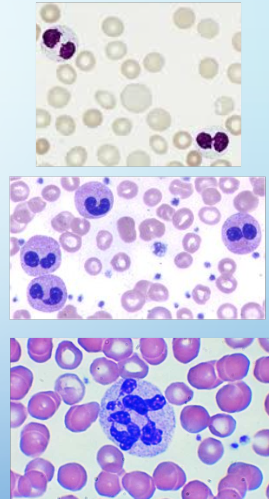
wbc abnormalities
Pelger-Huet nomality (autosomal dominant, all cells): bilobed or unilobed
Pseudo Pelger-Huet change (not all cells)
myeloid neoplasm (MDS, MPN, AML)
drug-induced
hypersegmented: >5
vit B12 or folate defic
myeloid neoplasm
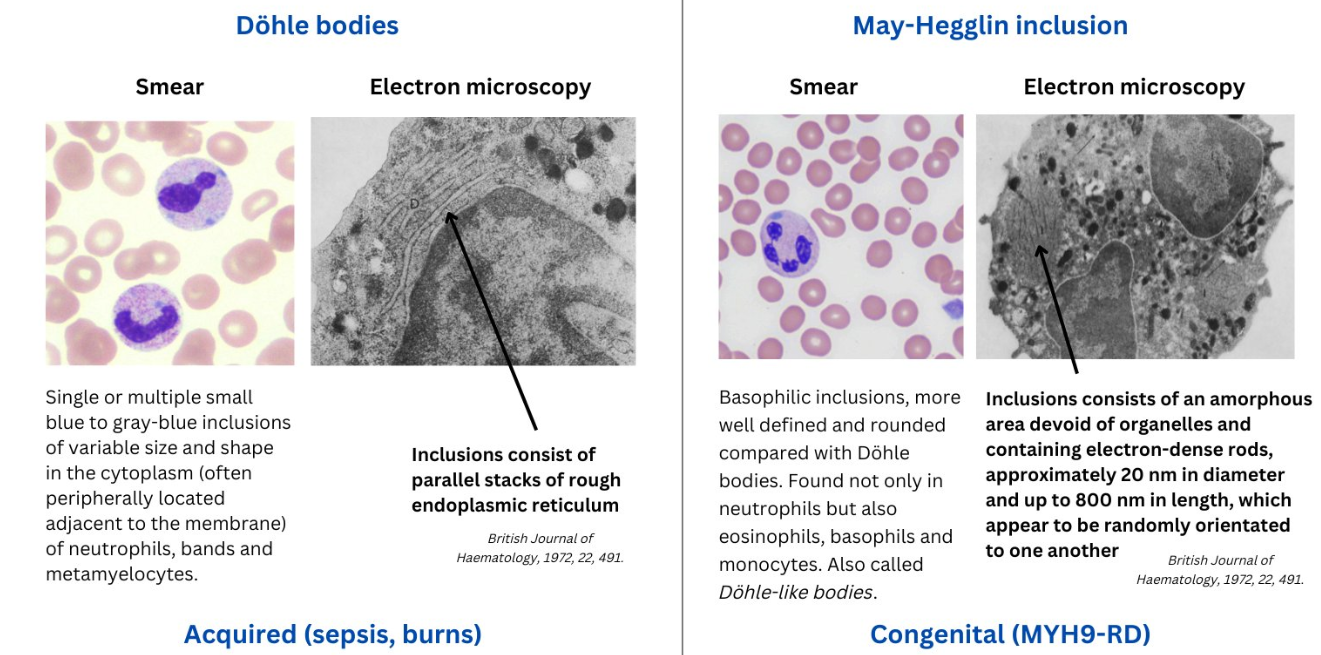
Dohle bodies
single or more blue CP inclusion
remnants of rough ER from earlier maturation stages
May-Hegglin anomaly: myosin heavy chain aggregates
associated w “left-shifts” & in conjunction w toxic granulation
abnormal granulation
toxic granulation: severe inflammatory states, azurophilic granules
degranulation: degeneration change, dysplasia
other: congential
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
May-Hegglin anomaly
Alder-Reilly anomaly
plt size
normal 2-3um
large >3 um
giant >RBC (7um)
plt satellitism & plt clumping
clumped around neutrophils (satellism only)
EDTA in-vitro induced artifact
no clinical signifance
falsely low plt countp