4.1 Cell Communication
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Cell Communication
cell-to-cell communication(signaling) is critical for the function and survival of cells
responsible for the growth and development of multicellular organisms
involves the transmission of signal from a sending cell to a receiving cell
cells communicate by direct contact and local or long distance signaling
Direct Contact
communication by cell-cell contact
2 types are direct channels of communication and cell-cell recognition
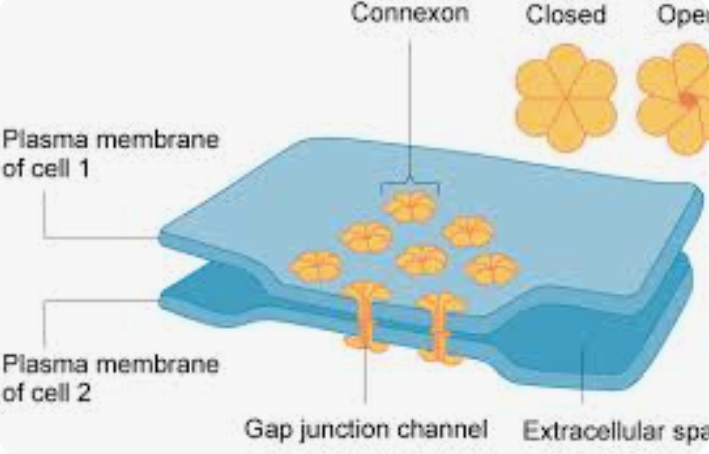
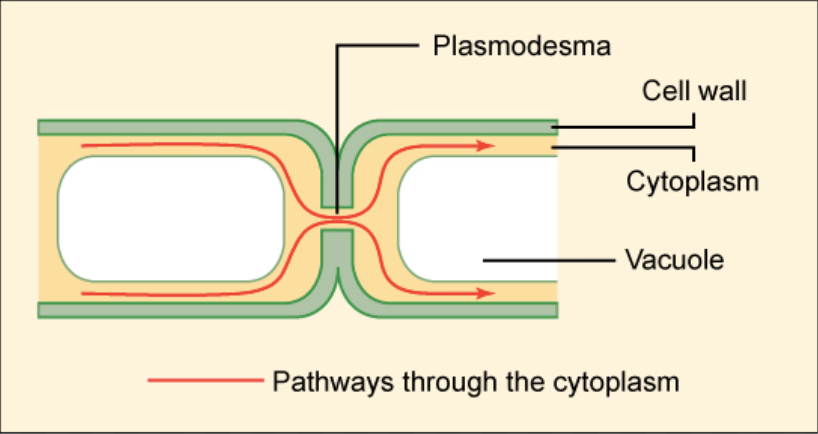
Direct channels of communication
signaling substances exchange directly between the cytoplasm of two adjacent cells via channels
animal cells: gap junctions
plants: plasmodesmata
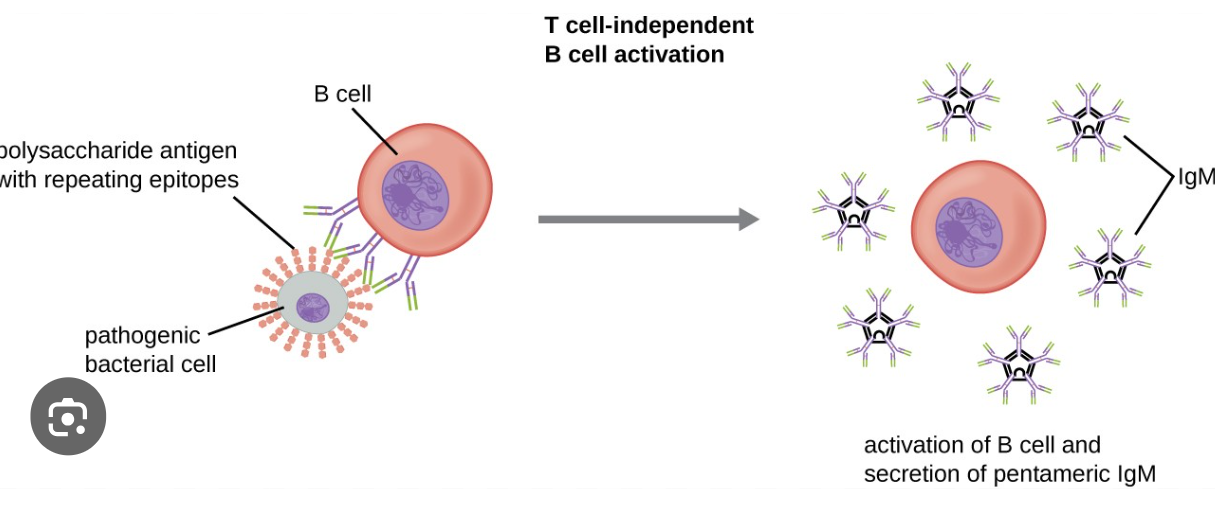
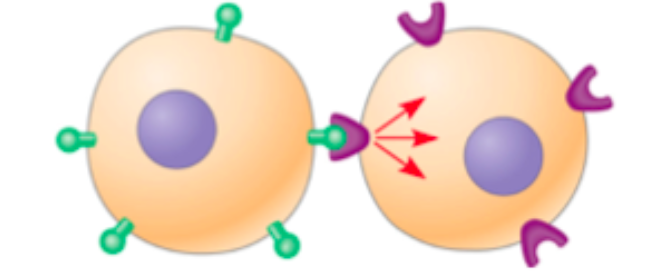
Cell-Cell recognition
complementary cell-surface molecules between adjacent cells can interact and bind to each other
ex. receptor/antigen interaction in immune system
Local Signaling
includes paracrine, synaptic, and autocrine signaling
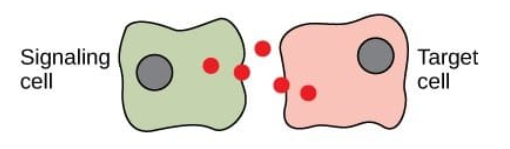
Paracrine signaling
a signaling cell will release chemical messages(local regulators/ligands) that travel a short distance through the extracellular fluid and cause a response in a nearby target cell
ex. when exposed to allergens, mast cells release histamine that signal for an inflammatory response in nearby cells
synaptic signaling is a special type of paracrine signaling
Synaptic signaling
occurs in animal nervous system (a special type of paracrine signaling)
neurons secrete neurotransmitters(signaling molecules) that diffuse across the synaptic gap/cleft (space between the nerve cells and the target cell) and bind to receptors, causing a chemical change inside the receiving cell
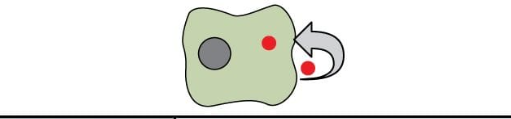
Autocrine signaling
a cell signals to itself
cell releases a ligand that binds to receptors on the same cell to initiate signaling
allows the cell to regulate itself through positive and/or negative feedback
ex. macrophage cells release cytokines that can signal to the macrophage itself to regulate activity
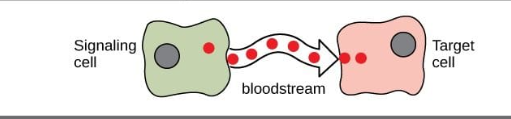
Long-Distance Signaling
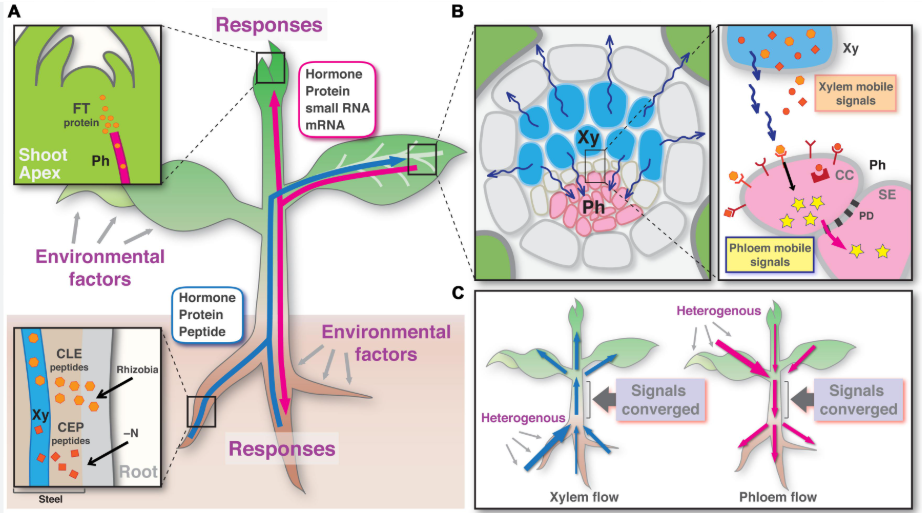
animals and plants use long-distance signaling molecules called hormones to produce a response in target cells that may be far from the signaling cell
plants release hormones that travel in the plant vascular tissue(xylem,water and phloem,food) or through the air to reach target tissues
animals use endocrine signaling-specialized cells release hormones into the circulatory system where they reach target cells ex. insulin
insulin is released by the pancreas into the bloodstream where it circulates through the body and binds to target cells