Lecture #4 | Chemical Causes of Cancer: Diet, Chemicals, and Biotransformation
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
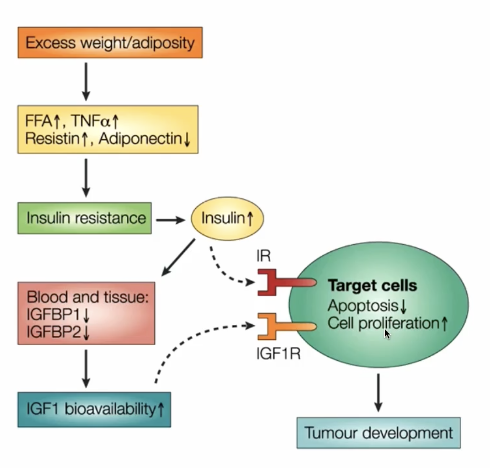
Mechanism #1: Fat may act a a tumor promoter
An excess of adipose tissue can cause an increase in FFA (free fatty acids), TNFa (tumor necrosis factor alpha), Resistin, decrease Adiponectin
Increases insulin causing insulin resistance, keeping blood glucose high
Excessive insulin increasing insulin-like-growth factor 1 causing a decrease in apoptosis and cell proliferation
Mechanism #2: Fat enhances free radicals via lipid peroxidation
Lipid peroxidation: poly unsaturated fats are more susceptible to free radicals damage due to double bonds
Chain reactions are created in which 1 free radical can oxidize 20-100 lipid molecules
free radicals damage DNA and lead to mutations
lipid radicals can also damage membranes and possibly affect signal transduction → tumor promoter
produces malondialdehyde which reacts with DNA
Palmitic acid
Lipid that is C16:0 (0 double bonds)
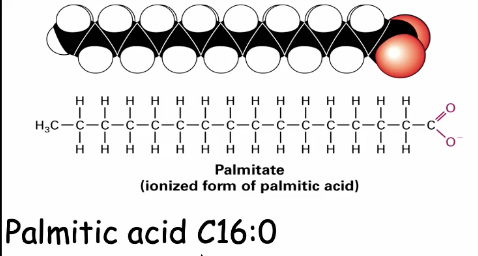
This is a saturated fat
Oleic Acid C18:1

Monounsaturated fatty acid
Linolic Acid C18:2
Polyunsaturated
essential fatty acids
Makes up cell membranes
More prone to being
Mechanism of lipid peroxidation
If the chain comes in contact with a carbon radical, it becomes rearranged
This causes a molecular rearrangement
This causes oxygen uptake
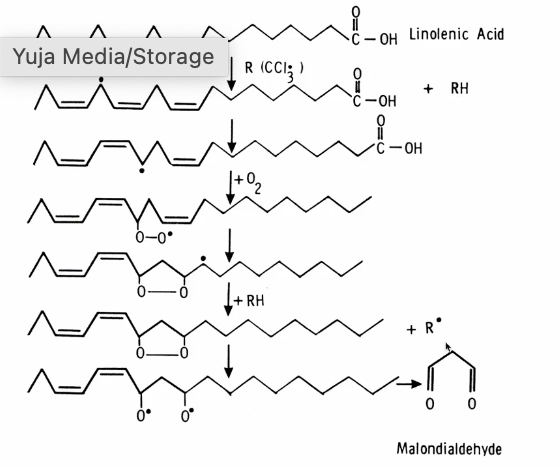
The result can degrade
known malondialdehyde
Malondialdehyde (MDA)
Mutagen and carcinogenic compound
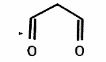
at pH 7.0, reacts with deoxyguanoside to produce M1G-deoxyriobose
Acts as a DNA adduct causing issues with transcription → mutations
5400 adducts per cell → same level of external carcinogen
Fiber correlation to cancer
Americans are consuming too little fiber
low fiber is associated with a high risk of colon cancer
Cannot be digested by enzymes in our gut
Theories on how fiber decreases colon cancer
Insoluable fiber
decreases stool transit time
increases mass of the stool
changes the composition of the bacteria in the gut
changes in gut microbiota are associated with colon cancer
Fruits and Vegetables
Americans eating too few fruits and vegetables
low intake are associated wit a risk of colon, breast, prostate, and other cancers
rich in fibers
induce some detoxification enzymes
anti-oxidants
Vitamin A
Retinol, fat soluble, converted from B carotene in orange yellow and dark leafy veggies
anti-oxidants
can be stored in body
Vitamin E
Alpha-tocopherol, fat soluble, in olive oil
protects lipids from peroxidation
can be stored in body
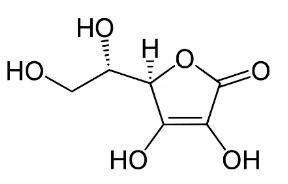
Vitamin C
l0ascorbic acid, water soluble, in citrus, good at inhibiting formation of nitrosamines
will be removed
Synthetic anti-oxidants
Preservatives added to meat and other foods to prevent color and flavor change
thought to protect against chemcially induced cancer in animals
HOWEVER: at high doses it promotes cancer in animals
BHA: Butylated hydroxyanisole
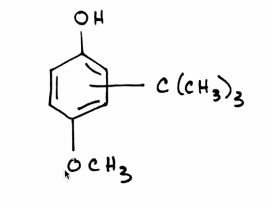
Synthetic antioxidant
BHT: butylated hydroxytoluene
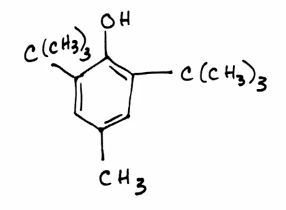
Synthetic antioxidant
How does nitrosamines increase cancer
Intake of red meat is associated with increased colon cancer
has high levels of nitrosamines due to preservatives and fertilizers
Very mutagenic
need to be metabolically activated
Mechanism that converts Nitrates to Nitrosamines
Nitrate is converted by micororganisms in the soil and our gut into nitrate
Nitrate reacts with secondary amines in acidic environments to produce nitrosamines
Secondary Amines
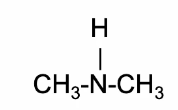
NDMA
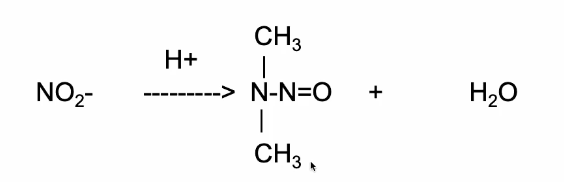
How are nitrosamines activated?
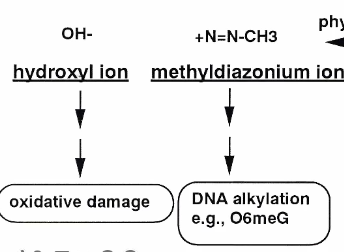
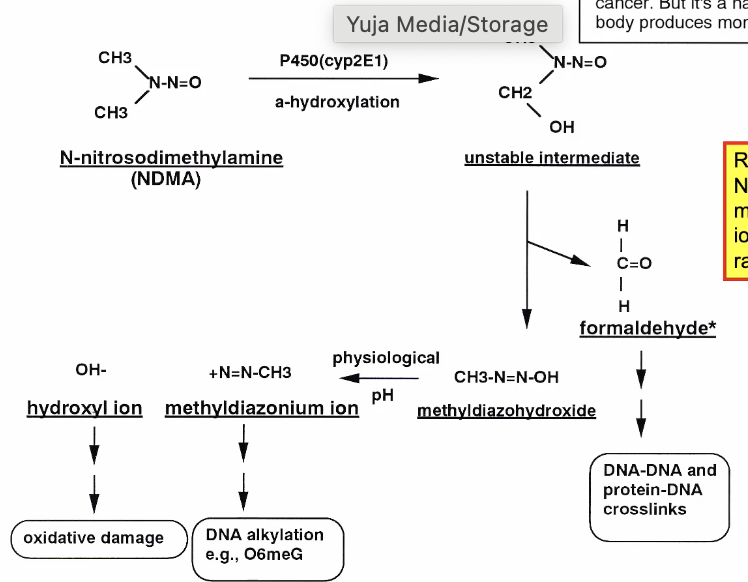
Alkylation of the DNA via methyldiazoniom ion
Adds on a -CH3 group
Crosslinking via formaldehyde
Metabolism of NDMA
Reagent: NDMA
Product: Hydroxyl ion and methyldiazonium ion

Other than smoking and diet, what is the next most important environmental factor
Chemicals
11% of causes
What is the first recorded link between chemicals and cancer in an occupational setting?
Chimney sweeps in 1775
recommendation to bathe right after
Occupational exposure
Repeated, high dose exposure that induce significant rates of cancer
associated with specific occupations
lower doses may also affect certain susceptible members of the general population, but it is more difficult to see the correlations with lower doses
How many chemical compounds are human carcinogens
256 (2021 data) chemical compounds are known or anticipated to be human carcinogens
63 known human carcinogens
193 reasonably anticipated human carcinogen
New:
Helicobacter: bacterium known for stomach cancer
Antimony trioxide: synergist for flame retardants
6 halo acetic acids: byproduct of disinfectants
Xenobiotics
Foreign (xeno) compounds that affect organisms
synthetic or natural (plants)
things that u eat or are otherwise exposed to
can be both water soluble or lipophilic
Nonpolar lipophilic are of greatest concern because they can easily get passed cell membrane
Major routes of absorption for xenobiotics
Skin, lung, and gut
What happens when a xenobiotic enters the body
Depends on the chemical structure and its initial site of absorption
Liver is the major detoxification organ
all ingested compounds go from the intestines to the liver via total vein
Metabolism of xenobiotics
Carried out primarily in the liver
also in kidney, lungs, and intestines
somewhat in skin, testes, placenta, and adrenals
How does xenobiotic detoxification vary based on chemical structure?
Polar/volatile compounds: Not changes → directly excreted
Nonpolar compounds → metabolized → makes them more water soluble
Goal is to detoxify and excrete compounds BUT sometimes intermediates are formed to make carcinogens
Primary types of biotransformation
Phase 1 reactions
Phase 2 reactions
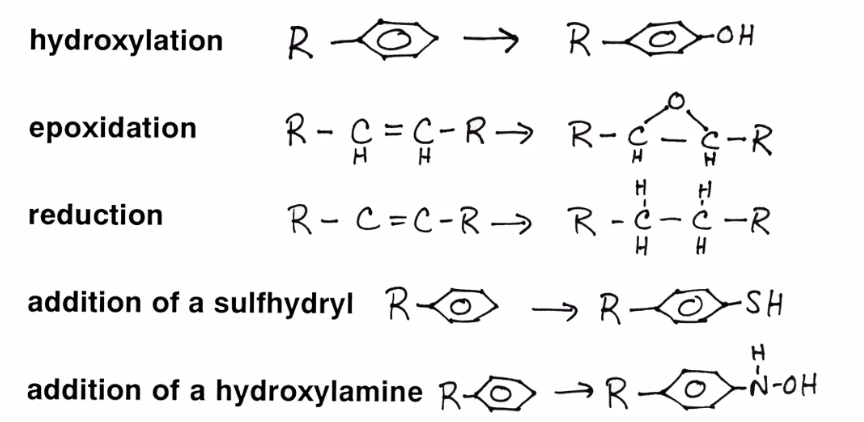
Phase 1
Expose a reactive polar functional group in lipophilic compounds
add a chemical handle to make it more portal
hydroxylation
epoxidation
reduction
addition of a sulhydridyl
addition of hydroxyl amines
Cytochrome p450 enzymes (mixed functional oxidases)
Enzymes that primarily carry out phase 1 reactions
superfamily of enzymes
all contain a cytochrome that absorbs light
present in all organisms from bacteria to man
ex: CYP3A metabolizes most dugs but grapefruit inhibits activity
Act on endogenous and exogenous substates
Regulates endogenous compound like steroids
removes exogenous compounds derived from other species
Constitutive and inducible
constitutively expressed in the liver
some are induced by the compound they act on or foods or antibiotics
Acts on many different substrates
Activity can’t be eliminated
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
Classical example of compounds that require metabolic activation by P450 enzymes
highly mutagenic compounds
must be metabolically activated
found in:
Coal tar
grilled and charcoal broiled meats
Benzo[a]pyrene
Best studied PAH
cigarette smoke, exhaust, charbroiled meat
HAS to be metabolized first by p450
Aromatic amino acids are converted to PAHs at high heat
Idole ring (Trp, Pro) inhibits the formation of PAH
Grains soy protein and pectin decrease the mutagen formation in hamburgers
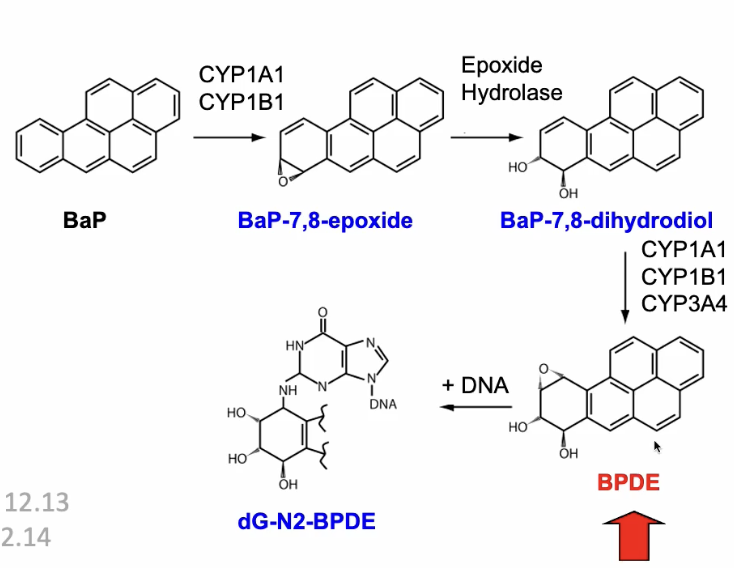
Metabolism of BAP
BaP is acted on by the P450 family members
Adds an oxygen and converts BaP-7,8-epoxide
Breaks up to a diol
Forms a BPDE (mutagenic)
Creates an adduct which interacts with DNA, allowing for more mutations