particles and radiation
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
What is the diameter of a nucleus?
1 femtometre
What is the diameter of an atom
10^-10 m
What is the charge of a proton?
+1.6x10^-19C
What is the charge of an electron? (e)
-1.6 x 10^-19 C
What is the mass of a proton and neutron? (u)
1.67 x 10^-27kg
What is the mass of an electron?
9.11 x 10^-31 kg
What is the value of a unified mass unit?
u
What is an isotope?
A variety of an element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
what physical properties do isotopes have?
Slightly different physical properties to the abundant element
What is the specific charge?
Charge per unit mass
What does specific mean?
per kg
What is the specific charge of an electron?
-1.76 x 10^11 Ckg^-1
What is the specific charge of a proton?
9.58 x 10^7 Ckg^-1
what are the four fundamental forces?
gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, weak nuclear
when does the maximum attraction of the strong nuclear force occur?
at 1.0 fm
what two things does the snf do?
provides an attractive force between nucleons with a range of about 3.0 fm
overcomes the repulsive electrostatic force exerted by positively charge protons on each other
at distances less that 0.5fm is the snf attractive or repulsive?
repulsive
at distances more that 0.5fm is the snf attractive or repulsive?
attractive
at what distance does the snf become insignificant?
3.0 fm
what does the snf work between?
all three combinations of nuclear particles
what does the electrostatic force do?
causes repulsion between protons
at what distance does the ef cause repulsion?
above 0.5fm
at what distance does is the snf larger than the ef? what does this cause the protons to do?
around 1.0fm (so protons attract)
at what distance does is the ef larger than the snf? what does this cause the protons to do?
above 3.0fm (so protons repel)
When does alpha radiation occur?
when the nucleus is very large
when does beta plus decay occur?
When a nucleus has too many protons
When does beta minus decay occur?
When the nucleus has too many neutrons
What is a alpha particle?
a helium nucleus
what does a Beta minus particle consist of?
a fast moving electron
what does a Beta plus particle consist of?
a fast moving positron
what does the neutron decay into after beta minus decay
a proton and electron
other than an electron what other particle is emitted after beta- decay
an antineutrino
how does the proton number change after beta- decay
proton number increases by 1
what does the proton decay into after beta+ decay?
a neutron and W+ boson
other than a positron what else is emitted in beta+ decay?
a neutrino
how does the proton number change after beta+ decay?
proton number decreases by 1
what is gamma radiation?
EM radiation emitted from an unstable nucleus
when does gamma radiation occur? why?
Straight after alpha or beta decay. The child nuclide formed often has excess energy (release as gamma)
properties of neutrinos
very difficult to detect
nearly zero mass and no charge
barely interact with matter
what does beta decay from a particular nuclide produce?
a constant amount of energy
what has to happen because beta particles emerge with a range of kinetic energy?
a neutrino must be emitted with the remaining kinetic energy
what is EM radiation?
radiation emitted by charged particles that are losing energy
what does EM radiation consist of?
two linked electric and magnetic fields that are both at right angles to each other and are in phase
what is the equation for wave speed?
frequency x wavelength
How is EM radiation emitted?
as short bursts of waves, each burst leaving the source in a different direction
what is a photon
a packet of waves
state the the equation linking photon energy and frequency
Photon energy = planck constant x frequency
state the equation linking photon energy, wavelength and wavespeed
photon energy = hc/wavelength
what is the value of planck’s constant
6.63×10^-34
what is the wavelength of a radio wave?
>0.1mm
what is the wavelength of microwave
0.1m - 1mm
what is the wavelength of infrared rays?
1-700mm
what is the wavelength of visible light
700mm - 400nm
what is the wavelength of ultraviolet?
400nm-1nm
what is the wavelength of x-rays
10nm—0.001nm
what is the wavelength of gamma rays
<1nm
what is a hypothesis?
A statement that links the independent and dependent variable
give two examples of a charged particle losing energy
a fast-moving electron is stopped or slowed down or changes direction
an electron in a shell of an atom moves to a different shell of lower energy
what is the einstein equation?
E = mc²
what is 1 electron volt equal to in joules
1.6 × 10^-19 J
what is an electron volt
the energy required to move an electron through the p.d of one volt
Properties of antimatter
same rest mass
opposite charge
3 examples of antimatter
antiproton, positron, antineutron
what is annihilation
when a particle and its corresponding antiparticle collide and as a result their masses are converted into energy. This energy as well as the kinetic energy is carried away by photons of equal frequency travelling in different directions in order to conserve momentum
what is pair production
when the rest energy of a photon is higher than the total rest energy of the particle and antiparticle being created. It usually occurs when the photon travels near a heavy nucleus (sudden change in environment)
what is the electromagnetic force?
a repulsive and attractive force that involves an exchange of virtual photons between charged particles
what is the weak nuclear force?
the force responsible for particle decay, it Is only significant in unstable nuclei.
what is the mass of a virtual photon?
zero
what is the charge of a photon?
zero
what is the range of the electromagnetic force?
infinite
what is the range of gravity?
infinite
what is the range of the weak force?
1 am
what is the relative strength of the EM force?
1
what is the relative strength of gravity?
10^-36
what is the relative strength of the snf?
100
what is the relative strength of the weak force?
10^-3
what is the exchange particle for EM?
virtual photons
what is the exchange particle for gravity?
graviton (undiscovered)
what are the exchange particle for the snf?
gluons and pions
what is the exchange particle for the weak force?
w and z bosons
the smaller the mass of the exchange particle the _____ it travels
further
how long does it take for a virtual photon to be exchanged
10^-18 s
how long does it take for a gluon/pion to be exchanged
10^-23 s
how long does it take for a w boson to be exchanged
10^-10s or longer
what is a feymann diagram
a diagram used to illistrate the interactions between sub atomic particles
do the lines on a FD represent the paths of the particles?
no
what are virtual photons exchanged by?
a wave
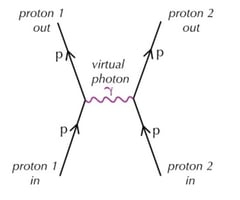
what interaction is this?
proton pair interaction
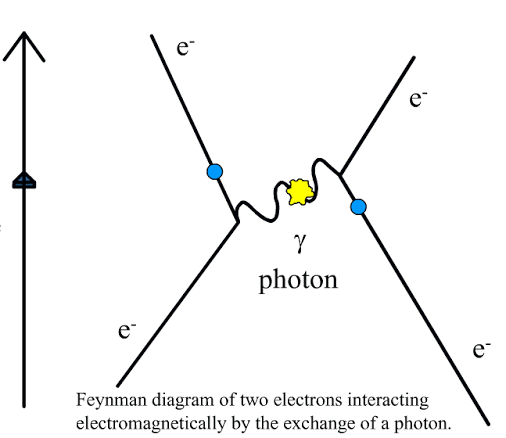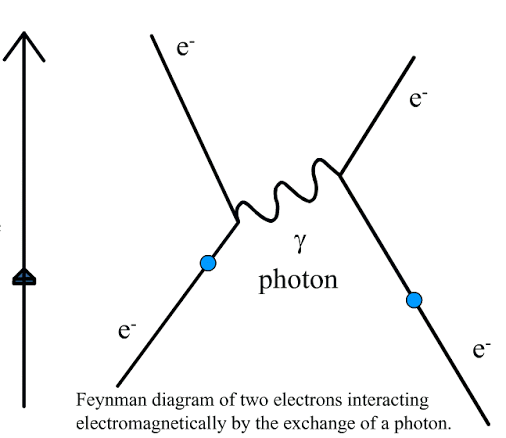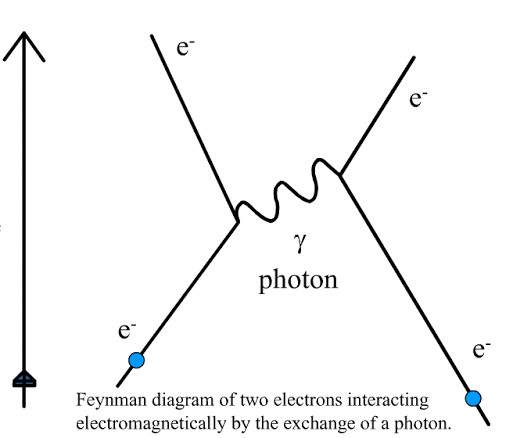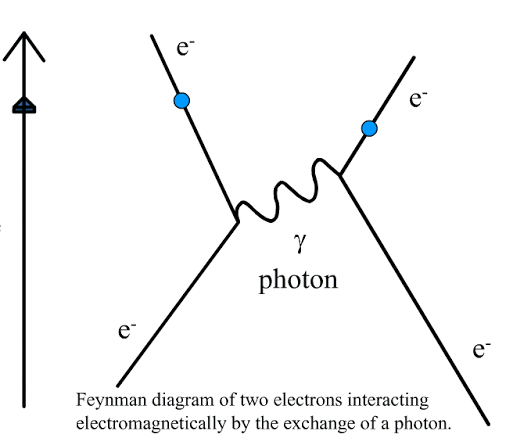
what interaction is this?
electron pair interaction
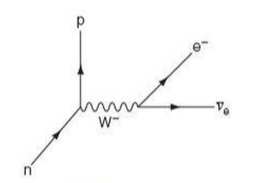
what interaction is this?
beta minus decay
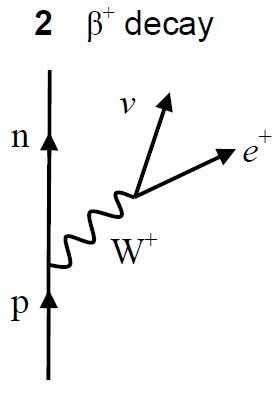
what interaction is this?
beta plus decay

what interaction is this?
electron capture
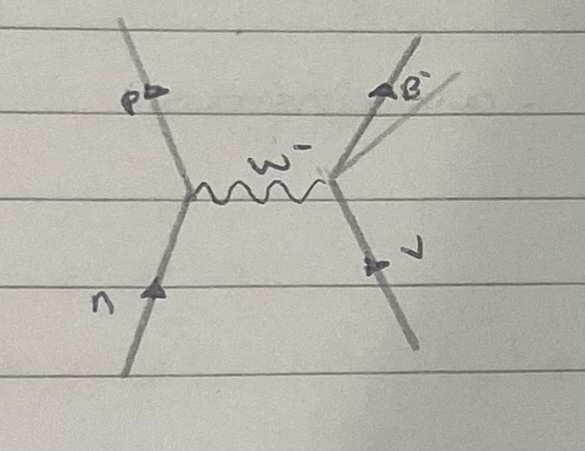
what interaction is this?
neutron and antineutrino interaction
what is the equation for proton antineutrino interaction with the exchange particle
p + v- → n + e (w+ boson involved)
what is the equation for a proton electron interaction (with exchange particle)
p + e → n + v (w- boson involved)
what is electron capture
when a proton from a very large nucleus attracts an electron from the inner shell into the nucleus
is charge conserved in neutron neutrino interaction?
yes
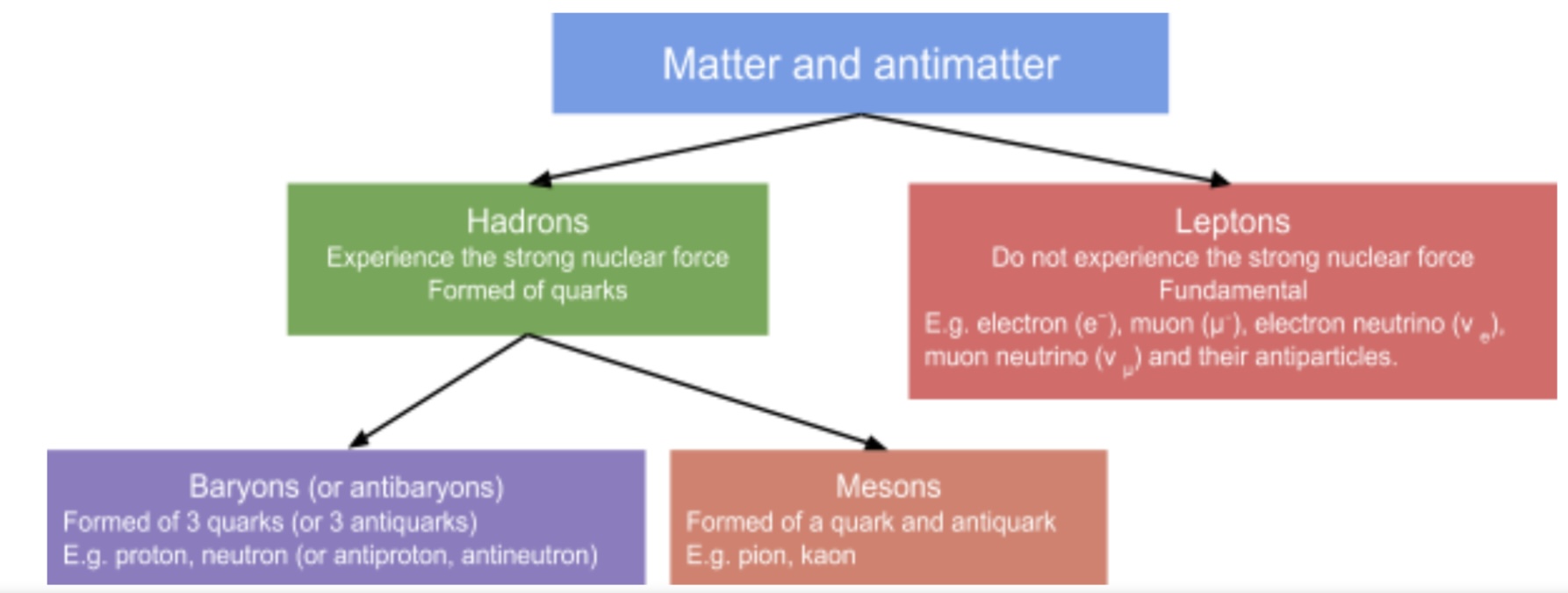
what is this?
the particle zoo
hadrons interact via…
the strong force
hadrons are made up of…
quarks