Treatment Options for Wounds in Small Animals
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what is surgical wound debridement
remove biofilm and devitalised tissue
what is mechanical wound debridement
-irrigation
-wet to dry dressing
-negative pressure wound therapy
what is autolytic wound debridement
-body's own enzymes beneath a dressing to liquefy tissues
-hydrocolloids, hydrogels, honey, foam, etc
what is enzymatic wound debridement
prescribed topical agent that chemical liquifies necrotic tissues with enzymes
what is biological wound debridement
-maggots
-luilia sericata (green bottle fly)
surgical wound debridement steps
-remove devitalised (necrotic, infected) tissue
-scrape outer surface of granulation (chronic granulation)
-preserve vital structures
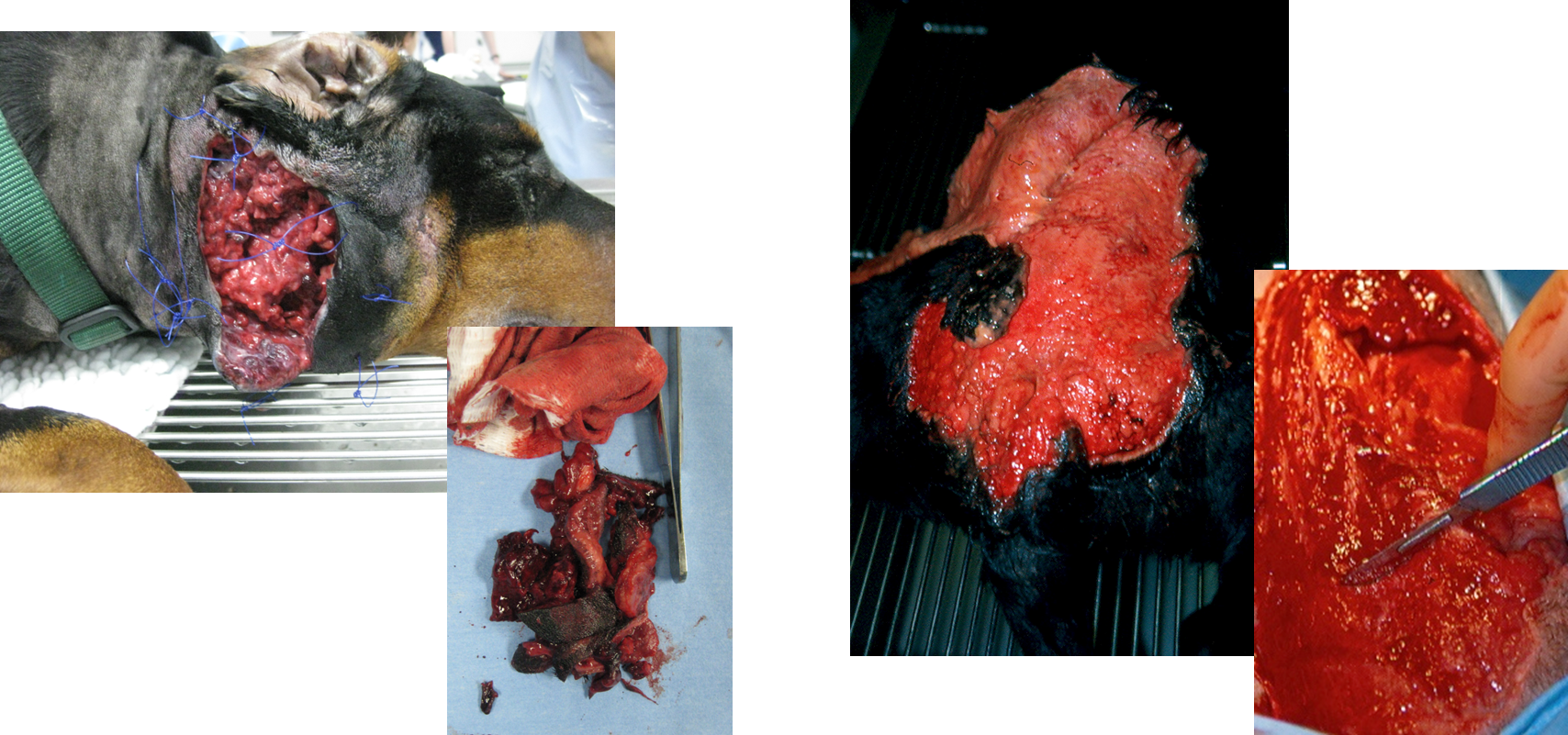
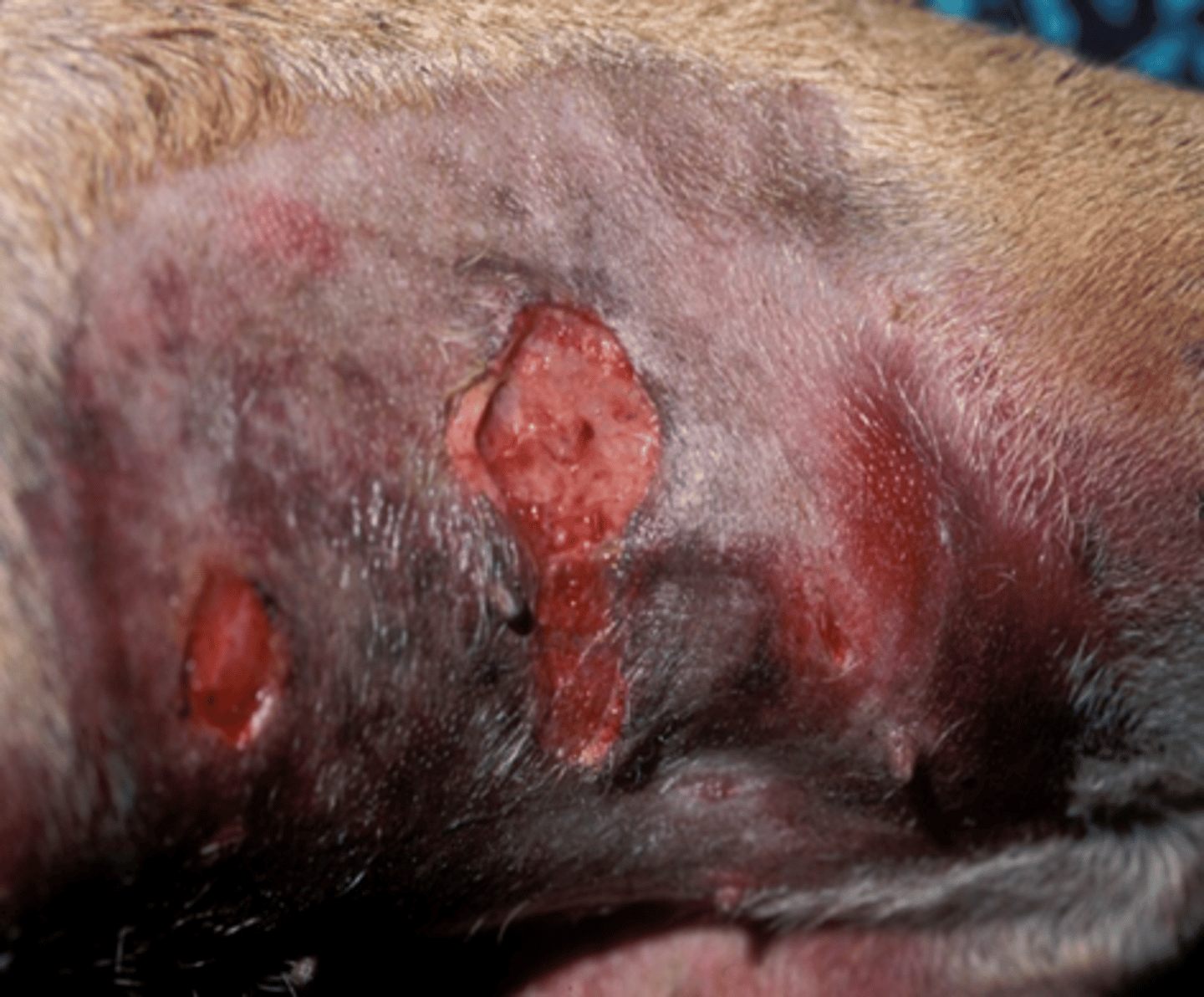
what is chronic granulation tissue
wound gets stuck at this stage so need to scrape the outer surface of granulation tissue away -> then can go onto heal
how do you lavage debride a wound
lactated ringers (hartmanns)
0.9% saline can be used
fluid at body temp
why is hartmanns used for debridement
ideal pH and compatible with tissue
how much fluid should be used for lavage debridement on new wounds
high volume
what syringe and needle is used for lavage debridement
-20-35ml syringe
-18G needle=7-8 psi
when should wet to dry debridement dressing be changed
-change every 24 hours
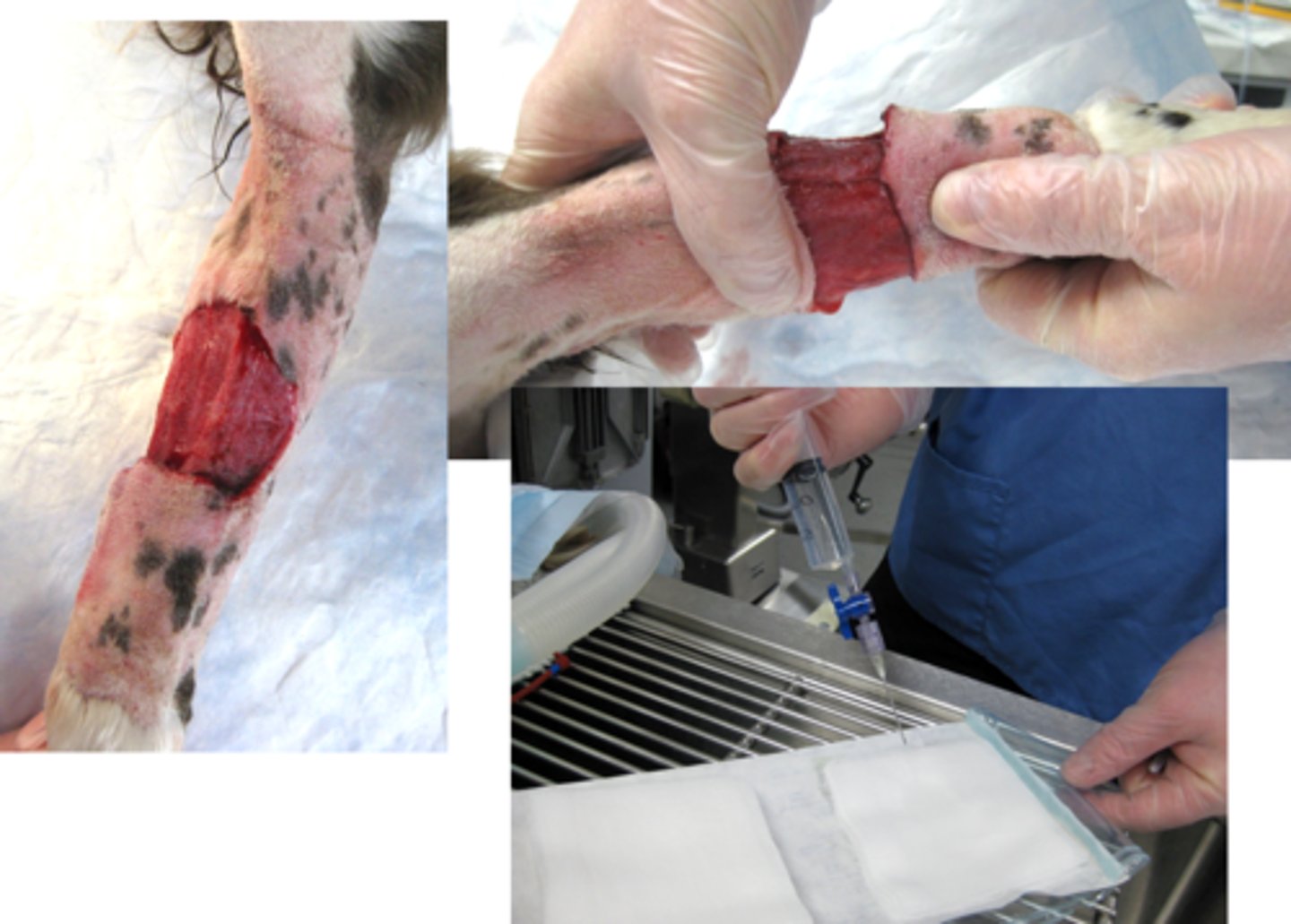
when can wet to dry debridement be used
-used on chronic granulation
Can then manage the healthy granulation bed after this
why do we debride wounds
Remove particulate matter and lower bact load
Getting the wound into a healthier state for wound closure or dressing
what do we have to be careful of when debriding wounds
we are trying to push out and move away, not push things into the wound
how do you apply wet to dry dressing
Take sterile swabs and soak in isotonic crystalloid solution (hartmanns)
Wring them out so arent dripping wet
Place directly onto wound
Place dry swabs on top
Conforming layer
Vet wrap/ bandage layer
how often are wet to dry dressing changed
Changed every 24hrs
how does topical negative wound therapy work
when turned on, pump gently reduces air pressure beneath dressing, drawing off exudate and reducing oedema in surrounding tissue
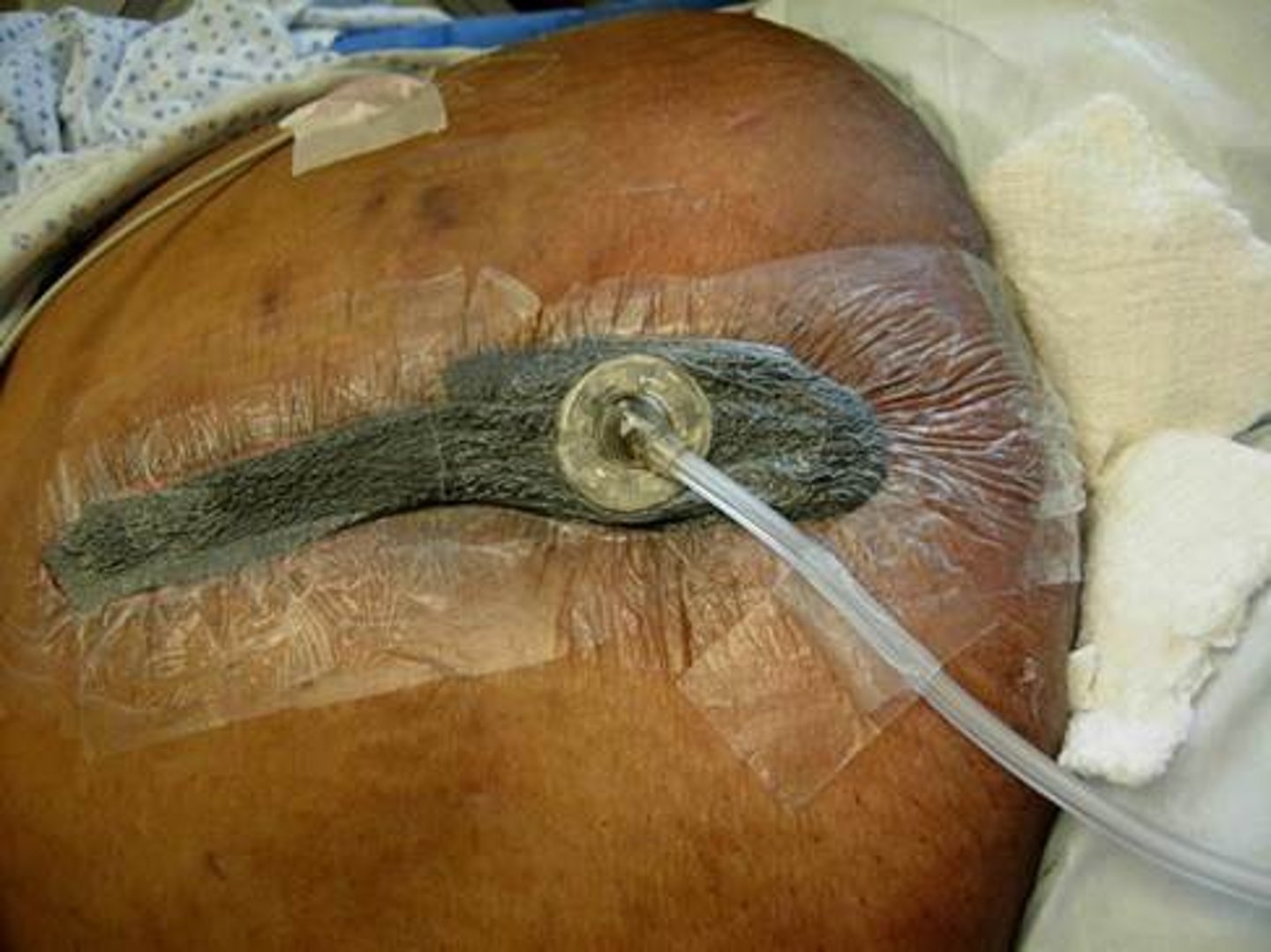
why topical negative pressure wound therapy
-reduces bacterial colonisation
-promotes granulation tissue development
-increases rate of cell mitosis
-spurs migration of epithelial cells within wound
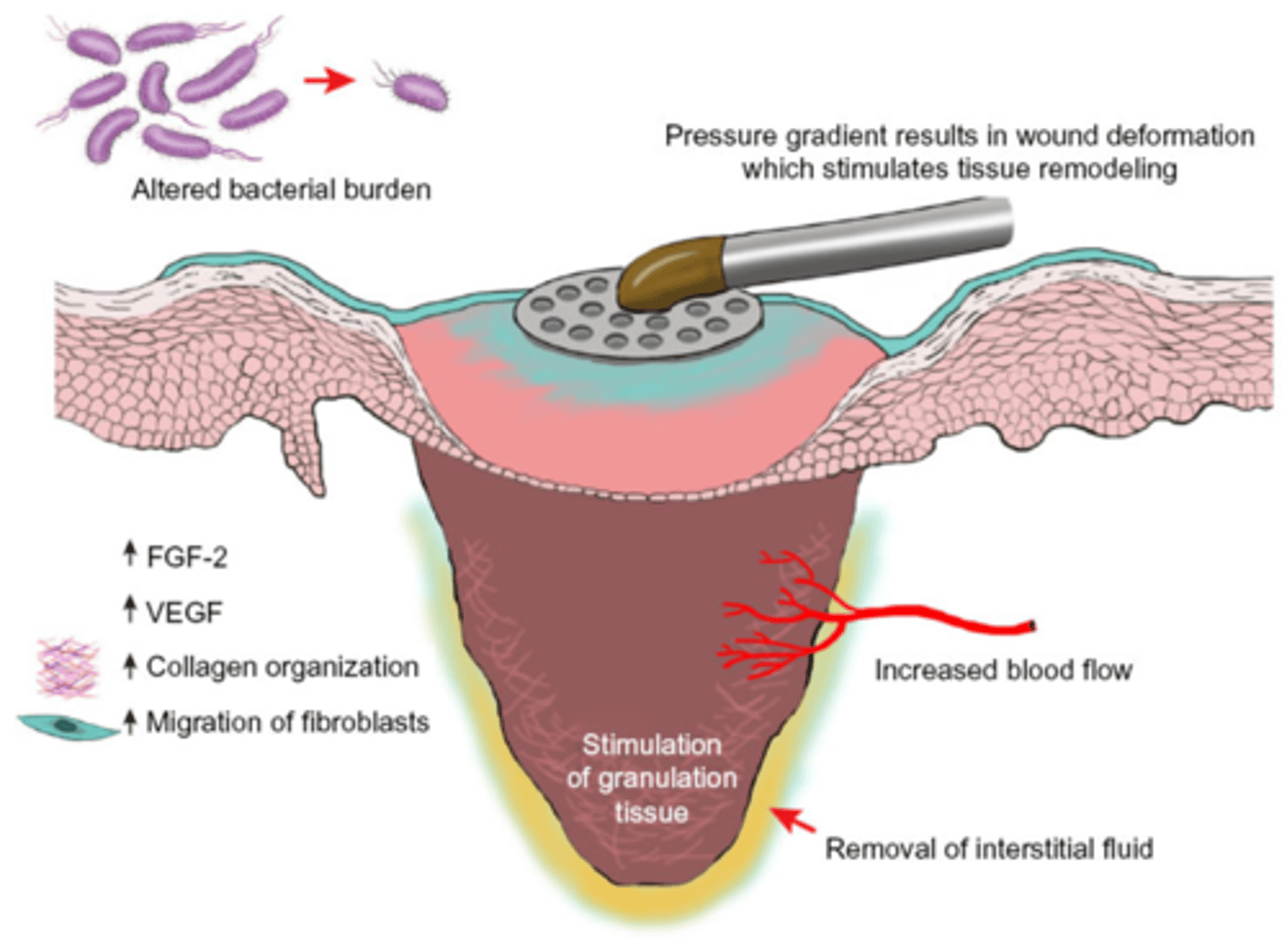
what else is needed for topical negative pressure wound therapy
waterproof airtight coating around outside
honey for debridement
-antibacterial
-healing stimulating
-debriding
-anti inflam
-odour reducing
-reduction in wound pain
-osomotic effect
how does honey have healing stimulating properties
r•eduction in wound size, healing time, complete healing, stimulation of granulation tissue and epithelialisation
how does honey debride wounds
•Low pH (approx. 3.7)
•Osmotic effect
•Both help draw up fluid from the wound area → debride at same time
how does honey have antimicrobial agents
Hydrogen peroxide (due to glucose oxidase)
Anti-oxidant (due to flavonoids)
High sugar content (so gives osmotic effect)
Acidic (pH 3.2 - 4.5)
Methylglyoxal (Manuka honey)
It’s potency as an antimicrobial can be measured by the Unique Manuka Factor® (UMF®)
+15 will ensure potent antimicrobial properties over and above those of standard honey
can regular/ table honey be used
Might not be sterile (e.g., Clostridium)
High sugar content (osmotic effect)
Acidic (pH 3.2 - 4.5)
The production process might have an adverse effect the activities of
Hydrogen peroxide (glucose oxidase)
Anti-oxidant (flavonoids)
so may grow other bacts
how long is topical negative pressure wound therapy left in for
Left insitu for 48-72hrs before needing to be change
what does a higher methylglyoxal amount in manuka honey mean
higher its unique manuka factor
So has higher antimicrobial factor
what is biological debridement
using maggots
speed to effect of debridement methods (fastest to slowest)
-scraping with scalpel
-maggots
-negative pressure wound therapy or wet to dry dressing
-flushing with hartmanns
-amorphous hydrogel or honey or foam dressing
expense of debridement treatment (most expensive to least)
-negative pressure wound therapy
-maggots
-amorphous hydrogel or honey or foam dressing
-flushing with hartmanns or wet to dry dressing
-scraping with scalpel
what are the best methods of debridement
scraping with scalpel blade
wet to dry dressing
what are the negatives of using maggots to debride
Don’t recognise healthy from unhealthy tissue
Can go off the wound
Not nice to look at