Gram Positive Bacterial Infection
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is characteristic of staphylococcus spp
Part of human flora; difficult to treat; can become abx resistant easily; cause disease by toxin production or penetration; food poisoning
What are extracellular toxins example
TSST, haemolysin etc
What is TSST
Superantigen
What are enterotoxin
heat stable toxin that cause food poisoning
Catalase function
HO → H2O + O2
What is catalase test used for
Diff staphylococci (POSITIVE) from streptococci (NEGATIVE)
What is staphylococci pathology
Adhere to damaged skin, cell wall proteins attach to tissue, protein A teichoic acid peptidoglycan etc interfere with opsonization
What are the clinical findings of staphylococcal infections
Local = pimple, hair follicle infection, abscess; food poisoning has short incubation period and NO FEVER; TSST has high fever, rash, vomiting and diarrhea
What are tests used to diag staph infections
Specimen, catalase test (positive), coagulase test (negative except for staph. aureus), novobiocin testing
What is characteristic of staph. aureus
Facultative anaerobe, grape like; beta-hemolytic; cause of pimples, sinusitis, food poisoning; opportunistic; drug resistant
Staph aureus uses what type of agar and what is the result
Mannitol salt agar which turns yellow
What is association of staph. aureus and TSST
Some staph strains can cause septic shock and release TSST into blood
What is staph. epidermidis
Commensal bacterium in skin and mucous membrane; non-hemolytic; nosocomial pathogen in biomaterials; form biofilms
Which staph form biofilm
staph. epidermidis
What agar is used for staph. epidermidis and what is the result
White blood agar; novobiocin sensitive
What are skin signs of staph. epidermidis
Impetigo (honey colored crust), cellulitis
What is staph. saprophyticus
Negative coagulase; novobiocin resistant; part of human flora; cause uncomplicated UTI; colonize bladder and ureter epithelium
What agar is used for staph. saprophyticus and what is the result
Bright white to creamy blood agar; novobiocin resistant
What is streptococcus spp
Chains or pairs, facultative anaerobes, catalase NEGATIVE; major normal flora in mouth
What is lancefield grouping
Test to classify streptococci spp based on polysaccharide and teichoic acid antigen in cell wall
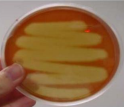
Beta hemolysis
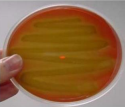
Alpha hemolysis
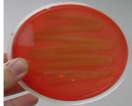
Gamma hemolysis
What is strep. pyogenes
Associated with local/systemic invasion; produce capsules of hyaluronic acid that delays phagocytosis; Group A streptococcus (GAS) that cause strep throat
Strep pyogenes is the causative agents of what
Necrotizing fasciitis, pharyngitis, impetigo, erysipelas, bacteremia/sepsis
What is a group A streptococcus
Strep. pyogenes
What is a group B streptococcus
Strep. agalactiae
What toxins are in strep. pyogenes
Streptokinase (fibrinolysin), deoxyribonuclease, hyaluronidase, pyrogenic exotoxin, hemolysin
What is process of streptococcal toxic shock
S. pyogenes grow in wound → GABHS enter bloodstream and produce superantigen → Fever, rash and shock
What causes scarlet fever
Pyrogenic exotoxin A-C associated with s. pyogenes pharyngitis, sore throat and swollen neck glands, sandpaper rash
What are pyogenes secreted factors
TSST-1 and SPEA
What is the difference between staph toxic shock and strep toxic shock
Staph: Fever > 38.9, rash, hypotension; strep: isolation of SPEA, hypotension
Strep. pyogenes can cause what disease
Strep throat; strep pyoderma (impetigo)
Post streptococcal diseases examples
Nephritis (glomerlonephritis), rheumatic fever
Mechanism of disease in strep. pyogenes
SPEA → STSS; Enzyme release → Local inflammation invasion of tissue → skin infection/pharyngitis/otitis media; bacteremia → meningitis/arthritis/osteomyelitis; antigen → immune complex formation → glomerulonephritis; antibody formation by B lymphocyte → rheumatic fever
What agar cultures streptococci pyogenes
Blood agar
What is strep. agalactiae
non-motile, no spores, facultative anaerobe, catalase negative, bacitracin resistant, beta hemolysis; Group B strep that cause neonatal sepsis and meningitis; colonize GI tract and vagina
What is strept. pneumoniae
gram positive, diplococci, facultative anaerobe, non-motile, no spores, alpha hemolytic, catalase negative; cause bacterial pneumonia, septicemia and meningitis
What is the pathogenesis of strep. pneumoniae
High temperature, aches and pains, headache; multiply in tissue; has capsule
What is non-invasive pneumococcal infections
Outside major organs in blood and less serious (bronchitis, otitis, sinusitis)
What is invasive pneumococcal infection
Inside major organs and more serious (bacteremia, septicemia, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, pneumonia, meningitis)
Clinical findings of strep. pneumoniae
Fever, chills and sharp pleural pain; sputum is bloody/rusty; can spread to mastoid in meninges
Lab diag for strep. pneumoniae
Blood, CSF and sputum samples; stained smears, capsule swelling tests, culture (blood agar), immunity
What is treatment for strep. pneumoniae
Penicillin G
What is corynebacterium diphtheriae
In respiratory tract, wounds and skin of infected people; spread by droplet/concent and grow on mucous membranes where it starts to produce toxin; heat labile; forms pseudomembrane
Clinical findings of corynebacterium dipherieae
Incuation period of 2-5 days; sore throat + low grade fever; pseudomembrane in posterior pharynx (sometimes obstruct airway); toxin can cause neuropathy
Diagnostic lab test of corynbacterium diphtheriae
Blood agar and selective medium; must warn lab beforehand
Treatment for corynbacterium diphtheriae
Antimicrobial drugs and antitoxin