trig derivatives, integrals, and identities
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
pythagorean identities
cos² + sin² = 1
1 + tan² = sec²
cot² + 1 = csc²
sin double angle
2 cos sin
cos double angle
cos² - sin²
1 - 2sin²
2cos² - 1
cos double angle solved for cos²
½ times 1 + cos2x
cos double angle solved for sin²
½ times 1 - cos2x
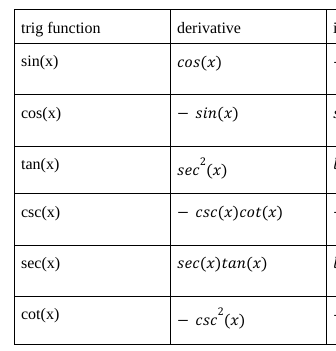
derivatives of all trig functions
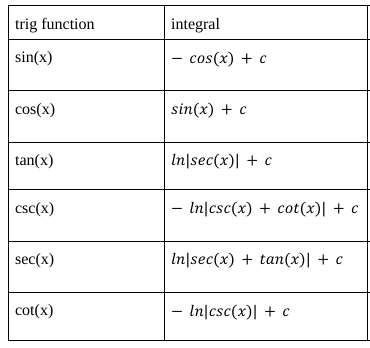
integrals of all trig functions
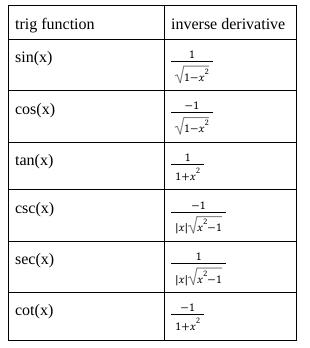
derivatives of all inverse trig functions
what is the integral of lnx
xlnx-x+C
things to remember
DON’T FORGET DX, +C, AND TRIG IDENTITIES
heaviside always works as long as it’s distinct
the integral of lnx is xlnx-x+c
you can integrate double angle but not trig squared (other than cos and sin)
if it gives you a rate and how many people infected, you can plug stuff back into og dy/dx equation to solve for K
remember the ln ends up being a fraction because one of them, the variable is negative so you have to subtract that ln not add
if you have to find the maximum rate of infection, set original dy/dx equation equal to 0
remember chain rule for inverse trig (numerator is usually not 1, but another integer)
remember ln isn’t always the end goal
factor out quadratic for odd/even trig
remember to use ln|x| not ln(x)
if you have y - a over y - b and want y by itself, you have to multiply both sides by denominator then factor it out then combine like terms to one side then factor again and divide
for sec of odd power you have to use u and du and get to a point where you have same integral with dif coefficient by using trig sub
only reassociate if you have to, like if there’s lnx, don’t do it for small polynomials just take the long way