SSEH1104 Active Leadership
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
4 factors that influence role perception
1. role ambiguity
2. role conflict
3. role acceptance
4. role efficacy
3 types of role conflict
1. intra-sender
2. inter-sender
3. person-role
Social facilitation
The effects on performance attributable to the presence of passive others.
audience effects
the impact of passive spectators on performance
co-actor effects
the impact of people doing the same activity on performance
First research period for social facilitation
Norman Triplett 1897 did studies on cyclists and found they performed better alongside others. Also did studies on fishing reel speed and found that an audience improved performance.
What was the lull in research on social facilitation?
1935-1965, because there was a report written which commented on poor methods and mixed findings in the field.
1965 Zajonc
Research created a framework which organised previous mixed findings.
"drive theory"/stern activation theory, "mere presence" of others improved frequency of dominant response and reduced frequency of non-dominant response.
Explain the Zajonc Solution to Social Facilitation.
That the 'mere presence' of others increases the frequency of the dominant response, and decreases the frequency of the non-dominant response.
So if someone scores most of the time on their own, then they will perform better with an audience. If they miss majority of the time on their own, then they will perform worse with an audience.
What was some later evidence to support Zajonc's drive theory?
Michaels 1982 - studied pool players and results matched Zajonc's theory.
What was an objection to Zajonc's drive theory?
Cottrell 1968 - not just 'mere presence'.
Had the idea that performance changes were due to evaluation apprehension- so the performer had to feel that the audience was evaluating them.
Evaluation apprehension
Cottrell 1968 - the extent to which a performer feels watchers are analysing the performance.
In contrast to Zajonc's (1965) "mere presence" conception.
Evidence for Cottrell's account of social facilitation?
Worringham & Messick (1983) - study of runners with attractive female. Pace picked up only in the condition where the woman was turned to face the track.
Two judgements which make a first impression
warmth and competence
3 researchers who found evidence for warmth & competence
Asch, Stogdill and Bass.
Halo effect and its impact on impressions
the tendency to draw a general impression about an individual on the basis of a single characteristic.
If we evaluate someone as warm, we're more likely to evaluate them as competent too. EXCEPT when there are 2 people being evaluated, one is warm and one is competent. Traits are compared and look weaker compared to the other.
Maintenance of perceptions of warmth and competence
Warmth - negative info. more influential than positive info. It's easy to appear warm, but one slip up could change someone's perception indefinitely.
Competence - positive info. more influential than negative info. Some mistakes are okay, but displays of competence have larger impact.
4 emotional impacts of perceptions of others
Cuddy (2007)
admiration - high warmth, low comp.
contempt - low warmth, low comp.
envy - low warmth, high comp.
pity - high warmth, low comp.
Behavioural impacts of perceptions of others
Cuddy (2007)
high warmth - active facilitation
low warmth - active harm
high competence - passive facilitation
low competence - passive harm
3 non-verbal strategies for positive impressions
1. duchenne smile
2. immediacy cues (nodding, leaning, eye contact)
3. mirroring
2 environmental strategies for positive impressions
1. physical/verbal suggestions of warmth or cold
2. set up environment to highlight power postures
Bandura - 4 causes of confidence
1. prior performance
2. vicarious experience
3. verbal persuasion
4. emotional arousal
Lent & Lopez (2002) - Tripartite Efficacy Theory
1. self efficacy
2. others efficacy
3. relation-inferred self-efficacy
RISE
relation- inferred self-efficacy
4 strategies to improve RISE
- positive feedback
- give opportunities to show skills
- set challenging goals to demonstrate confidence
- devote time
optimal distinctiveness theory
Brewer (1991) suggests that we vacillate between wanting to be unique and also belong to a group. Accounts for people's motivations in seeking group identification.
counter-vailing needs
differentiation and assimilation
optimal distinctiveness
occurs when an environment offers equal satisfaction of both differentiation and similarity eneds.
Big Five Model of Personality
McCrae & Costa (1997)
OCEAN
openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism
Which personality traits are associated with leadership emergence?
Extraversion, openness and conscientiousness
Do opposite personalities work well together?
Jackson (2011)
Opposites don't attract in working relationships.
How does personality impact cohesion in teams?
as average extraversion increases and neuroticism decreases, social cohesion increases.
as average agreeableness and conscientiousness increases, task cohesion increases.
Energy Sappers
Members of a team who disrupt cohesion.
e.g. one neurotic person can disrupt social cohesion, or
one lazy or uncooperative person can disrupt task cohesion.
4 emotional abilities (Mayer & Salovey 1997)
1. perceiving emotion
2. using emotion
3. understanding emotion
4. managing emotion
PUUM
Can emotional intelligence be trained?
Yes.
Perceiving emotions
the ability to detect emotions in oneself and others.
internal cues, body language, communication.
Using emotions
The ability to generate emotions in oneself and others.
Understanding Emotions
The ability to know what causes emotions and their consequences.
Managing emotions
The ability to regulate one's own emotions and influence those of others
What's wrong with survey methods to assess emotional intelligence?
Social desirability bias in self-report measures.
Alternative objective emotional intelligence test
Mayor Salovey Caruso Emot Intell test
4 stages of team development
Tuckman & Jenson (1977)
1. Forming
2. Storming
3. Norming
4. Performing
- transforming/adjourning
Forming stage team characteristics
- need to feel included
- pressure to conform
- depend on the leader
- anxious about purpose and goals
Forming stage leader strategies
- develop cohesion
- encourage role differentiation
- clarify expectations
- set short term achievable goals
Storming stage characteristics
- challenge authority/competence of leader
- assert individual will
- conflicts
- defensive about feedback
- test limits
- resist discussions
Storming stage leader strategies
- give non-defensive, firm guidance
- acknowledge individual differences
- foster interdependence
- positive corrective feedback
Norming stage characteristics
- group norms emerge
- goal and result focussed
- feedback welcomed
- share, trust and develop harmony
Norming stage leader strategies
- encourage cohesion
- repair damage from storming
- focus on feedback
- set more challenging goals
- don't fear reverting to storming stage
Performing stage characteristics
- team focusses on common tasks
- group think, exclude non-contributors
- possible demotivation
Performing stage leader strategies
- acknowledge individual contributions
- challenge group think
- encourage creative problem-solving
- maintain focus
- set more challenging goals
Transforming/adjourning stage
task complete, disband team, encourage skill transfer to other situations. Phase out team meetings.
3 types of motivation according to Self Determination Theory
1. intrinsic motivation
2. amotivation
3. extrinsic motivation
rank the 6 types of motivation from least to most effective.
1. amotivation
2. external regulation
3. introjected regulation
4. identified regulation
5. integrated regulation
6. intrinsic motivation
external regulation
when you engage in a task for an external demand or reward. e.g. operant conditioning
introjected regulation
when you're driven by a desire to avoid guilt or anxiety, or attain ego enhancement.
integrated regulation
when you integrate extrinsic regulations into your sense of self, your values and needs, but still performed for outcomes other than enjoyment
identified regulation
valuing the outcome of the task but not doing it just because it's pleasant in itself.
3 psychological needs according to SDT
autonomy, competence and relatedness
how do you provide competence support?
- reward for effort not just results
- help plan for challenges
- cater for difference learning preferences
self-control
the capacity for altering one's own responses, especially to bring them into line with standards such as ideals, values, morals and social expectations, and to support the pursuit of long-term goals.
trait self-control
one's overall, stable level of self-control or willpower across all settings.
state approach to self control
Depleted resource hypothesis - every act of self control draws from a limited pool of resources.
ego depletion
when people have diminished their self-control resources, 'tank is empty'. We are much more susceptible to self-control failures in an ego-depleted state.
2 examples of self-control research
Englert - sprint start after transcribing a text omitting e's and n's.
Furley - basketball players had to choose the best option when shown a picture. Ego depleted from transcription too.
Stuck & Baumeister - ego depleted participants rated the experimenter less positively.
negative effects of low self-control resources in team
- conflict
- poor communication
- poor performance under pressure
- concentration lapses
how can you develop self control?
train to overcome ego depletion.
e.g. using non-dominant hand, cut back on lollies, improve posture.
how can you improve self-control resources in your team?
- training
- choice
- thoughtful scheduling
- make tasks enjoyable
self-compassion
- being kind and understanding to oneself
- seeing one's fallibility as a part of the larger human condition rather than as isolating
- being mindful of painful thoughts and feelings but not identifying with them.
two self-compassion programs
Gilbert 2009 - compassion-focussed therapy
Germer 2013 - 8 week mindful self-compassion program
Ben Shahar
Harvard university lecture course on happiness
Can money bring happiness?
Ben Shahar says yes, if it is used to to contribute to your values.
Ben Shahar's 4 archetypes
1. hedonist - short-term gain causing future detriment
2. rat-racer - future benefit causing present detriment
3. nihilist - present and future detriment
4. happiness - present and future enjoyment
state of flow
occurs when tasks are just difficult enough that they're not boring nor cause anxiety.
Cialdini's 6 Principles of Influence
1. Liking
2. Reciprocity
3. Social Proof
4. Consistency
5. Authority
6. Scarcity
rule of reciprocity
'web of indebtedness' means that we try to repay in kind what other people give to us.
e.g. Regan 1971 - art appreciation
people were more likely to sell raffle tickets if they were given a coke, regardless of whether or not they liked the person.
Cialdini 1975 - rejection then retreat 'door in face' technique.
Commitment and Consistency
people feel pressure to conform to their past commitments and behaviors, especially in public. Ask for small commitments from people.
Moriarty 1975 - beach belongings experiment
95% of people protected the items of a stranger when agreeing to do so.
Social proof
influence tactic that relies on the tendency people have to behave in a particular way because others are doing so. Works best when person id uncertain and feels similar to leaders.
Provine 2000 - 'canned' laughter
e.g. tip jars, 'most popular', real estate hired help
Liking
more likely to say yes to people we know and like.
4 reasons people may like someone
1. physical attractiveness
2. similarity
3. compliments - like people who like us
4. contact and cooperation
Authority
more likely to be influenced by someone who is an expert/we think knows better than us.
Scarcity
opportunities seem more valuable to us when they are less available.
4 ways goals improve performance
1. focus
2. energy
3. persistence
4. strategy
3 ways of increasing the power of goals
1. make the outcomes relevant to people
2. make people feel capable of achieving them
3. give feedback regarding progress
SMARTER goals
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Relevant
Time-framed
Exciting
Reviewed
3 types of goals
1. Outcome - an end to a result
2. Performance - focus on one's own performance e.g. 80% accuracy
3. Process - not on results or performance, but learning, skill development, technical aspects.
autonomous goals vs controlled goals
autonomous - goals that are pursued because they are interesting, important, valuable or fun for you
controlled - goals that someone else wants you to do that you pursue because of guilt or pressure
Goal staircase
setting short-term or proximal goals to reach the ultimate goal eventually.
two types of planning
1. action planning - what, where, when, how
2. coping planning - anticipating risks and challenges
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
self-actualisation
esteem needs
social needs
safety needs
physiological needs
What was Herzberg's theory?
Two-factor theory of motivation-hygiene.
Two factors in herzberg's theory
1. motivator factors
2. hygiene factors
motivator factors
related to content of the work
e.g. achievement, recognition, responsibility, growth/advancement
hygiene factors
related to the context in which work is carried out.
e.g. admin, supervision, interpersonal relationships, conditions, salary, security, etc.
the presence of motivators is ____ and the absence of them is a ____ state.
satisfaction, neutral
the presence of hygiene factors is a ____ state and the absence of them is ____.
neutral, dissatisfaction.
Job characteristics model - 5 core job characteristics
Hackman & Oldham (1980)
1. skill variety
2. autonomy
3. task identity
4. job feedback
5. task significance
2 critical psychological states in the job characteristics model
1. experienced responsibility for outcomes
2. knowledge of results
motivating potential formula
motivating potential = (skill variety +task identity + task significance)/3 x Autonomy x feedback
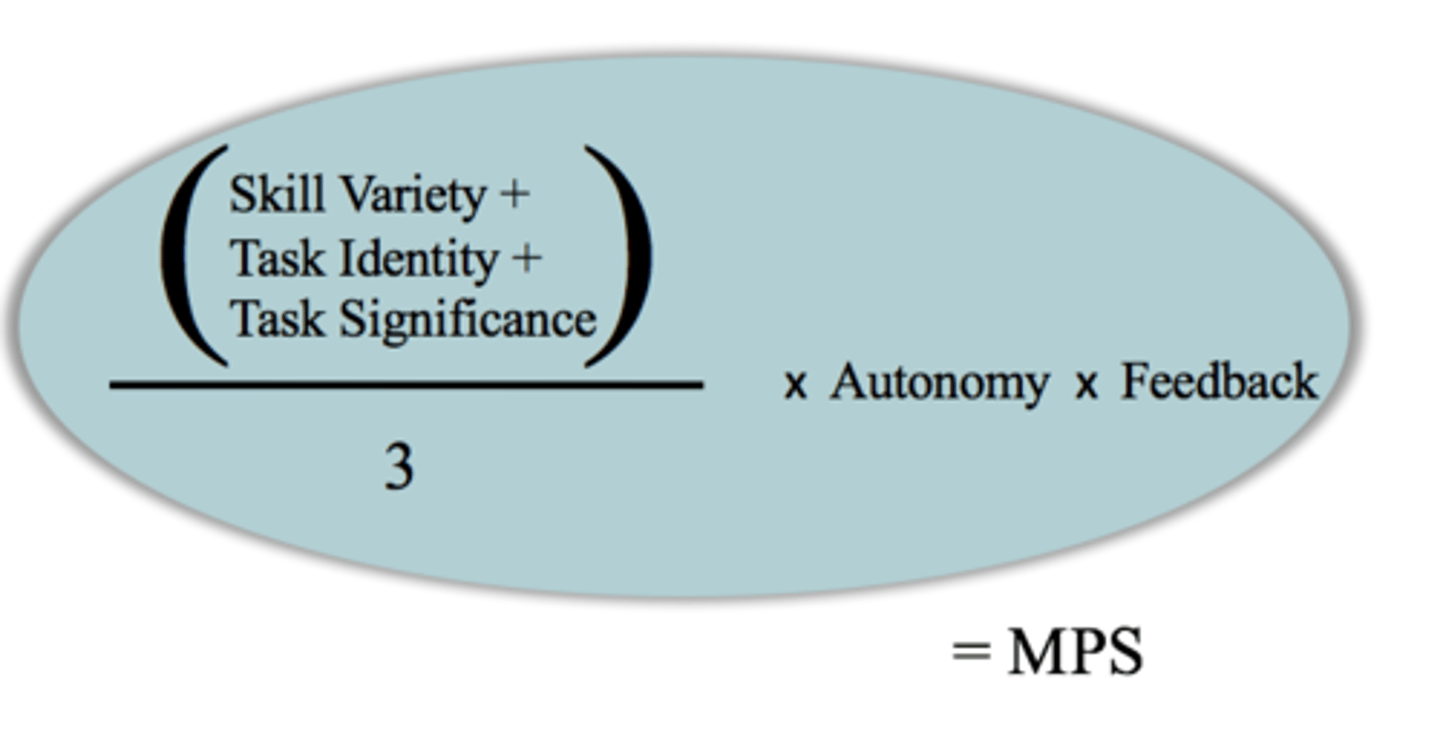
which factors are most important in the job characteristics model?
autonomy and feedback
two styles of negotiation
soft and hard