Tissues -- Anatomy and Physiology
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Definition of a tissue
groups of cells similar in structure and function
4 main types of tissues and their locations
1) Epithelial -- found on external surfaces and internal cavities
2) Connective tissue -- cells and matrix that structure and anchor
3) Muscle Tissue -- cells that receive contact and cause movement
4) Nervous tissue -- receive/process/transmit messages
Epithelial tissue functions
protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion, and sensory recognition.
Epithelial tissue characteristics
*** apical-basal polarity
apical = top and exposed to the outside
basal = bottom and attached to the lower tissue membranes
*** on top of connective tissue
+++ avascular
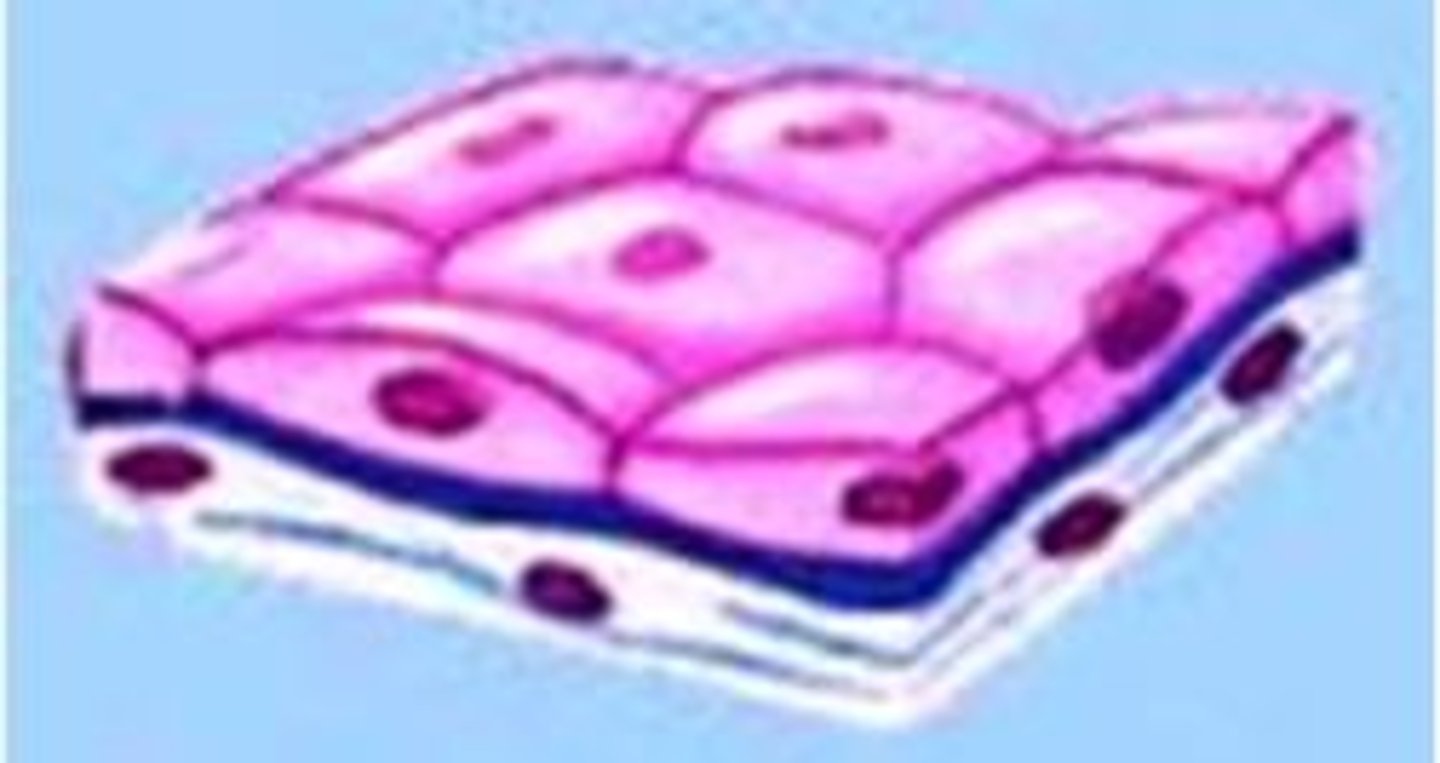
Squamous
flat, scale-like epithelial cell
Cubodial
cube-shaped epithelial cells
Columnar
column-shaped epithelial cells
Simple
1 layer
Stratified
more than one layer
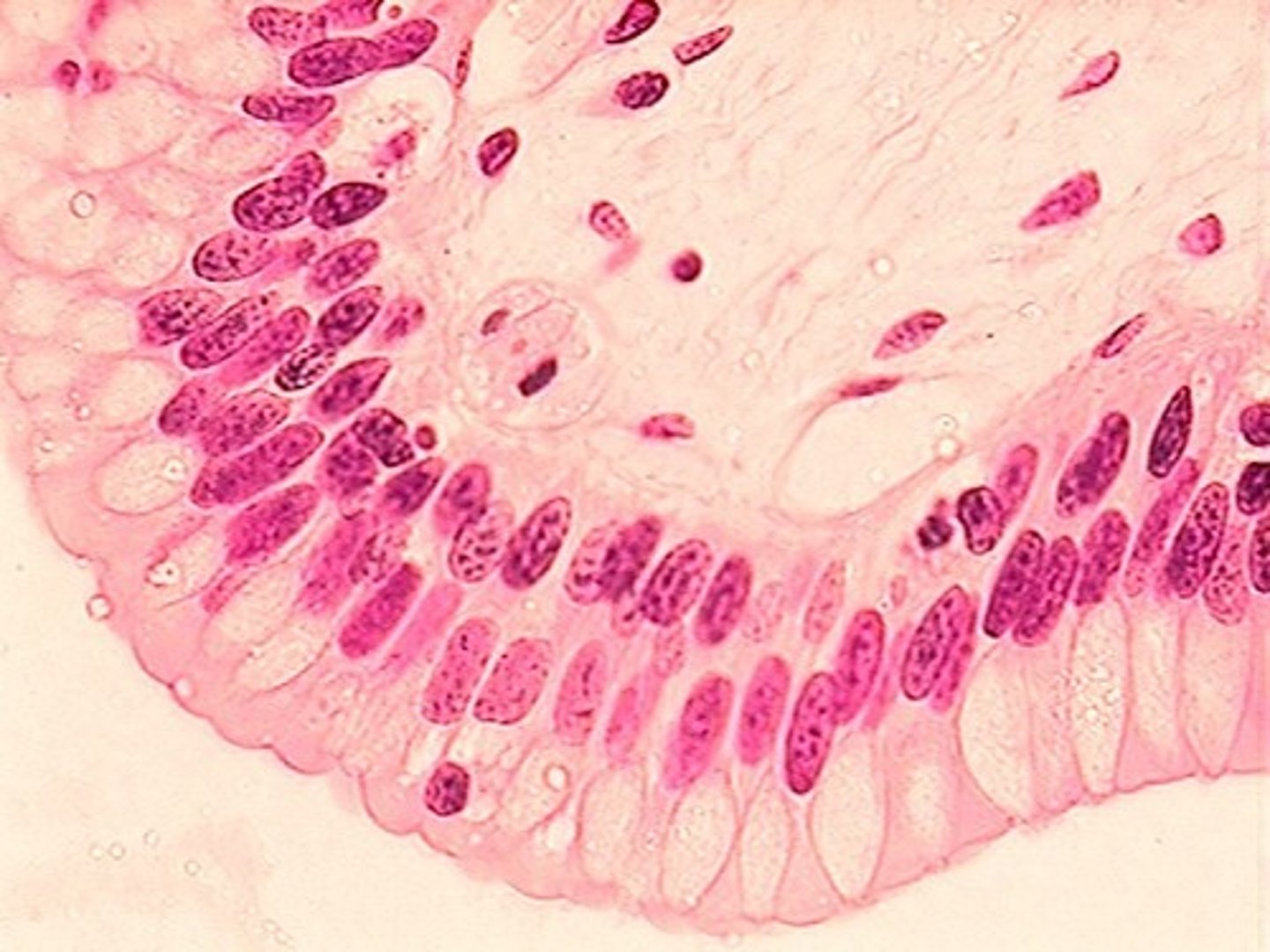
pseudostratified
one layer but appears to be multilayer because cells are different lengths
Transitional
several layers
9 types of epithelial tissue
simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified columnar, stratified squamous, stratified cuboidal, stratified columnar, transitional epithelium, glandular
Simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flattened cells
located in lining capillaries (small blood vessels), alveoli (air sacs), glomeruli (kidney blood vessels), mesothelium (around abdominopelvic areas)
Allowing diffusion and absorption.
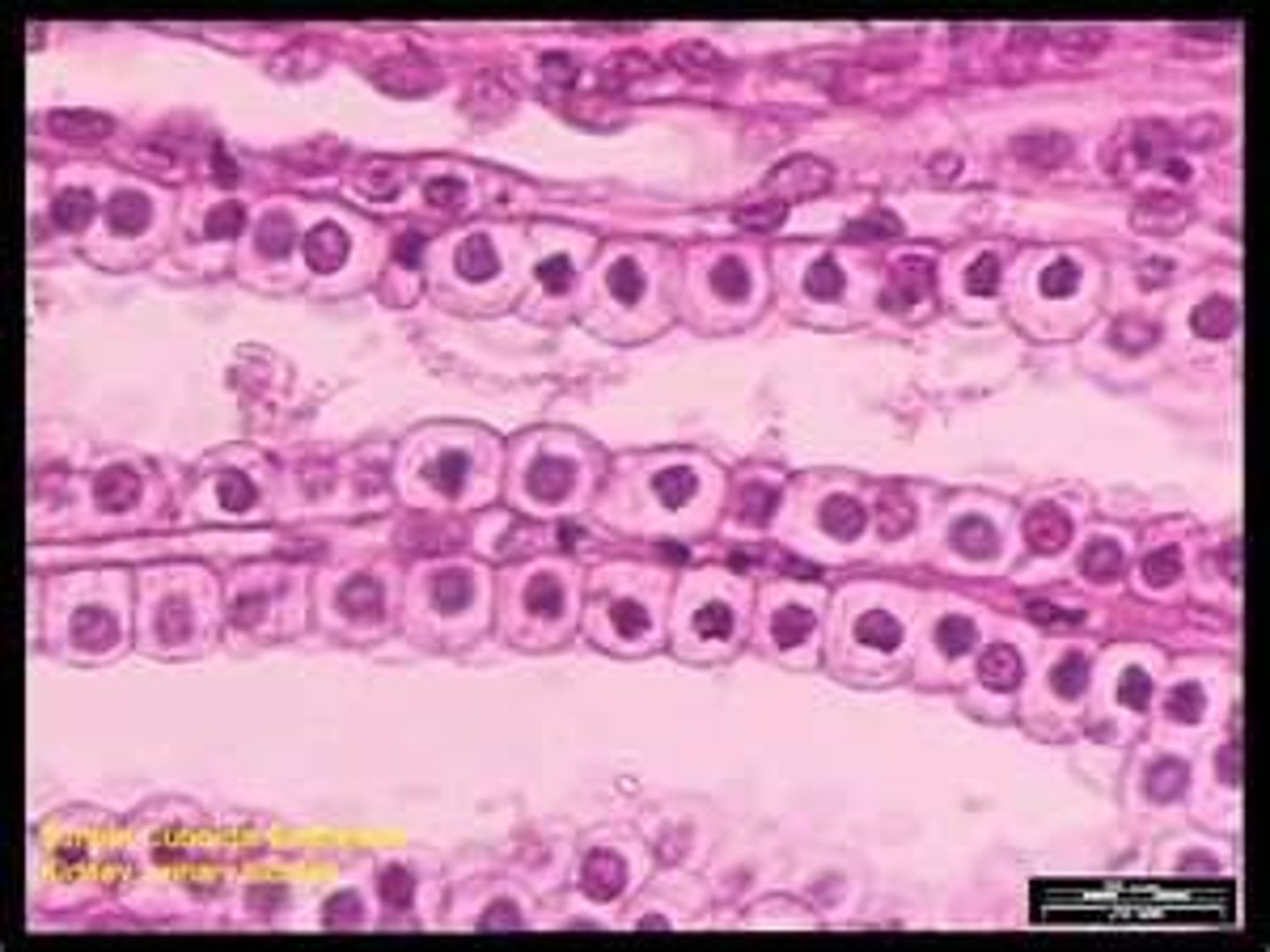
Simple Cubodial Epithelial Tissue
single layer of cube shaped cells
kidney tubules, ducts of glands, ovaries, and seminiferous tubules
secretion and absorption
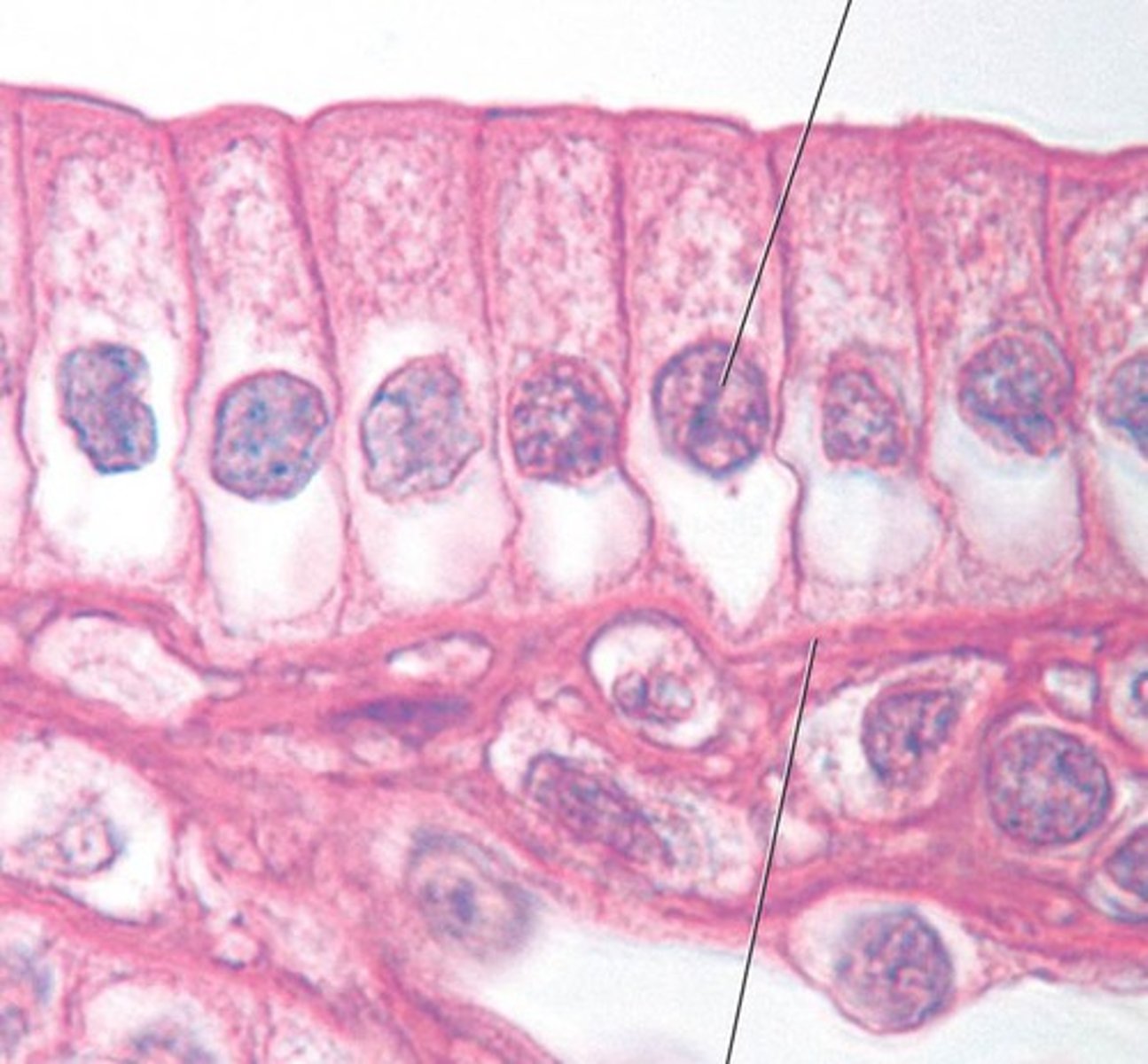
simple columnar epithelium
single layer of column shaped cells
Non-ciliated are responsible for secretion and absorption in the digestive tract, ducts of glands
Ciliated are responsible for movement of the uterus and oviducts.
Pseudostratified epithelial
single layer which appears to be many
located in the upper respiratory tract and reproductive system
allowing for secretion and movement
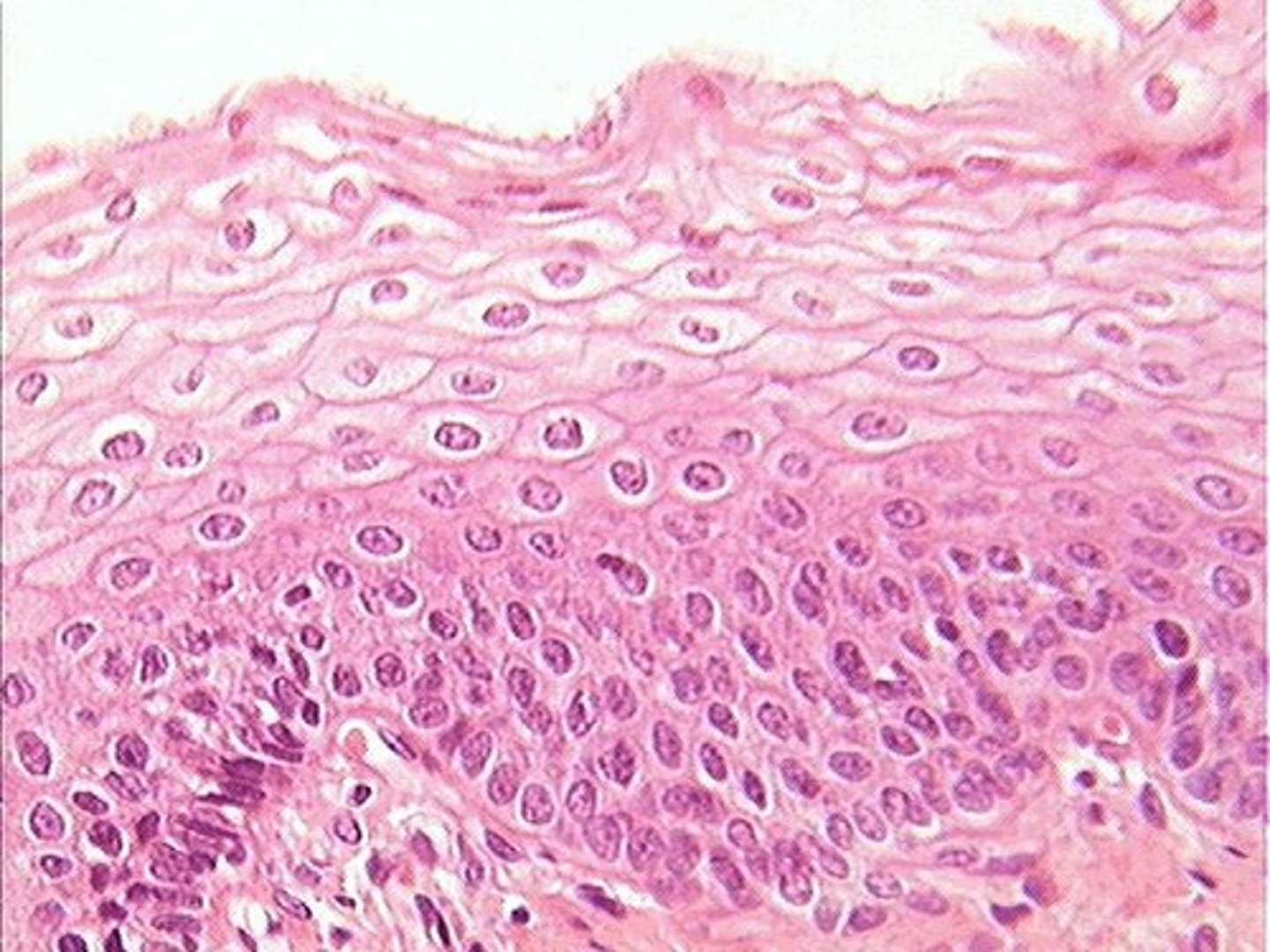
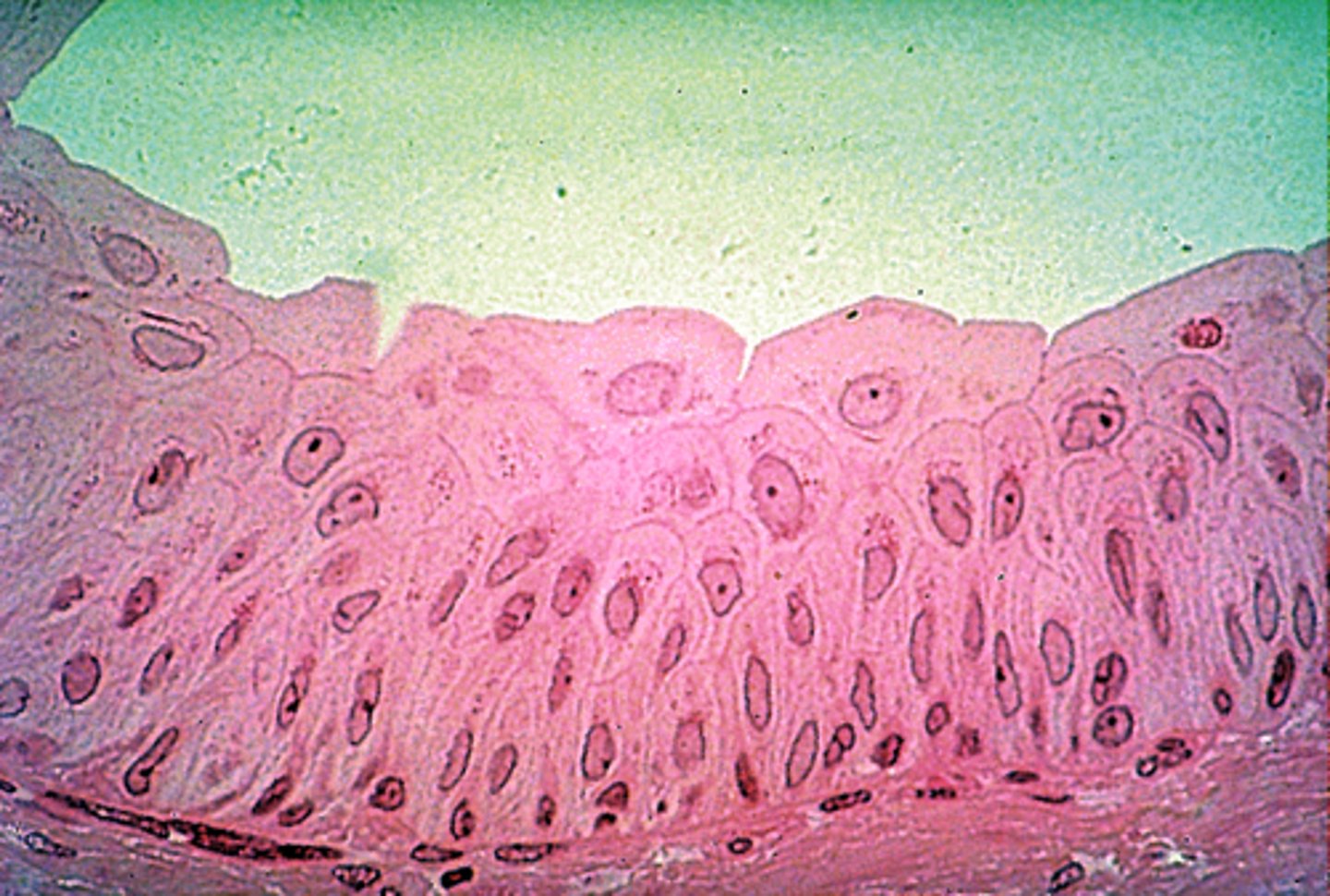
Stratified squamous epithelium
more than one thin layer of cells
Keratinized = skin
Non-keratinized = mouth, vagina, rectum
Protection from abrasions
stratified cuboidal epithelium
more than one layer of cube shaped cells
salivary glands, sweat glands, mammary glands
Secretion and strengthening of glands
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
more than one layer of column-like cells
pharynx, urethra, conjunctiva
protection and secretion
Transitional epithelium
several layers which stretches and protects the urinary bladder from urine.
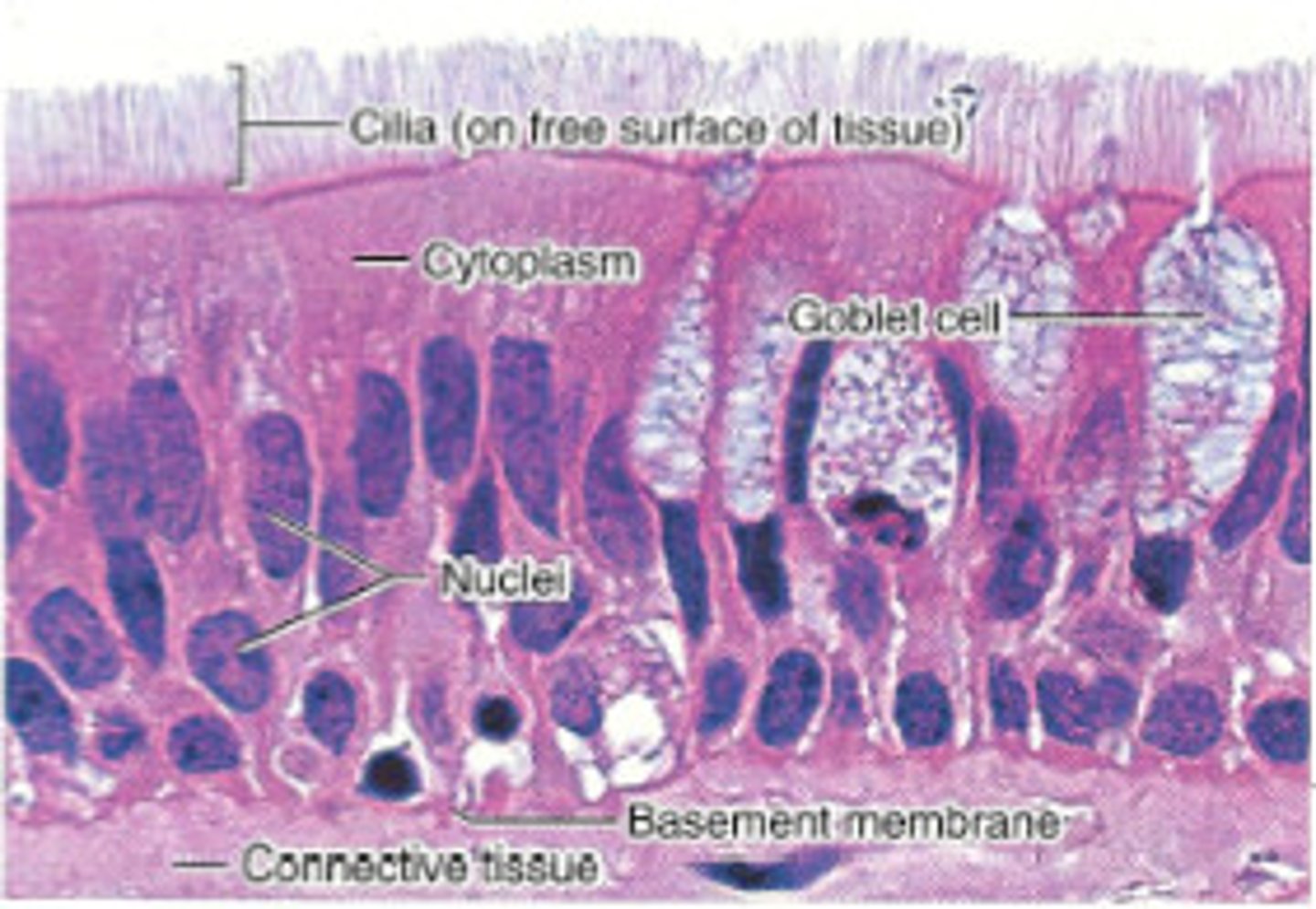
Glandular Epithelium
composed of cells that ae specialized to produce and secrete chemical substances
-- endocrine and exocrine
Endocrine glands
secrete into the bloodstream
-- hormones
Exocrine glands
excrete out of the body or an organ or ducts
-- sweat, saliva, mucus, digestive enzymes
Tight junction
form a leak-proof barrier ; found in areas where fluids need to be kept separate (ex the BBB)
Gap junction
direct channel between epithelial cells
Desmosomes
structural reinforcement in areas that stretch
Hemidesmosomes
attach epithelial cells to the basement membrane
Cilia
hairlike projections that allow for movement
Microvilli
increase surface area
Connective tissue
A body tissue that provides support for the body and connects all of its parts
Components of connective tissue
fibers and cells
Fibers in connective tissue
help provide structure and support
-- collagen fibers = strong thick hairs
-- elastic fibers = thin and stretchable
-- reticular fibers = delicate and net like
Cells in connective tissue are
named by function
*** -blast cells : immature building blocks
*** -cyte cells : mature and only consisting of the existing matrix
Fibroblasts
fiber building cells in connective tissue
Chondrocytes
mature cartilage cells
Osteocytes
mature bone cells
Erythrocytes and Leukocytes
mature blood cells
Functions of connective tissue
binding, support, protection, insulation, energy storage, and transport
Connective tissue proper
1) Loose
- Areolar
- Adipose
- Reticular
2) Dense
- Regular
- Irregular
- Elastic
areolar connective tissue
wraps and conditions organs in addition to retaining extracellular fluid
contain collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers
visible fibroblasts and leukocytes
found surrounding organs and below the epilelium
Adipose tissue
fatty tissue composed of adipocytes located in the abdominal cavity, under the skin, and breasts.
function as lipid storage, protection, and insulation
have nucleus on the side of the cell and are filled with a lipid droplet
Reticular tissue
containing reticular fibers which contain leukocytes and erythrocytes.
Located in the lymph nodes,, the spleen, liver, and bone marrow.
Functions to support blood cells and assists in filtration.
Regular Connective tissue
tendons, aponeurosis and ligaments
all parallel with fibroblasts squished between the fibers
allows for strong attachment for bones and muscles
withstands pulling in one direction
Irregular Connective Tissue
many collagen fibers arranged irregularly located in the reticular layer of dermis and capsules around joints and organs.
withstands pulling in many directions
Elastic Connective Tissue
elastic fibers that appear dark purple in color when stained located in walls of large arteries and walls of bronchial tubes in the lungs.
Allows for stretching and recoiling
Cartilage
tough and dense flexible membranes
- chondrocytes: sparsely distributed cells in the lacunae surrounded by perichondrium (dense irregular connective tissues)
*** avascular
Functions of cartillage
-- strong and flexible to protect joints
-- helps joint shape when moving
-- absorbs shock
hydraline cartilage
cells are chondrocytes, found in lacuna and are glass like.
Found in the fetal skeletons, some joints, and nose
Template for bone and support and reinforcement.
Elastic cartilage
contains elastic fibers
located in external ear and epiglottis
Maintain shape and felxibility
Fibrocartilage
thick visible collagen fibers
- stain blue
- chondrocytes stain pink
Located in the intervertebral discs on the spine, knee, and temporomandibular joint
Provide strong support and absorb shock
Compact bone
contains calcium phosphate and collagen
- osteocytes arranged in osteons called lamellae
- blood supply is the Haversian canal
Outside of the bone
Allows for support and protection, muscle attachment site, and calcium storage.
Spongy bone
has trabeculae ( little columns that distribute force )
Found beneath compact bone
functions to form erythrocytes and store fat
Blood Connective Tissue
extracellular matrix of blood is plasma
-- plasma surrounds and supports cells
-- containing blood clotting proteins, nutrience, clotting proteins, hormones, gases, and water
Platelets: initiate clotting
Erythrocytes: O2 and CO2 transport
Leukocytes: immunity
Nervous tissue
detects and responds to stimuli
Neurons send impulses and glial cells help the neurons
Membranes are composed of....
epithelial tissue + connective tissue
Mucus membranes
linings of natural body openings, such as mouth, nose, rectum, genitals and eyes
Serous membranes
on organs in the ventral cavities
Cutaneous membranes
the skin
Skeletal muscle
- striated
- attached to bones and allows for the movement of the secretion
- multinuclear
- unbranched
- activity is voluntary ( signal needs to be received from the brain )
Cardiac muscle
- striated
- on the heart and pumps blood
- 1 or 2 nuclei
- branched: intercalated discs form direct cytoplasmic connection end to end
- activity is involuntary ( signal does not need to be received from the brain )
Smooth muscle
- not stratified
- on hollow organs, blood vessels, etc...
- moves food, helps regulate blood pressure, etc...
- single nuclei
- unbranched
- activity is involuntary
The type of tissue that protects, insulates, and stores lipids is __________ connective tissue.
adipose tissue
Transitional epithelium is found lining which of the following?
urinary bladder
Glandular epithelium contains glands that secrete specialized materials. If the materials are secreted into the bloodstream, the gland is termed ________. If they are secreted out of the body or an organ via ducts, the gland is termed _____________.
1) Endocrine
2) Exocrine
The dominant thick strong fiber types found in dense connective tissue are _____ fibers.
collagen
This connective tissue that is mostly fibers with few cells, contains all three fiber types is:
areolar
Chondrocytes are to cartilage as osteocytes are to:
bone
Hematopoiesis in spongy bone means:
making red blood cells
What is the major component of plasma
water
Muscle tissue with no striation is....
smooth
The delicate, net-like framework of organs is made of the following type of connective tissue.
recticular
The two types of connective tissues whose living cells are found in in lacunae are:
cartilage and bone
Which kind of intercellular junctions would you find in transitional epithelium?
desmosome
Multinucleated cells are found in __________ muscle.
skeletal
What is a tissue?
a group of cells plus extracellular materials
The type of intercellular junctions that anchor epithelial cells to underlying connective tissue is
hemidesmosome
The type of epithelial tissue that is best for absorption and secretion is __________ epithelium
simple squamous epithelium
The type of tissue found on external surfaces and internal cavities is ____________.
epithelial
The type of intercellular junctions that prevents leaking between cells are ___________ junctions.
tight
The tough cartilage with thick collagen fibers found in the intervertebral discs, knee, and temporomandibular joint is
fibrocartilage
A major function of smooth muscle is to
move food
The tissue that always has an apical and a basal surface is __________ tissue.
epithelial
The extracellular matrix of bone contains:
calcium phosphate and collagen
Which of the following types of cells are part of the immune system?
leukocytes
Of the following types of epithelial tissue, which is most protective from abrasion?
stratified squamous epithelium
Whate type of cartilage is found in the epiglottis?
elastic cartilage
true or false: at least one type of cartilage is vascular
false -- cartilage is avascular
Epithelial tissue adapted for aborption and secretion will have what on their surface?
microvilli -- to increase surface area