immunologic procedures - precipitation and diffusion assays
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is specificity?
The ability of a particular antibody to combine with one antigen over another
What site on the antibody is responsible for specificity?
Fab region, or variable region
How do antigens bind to antibodies?
With weak, reversible, non-covalent bonds
What influences immune complex formation?
The goodness of fit, strong forces, and high affinity
What is affinity?
The bond that can form between a single antigenic determinant and a paratope (variable region on Ab)
What is avidity?
The overall bond strength between a multivalent antibody and the antigen
What is cross reactivity?
When a second structurally similar antigen can bind to an antibody
What are factors that influence antigen:antibody binding (or reaction)?
The pH, temperature, Ig type, and concentration of Ab or Ag
Which Ig is the most efficient for forming immune complexes?
IgM
What is sensitivity?
The lowest detectable amount of an Ag or Ab required to elicit an immune response
What is precipitation?
The combination of soluble Ag to soluble Ab to produce insoluble complexes, or the aggregation of soluble antigens
What is the prozone?
The zone where antibody concentration exceeds antibody concentration
Ratio is NOT 1:1
No lattice formation
What is the zone of equivalence?
The zone of precipitation where there are almost equal concentrations of antigens and antibodies
Ratio is 1:1
Lattice formation occurs and precipitation is seen
What is the postzone?
The zone of precipitation where the concentration of antigens exceeds antibodies
Ratio is NOT 1:1
No lattice formation occurs
What is the result if a precipitation test shows no reaction?
A false negative
What causes false negatives in precipitation reactions?
When there is either too much antibody (prozone false negative) or too much antigen (postzone false negative)
How do we correct for a false negative?
Serially dilute the specimen
How do we report out the result of a precipitation test?
The titer, or the highest dilution of serum that shows a positive reaction (clumping)
What is immunodiffusion?
Where antigens and antibodies precipitate through passive diffusion, no electrical current
What is the Oudin single diffusion test? What does it detect?
Single diffusion test that occurs in a tube
It detects antigens or antibodies
What is the radial diffusion test? What does it detect?
Single diffusion that measures the diameter of the precipitation ring after 18 hours
Detects blood proteins, or antigens in general
What is the Ouchterlony double diffusion test? What does it detect?
Double diffusion of both antigen and antibody in agar that are opposite of each other. When antigen and antibody cross paths, they form a line
Detects fungal antigens and autoantigens
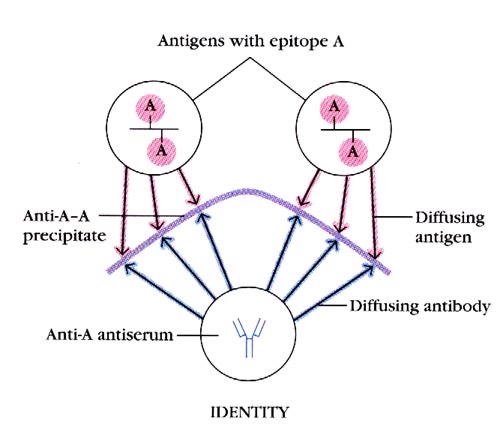
What does the identity pattern look like on an Ouchterlony test? What is the interpretation?
When two antigens with the same epitope come into contact with the antibody, an arc line forms in the gel
Interpretation: identity of both epitopes, common determinant
What does the non-identity pattern look like on an Ouchterlony test? What is the interpretation?
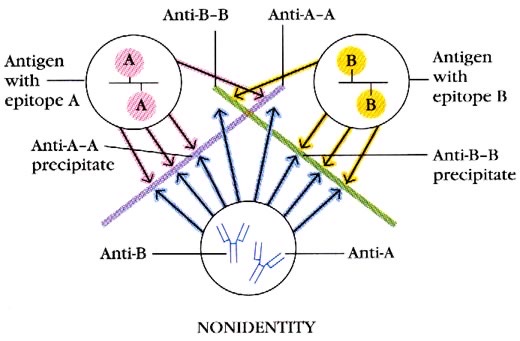
When two different epitopes interact with an antibody, the precipitation lines cross
Interpretation: Non-identity, no common determinant
What does the partial identity pattern look like on an Ouchterlony test? What is the interpretation?
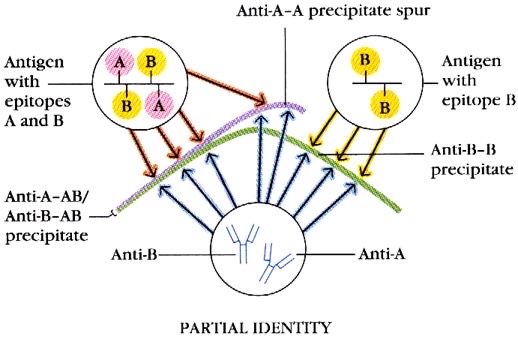
When two antigens with a shared common determinant and one non-shared determinant interact with the antibody, an arc line is formed with the more complex antigen creating a spur line pointing towards the simpler antigen
Interpretation: partial identity and partial common determinant
How can we measure precipitation in a fluid model?
Through turbidity and nephelometry
For turbidity, how do we measure the results?
Through light absorbed, reflected, or scattered
What is nephelometry?
Light scattering from a liquid sample at a particular angle
For nephelometry, what do we measure?
The relative light scatter of macromolecular complexes, which is proportional to the immunoglobulin concentration