ANTR 350 MSU Exam 1 (Lindsey)
1/285
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
286 Terms
In-Class Lecture 1: Introduction to Anatomy Lecture 9/4
Define gross anatomy
Naming and descibing relationships between structures of the body that can be seen with the naked eye.
Define anatomical position
Refers to a pose where the body is standing erect (upright), feet together, with eyes facing forward, arms by the side, and palms facing forward.
Patient's Perspective
Always describe as if we are looking from the patient's perspective.
Where is the arm?
Between the shoulder and elbow.
Where is the leg?
Between the kneecap and ankle.
Anterior (Ventral)
Front of the body; Sternum is anterior to the spine.
Posterior (Dorsal)
back of body; The buttocks are posterior and the umbilicus is anterior
Definition of Midline
Divides the body into left and right halves.
Medial
closer to the midline
Lateral
away from the midline
Proximal
Closer to the trunk (referring to limbs); The toes are distal to the ankle.
Distal
Opposite of Proxmial (Refers to limbs); The toes are distal to the ankle.
Superior
Closer to head
Inferioor
Toward the feet
Superficial
Surface of the skin (Superficial)
Deep
deeper in the body
a. Cephalic
Head
b. Buccal
Cheek
c. Cervical
Neck
d. Acromial
Shoulder
e. Axillary
Armpit
f. Brachial
Arm
g. Antebrachial
Forearm
h. Palmar
Palm
i. Mammary
Breasts
j. Sternal
Breastbone
k. Abdominal
Abdomen
l. Pelvic
Pelvis
m. Inguinal
Groin
n. Femoral
Thigh
o. Crural
Leg
p. Pedal
Feet
q. Lumbar Loin (lower back)
r. Gluteal
Buttock
s. Popliteal
Back of Knee (Dorsal)
t. Sural
Calf
Plantar
Sole
Sagittal
A plane that divides the body into right and left portions.
parasagittal plane
Divides body into unequal right and left sides
midsagittal plane
divides the body into equal right and left sides
frontal (coronal) plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
transverse (horizontal) plane
divides the body into superior and inferior parts
oblique plane
passes through the body at an angle
Right Upper Quadrant
Right Kidney, gallbladder, most of the liver, part of the stomach, part of the pancreas, and parts of the small and large intestines.
Left Upper Quadrant
Spleen, left kidney, most of the stomach, left lobe of the liver, part of the pancreas, and parts of the small and large intestines.
Right Lower Quadrant
contains parts of the small and large intestine including the appendix and cecum, ureter, and part of the bladder when full. The right ovary, uterine tube, and part of the uterus (if enlarged) are also present in females.
Left Lower Quadrant
contains parts of the small and large intestine, the left ureter, and part of the bladder when full. The left ovary, uterine tube, and part of the uterus (if enlarged) are also present in females.
what planes make up the 9 abdominal regions?
Left and Right Midclavicular planes, subcostal plane, and supracristal plane.
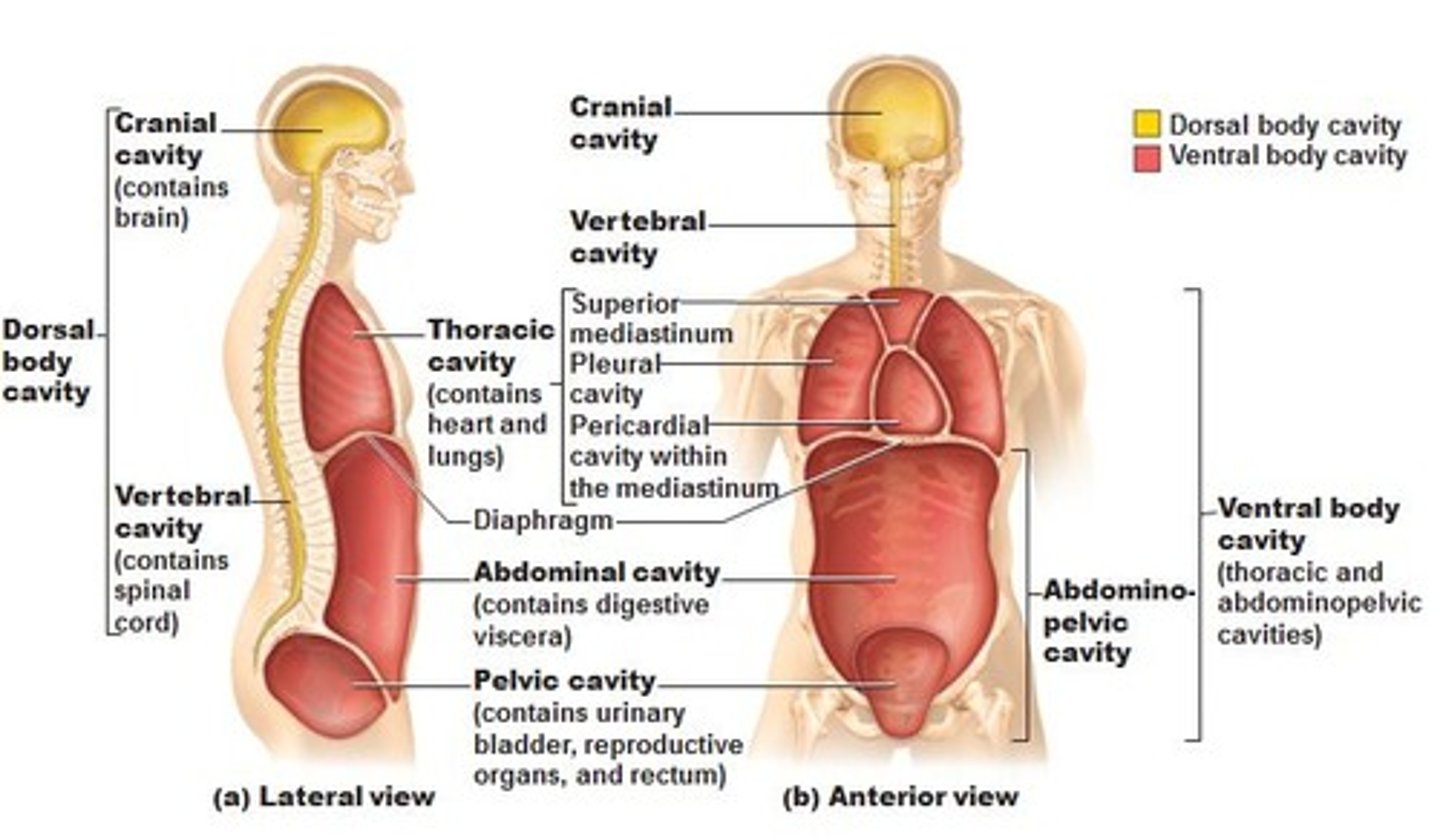
ventral body cavity (refer to notes)
Define tissue
group of cells that are similar in structure and function; cardiac muscles
Define organ
A group of tissues that perform a specific function or group of functions.; your heart
Organ system
group of organs that work together to perform a specific function; digestive system (includes stomach, small intestine, liver, etc)
What are the 4 principle tissues?
Connective, Muscle, Nervous, Epithelial.
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
Forms two surfaces: apical and basolateral. Causes a polarization which translates to an environment for movement of nutrients between the two surfaces. Critical for homeostasis.
Where is epithelial tissue found?
Covering and lining epithelium forms the outer layer of the skin (epidermis), dips into and lines the open cavities of the cardiovascular, digestive, and respiratory systems, and covers the walls of organs of the closed ventral body cavity. Glandular epithelium fashions the glands of the body.
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal (Voluntary), Smooth (Involuntary), Cardiac (Involuntary).
Skeletal Muscle (Voluntary)
Allows us to choose when and how to move. Everywhere in the body.
Smooth Muscle (Involuntary)
They provide motor power for regulating the internal environment related to digestion, circulation, secretion, and excretion
Found in the stomach, intestines, blood vessels.
Cardiac Muscle (Involuntary)
Exists only in the heart; helps pump blood
Glia
cells found throughout the nervous system that provide various types of support for neurons
Neurons
Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information.
What is the function of connective tissue?
Framework of the body. Provides support and structure to organs.
What are two types of connective tissue?
Loose (Hyaline Cartilage) = Flexible
Dense (Ligament) = Inflexible
Intergumentary system
Major organs: skin, hair, sweat glands, nails; Protection, defense, and regulation of body temperature.
Endocrine System
Consists of glands that control many of the body's activities by producing hormones.
Reproductive System
system of organs involved in producing offspring
nervous system
the network of nerve cells and fibers that transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body. (brain, spinal cord, nerves)
Immune/Lymphatic System
Helps protect the body from disease; collects fluid lost from blood vessels and returns it to the circulatory system
circulatory system
Transports oxygen, waste, nutrients, hormones, heat, etc... around the body (heart, blood)
respiratory system
A system of organs, functioning in the process of gas exchange between the body and the environment, consisting especially of the nose, nasal passages, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
urinary system
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra; filtration of blood and wastes.
musculoskeletal system
the system of bones and skeletal muscles that support and protect the body and permit movement
digestive system
Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells.
mediastinum cavity
contains the pericardial cavity, and surrounds the remaining thoracic organs
pericardial cavity
contains the heart; located inside the mediastinum
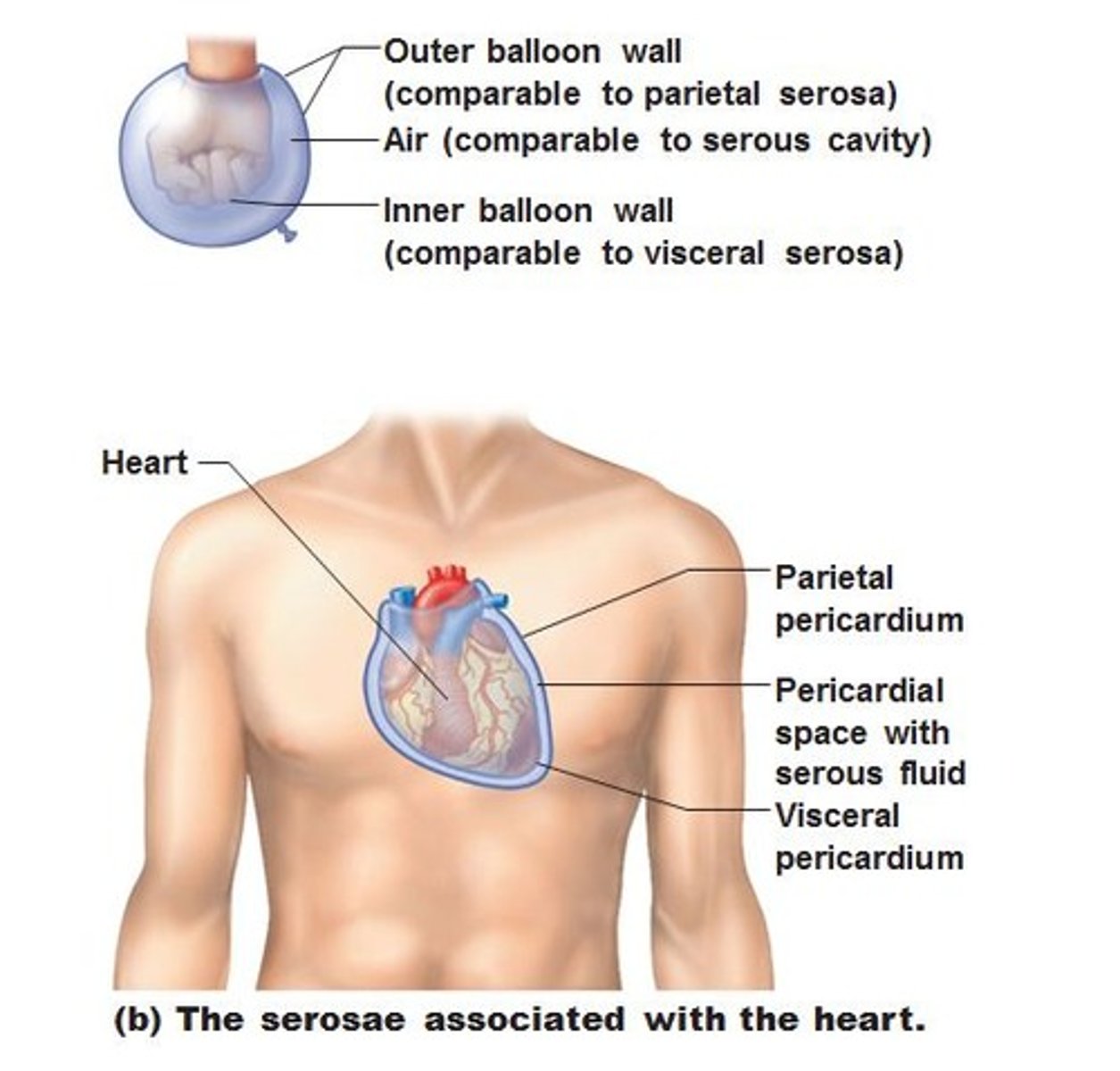
parietal layer
lines the internal surface of the body wall (part of the balloon that touches the bowl)
visceral layer
covers an organ; part of organ that is touching your fist
serous cavity
potential space between membranes (air inside of the balloon)
Serous Membranes of Ventral Body Cavity (Identify)
How are skeletal muscles named?
size, shape, location, direction of muscle fiber, attachment, number of attachments, action
Action
Flexor carpi ulnaris = flexes the wrist; Extensor Digitorum = extends the fingers
Shape
Trapezius, Rhombus
Size
Rhomboid Major, Rhomboid Minor
Location
Biceps brachii (in the arm); Quadriceps femoris (in the thigh
Fiber Orientation
Rectus = Straight Lines; Oblique = angled
Number of Heads
biceps, triceps, quadriceps
Attachment
Sternohyoid attaches the sternum and hyoid bone; Infraspinatus attaches the infraspinous fossa of the scapula
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell formation; serves as attachment sites for adjusting posture of head, neck, trunk, expand thoracic cage, stabilize appendicular skeleton.
Long Bone
Phalanges that form the fingers, toes, humerus of arm, and femur of leg.
Short Bone
carpals and tarsals (cube in shape)
Flat Bone
thin and curved bone; serves as a point of attachment for muscles and protects internal organs; cranial vault, sternum, sternum and ribs.
Sesamoid Bone
small, round bone embedded in a tendon; protects the tendon from compressive forces; patella or knee cap
Irregular
not following a pattern; not regular; verterae, ethmoid, sphenoid bone, and ox coxae (hip bones)
Structure of a Long Bone
Outside -> In
Periosteum -> Compact -> Spongy Bone -> Endosteum -> Trabeculae -> Marrow
intramembranous ossification
process by which bone forms directly from membrane to bone. Forms flat bones such as parietals, occipatals, and frontal bones.
endochondral ossification
Mesenchymal cells form -> Cartilaginous model -> Ossfies as bone replaces cartilage. (commonly happens to long bones) (refer to notes)
steps of endochondral ossification
1. Fetal hyaline cartilage model forms
2. Cartilage calcifies & bone collar forms around diaphysis
3. Primary ossification forms inside diaphysis
4. Secondary ossification centers form inside epiphyses
5. Bone replaces cartilages as diaphysis grows in length-epiphyseal plates are open
6. Epiphyseal plates close-growth is complete.
osteoproginator cells
comes from red bone marrow (embryonic messenchymal cells) and are able to differentiate into osteoblasts or osteoclasts
located close to the periosteum and endosteum
Osteoblasts
Bone building cells