MODULE 4 - Projectile Motion
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is a projectile?
a body in free fall that is subject only to the forces of gravity and air resistance
is an airplane a projectile
Since multiple forces are acting on it (lift, thrust, drag, gravity), it does not follow projectile motion which are only subject to gravity and airresistance
Why do we analyze the horizontal and vertical components of projectile motion separately?
vertical is influence by gravity and air resistance
horizontal is only influenced by air resistance
*so there will be an acceleration vertically but not horizontally
**also air resistance often small and neglected
what is the effect of gravity
The force of gravity produces a constant acceleration of -9.81 m/s2 on bodies near the surface of the earth
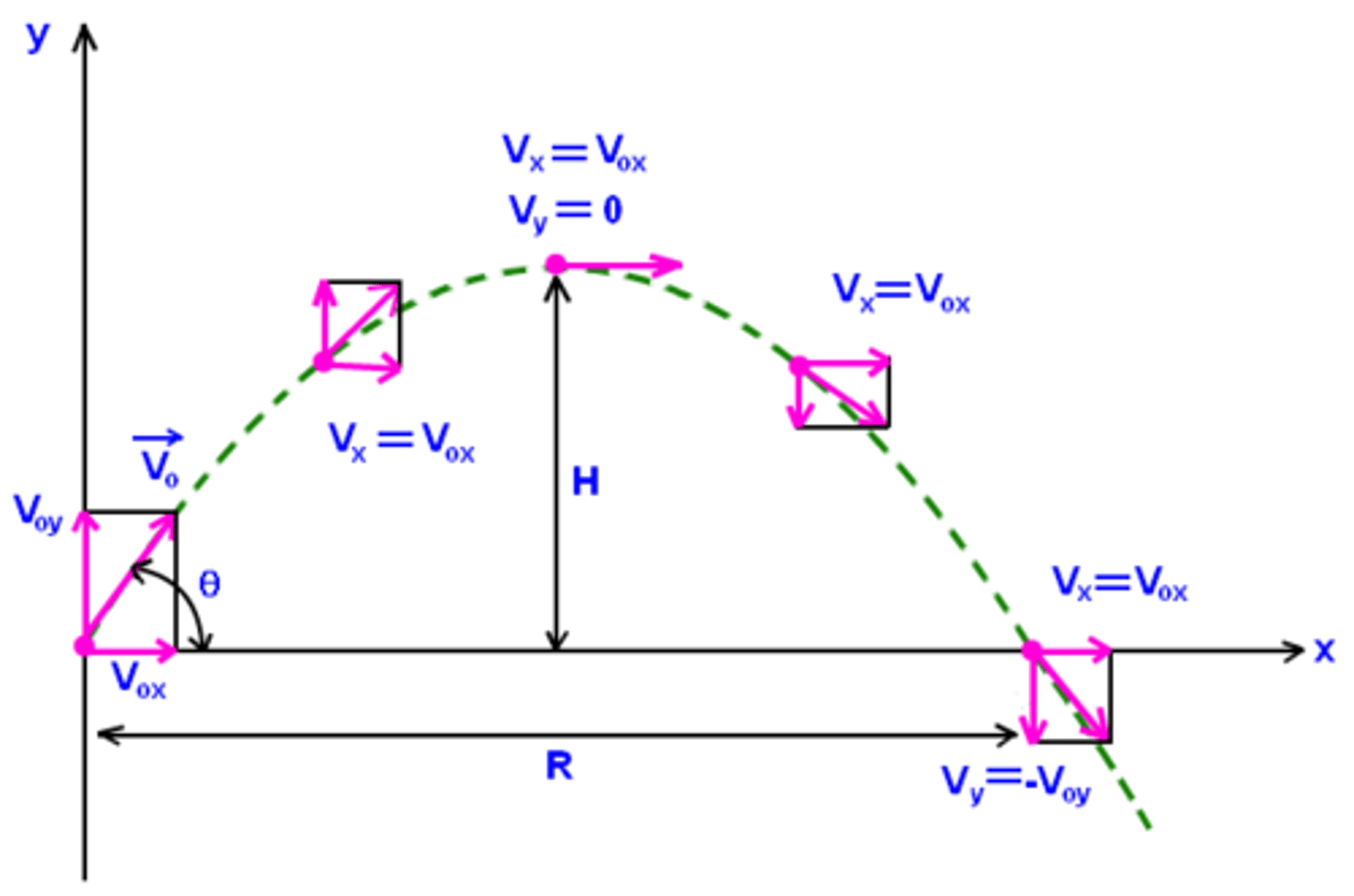
Q: What is the pattern in the change of vertical velocity during projectile motion?
Predictsble + symetrical about the appex (Magnitude of vertical velocity decreases as the ball rises and increases as the ball falls due to the influence of gravity)
As a projectile moves upward, gravity pulls downward, causing its vertical velocity to gradually decrease until it reaches zero at the highest point (the apex). At the apex, the projectile is not stopped—gravity is still acting on it. As the projectile moves downward, gravity continues to act in the same direction as the motion, causing the vertical velocity to increase in magnitude. This change in vertical velocity is predictable and symmetrical about the apex, meaning the projectile has the same vertical speed at equal heights on the way up and on the way down, but in opposite directions
What if 2 balls drop, one straight down and one projected horizontally at the same height??
Both will land at the same time!
How?
gravity affects their vertical velocities equally and has no effect on the horizontal velocity
Even if they are diff masses (as long as they are same shape therefore same air resistance)
**recall gravity has no effect on horrizontal motion!!!
what is trajectory
he flight path of the centre of gravity of a projectile
What factors influence Trajectory?
1. Projection angle
2. projection speed
3. realtive height of projection
projection angle
= the direction of the instantaneous velocity at take off with respect to the horizontal
**most optimal for greatance distance is 45º
***angles come in pairs interms of their ranges eg. 2º and 80º both travel 3m
Projection speed
= the magnitude of instantaneous velocity at take off
3 different throws all at the same projection angle at 3 different projection speeds
The greater the projection speed the greater the range and max height
Relative height of projection
= the difference between height at release and height at landing
The optimum projection angle depends on the relative height of the projection
Higher that landing point = < 45º optimal
Lower than landing point = > 45º optimal
factors affectinf flight time of a projectile?
- inital vertical velocity (determined from projection speed and angle by resolving the initial velocity)
- relative projection height
factors that effect the horizontla displacment of a projectile
- horizontal veolocity*
- inital vertical velocity *
(*determined from projection speed and angle by resolving the initial velocity)
- relative projection height
peak height of a projectile is influecned by..
- inital vertical velocity (determined from projection speed and angle by resolving the initial velocity)