Inorganic Chemistry
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Flux (J)
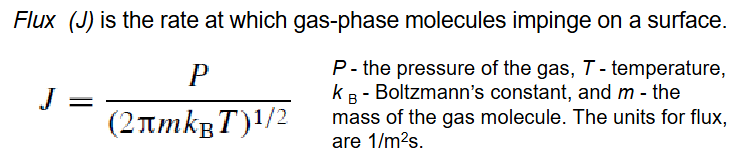
Mean free path (lambda)

Solid vapour reactions, outline the different flow regions
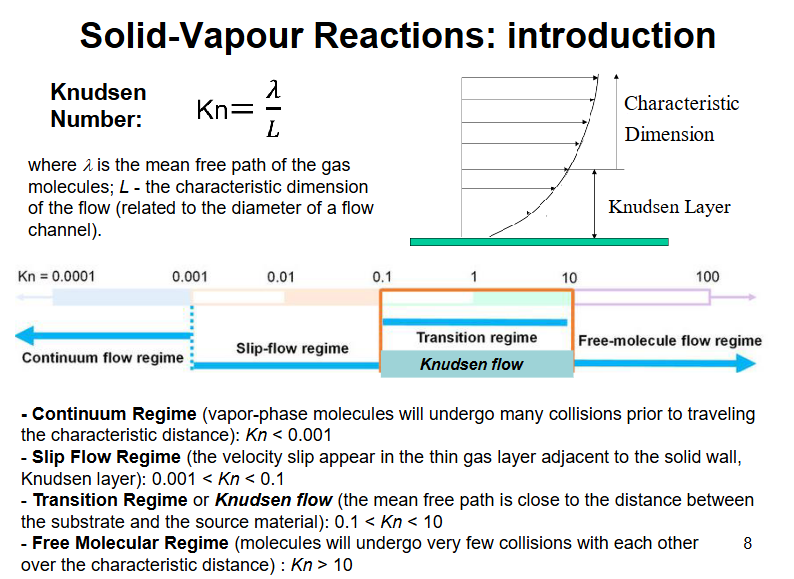
Knudsen / stagnant / boundary layer
Layer of gas flowing close to the wall that slows down significantly due to the proximity to the wall the molecules in the gas heat the wall and therefore slow down themselves.
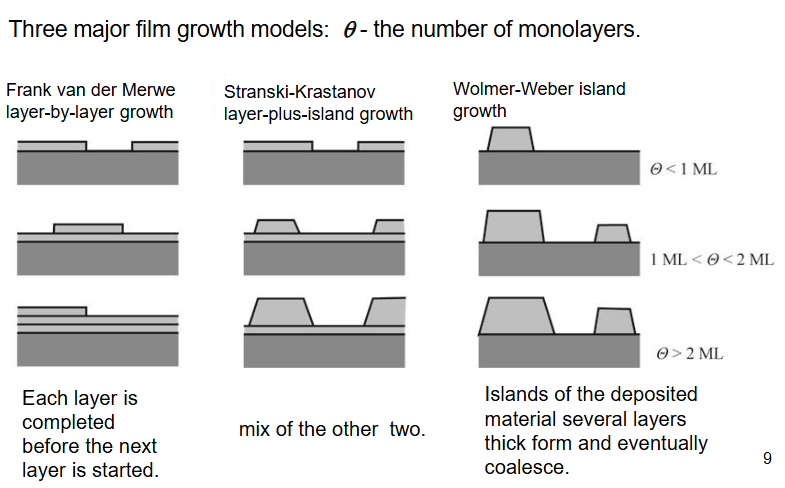
The three major film growth methods with examples
F.v.d.M. silicon on silicon, same lattice parameter and likes to stick to each other (sticks by physi/chemi-sorption then crystal growth them grain boundary growth)
S.K. aluminium oxide on silica, first layer nice w. chemical bonding, oxygen bond. Islands form after due to different lattice parameter between aluminium and silica
W.-W. GaAs on Si has different lattice parameter so it doesn’t like to bond, forms islands
average velocity
sq.rt. of 8kT/(pi*m)
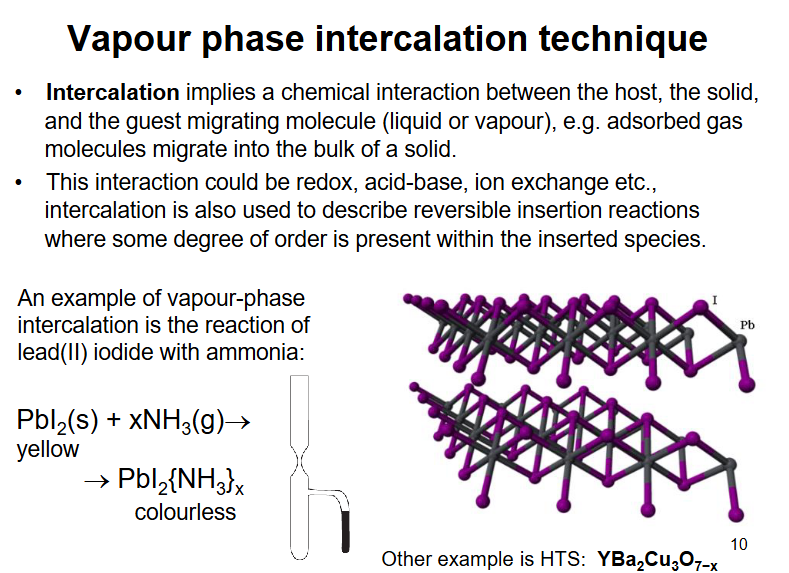
vapour phase intercalation technique
needs porous / layered material to work and the gas needs affinity to the layers otherwise no bonding would occur. ex. lithium through graphite goes to LiC_6 and other ex. on slide
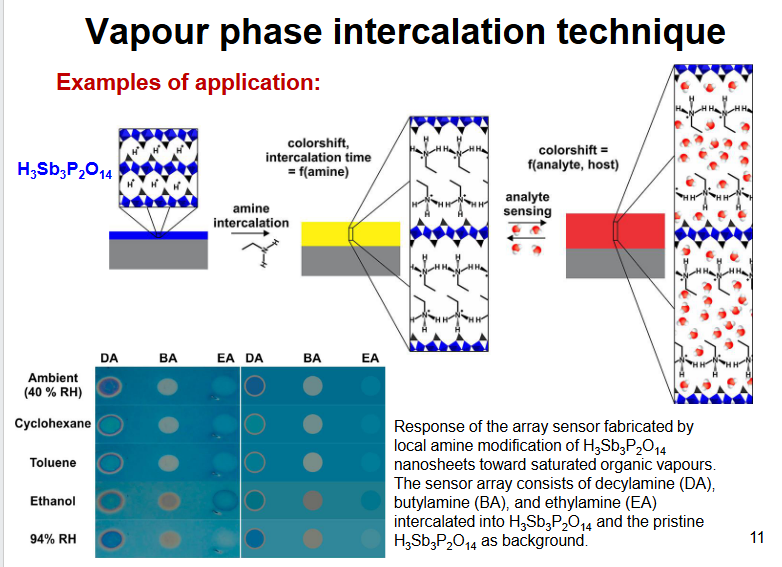
vapour phase intercalation technique applications
H+ protonates amines, expand layer changes colour, then analyte sensing expand layer, change colour, bigger layer longer wavelength so change colour
PVD growth rate
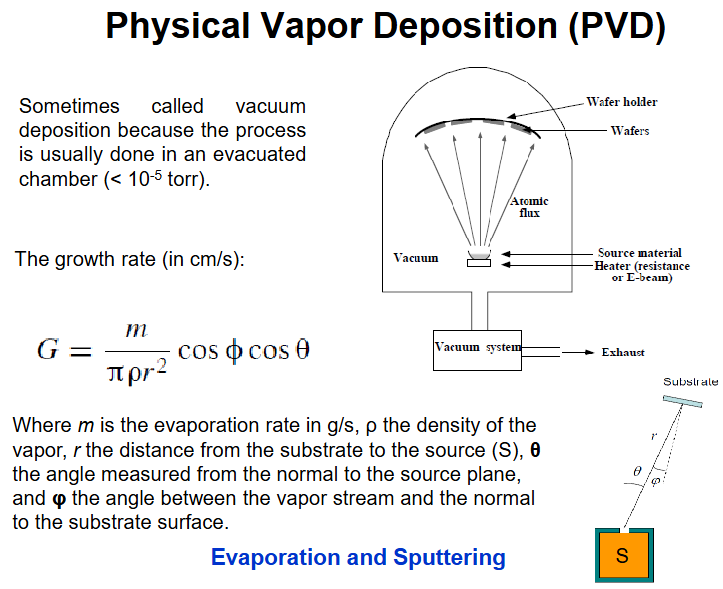
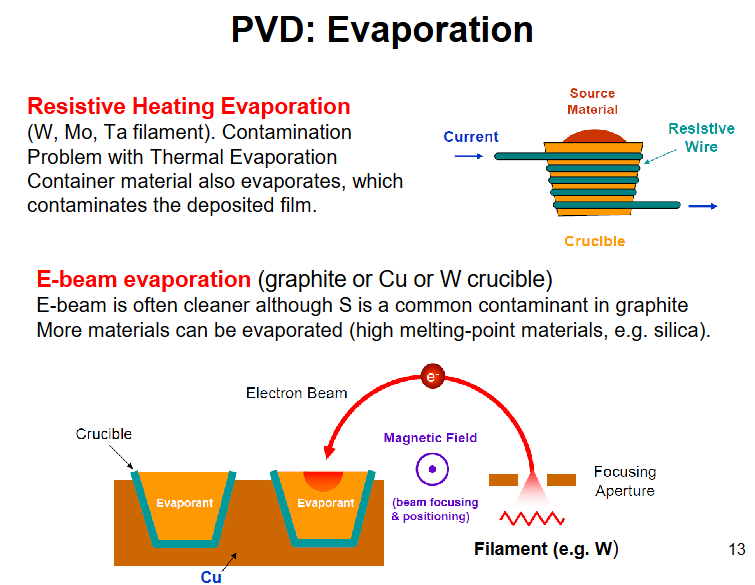
PVD evaporation, 2 types
e-beam, high voltage, gererate e-, focus with magnet at the material in crucible, crucible isnt being heated but needs to be conducting otherwise charging occurs can cause explosion. can even get non-volatile to fly (silica)