BIO 189- Chapter 7: DNA Structure and Gene Function
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
What are nucleic acids?
Polymers made up of nucleotide monomers
What does DNA function as?
Information-bearing molecules of all life on earth
What are the nitrogenous bases of DNA
Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, and Thymine
In RNA, instead of having thymine it has what?
Uracil
Since when was DNA described and when was it’s structure & function confirmed?
1869 and 1950s
What was known about DNA before the 1950s?
Nucleotides were the building blocks and that there were four different nitrogenous bases
Which bases are purines (2 rings)
Adenine and Guanine
What bases are pyrimidines? (1 ring)
Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil
What did Erwin Chargaff discover in 1950?
“Chargaff’s Rule”
Amount of G was around the same amount of C
Amount of A was around the same amount of T
Who were the people that used x-ray crystallography in 1952?
Rosalind Franklin, Raymond Gosling, and Maurice Wilkins
What are the four things that the x-ray crystallography discovered about DNA?
X shape indicted a twisting helix shape
Dots indicated size of one helix turn (34 angstrom)
Indicated how many base pairs per turn (10 bases)
Franklin deduced phosphate groups arranged on the outside of the helix
Who formalized the DNA structure in 1953?
Francis Crick and James Watson
What are the “rails” of a DNA molecule?
Sugar and phosphate groups
What are the “rungs” of the DNA structure?
The paired nitrogenous bases joined with hydrogen bonds
DNA strands have ______ and the strands run ________ to each other
Directionality; anti-parallel
What are the DNA anti-parallel directions
One strand: 5’ to 3’
Other strand: 3’ to 5’
What is semi-conservative DNA replication?
1 parental strand and 1 “new” strand that’s made through base pairing
What are the basic mechanisms of DNA replication?
DNA strands are split apart
Each “old strand serves as template for DNA building enzyme (DNA polymerase)
DNA polymerase reads the template strand and adds the complementary bases as it moves along
What is a genome?
All native DNA inside of a cell and size is not related to complexity
How does all the DNA genomes fit?
“Naked’ DNA wrapped around histone proteins
What do histones coil into?
Chromosomes
Prokaryotes have a _______________ chromosomes with histone like proteins while eukaryotes have _____ linear chromosomes
Singular circular; multiple
What is karyotype?
An image showing all chromosomes from an organism
In sexually reproducing organisms chromones come in what?
Pairs (one from the mother and one from the father)
In humans what are the pairs 1-22 known as?
Autosomes (contain instructions of general life processes)
What does Chromosome 23 determine?
Sex
What is a gene?
A segment of DNA that contains instructions to make a specific functional RNA or protein molecule
In sexually reproducing Eukaryotes, what are chromosomes that come in pairs called?
Homologous chromosomes
What are gene variants called?
Alleles
What do genes dictate?
The RNA and proteins made by an organism’s cells
What does the central dogma do?
Describes the flow of information form DNA to RNA to protein
What are the two phases of the central dogma?
Transcription and Translation
What happens during transcription?
(Occurs in the nucleus); a gene’s DNA sequence is converted into a sequence of RNA nucleotides known as messenger RNA (mRna)
What happens during translation?
(Occurs int he cytoplasm) mRNA molecule leaves the nucleus and finds a ribosome (free or bound) where the mRNA sequence is converted int specific amino acids
What are the three main steps of transcription?
Initiation, Elongation, Termination
In initiation what does the promoter region do? (in transcription)
Acts as a signal for where the gene starts and what strand to use as template
What are transcription factors?
Proteins recruited to promoter and guide RNA polymerase enzyme to bind to template DNA strand at the correct location
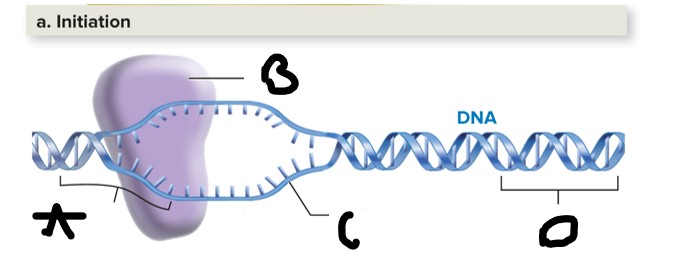
Label Initiation (in transcription)
A- Promoter
B-RNA polymerase enzyme
C- DNA template Strand
D- Terminator
Where does transcription take place and what is it performed by?
In the nucleus and by RNA polymerase
What happens during elongation? (In transcription)
RNA polymerase moves along DNA strand and reads the DNA template, adds complementary RNA to growing molecule
What happens during termination? (In transcription)
RNA polymerase recognizes the termination sequence and releases from the DNA, (specific sequence indicated end of gene) and mRNA is released
Before leaving the nucleus, mature mRNA must be processed from what?
pre-mRNA
How does the processing of pre-mRNA function?
Add mRNA cap: modified nucleotide that’s a recognition signal for ribosomes
Add Poly-a-tail: 100-200 protects mRNA from degradation in cytoplasm
mRNA splicing: segments of RNA are removed and remains are joined together
What are introns?
Segments removed from pre-mRNA= trash RNA
What are exons?
Segments joined together to make mature mRNA
What is splicing?
The process of removing introns and connecting exons from pre-RNA to form mature mRNA
What happens during translation, what is it performed by and where does it occur?
Performed by ribosomes, it converts mRNA code into a polypeptide (protein), and it occurs in the cytoplasm
What is a codon?
3 mRNA bases read by ribosomes, and each is specific for a specific amino acid
The protein code needs at least how many unique amin acids?
20 (3 nucleotides= 1 amino acids—- 4^3= 64 combinations)
What are specialized RNA molecules that carry specific amino acids to the ribosome?
Transfer RNA/ t-RNA
What are tRNA molecules and where are they located?
Short RNA molecules that fold into unique “t” shape, one end binds to amino acids the other end has 3 complementary nucleotides and millions of free tRNA are in cytoplasm
How is the new amino acid bound to the previous amino acid in the polypeptide chain?
Covalently
What are the three steps of translation?
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
What happens during initiation (In translation)?
mRNA cap helps mRNA associate with ribosomes but not to any specific amino acids
Where does translation occur?
Cytoplasm
What are start codon?
Specific codon that starts amino acid incorporation
What is the eukaryotic start codon and what are they the codes for?
AUG and Methionine (met)
What do all eukaryotic polypeptide sequences have?
Methionine
What occurs during elongation (in translation)?
After Met., the next codon recruits appropriate tRNA to enter ribosome, then covalent peptide bonds are made, the tRNA is kicked out
What happens during termination (in translation)?
Stop codons tell proteins where to stop, protein release factors bind to the stop codons and cause ribosomes to release from mRNA
What are polysomes?
Increase protein synthesis efficiency
When multiple ribosomes on a single mRNA what happens?
Massive increase in protein production levels
What regulates gene expression?
Cells; expressing unnecessary genes wastes energy and they have evolved ways to control what is expressed or not
How do Prokaryotes regulate gene expression?
Can turn genes on or off depending on what resources are available
What are operon?
A clustered group of genes related to a specific function that can be turned on or off as needed
What is lac operon?
A group of genes that function to break down lactose sugar but expressed only in the presence of lactose sugar
What do operons contain?
Promotor: Site where RNA polymerase binds
Operator: A DNA sequence between he promotor and the protein coding genes are a regulatory region
Operon Genes: Code that requires proteins
What happens when there’s no lactose?
Repressor proteins bind to the operator and physically blocks RNA polymerase and operon gene expression
What happens when lactose is present?
Lactose binds to the repressor and repressor falls of the operator (RNA polymerase can now transcribe the genes in operon)
What are the six mechanisms that Eukaryotes use to regulate gene expression?
DNA Availability
Transcript factor availability
mRNA processing
mRNA transport from nucleus
RNA Degradation
Protein processing and degradation
In Eukaryotes, there are 6 mechanisms for gene expression regulation, what does DNA Availability mean?
DNA can be tightly bound to histone proteins that prevent gene expression, modifications can open or close off DNA for transcription
In Eukaryotes, there are 6 mechanisms for gene expression regulation, what does Transcription Factor Availability mean?
Proteins bind to promoter regions of DNA and help direct RNA polymerase to gene (no T.F no G.E)
In Eukaryotes, there are 6 mechanisms for gene expression regulation, what does mRNA Processing mean?
Alternative Splicing: removal of certain introns/exons which can have dramatic effects in protein products
In Eukaryotes, there are 6 mechanisms for gene expression regulation, what does mRNA Transport from Nucleus mean?
If mRNA is not specifically transported from nucleus it will not meet a ribosome and will not be translated into protein
In Eukaryotes, there are 6 mechanisms for gene expression regulation, what does RNA Degradation mean?
Enzymes actively degrade RNA in cytoplasm, modifications can change lifespan of mRNA which changes the likelihood of it being transcribed into a protein or not
In Eukaryotes, there are 6 mechanisms for gene expression regulation, what does Protein Processing and Degradation mean?
Proteins can be regulated; some get degraded as they’re transcribed while others are maintained long after production
Proteins can have what type of modifications and what does that mean?
Post-Translational, it increases the functional outcomes of proteins in an organism
The number of genes in a genome underestimates the total number of what?
Unique proteins in the cell (proteome)
What are mutations?
Any unintended changes in the cell’s DNA sequence
What are the types of small-scale DNA mutations?
Insertion and Deletion
Point and substitution
Insertion and Deletion are what type of small-scale mutations?
Frameshift Mutations which cause the reading frame for a protein to be altered
What type of small-scale mutation is point mutation?
Silent mutation which do not change the protein’s amino acid sequence
Genetic code redundancy tolerates mutations in what base position of a codon?
Third base wobble position
What are the types of large-scale mutations?
Deletion, Duplication, Inversion
Translocation
Insertion
When do Spontaneous point mutations occur?
During cell division
What is the first-pass DNA polymerase error rate?
1 wrong nucleotide per 100,000 base pairs
What is the DNA polymerase error rate after proofreading?
1 error per 1 billion base pairs
DNA point mutations become what if not corrected before cell division?
Permanent
What are other causes of mutations?
Mutagens: any external agent that induces mutations
What are the three types of mutagens?
Radiation, Chemicals, and Infectious Agents
What are mutagens that fall under radiation?
UV and X-Rays
What are mutagens that fall under chemicals?
Carcinogens, Processed foods, Cosmetics and Cleaning products
What are mutagens that fall under Infectious Agents?
Viruses and Bacteria
What are viruses?
Very small protein particles that contain genetic material made of either DNA or RNA
What is the function of a virus?
To survive, replicate, and propagate
What are the five stages of viral replication?
Attachment
Penetration
Synthesis
Assembly
Release
What happens during the attachment stage of viral replication?
Virus binds to host cell surface receptors
What happens during the penetration stage of viral replication?
Virus genome enters the host cell (phagocytosis or injection)
What happens during the synthesis stage of viral replication?
The host cell is hijacked to produce millions of copies and provides resources for viral proteins and genome
What happens during the assembly stage of viral replication?
The viral particles assemble, and genetic information moves inside