Week 3 - Neurotransmitters and Neuroplasticity
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Neurotransmitters
Are them substances that are signals from one neuron to another
Stores in vesicles inside the terminal button
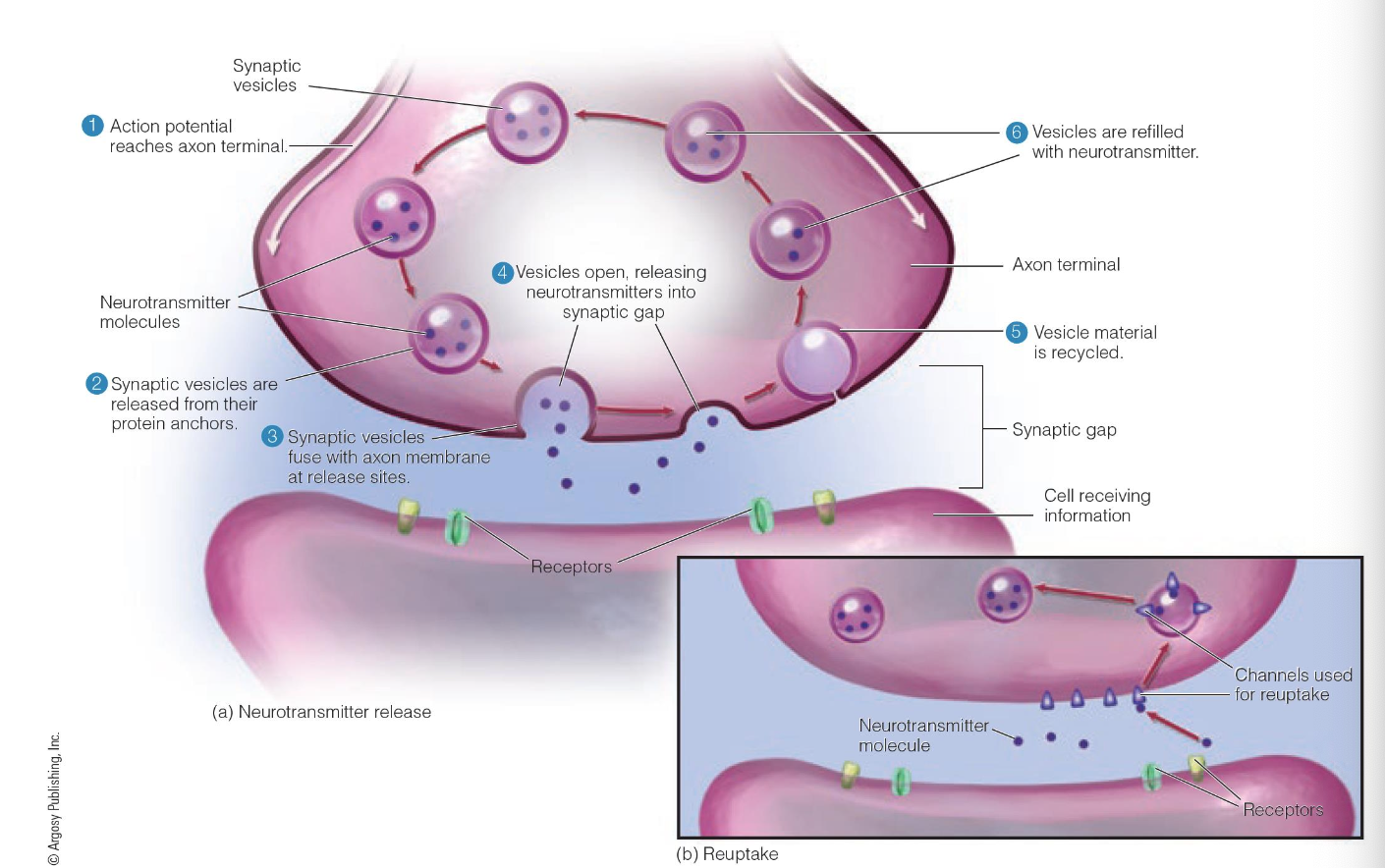
Presynaptic membrane vs postsynaptic membrane
Presynaptic membrane: the membrane of the neuron sending the signal
Postsynaptic membrane: membrane of the neuron that is receiving the signal
The synaptic gap: the gap between the presynaptic and postsynaptic
Neuaortransmittors are not random, must have a particular type of receptor to be able to receive those signals
Vesicles are recycled and reused
Important Neurotransmitters
Glutamate: a primary excitatory neurotransmittor
GABA: Primary inhibitory neurotransmittor: decreases activity in the neuron system
Serotonin: mood, impulse, hunger sleep
Dopamine: reward and motivations, voluntary movement
Acetylcholine: movement: memory, cognition, sleep
Epinephrine and norepinephrine (adrenaline): stress response
How do drugs work? (2 ways it can work, name, definition, how do they do it?, some examples)
Agonists: a chemical agent binds to a particular receptor to mimic the effect of an endogenous neurotransmitter
Endogenous: the natural making of neurotransmitter by the brain
Either increase the release of neurotransmittors or blocks the re-uptake of neurotransmitters
e.g. morphine, cocaine
Antagonists → inhibit the action of an endogenous neurotransmitter
Block the release
Destroy the neurotransmitters
Mimic a neurotransmitter to block the actual neurotransmitter
e.g. beta-blockers (for heart attacks), botulinum toxin (paralyses the wrinkles)