Psychology: Individual Differences and Gender
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are Chromosomes?
Are the packages of DNA that carry our genes
Typically, humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one of each pair provided by each parent
The 23rd pair differs across the sexes and is referred to as the sex chromosomes because the pair determines a person’s genetic sex
What Are the Theories of Gender Development?
Biological Approaches to Gender Development
Behavioural difference in newborns and infants
Evolutionary Psychology Explain Gender Differences
Sexual selection
Male and female members of a species differ from each other because of differences in competition and choice
Competition
Occurs among members of the same sex as they vie for the opportunity to mate with members of the opposite sex
Social Cognitive
Social Role

What Is the Psychology of Gender Differences?
The psychology of gender differences explores variations in mental functions and behaviors between sexes, arising from a complex mix of biology (genes, hormones, brain structure) and culture (socialization, stereotypes, roles). Key areas of difference, often moderate, include aggression (males higher), empathy/care (females higher), communication styles (agentic/instrumental for men, communal/expressive for women), personality traits (e.g., assertiveness vs. warmth), and stress responses (fight-or-flight for men, tend-and-befriend for women). Modern psychology emphasizes these differences are averages, with significant overlap and variation within genders, influenced by how society shapes these innate predispositions.
What Is Sexual Orientation?
Direction of erotic interests; refers to more than just sexual behaviour
Orientations
Straight
Gay
Bisexual
Pansexual
Asexual
“Two-spirit”
Term used by Indigenous people to refer to Indigenous people who identify with nontraditional sexual orientation and gender identity
What Are Different Sexual Behaviours and Practices?
What Constitutes Sexual Behavior?
Infidelity or loss of virginity
Activities involved in reproduction
Arousal and sexual response
Unusually intimate and personal activity as defined by the participants
What is WEIRD Psychology?
WEIRD stands for; Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, and Democratic
Research in psychology has been largely the study of WEIRD people
This WEIRD bias continues to be evident in recent psychological research
We have to accept the research that is done according to and in settings that are WEIRD
What is Sex?
Refers to the properties of people that determine their classification as male or female. In this section we review five physical characteristics used to classify sex, including chromosomes, gonads, hormones, genitalia, and secondary sex characteristics
What is Gender?
Refers to the social and psychological aspects of being female or male
Goes beyond biological sex to include a person’s understanding of the meaning of being male or female
What is Sexuality?
Sexuality is a broad, multifaceted aspect of being human, encompassing our sexual feelings, thoughts, attractions, identities, and behaviors, extending beyond just physical acts to include emotional, psychological, and social elements like gender identity, orientation (who you're attracted to), intimacy, and body image, all unique to each person and evolving throughout life
What are Gonads?
Part of the endocrine system
Glands that produce sex hormones
Generate ova (eggs) in females and sperm in males—the cells used in reproduction
Female gonads are the ovaries
Located on either side of the abdomen
Male gonads are the testes
Located in the scrotum, the pouch of skin that hangs below the penis
What are Hormones?
The hormones estrogen and progesterone are higher in females and the hormones called androgens
The most common is testosterone - are higher in males
In females, androgens are produced by the adrenal glands
In males some of the androgens that are produced by the testes are converted into estrogens
What are Variances in Sexual Development (VSD)?
Congenital conditions in which the development of chromosomal, gonadal, or anatomical sex is atypical
“Congenital” means these conditions are present from birth
An infant with a VSD might have genitals that are not typical, or their genitals may appear to be female or male when the child’s genes indicate the opposite sex
What is Gender Identity?
Is an individual’s sense of belonging to the male, female, or an alternate gender.
What is Gender expression?
Refers to how individuals present themselves in terms of their behaviours, interests, and appearance
In dimensions related to gender and especially to the continuum from femininity to masculinity
What is being Transgender?
Refers to experiencing one’s psychological gender as different from one’s biological or “natal” (meaning “at birth”) sex
Transgender individuals can be genetically and anatomically males (or females) who identify as females (or males)
Caitlyn Jenner was lauded for her courage in coming out as transgender
What aspects are part of the Transgender experience?
Gender Dysphoria
Refers to a person’s discomfort with their natal gender
Transition for transgender
Individuals involves gradual stages that move from reversible treatments to permanent ones
Gender affirming surgery
Sex reassignment surgery
What influences Sexual Orientation?
Orientation is influenced by:
Genetics
Prenatal hormones
Brain structures
Social factors (gender non-conforming behaviour)
What is Pedophillic Disorder?
It’s a psychological disorder in which an adult or an older adolescent sexually fantasizes about or engages in sexual behaviour with individuals who have not reached puberty
Pedophilic disorder is more common in men than women
What are the Paraphllic Disorders?
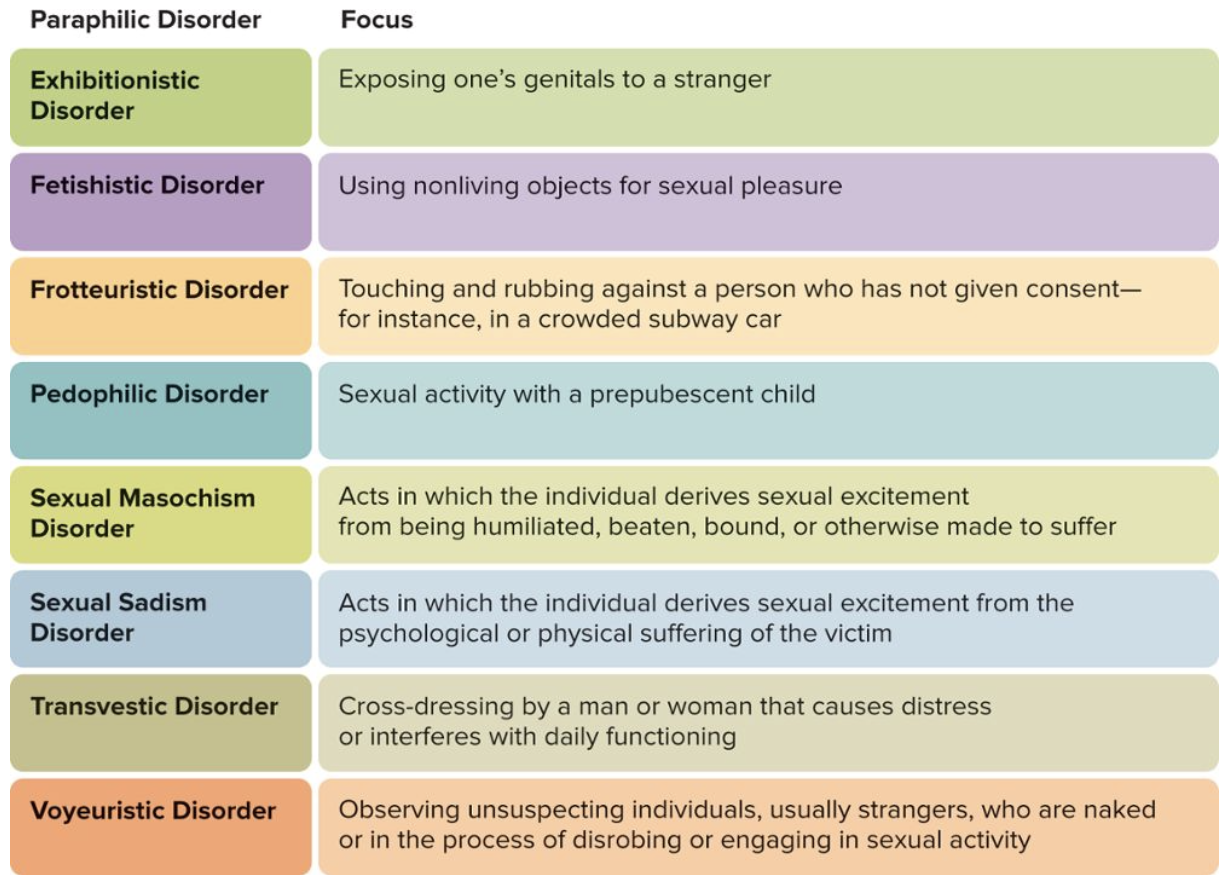
What’s a Disorder?
A disorder is a disruption or abnormality in the normal physical or mental functioning of the body, causing significant difficulty, distress, or impairment in daily life, often without a clear, single cause like an infection, and can involve emotional, behavioral, or functional issues.
What is a Fetish?
A fetish is an object that arouses atypical sexual interest and desire, such as a piece of clothing or body part that is not usually associated with sexual gratification.
The most common fetish is soiled panties/ underwear.
What are some disorders of Sexual Desire/ response?
Female dysfunction in arousal
Erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation
What are the stages of our sexual response?
William Masters and Virginia Johnson (1966)
Four phases: excitement, plateau, orgasm, and resolution.
Excitement
Plateau
Orgasm
Resolution/Male Refractory Period
Helen Singer Kaplan (1974)
Added Desire
To Masters and Johnson’s four phases of sexual response
What are the Orgins of Sexual Orientation?
Probably not a single cause
Within-group variation
Research challenges such as recruitment
Considering more than just straight or gay orientations
Where is the differentiation between Chromosomes in females vs males?
On the 23rd pair (bottom right)
Males
Have one x and one y chromosome—the latter looks similar to an upside-down Y
Females
Both sex chromosomes are alike and are called X chromosomes because they each look like an X.
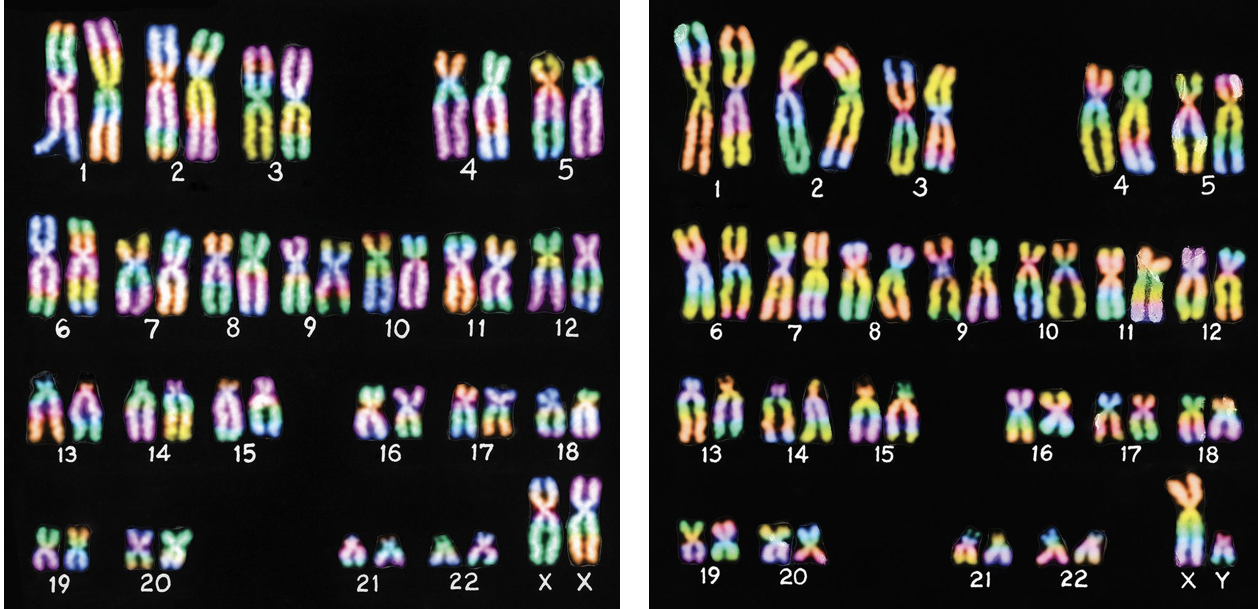
Can a man get pregnant?
Depends on your definition of a man. If you notion of what a man is people who have XY chromosomes then no as there is are genetic disorders such as Swyer Syndrome which is a rare condition where individuals have XY (male) chromosomes but develop female external genitalia and internal structures like a uterus, because their gonads (sex glands) fail to develop into functional testes or ovaries, instead becoming underdeveloped "streak gonads". Because of this where someone with 46 XY (Swyer syndrome) chromosomes can have a child.
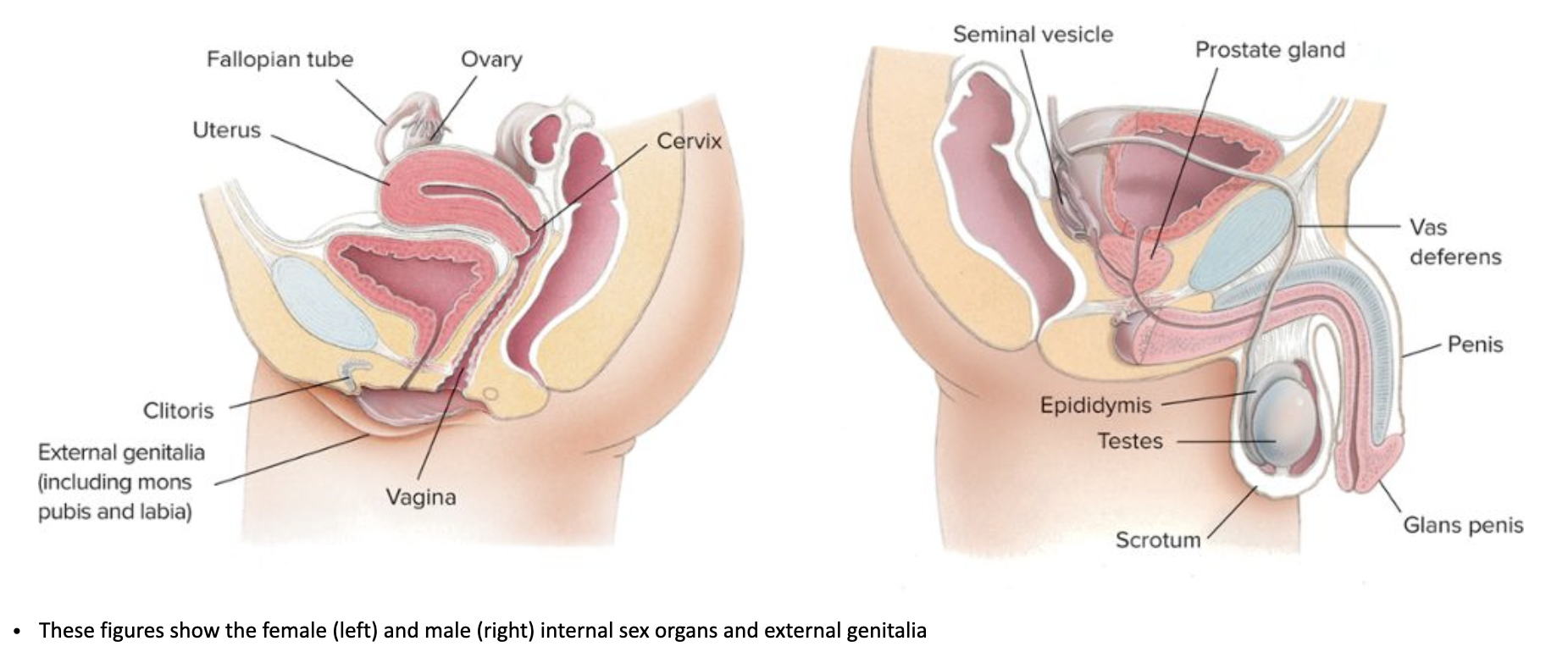
Where is the differentiation between external genitalia in females vs males?
Hormones: Fetal testicular androgens (like testosterone) drive the male pathway; their absence leads to the female (default) pathway.
Fusion/Separation: Folds fuse in males (penis, scrotum) but remain separate in females (labia).
Growth: Phallic growth is prominent in males, while female structures remain smaller externally.
What is Puberty?
Puberty is the natural process where a child's body transforms into an adult body, becoming capable of reproduction, marked by significant hormonal, physical, and emotional changes like growth spurts, hair growth, development of sexual organs, and menstruation in girls
Why are girls experiencing their period at younger ages?
Recent studies have shown that girls are experiencing their period at younger agesthan ever, around the ages 8-9. A viable reason for this is that puberty follows BMI level, the larger BMI the earlier you will have your period as weight impacts your hormones and your ability to lose weight (insulin resistance). This follows evolutionary theories on gender development as gaining weight evolutionarily speaking means you have stable access to food.
Other contributors include stress, changes in diet (more processed foods/sugar, less vegetable protein), urban living, socioeconomic factors, and possibly genetics, leading to earlier hormonal activation and puberty.
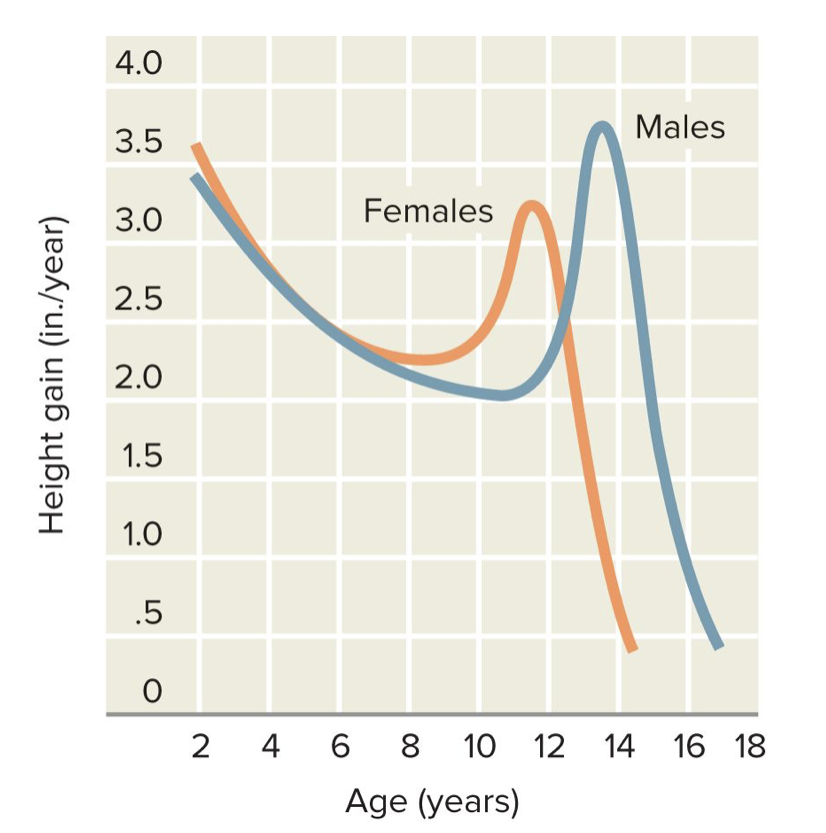
Where is the differentiation in puberty in females vs males?
On average, the pubertal growth spurt begins and peaks about two years earlier for girls
Girls (starts at age 9, peaks at 11½)
Boys (starts at age 11½, peaks at 13½)
What are gender identities?
Cis-gender;
Female; woman, girl, etc.
Male; man, boy, etc.
Intersex: someone ;s biological categorizations of sex that does not fit within the female and male definitions of gender.
There are people who are intersex but can identify as a man, woman, neither, both, etc.
Transgender;
Non- binary: may identify or express their gender as both male and female or as neither
Genderqueer.
What is being Androgynous mean?
Having attributes that are typically associate with both genders
People who are low on both dimensions are referred to as undifferentiated