Herpetology
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
herpetology
study of amphibians and reptiles (polyphyletic)
Polyphyletic
group of organisms that have been grouped together but do not share an immediate common ancestor
Batrachology
study of amphibians
Gladwyn Kingsley Noble
textbook on amphibians
KP Schmidt
curator of american museum of natural history
checklist of reptiles + amphibians of NA accepted by itchyologists + herp society
notes on snake bite symtpoms
Roger Conant
first comprehensive field guide on herps in eastern US
Hobart Smith
major herpetologist, manuscripts on fauna
James R Dixon
300 manuscripts, texas herpetofauna descriptions
Mary Cynthia Dickerson
described 20+ new reptile species
Joan Beauchamp Procter
first curator of reptiles at the london zoo
Bernard Martoff
chair of zoo department at ncsu, first guide to herps of carolinas
type(s)
refers to a specific specimen
holotype
museum type specimen used to describe/represent a species
neotype
replaces a holotype if missing
syntype
multiple specimens to describe a species, no single representative
paratype
holotype + additional speciments
allotype
holotype of opposite sex
Superclass Tetrapoda
arise during devonian ~385 mya from
Actinistia
coelocanths (sarcopterydians)
2 extant species (latimeria)
Dipnoi
lungfish (sarcopterydians) —> evolved to tetrapods based on skeleton and presence of choana
lungs homologous to first tetrapods
6 extant species
choana
nostrils connect nasal cavity to mouth - allows for closed mouth breathing

Eusthenopteron
Class sarcopterygii
385 mya - northern hemisphere
skeletal fin features = appendicular bones
ambush predator in shallow, heavily vegetated, low o2 water
Romer’s Gap
360-345 mya lack of fossils described by Alfred Romer

Panderichthys
Class sarcopterygii
380 mya - Latvia
best known transitional prototetrapod
flat head, long snout, dorsally positioned eyes
dorsoventrally flattened tetrapod-like humerus
fin rays (not digits)
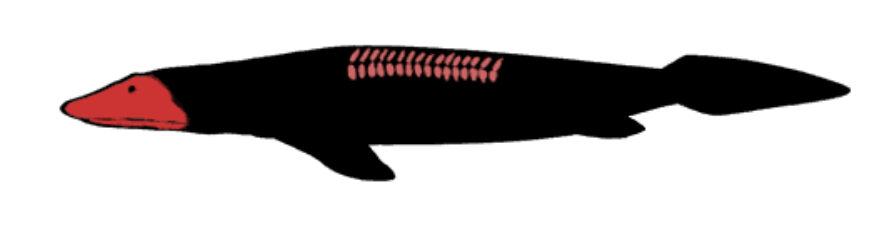
Elpistostege
Late devonian - Canada
Skull + backbone fragments
Most close to Tiktaalik
estuarine environment
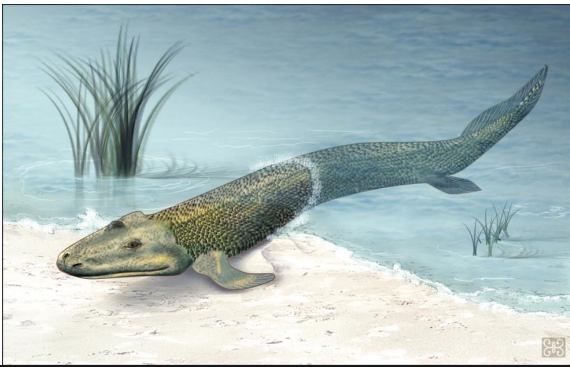
Tiktaalik
375 mya - Canada
significant fossil discovery in 2004
wrist bones, arm like structures, flat body, revised dorsal eyes, wide skull + mobile neck, pectoral girdle separate from skull

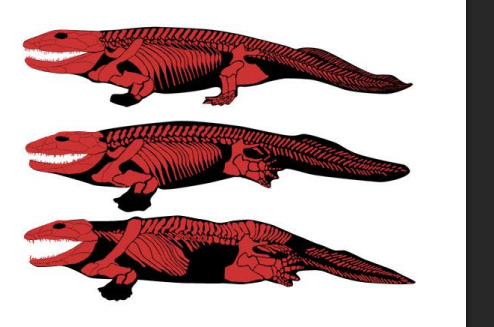
Acanthostega
365 mya - Greenland
best known tetrapod, changed early understanding of evolution
had 2/3 of 41 unique tetrapod characteristics
freshwater rivers
8 digits (first digits) - came before walking on land
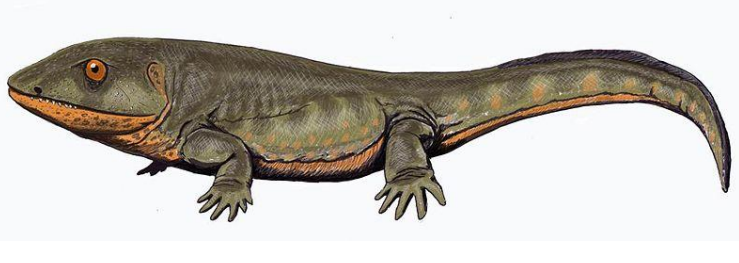
Ichthyostega
375-360 mya - Greenland
original transitional fossil
hind limb with 7 digits
primarily rely on lungs, completely leave water temporarily
freshwater streams
Tulerpeton
365 mya - Russia
no gills, less aquatic, marine but capable of terrestrial movement
6 digits
more robust petoral girdle
5 Pre-Adapted features to transition
respiration
movement
feeding
skin
sense organs
Respiration Adaptations
lungs appear in bony fish evolution, predecessors to swim bladder
led to buccal and costal pumping mechanisms
buccal pumping
using muscles to push air down
Costal pumping
changing volume of thorassic cavity to create negative pressure
Movement adaptations
limbs —> move to land
rowing —> bottom walking required bending of fin-limb
fin rays lost, replaced by short, robust digits
pectoral girdle disconnected from skull (mobile neck)
vertebral column more robust
limb girdles become supportive
Feeding adaptations
head movement (predation)
shallow water or out of water advatage
elongate snout + jaw
Skin adaptations
increased epidermis layers
increased keratinization
protect against abrasian, desiccation
Sense organ adaptations
lateral line + electric organ function only in water, lost except in larval stage of aquatic species
hearing and middle ear structure appeared
eye structure for aerial vision
dual channel nasal passages for respiration and olfaction
Biogeography
distributions of organisms across the planet and through timefather of
Alfred Russel Wallace
father of biogeography, theory of evolution + natural selection, developed idea separate from Darwin
Ecological Biogeography
geographic patterns in community structure
descriptions of biomes + regions = ecological categories
Historical biogeography
relationships + origins of taxa, reinvented in the late 20th century (dna discovery)
molecular clocks, phylogeography
emphasizes how phylogenetic affinities relate to distributional pattern history of a species/group
Cladograms
vicariance (change) - an ancestral species' range splits into separate parts due to a new physical barrier
dispersal
area cladograms - geographical distributions
Amphibian and reptile biogeography
plate tectonics
major divergence since break up of pangaea (200 mya)
late cretaceous (100-66mya) amphibians may have experienced diversification inconsistent with current tectonic theory
Order Anura species + hotspots
South america, west africa, eastern US
7935
Amphibian characteristics
ectothermic
pectoral girdle not attached to skull
pectoral+pelvic anchor arms and legs
vertebral column suspended between girdles, requiring special joints for stability and flexibility
Amphibian reproduction
most lay eggs in/near water
~30 different modes of reproduction
most undergo metamorphosis (larvae with gills, adult w lungs)
direct development - frogs, salamanders, caecilians
live young (ovoviparous, viviparous) - frogs, salamanders, caecilians
Amphibian respiration
lungs primitive, lack a true diaphragm, use buccal pumping
cutaneous
lunglessness - lost/vestigal, one frog, salamander family plethodontidae
Amphibian nervous system
brain less developed but still advanced
limb-opercular - vibrations felt through legs + sent to ear
lateral line in most tadpoles
pair of sensory papilla in inner ear
double auditory transmission channels in the middle ear
columnar (air filled sac in anurans)/stapes
opercular made of protein senses vibrations
amphibian vision
color, depth of focus
4 specialized receptors in the retina
green and red appearing rods (anurans only have green) sight of G+B
sensitive to all wavelengths
register only presence/absence of light
single + double cones (for movement), color vision/sensitive to narrow wavelengths
amphibian skin
2 layers: epidermis and dermis
epidermis
stratum corneum (outermost) (ecdysis)
keratinization present
stratum germanitivum
dermis
location of pigment production and glands
stratum spongiosum (DCU)
stratum compactum
Chromatophores
pigment-producing cells
dermal chromatophore unit in stratum spongiosum
Xanthophores: yellow-red
iridophores: white-blue
melanophores: black-red
fixed shape
color change = dispersion or aggregation of granules within
Mucous glands
dermis
moistens skin, optomizes oxygen exchange, protection from desiccation
Granular glands
dermis
secretes poison (paratoid)
poison typically requires a precursor
lipid glands
dermis
waxy coating (phyllomedusa sunscreen)
hatching glands
dermis
around snout, secretes enzymes to break down egg casing in larvae
hedonic glands
dermis
caudata and some reptiles
pheremones for courtship
merkel glands
mechanoreceptors ?
flask glands
salt and water balance ?
ecdysis
skin shedding
stratum corneum only
Caecillian teeth
pedicellate (sit on pedestal)
bicuspid
evolution of amphibia
upper mississippian/lower pennsylvanian fossils reappear (335mya)
12+ clades - anthracosaurs
amniotes
lack amniotic membrane
temnospondyli
“cut vertebrae”
vertebrae divided into 3 parts
possibly ancestors of modern amphibians
wide range of environments / every continent
lepospondyli
early amphibians/reptiles? polyphyletic?
triassic
250-200 mya
7 amphibian groups (including lissamphibia)
small to large
mostly aquatic
most disappear by mid jurassic
fossils say frogs came before caecilians
triadobatrachus
oldest true frog
250 mya
madagascar
Order Gymnophiona (apoda)
diverged first - poor fossil record
10 families, 231 species
pantropical distribution - south america, australia
majority fossorial except typhlonectidae (aquatic)
no limbs/limb girdles
tail reduced or absent
no ear openings, but do have collumella bones (stapes)
annuli present - ring-like divits in skin - segments with single vertebrae
paired tentacles between eyes and nostrils
smell derived from tear duct + extrinsic eye muscles
eyes vestigial and skin covered - sense light vs dark
dermal scales (often) layers of fiber tissue covered by mineralized nodules
vertebrae are amphicoelous
skull heavily ossified - aids in digging/burrowing
dual jaw closing mechanism
Order Caudata species + hotspots
828
North carolina, Eastern US
Order Gymnophiona species + hotspots
231
South America
Subclass Lissamphibia
~9k species
~8k assessed by IUCN
41% threatened
Salamanders most threatened (agriculture)
monophyletic
an organism and all its descendants
paraphyletic
an organism and some of its descendants
Eocaecilia
Earliest caecilian fossil
200 mya jurassic
legs, good vision
Amphicoelous
concave on anterior and posterior side of centrum (allows movement in all directions)
concertina and undulatory locomotion
gymnophiona dual jaw mechanism
masseter adductor mandibulae pulls lower jaw up
masseter interhyoideus posterior pulls down on processus retroarticularis (used for extra help, unique to this order, necessary bc of ossified skull)
Expatation
existing structure develops a new feature
Order caudata (urodela)
10 families
holoarctic with exception of some plethodontidae in neotropics
well developed tails, cylindrical/elongate bodies
distinct head, well developed limbs
reduced skull elements
model systems for regeneration
varied reproductive models (cryptobranchidae + sirenidae external fert)
derived lineages (internal fert, spermatophore deposited by male, collected with female cloaca, eggs deposited in damp areas)
external development (mostly directly to juvenile, some via larval stage)
heterochrony
Karaurus
first true salamander (caudata)
150 mya
Major synapomorphies of caudata
ossification sequence of skull
remodeling of palate during metamorphosis
absence of middle ear/cavity (only have a few ossicles)
presence of gill slits/external gills in aquatic larvae
heterochrony
change in timing of developmental events
Neoteny
larval appearance with reproductive maturity - somatic development slowed down
paedomorphosis
retention of ancestral juvenile traits in ontogenic stages of descendants
paedogenesis
speed up of reproductive, somatic development stays the same
ontogeny
development of organism from zygote to adult
obligate neoteny
organism will not metamorphose in nature due to external conditions or stimuli
inducible obligate neoteny
organism can be forced to metamorphose through manipulation of thyroid in a lab
facultative neoteny
may metamorphose in nature due to external stimuli (predators, drying of environment)
thyrokine
hormone that induces metamorphosis, produced by pituitary gland
Sirenidae
6 species
coastal southeastern north america and mississippi river valley
aquatic, muddy substrates with dense vegetation
moderately slender, eel-like
small forelimbs, hind and pelvic girdle absent
up to 0.9 m total length
all neotenic (obligate): external gills, gill slits, no eyelids
costal grooves present, nasiolabial absent
lungs present but small
fert presumed external
females lack spermathecae, males lack repro glands in cloaca
interventicular septum present in heart (almost 4 chamers, separates oxy and deoxy blood)
Cryptobranchidae
suborder cryptobranchoidea
6 species
asiatic giant salamanders, hellbenders
east-central china, japan, app + ozark mntns in US
clear, cold, mountain streams - aquatic
largest living salamanders
short, well developed limbs
heavy, laterally compressed tail
neotenic obligate traits
almost all respiration through skin → wrinkly
no costal grooves or nasolabial
lungs present but vestigal
external fert, females lack spermathecae
lack typical courtship displays
Ambystomatidae
suborder salamandroidea
33 species, 1 genus
north american to southern rim of mexican plateau
mole salamander
mostly terrestrial, return to water for repro
forest floorplains - upland forests
heavy bodied and tailed
4 short, well developed limbs
adults lack gills + slits
moveable eyelids
inducible obligate or facultative
costal grove present, nasiolabial absent
well developed + functioning lungs
internal fert
males have 6 sets of cloacal glands
courtship present
winter breeders
Salamandridae
103 species, 21 genus
holoarctic - europe, eastern to central russia
aquatic to terrestrial, most return to water for repro
less than 200 mm
slender to robust bodies
limbs well developed and moderately short
most adults lack gills/slits
moveable eyelids
eastern newt has triphasic life cycle: aquatic larvae, terrestrial efts, aquatic adults - may remain neotenic
costal grooves + nasolabial absent
lungs present and functional
internal fert, males have 5 sets of glands
courtships
more granular/rugose skin due to abundance of poison glands
most toxic of all salamanders
proteidae
6 species, 2 genus
eastern half of NC, eastern adriatic coast of europe
olms, mud puppies, waterdogs
aquatic
moderately robust bodies, short + well developed limbs, laterally compressed tails
obligate neoteny
external gills
costal and nasolabial grooves absent
lungs present but small
internal fert, males 6 sets of glands
Some surface dwellers, some cave dwellers, one in groundwater systems
amphiumidae
southeastern us
heavy bodied, tiny weak limbs
aquatic, eel like
direct internal fert, 5 sets glands
obligate neotenic - lose external gills during partial metamorphosis
eyelids and tongues absent
costal grooves present, nasolabial absent
lungs present
courtship, females protect eggs
plethodontidae
433 species, 25 gen
americas, southern canada to southwestern brazil, southern europe and korea
lungless salamanders - lungs absent
25-320 mm
diversity of body shapes, all have 4 limbs
adults lack gills and gill slits, have moveable eyelids, except in paedomorphic taxa
costal and nasolabial present
internal fert, 6 sets of glands
courtship
4 subfamilies
Order Anura (salienta)
cosmopolitan except extreme northern latitudes
geroabtrachus 290 mya in texas
triadobatrachus 250 mya (triassic) madagascar
body form evolved for saltatory movement
short, tailless body, broad flat heads, long muscular hind limbs
external fert, few exceptions, males amplex females, cloacae juxtaposed to ensure fert
indirect dev common, direct also widespread
major reorganization of anatomy and physiology during metamorphosis
contrasting body form + lifestyle partially explain lack of neoteny
taxonomy under rapid growth + change
inguinal amplexus
grabs hips
axillary amplexus
grabs shoulders