Language Acquisition - Test 2
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Voice Onset Time (VOT)
the amount of time that elapses between the bursts of air and when the vocal folds in the larynx start to vibrate.
What was the finding of the HAS technique for Categorical Perception in Infants?
when 40 msec was introduced to the child, their sucking rate increased
when there was a change in 40 msec into 60 msec there was no change since 40 and 60 VOT sounds the same.
Draw the VOT scale:
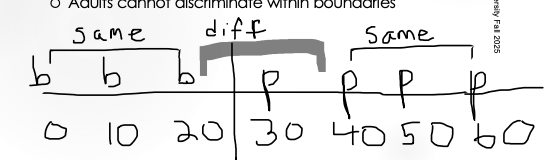
What was the finding between lower SES kids and higher SES kids?
by 3 years old higher SES children had heard 30 million more words than lower SES kids.
by 3 years higher SES children had 1000 words and lower SES kids had 500.
higher SES kids were exposed to more words and richer vocab.
What was some criticisms of Hart and Risley (1995) study (SES)?
ignores variation within SES groups
does not take into account speech from other caregivers
doesn’t take into account ‘overheard’ speech
BUT “quantity” doesn’t matter, “quality” matters.
Why do Infants prefer infant directed speech?
they like everything about it, especially the pitch contour that occurs.
what is the benefit of infant directed speech?
prosodic bootstrapping (bringing the child into language acquisition
accessible content
Syntactic Bootstrapping
cues to identify nouns and verbs
Prosodic Bootstrapping
intonation and pausing - phrase and clause boundaries
stress differences for content and function words
stress difference for nouns and verbs.
What is the maternal responsivity in environmental supports?
mothers treat babies as conversation partners.
language skills of infants wih responsive communication partners are more advanced.
Components of Language: Form
phonology, morphology, syntax
5 stages of Prespeech Vocal Development
Reflexive Crying and Vegetative Sounds (birth)
Cooing and Laughter (2 months - 16 weeks)
Vocal Play (4 months)
Reduplicated Babbling (6-9 months)
Non Reduplicated Babbling (12 months)
Why is the stages of pre speech vocal development universal?
all infants in different cultures go through these stages.
Components of Stage 1 of Preschool Vocal Development
sounds: vibration and stop/start airflow
crying: some vowel-like sounds
vegetative sounds
Components of Stage 2 of Preschool Vocal Development
sounds: single long vowel - series of vowels sounds strung together separated by intakes of breath, back vowels, some back consonants.
learned through social interaction
Components of Stage 3 of Preschool Vocal Development
range of vocal qualities; loud + soft, high + low, bilabial trills, sustain vowels, marginal babbling
also known as the experimental phase because the baby is starting to experiment with their sounds.
Components of Stage 4 of Preschool Vocal Development
sequences of identical CV syllables with adult-like timing
environment is important
Components of stage 5 of preschool vocal development
syllable strings with varying consonants and vowels
greater range of consonants and vowels'
jargon
jargon
string of sounds and syllables uttered with rich variety of stress and intonation.
mimics adult conversation
vegetative sounds
sounds accompanied by biological functions i.e., breathing, eating, sneezing, etc.
Movement through Vocal stages is due to:
Physical growth of vocal tract, oral cavity, head and neck
Nervous system maturation
Experience: 3 part
being exposed to the speech of other ex. babbling drift
hearing themselves talk (their own onset - deaf babies do not get these babbling)
social feedback/interaction
parental responsivity
the more the parents responds to the babbling the more the baby will continue to babble
protowords + what does it show
“invented” words used recurrently with an intended meaning (ex. ‘na’= give)
shows: voluntary control vocalization + recognition that sounds have meaning
Factors that influence Order of Acquisition
Motor complexity - stops sounds vs. fricative and affricates
visibility - front sounds (bilabial and alveolar)
frequency
functionality
What does word accuracy depend on?
word position
neighbouring sounds