radiographic anatomy test #1
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
Anatomical study
Measuring an organ's size, shape, & weight; studied in dead specimen; involves dissection, observation, and directional terms; static (still-not moving). Example: Weighing a kidney during a transplant surgery procedure.
Physiological study
Often study in living subjects; involves chemistry principles, physics principles, observation of a part in motion or in function, experimentation; dynamic (moving-motion). Example: Measuring the acid content of the stomach.
The Principle of Complementarity of Structure and Function
Function always follows structure; both are needed to have a properly functioning body part; they complement each other.
Anatomy
The study of internal and external structures of the body and their relationships.
Physiology
The study of how organisms perform their vital functions.
Microscopic Anatomy
Structures cannot be seen without magnification.
Gross (Macroscopic) Anatomy
Structures can be seen with the human eye.
Cytology
The study of cells.
Histology
The study of tissues.
Surface Anatomy
The study of general form and superficial markings.
Regional Anatomy
The study of specific body areas.
Systemic Anatomy
The study of organ systems.
Developmental Anatomy
The study of changes in the body from conception to physical maturity.
Medical Anatomy
The study of anatomy during an illness.
Radiographic Anatomy
The study of anatomy using medical imaging techniques.
Surgical Anatomy
The study of anatomy during surgery.
Cell Physiology
The study of cellular functions.
Special Physiology
The study of the function of a specific organ.
Systemic Physiology
The study of the functions of organ systems.
Pathological P
Study of the effects of diseases on organ or system functions.
Hierarchy of structural organizations
Chemical (molecular) level, Cellular level, Tissue level, Organ level, Organ system level, Organismal level.
Atoms
Smallest unit of matter.
Molecules
Smallest subdivision of a substance.
Organelles
Structures within cells that perform specific functions.
Cells
Organelle's structural/functional units.
Tissue
Groups of similar cells that perform a specific function.
Organ
A structure composed of two or more tissue types that performs a specific function.
Organ System
A group of organs that work together to perform complex functions.
Organism
The highest level of organization, a living being.
Integumentary System
Includes hair, skin, nails; protects internal organs from drying out and senses pain, pressure, and temperature.
Skeletal System
Includes bones, joints, cartilages; protects, supports, moves, provides levers for movement, mineral storage, and blood forming (bone marrow).
Muscular System
Includes skeletal muscles; moves the limbs and other parts of the skeleton and produces heat.
Nervous System
Includes brain, nerves, spinal cord, sensory receptors; fast-acting control system of the body that helps maintain homeostasis.
Endocrine System
Includes glands such as pituitary & thyroid; regulates growth, reproduction, nutrient use, and directs long-term responses to change.
Cardiovascular System
Includes heart & great vessels; pumps blood, carries O2, exchanges CO2, nutrients, and wastes.
Lymphatic System
Includes thoracic duct, lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, spleen; disposes of debris and is part of the immune system.
Immune System
Includes thymus, lymph nodes, red bone marrow, spleen, lymphocytes; protects the body and destroys bacteria & tumor cells.
Respiratory System
Includes nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus, lungs, alveoli; removes CO2 from the blood.
Digestive System
Includes oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus; breaks down food for nutrients.
Urinary System
Includes kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra; rids body of nitrogenous wastes and eliminates excesses.
Reproductive System
Male: seminal vesicles, prostate gland, vas deferens, testis, scrotum, penis; Female: ovary, uterine tube, uterus, vagina; allows for conception & child bearing.
Maintenance of Life: Organization
Systematic arrangement of the body systems.
Metabolism
All chemical reactions that occur in the body; waste products are excreted.
Catabolism
Breaks down complex substances into simple ones.
Anabolism
Builds up simple substances into complex ones.
Responsiveness
Irritability; ability of sensing stimuli and then reacting to it.
Movement
Movements caused by the muscular system.
Reproduction
Reproduces offspring.
Growth
An increase in size.
Differentiation
Developmental process by which unspecialized cells change into specialized cells.
Respiration
Exchange of O and CO2 between cells and the external environment.
Digestion
Processing of breaking down ingested foodstuffs to provide nutrients.
Excretion
Removing excess wastes.
Maintenance of boundaries
Keeps things inside that are supposed to be inside and things outside that are supposed to be outside.
Nutrients
Needed for energy and cell building.
Carbohydrates
Major fuel for body cells.
Oxygen
Needed for chemical actions which release nutrients.
Water
60-80% of total body weight.
Heat/Temperature regulation
Needs to be in a normal body range.
Atmospheric pressure regulation
Breathing and exchange of O2 and CO2 in the lungs depend on atmospheric pressure.
Homeostasis
A state of body equilibrium or the maintenance of a stable internal environment of the body.
Negative feedback
Turns off or reduces the original stimulus (e.g., body temperature, heart rate, breathing rate).
Positive feedback
Enhances the initial stimulus, leading to an enhancement of the response (e.g., blood clotting and labor contractions).
Homeostatic imbalance
Things 'out-of-wack'.
Thoracic cavity
Located in the chest.
Abdominal cavity
Located in the abdomen.
Pelvic cavity
Located in the pelvis.
Diaphragm
Separates Thoracic & Abdominal cavities.
Peritoneum
Separates Abdominal & Pelvic cavities.
Mediastinum
Separates right & left pleural cavities in the chest.
Cranial cavity
Contains the skull and brain.
Vertebral cavity
Also known as the spinal cavity.
Oral cavity
Contains the mouth.
Nasal cavity
Contains the nose.
Orbital cavity
Contains the eye.
Middle Ear cavity
Contains structures for hearing.
Synovial cavity
Contains joint spaces.
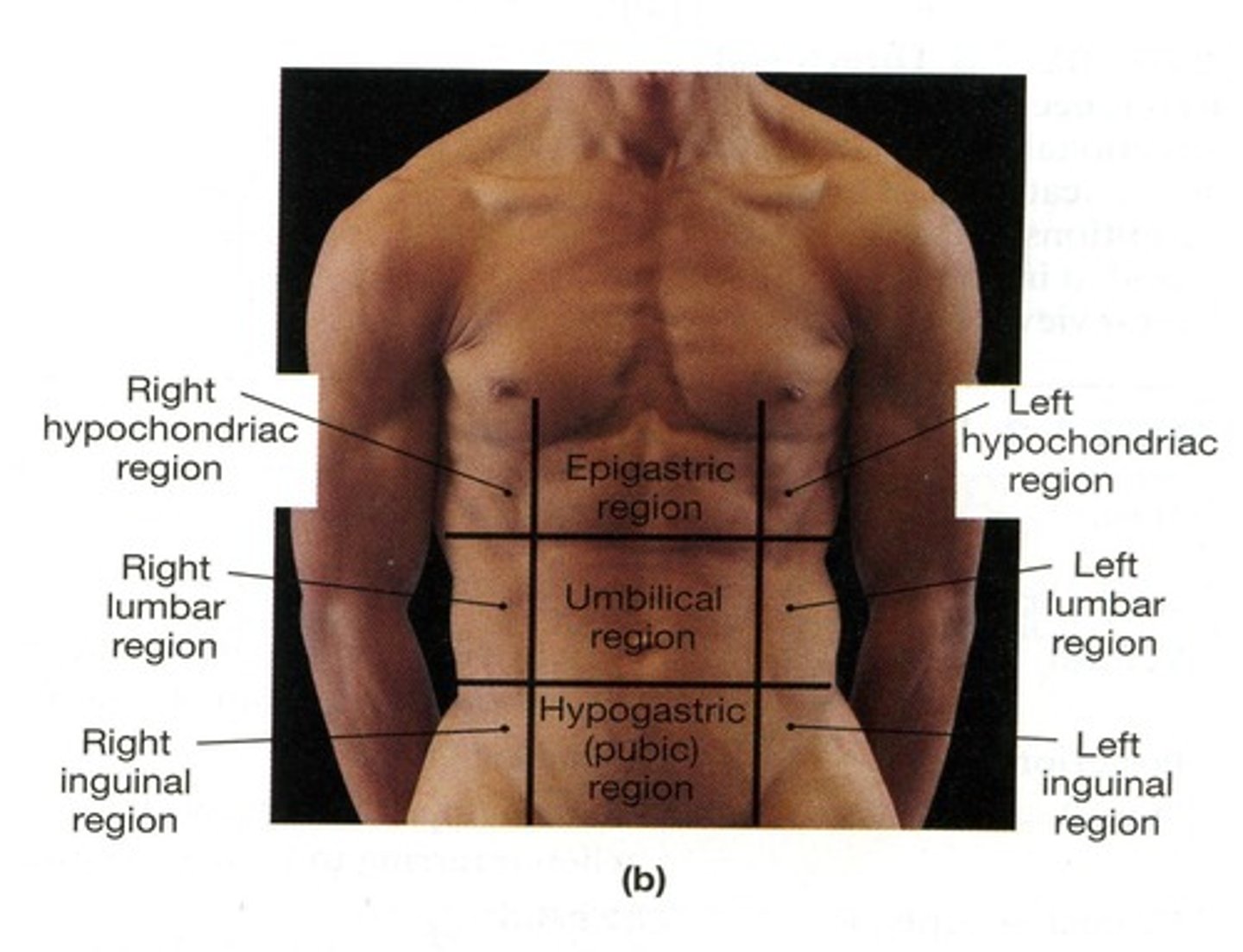
Inguinal
Also known as Iliac.
Digestive organs
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anal canal.
Accessory digestive organs
Includes salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gallbladder, and biliary system.
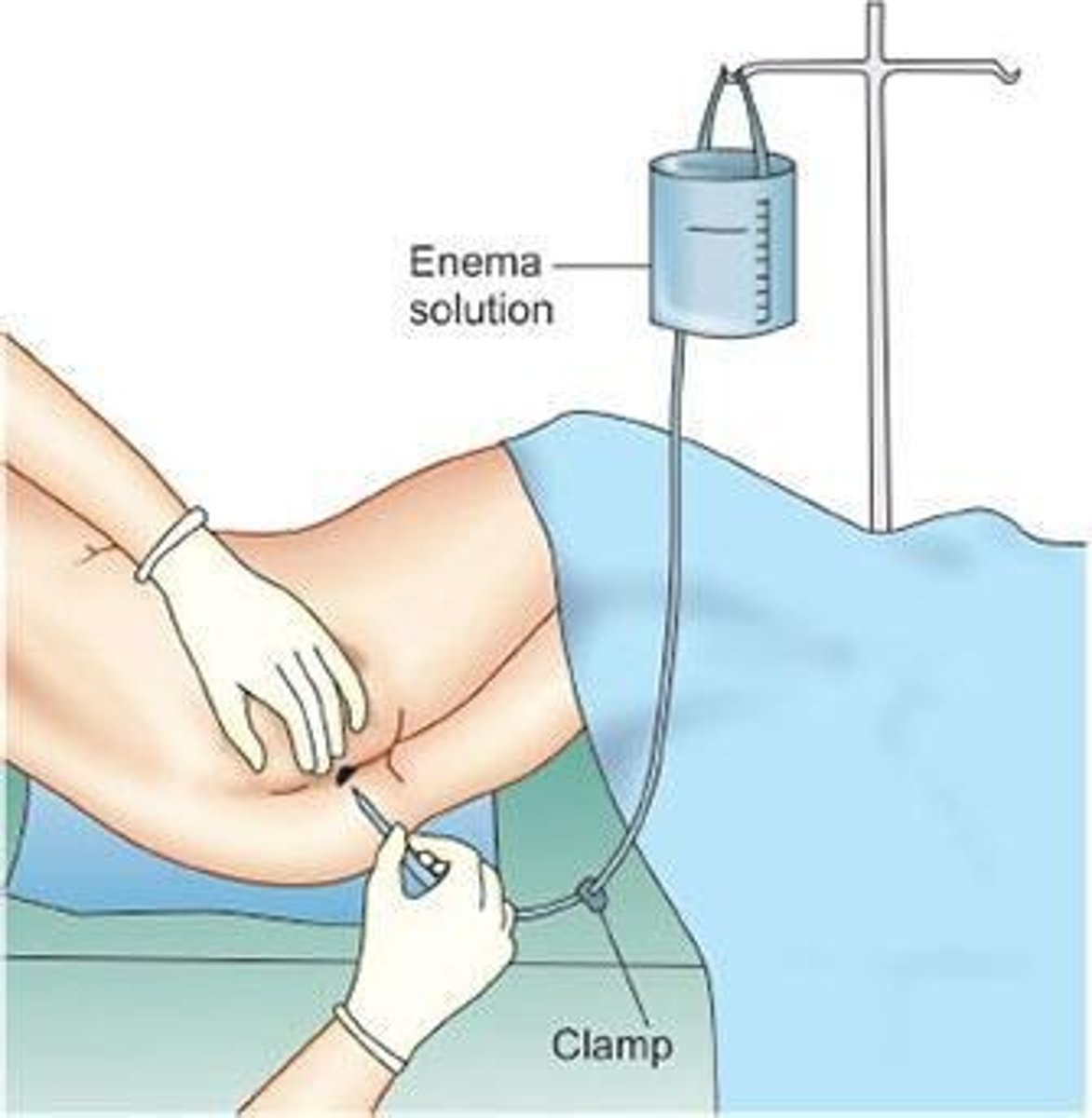
Barium Enema
A procedure for imaging the colon.
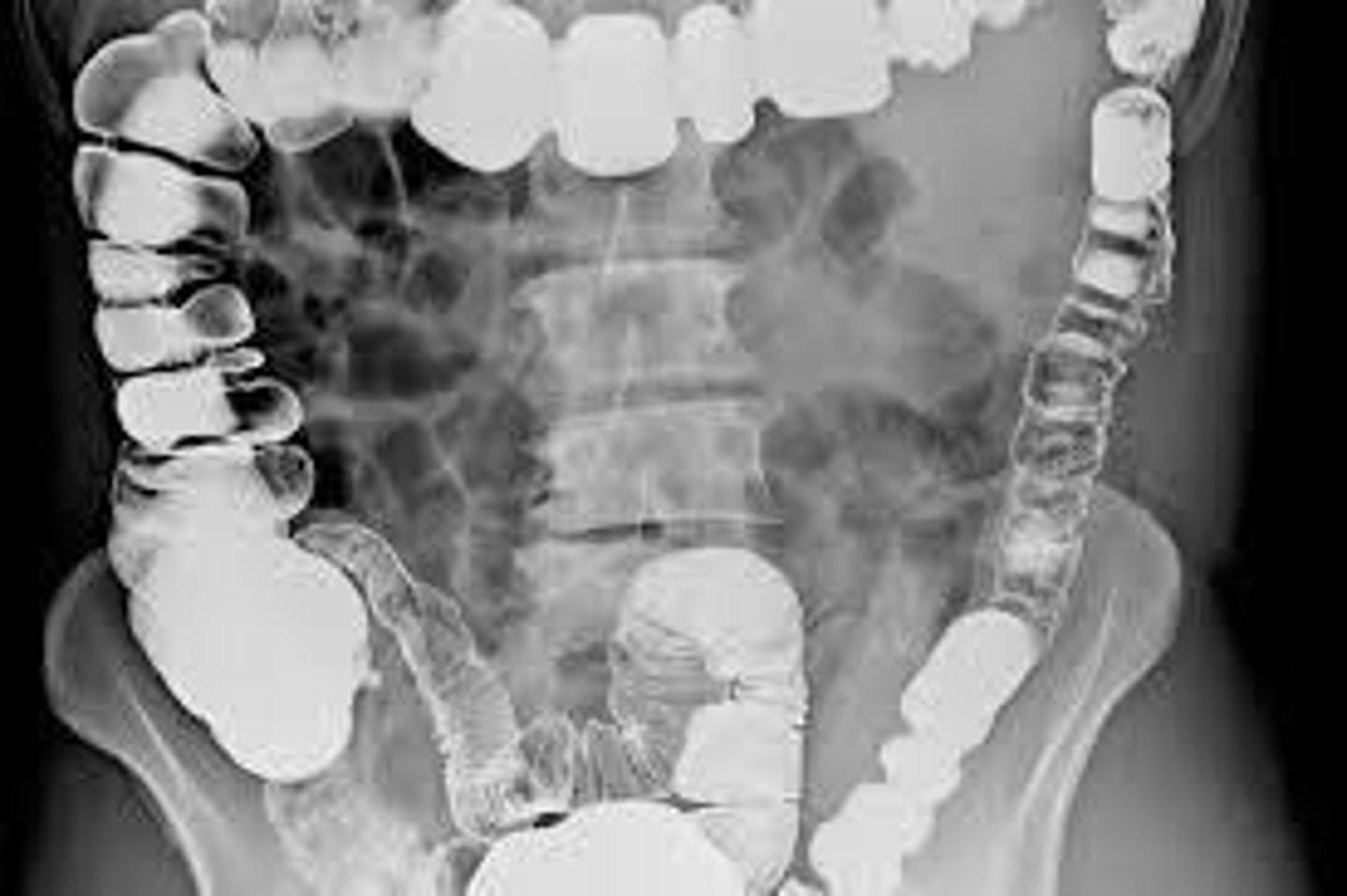
Patient Position for Barium Enema
Left lateral position (Sim's) with right knee drawn up towards the chest.
Hepatic flexure of colon
Located near the liver.
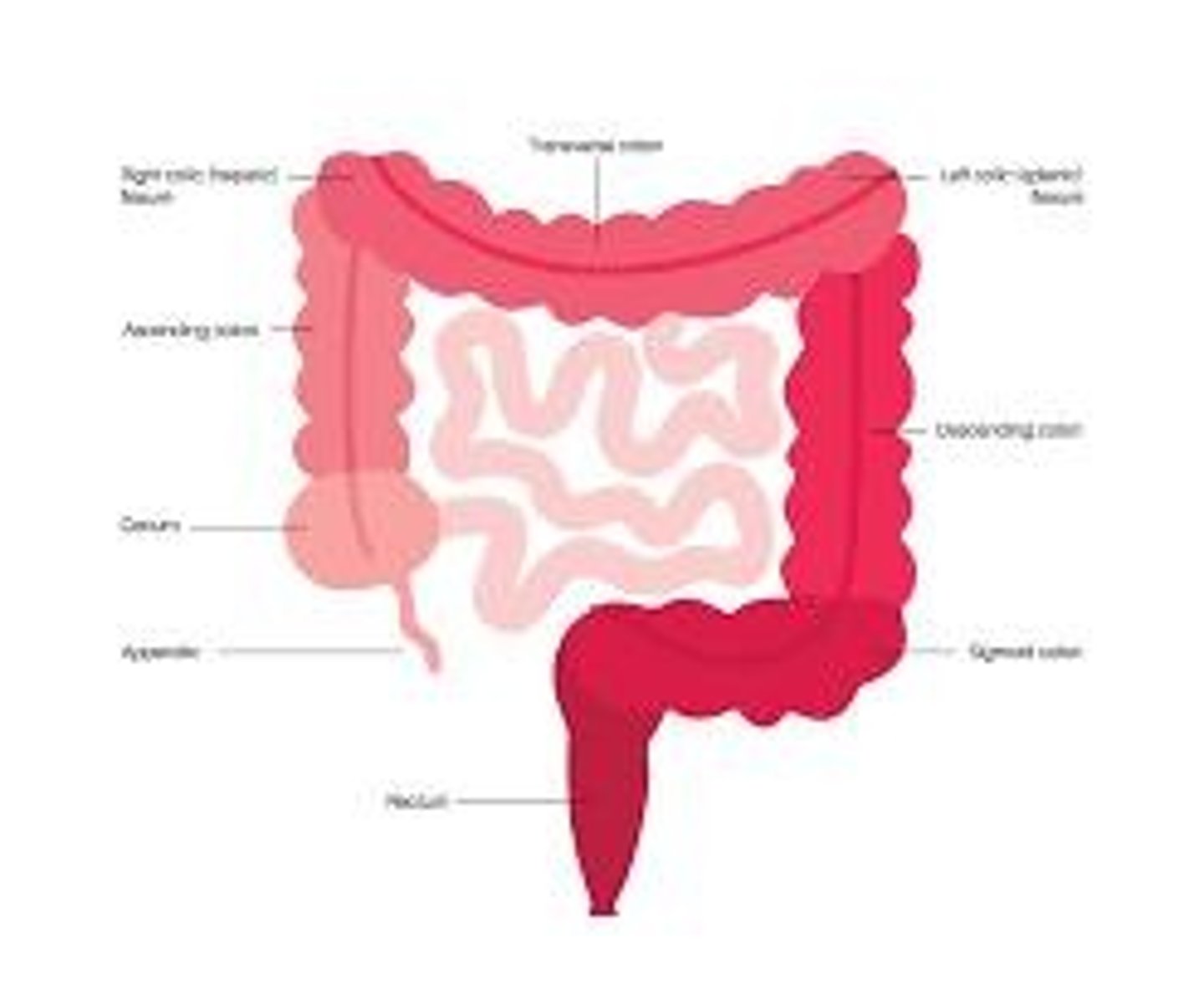
Splenic flexure of colon
Located near the spleen.
Directional Terms
Describes the position of body parts relative to each other.
KUB
Kidneys, Ureters, Bladder
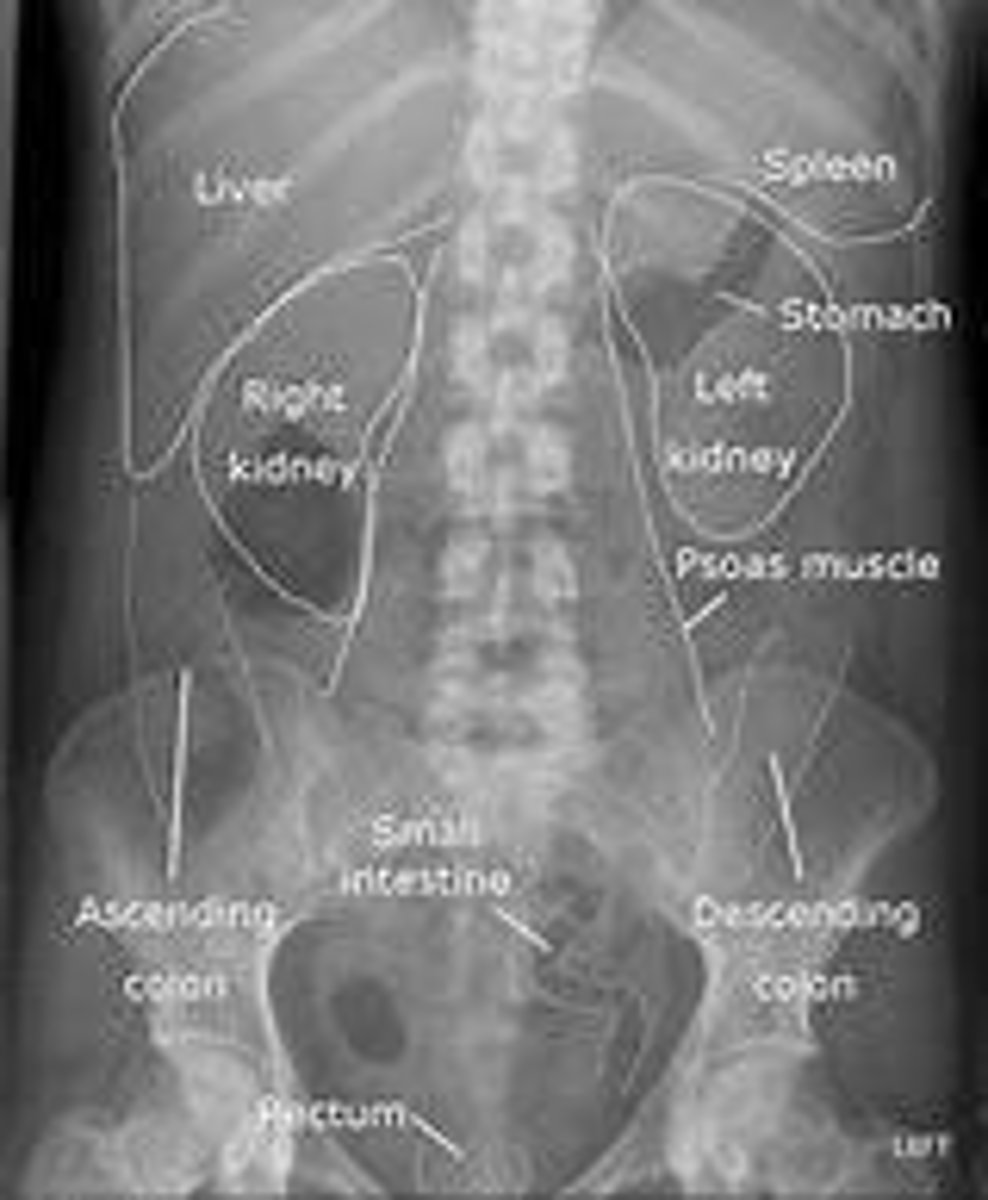
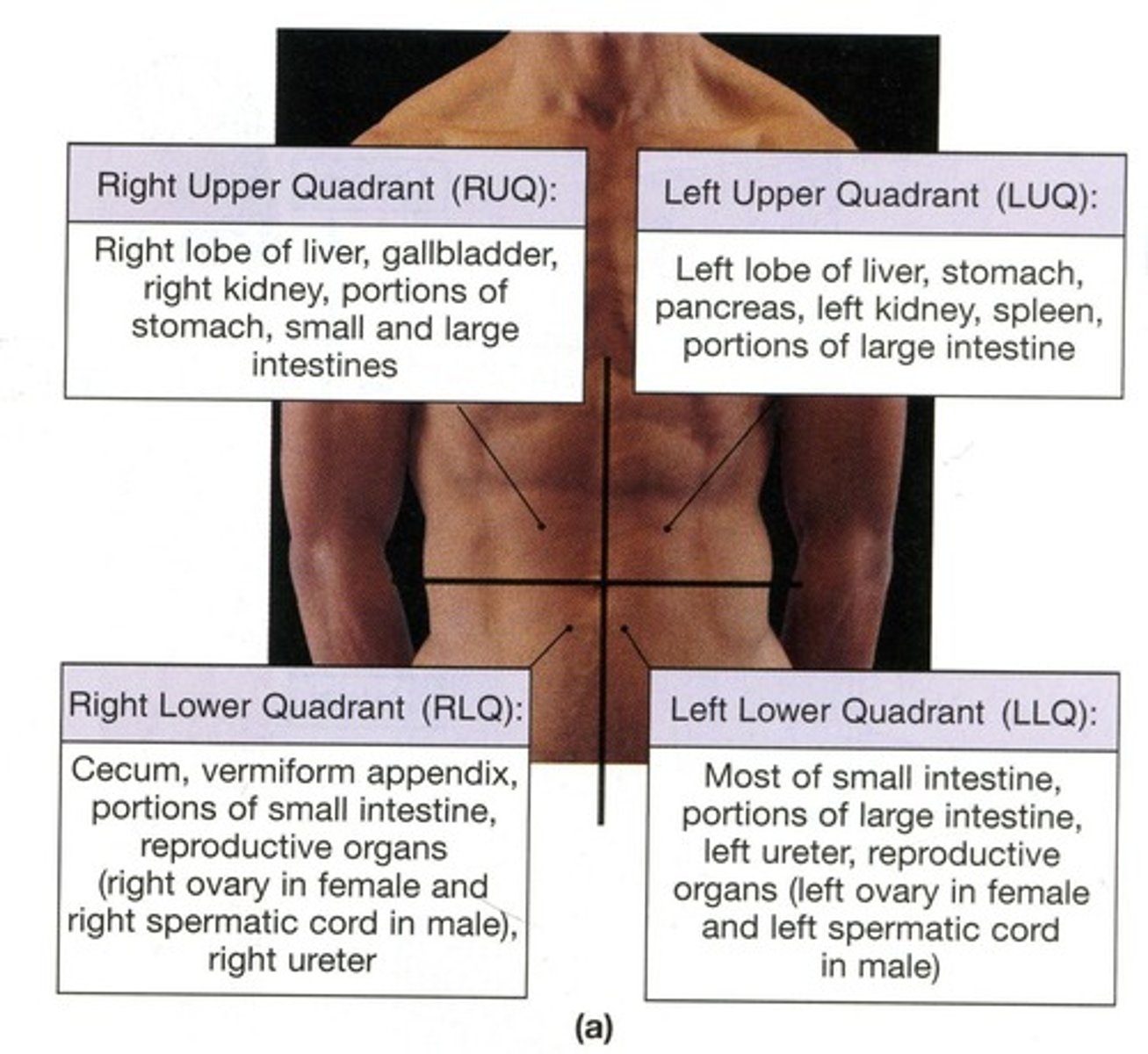
RLQ
Right Lower Quadrant
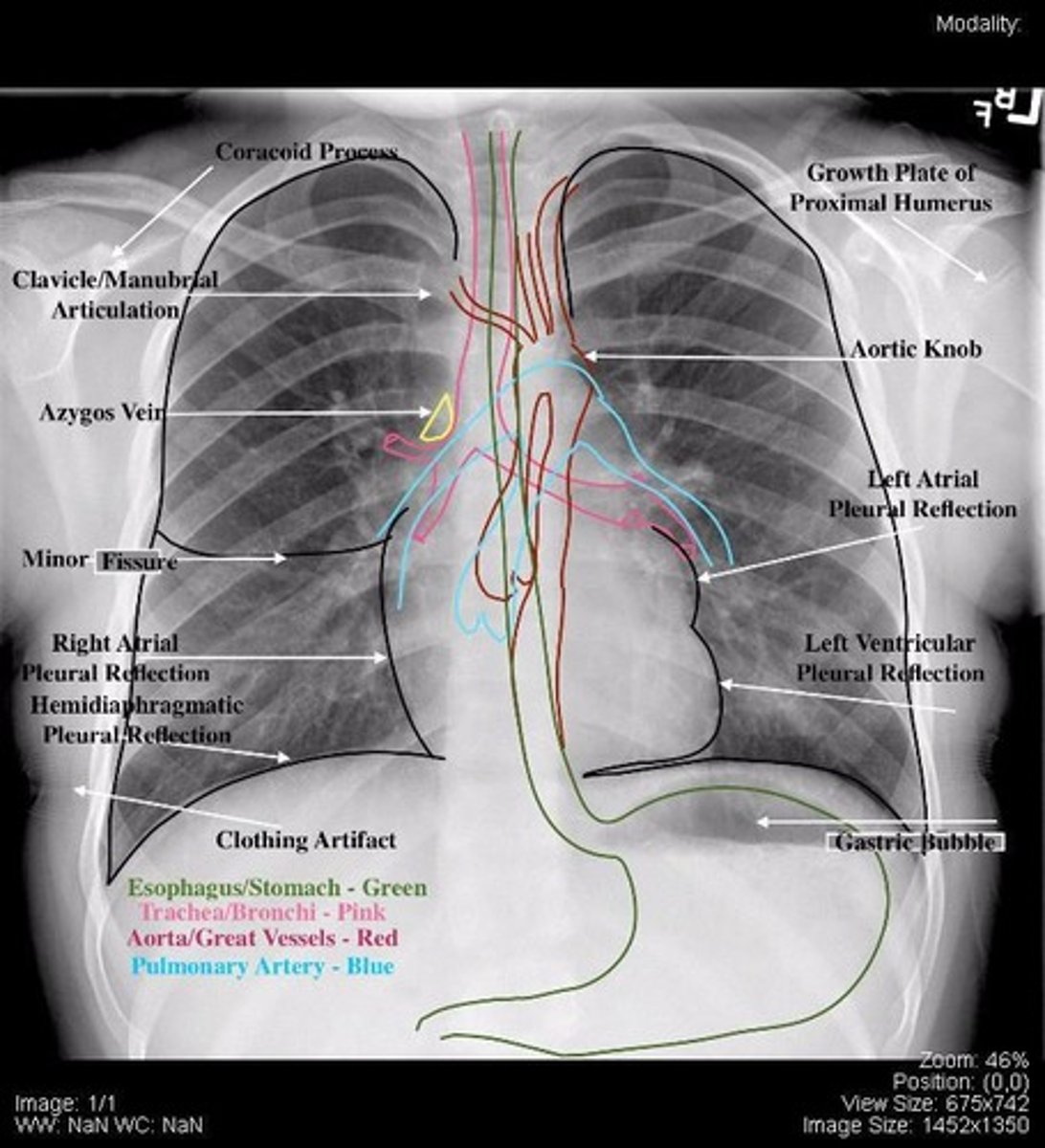
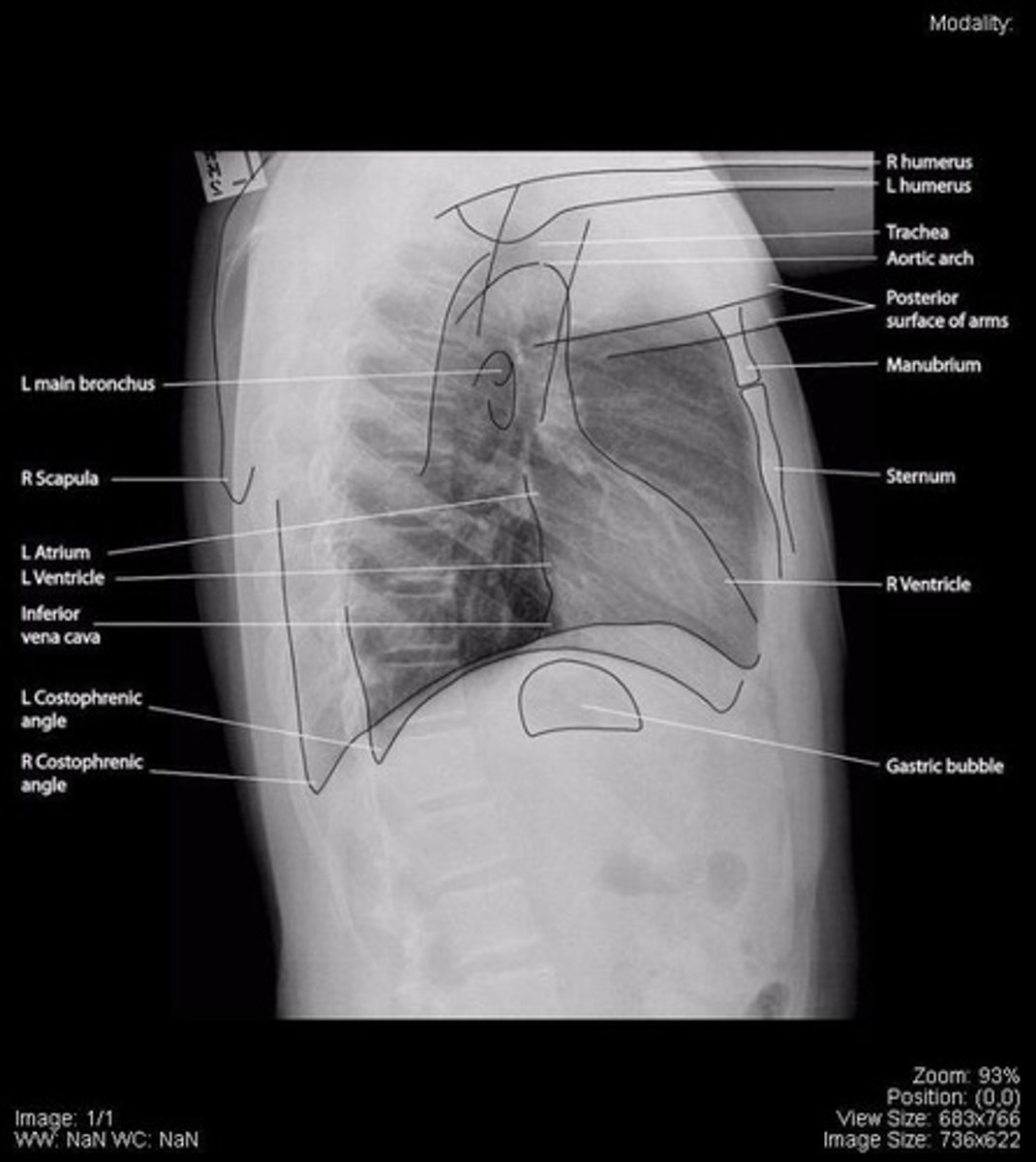
CXR
Chest X-ray
R/O
Rule Out
Dx
Diagnosis
Rx
Prescription/Therapy
Hx
History
ASAP
As Soon As Possible
STAT
Immediately
ED or ER
Emergency Department or Room
US
Ultrasound (Sonography)
NMT
Nuclear Medicine Technology
CT
Computed Tomography
AP
Anterior Posterior
PA
Posterior Anterior