quiz eight - metabolism I
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what are the steps of aerobic respiration?
glycolysis, TCA (citric acid cycle), electron transport chain
does glycolysis require oxygen?
no
where does glycolysis occur?
cytoplasm
what are the products of glycolysis?
net ATP production = 2 (4 produced, 2 used)
2 pyruvate
2 NADH
diagram the format of glycolysis.

what is the requirement for the citric acid cycle and electron transport chain to occur?
only occurs if oxygen is available
where does TSA cycle occur?
mitochondria (matrix)
products of TCA cycle
1 ATP per pyruvate molecule
3 CO2 (2 from cycle, 1 from acetyl-CoA creation)
3 NADH
1 FADH2
define the electron transport chain
electrons from carrier proteins are used to make an H+ concentration gradient that powers ATP synthesis
where does the electron transport chain occur?
inner mitochondrial membrane
products of electron transport chain
3 ATP per NADH (30 ATP total)
2 ATP per FADH2 (4 ATP total)
H2O
FAD
define redox reactions
the transfer of electrons
oxidation
loses electrons (charge becomes more positive)
reduction
gains electrons (charge becomes more negative)
what is the DCPIP assay
an electron acceptor (has a high affinity for electrons), transfers electrons to FAD+
what is the oxidized state of the DCPIP assay?
blue
what is the reduced state of the DCPIP assay?
colorless
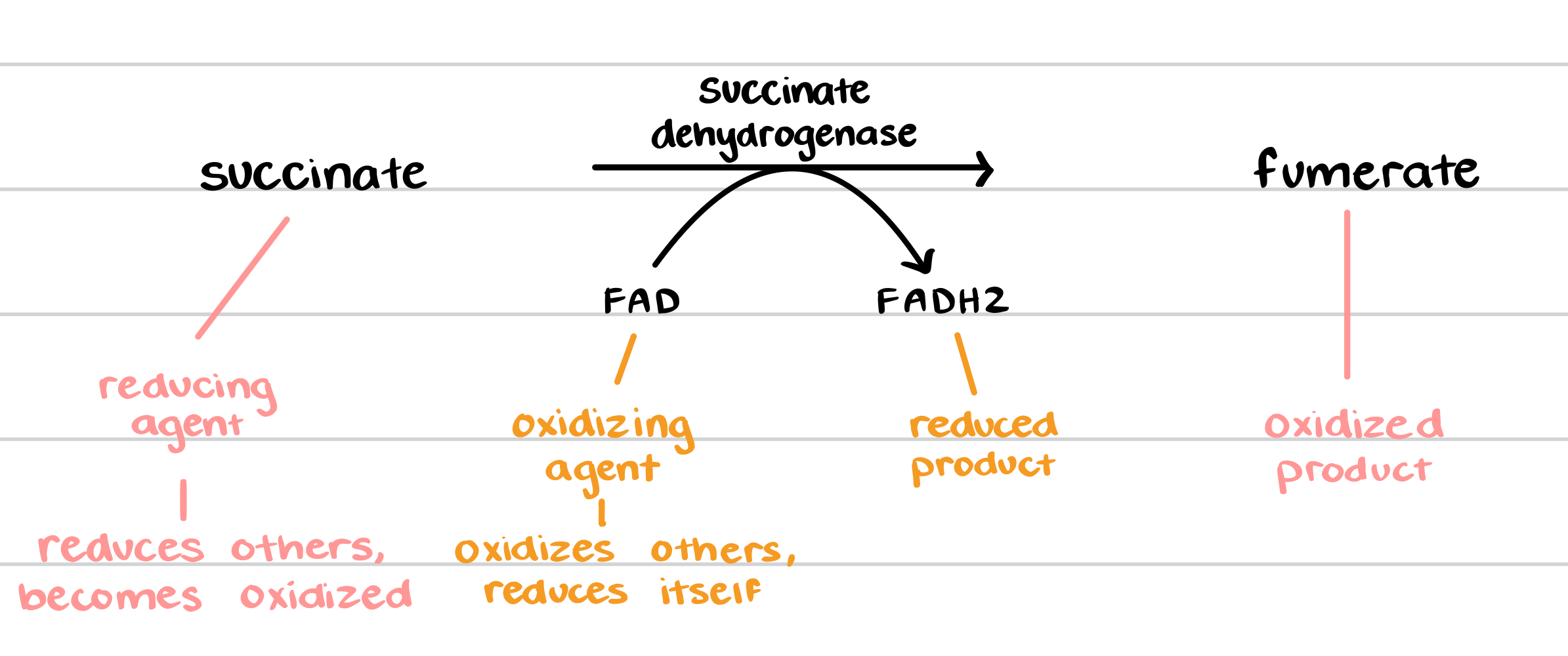
what is the reducing agent of the DCPIP assay?
succinate
what is the oxidizing agent of the DCPIP assay?
FAD
what is the reduced product of the DCPIP assay?
FADH2
what is the oxidized product of the DCPIP assay?
fumerate
what is the enzyme in the DCPIP assay reaction, and what type of enzyme is it?
succinate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial enzyme
what is a stronger oxidizing agent, DCPIP or FAD?
DCPIP is a stronger oxidizing agent than FAD
what is the dependent variable in the DCPIP assay?
the amount of light transmitted through the DCPIP solution
diagram the DCPIP assay reaction
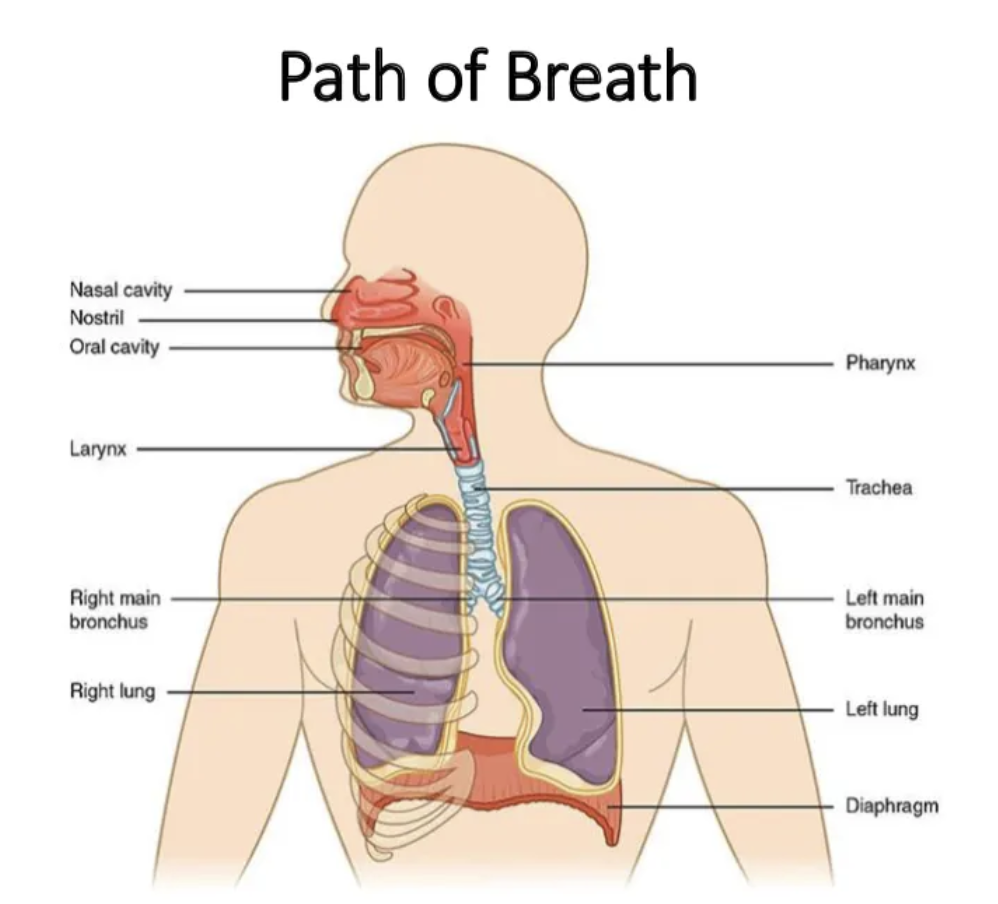
name every body part pointed out.
name every part of the alveoli
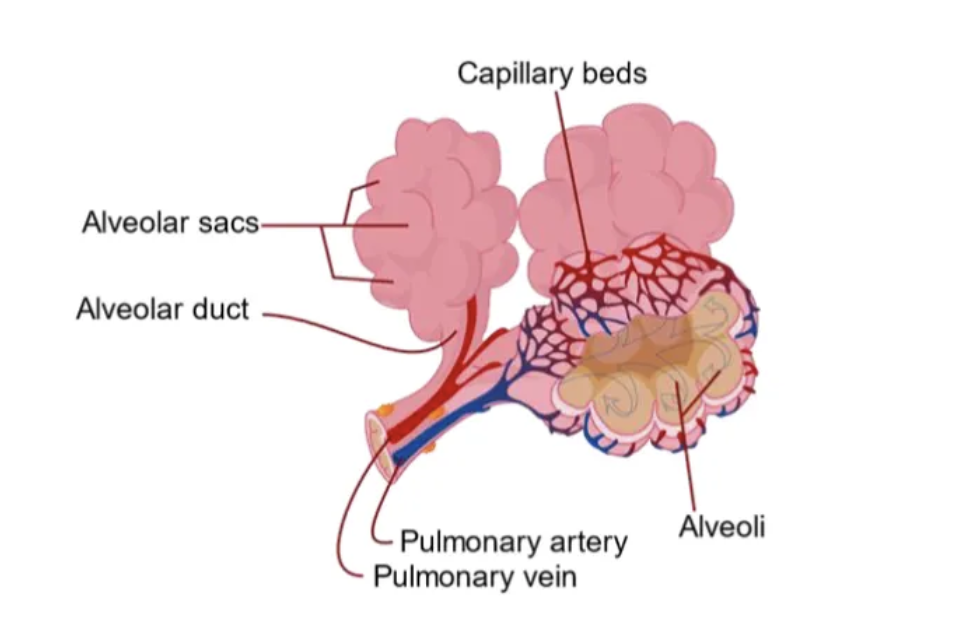
diagram the path of breath.

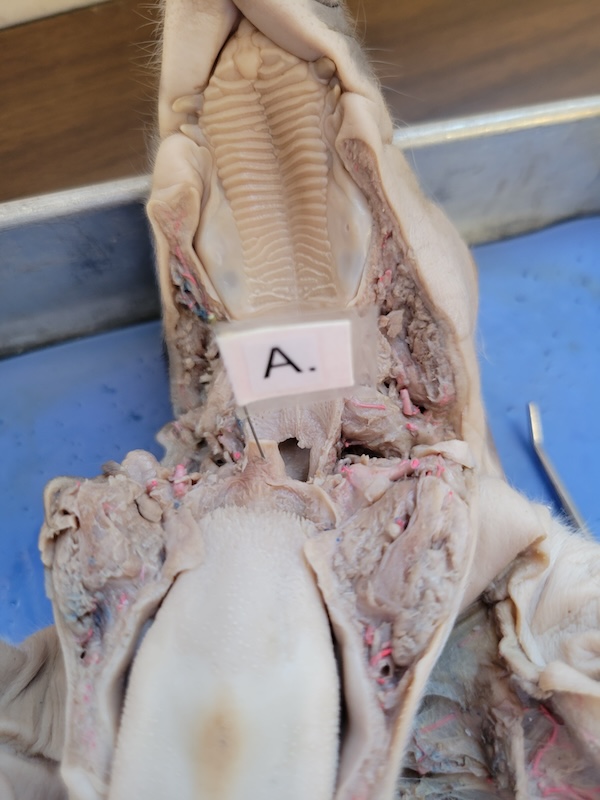
epiglottis
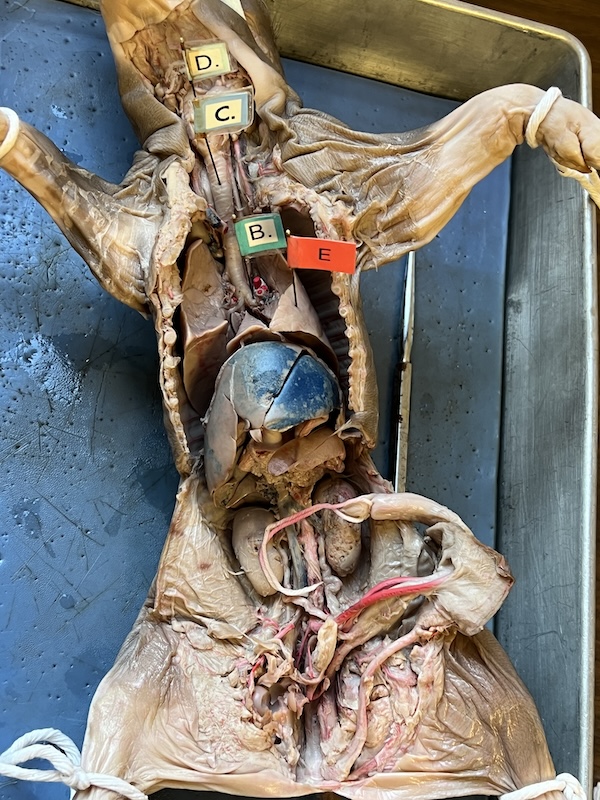
identify B
primary bronchi
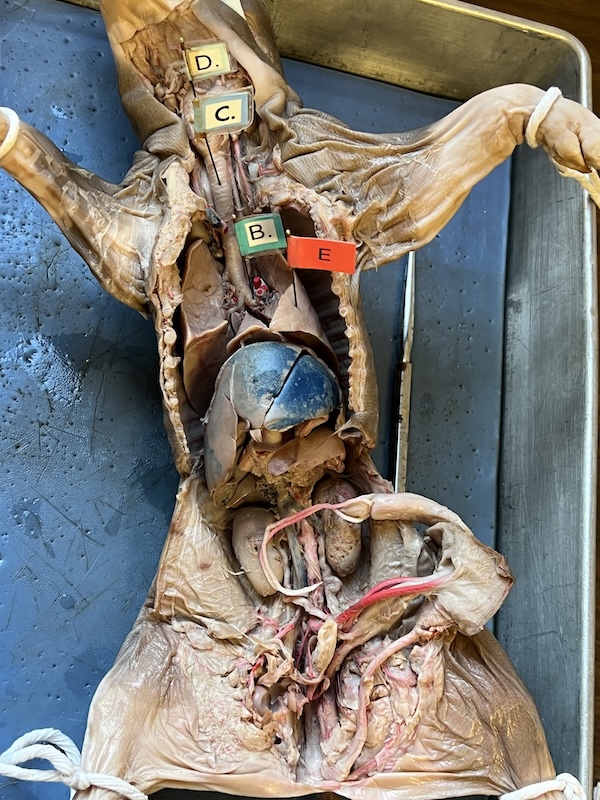
identify C
trachea
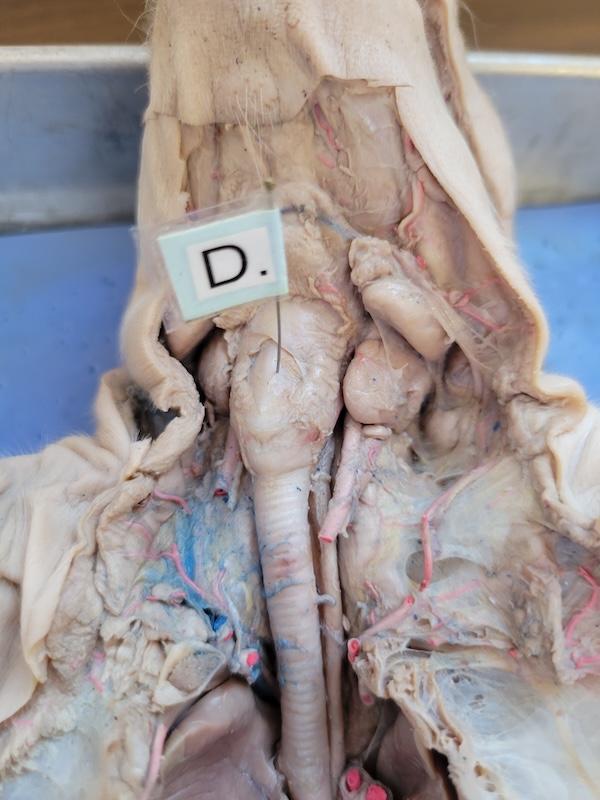
larynx
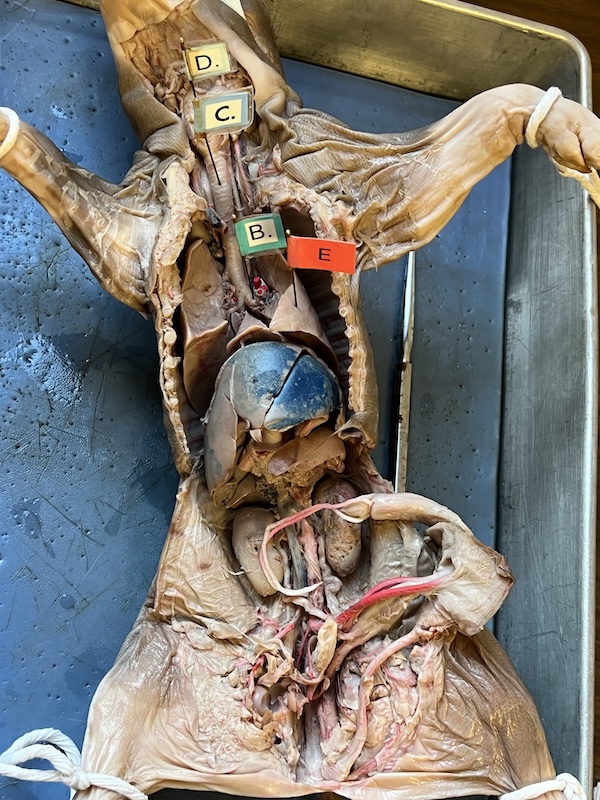
identify E
lungs