Unit 2: Body Composition, Cardiovascular Health & Nutrition
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key concepts from the Unit 2 study guide: body composition, cardiovascular disease, nutrition, and general wellness.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Body Composition
The proportion of fat, muscle, bone, and water that together make up a person’s body.
Fat Mass
The total amount of fat in the body, including essential and stored fat.
Fat-Free Mass
All non-fat components of the body—muscle, bone, water, organs, etc.
Subcutaneous Fat
Fat stored directly beneath the skin, the type you can pinch.
Excess Body Fat
Carrying too much body fat, which raises the risk of heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, cancer, joint pain, sleep problems, and low energy.
Android (Apple) Body Shape
Fat concentrated around the abdomen and upper body; linked to higher cardiovascular and metabolic risk.
Gynoid (Pear) Body Shape
Fat stored mainly in the hips and thighs; generally lower health risk than android fat distribution.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
A ratio of weight to height squared used to classify underweight, healthy weight, overweight, and obesity.
Quetelet’s Index
The principle underpinning BMI that body weight should be proportional to the square of height.
Skinfold Calipers
Instruments that measure the thickness of skin-folds to estimate body-fat percentage.
Hypertension
Abnormally high blood pressure; the strongest single predictor of cardiovascular disease.
Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke)
A sudden loss of brain function due to interrupted blood flow.
Coronary Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease)
Narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries that supply the heart muscle.
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
The ‘good’ cholesterol that helps remove cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
The ‘bad’ cholesterol that can deposit in artery walls and promote heart disease.
Fiber
Fiber is an essential part of nutritional intake that is know. To lower risk of heart disease and cancer.
Types of Fiver
Soluble - This type of fiber binds to cholesterol containing items and helps remove them from the body; lowers risk of heart disease
insoluble: binds to water in the intestines and softens stool.
Water
Water is used for food absorbing, joint lubrication, blood flow, and most chemical reactions in the body.
Proteins
Proteins are used to build the solid structures of the body; including hair, nails, connective tissues, enzymes, red blood cells, and some hormones.
Protein Types
Complete - Typical sources are animal products
Incomplete- Typical sources are plant products
Total Cholesterol
Combined amount of HDL, LDL, and other lipid components; healthy level is below 200 mg/dL.
Lifestyle Changes for Heart Health
Healthy diet, regular physical activity, and quitting smoking to lower heart-disease risk.
Carbohydrates
The body’s primary energy source, especially for the brain and muscles.
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the nutrients the body needs in larger amounts.
Nutrients required in large amounts—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—that provide energy and support growth.
3 main Macronutrients: Fats, Carbohydrates, and Proteins

Macronutrients (PT. 2)
Macronutrients are defined as these:
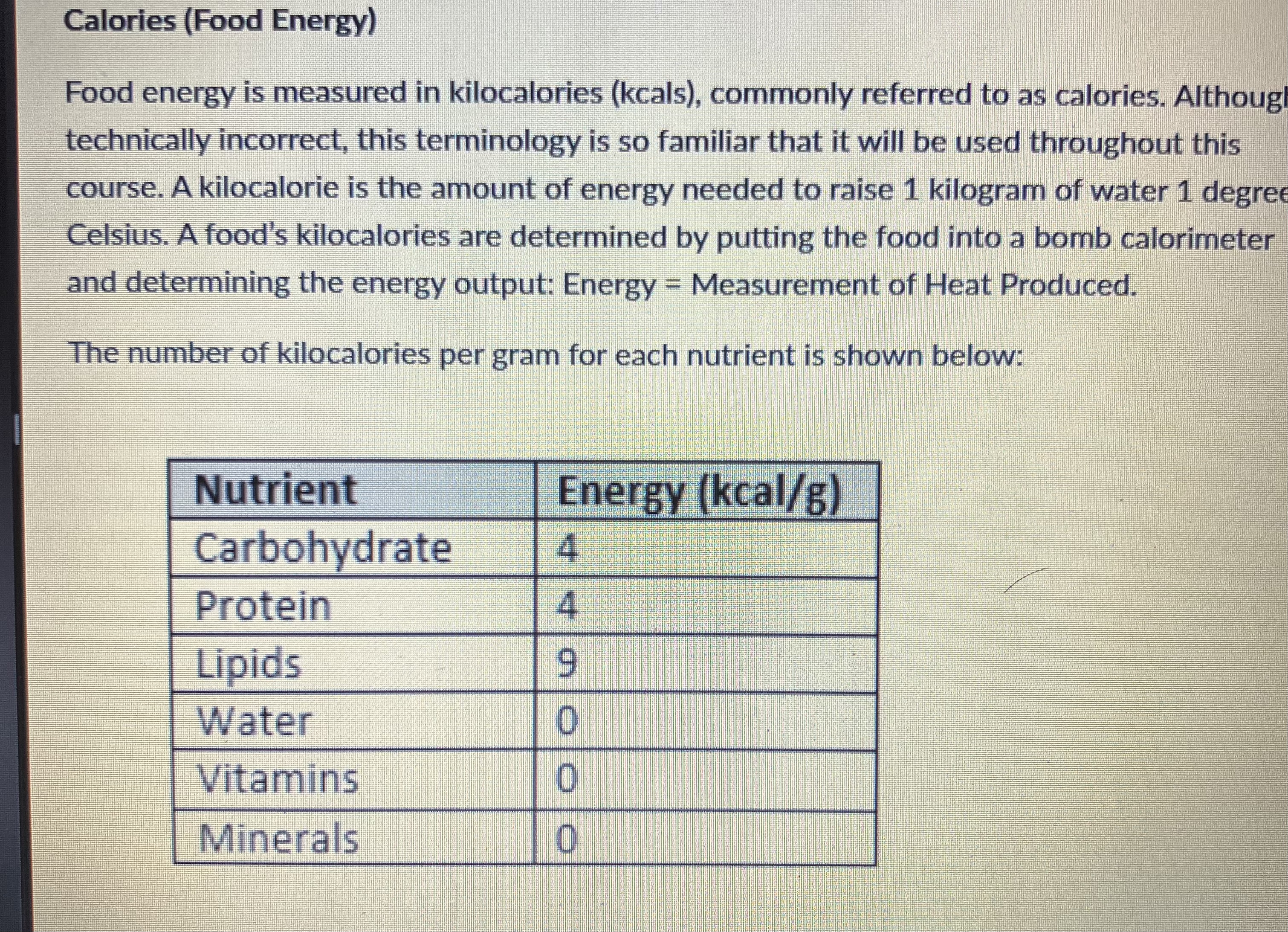
Fats - 9 Calories per gram
Carbohydrates- 4 Calories per gram
Protein - 4 Calories per gram
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are also important nutrients, but the body needs in smaller amounts. Vitamins and minerals needed in small amounts to support functions like immunity and bone health.
Examples: Vitamins, Minerals, and Water
Saturated Fats
Fats mainly from animal products (butter, cheese, fatty meat) and some tropical oils; can raise LDL.
Unsaturated Fats
Heart-healthy fats found in plant oils, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
Trans Fats (Partially Hydrogenated Oils)
Chemically altered fats that raise LDL and lower HDL; should be avoided.
Soluble Fiber
Fiber that dissolves in water, helping lower cholesterol and stabilize blood sugar.
Insoluble Fiber
Fiber that adds bulk and speeds stool passage, preventing constipation.
Electrolytes
Minerals such as sodium and potassium that carry electrical charges and regulate fluid balance.
Nutrition Facts Label
Panel on food packaging that lists calories and nutrient content to guide healthier choices.
Safe Food Handling
The four steps—clean, separate, cook, chill—that prevent foodborne illness.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
The calories required to maintain basic bodily functions at rest.
MyPlate
U.S. visual guide showing recommended portions of fruits, vegetables, grains, protein, and dairy.
Food Nutrition Label
A nutrition facts label is a standardized format used on food packaging to provide consumers with information about the nutritional content of a product
Balanced Breakfast
The morning meal supplying roughly 20–25 % of daily calorie needs.
Calories
Units of energy