1.5. Vorticity equations
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
General integral form of conservation of mass (formula) (Navier Stokes equation)
formula
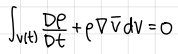
General integral form of conservation of momentum (formula) (Navier Stokes equation)
formula
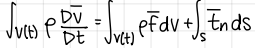
General integral form of conservation of total energy (formula) (Navier Stokes equation)
formula
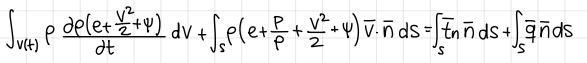
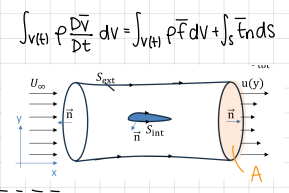
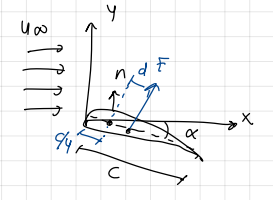
developing of aerodynamic force of an airfoil
developing
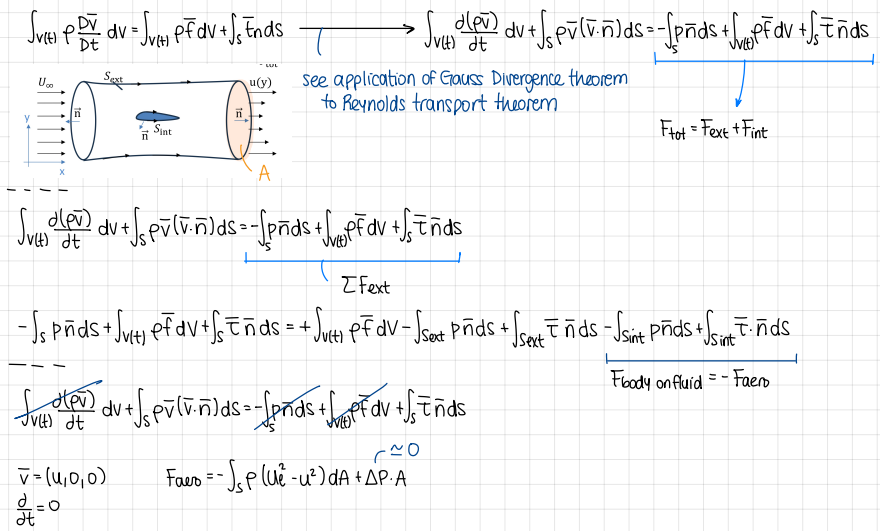
origin of aerodynamic forces (formula)
formula
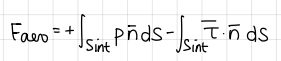
differential form of conservation of mass (formula) (Navier Stokes equation)
formula
1eq, 4ukn
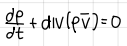
differential form of conservation of momentum (formula) (Navier Stokes equation)
formula
3eqs, 7ukn
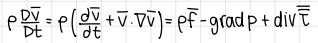
differential form of conservation of energy (formula) (Navier Stokes equation)
formula
1eq, 2ukn
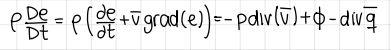
Constitutive equations (4 formulas) (Navier Stokes equation)
formulas
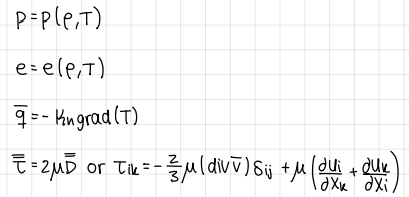
Initial conditions (3 IC) (Navier Stokes equation)
IC

Boundary conditions (2 BC) (Navier Stokes equation)
BC
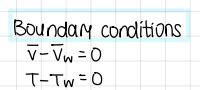
differential form of conservation of mass (formula) (INCOMPRESSIBLE Navier Stokes equation)
formula
1eq, ukn
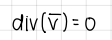
differential form of conservation of momentum (formula) (INCOMPRESSIBLE Navier Stokes equation)
formula
3eqs, ukn
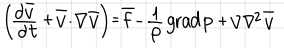
differential form of conservation of energy (formula) (INCOMPRESSIBLE Navier Stokes equation)
formula
in general only needed for non-adiabatic flows
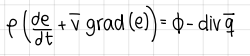
Constitutive equations (4 formulas) (INCOMPRESSIBLE Navier Stokes equation)
formulas
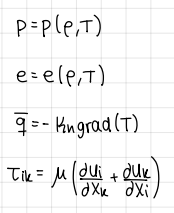
Initial conditions (3 IC) (INCOMPRESSIBLE Navier Stokes equation)
IC

Boundary conditions (2 BC) (INCOMPRESSIBLE Navier Stokes equation)
BC
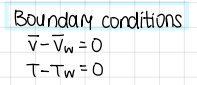
Consequences of incompressible flow model
Density is constant everywhere
Compressibility is zero → infinite speed of sound
Any change of flow is felt instantly in every point of the field (not possible to model sound transmission)
Energy equation is decoupled from momentum and mass conservation (often not necessary)
M=0 → strictly valid only for low speed flows (but physical mechanisms are valid up to higher Mach numbers (with corrections))
Development and equation of vorticity and viscous term
development and equation
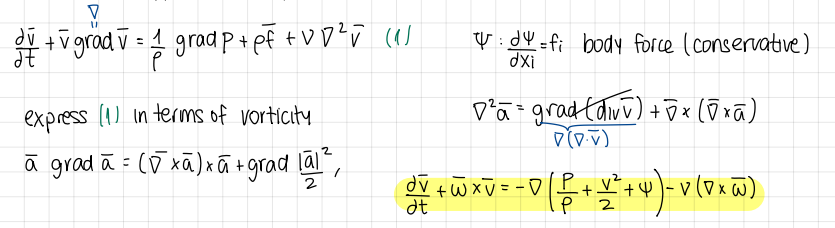
what is ψ?
body force (conservative)
development and equation of Bernoulli’s theorem.
development and equation
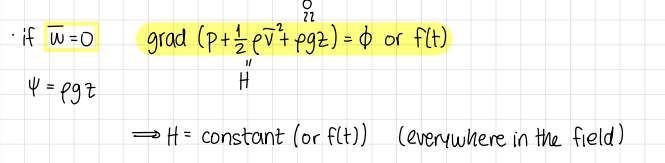
what is H in Bernoulli’s theorem?
constant everywhere in the field
what does it mean when a field is conservative?
the work done to move between two points doesn't depend on the path taken
The generalized Bernoulli’s theorem is also called…
weak form of Bernoulli’s theorem
generalized version (weak form) of Bernoulli’s theorem: development
development
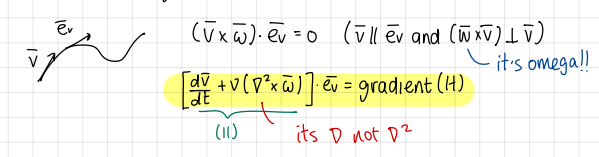
Streamline definition
line tangent to the velocity of the flow at every point
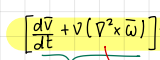
if this term of the generalized Bernoulli’s theorem is zero, …
H is constant along streamlines
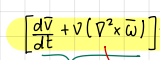
this term of the generalized Bernoulli’s theorem is constant if…
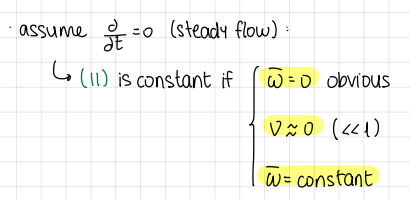
assume steady flow (d/dt=0)
omega=0
upsilon«1
omega is constant
Flow types with constant or zero vorticity
Solid body rotation
Uniform flow
Ideal vortex
Rankine vortex
Solid body rotation: drawing and equations
drawing and equations
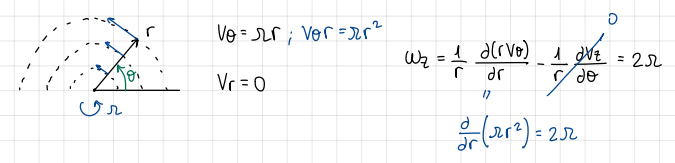
Uniform flow: drawing and equations
drawing and equations
Ideal vortex: drawing and equations
drawing and equations
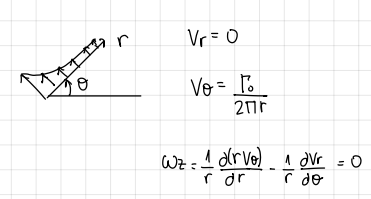
Rankine vortex: drawing
drawing

In order to have velocity potentials, the flow must be…
invsicid/irrotational
Development of velocity potential (inviscid/irrotational flows)
development
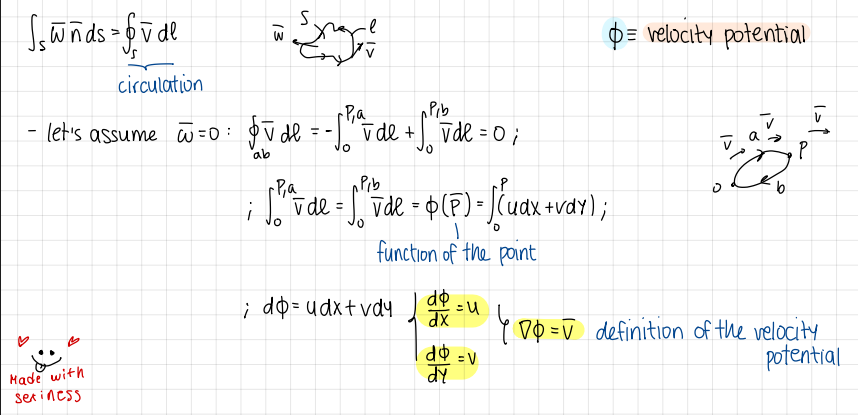
write the 3 equations + condition of the potential flow model
equations

General results for incompressible flow model
Aerodynamic force
Kutta-Jukovsky theorem
Circulation
D’Alembert paradox
Amount of solutions
Kutta condition
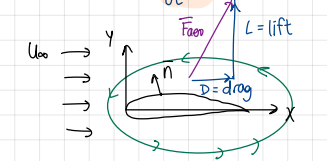
Aerodynamic force formula (general results for incompressible flow model)
formula
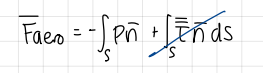
Kutta-Jukovsky theorem formula (general results for incompressible flow model)
formula
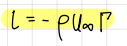
Circulation formula (general results for incompressible flow model)
formula
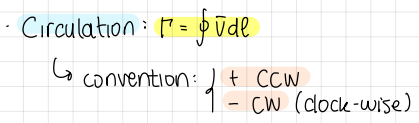
D’Alembert paradox formula (general results for incompressible flow model)
formula
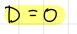
Amount of solutions (general results for incompressible flow model)
infinite solutions for a given geometry (one for each circulation (Gamma) value)
Kutta condition (general results for incompressible flow model)
velocity at the trailing edge is zero (it’s a stagnation point)
Computational methods to solve potential flow equations
Fundamental solution of Laplace equations (cylinder with and without circulation)
Conformal mapping (map cylinder into airfoil-shape body)
Thin airfoil theory (neglect thickness distribution)
Panel methods (discretized solution on realistic shapes)
Main results for thin airfoils (formulas)
formulas
quite realistic results for streamlined bodies (airfoils) of finite thickness

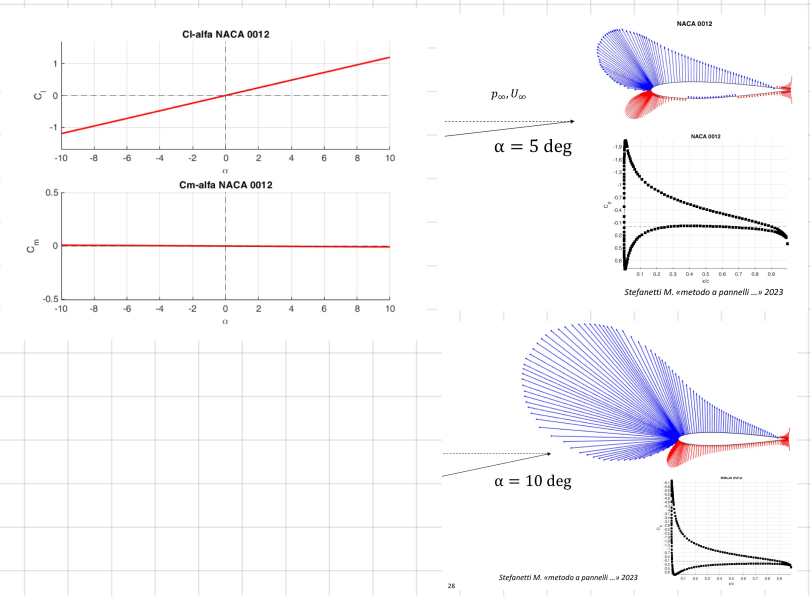
Main results for thin airfoils: pressure distributions (graphs)
graphs
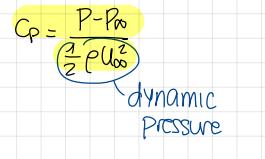
Formula of pressure coefficent Cp
formula
What happens to the pressure coefficent at a stagnation point?
Cp=1
(U=0)

Issues and limits of potential flow models
solution of potential flow model for streamlined bodies turn out to provide a good approximation of real flows, and reasonably good estimates for Lift and Aerodynamic moments at limited angles of attack, but :
what is the physical rationale for using the slip-velocity boundary condition?
can the flow really be considered irrotational?
what is the physical origin of Circulation (Lift)?
how can we compute maximum CL values (stall)?
what is the physical origin of drag?
how can we model/estimate drag?
what about less streamlined body shapes?
Aerodynamic loads on a solid body arise from…
We need to solve equations to…
the integral of normal and tangential stresses acting on the body surface
determine the distribution of normal and tangential stresses
Viscous effects are strictly related to…
the vorticity field (kinematic effects) → if vorticity is zero the flow is inviscid
If a flow is inviscid, we can…
derive a linear system of equations that can describe the slipping motion of a fluid around a solid body
For a 2D body lift (related to normal stresses) can be calculated from…
Drag is always equal to…
the circulation of the velocity (Kutta-Jukowsky theorem)
zero for an inviscid 2D body
We need to evaluate origin and dynamic of vorticity to…
to give a physical interpretation of the potential flow model
to evaluate viscous phenomena (stall , separation, drag...)