Capacitors
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Define capacitance.
Capacitance is the charge stored per unit potential difference across an object.
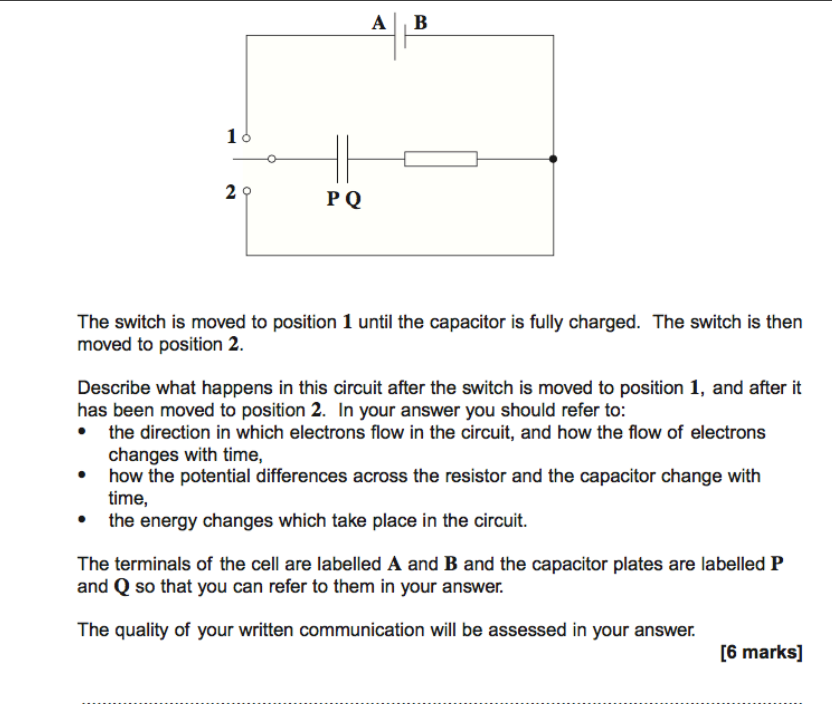


Limits are always the size of the capacitor would be extremely large and capacitors can only power electric devices for short time

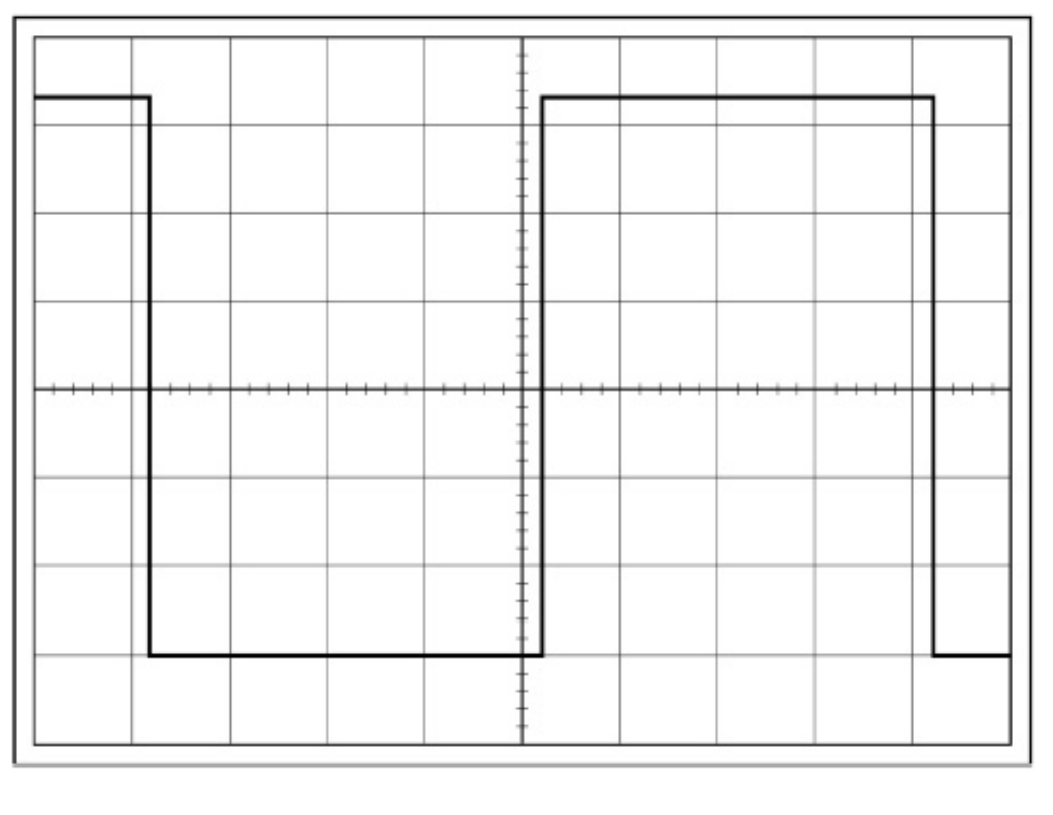
Given time-base = 0.5ms and Y-voltage gain = 1v, what is the peak to peak voltage and the frequency?
Remember 1 “large” square is 1V so each smaller reading is 0.2v so peak to peak voltage is 6.3V
Each large square on x axis is 0.5ms and 1 period goes from one complete cycle, 8 divisions so 8 × 0.5ms = 4ms, so f = 1/T 1/40×10^-3 is 250hz
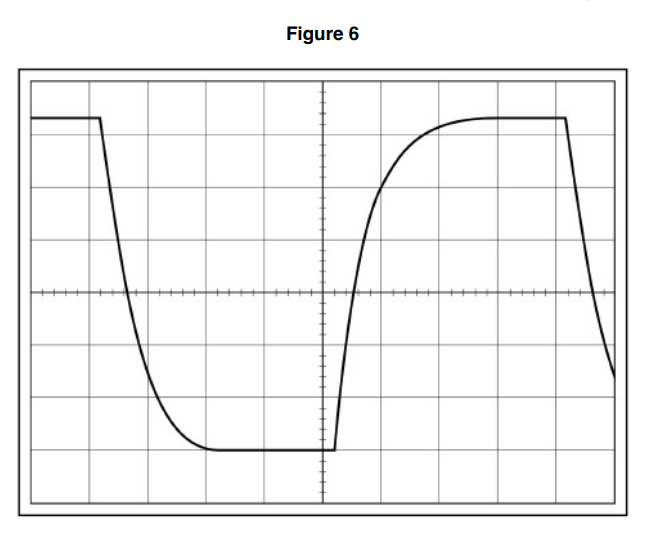
Time-base = 0.5ms and Y-voltage gain = 1v, calculate time constant.

Given time-base originally 0.5ms div^-1
IN ANY EXPlain question, and given a value, must do a calculation…
If originally 0.5ms now to 0.2ms, then there is a horizontal stretch of 2.5 so larger distance so uncertainty reduces.

What is the time constant?
Time taken for the charge on a discharging capacitor to fall to 37% of original value / Rise to 63% of original value for charging.
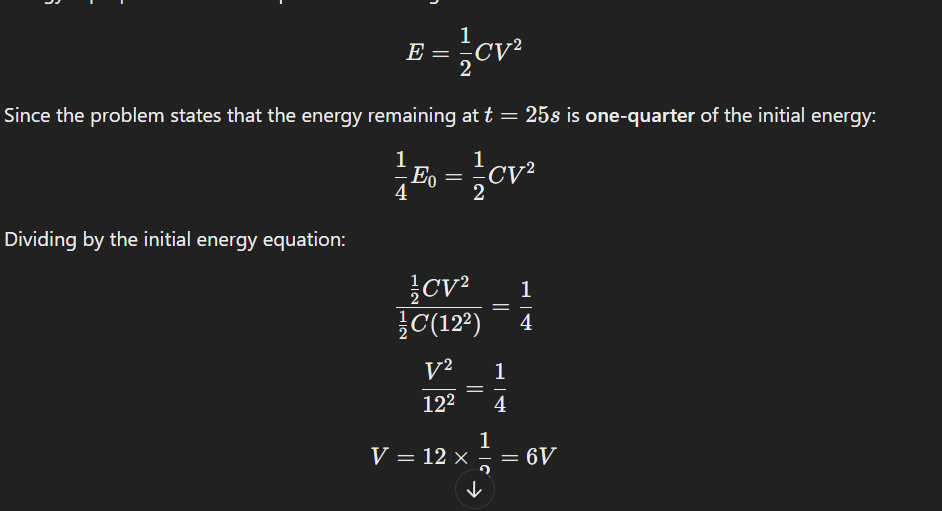

???
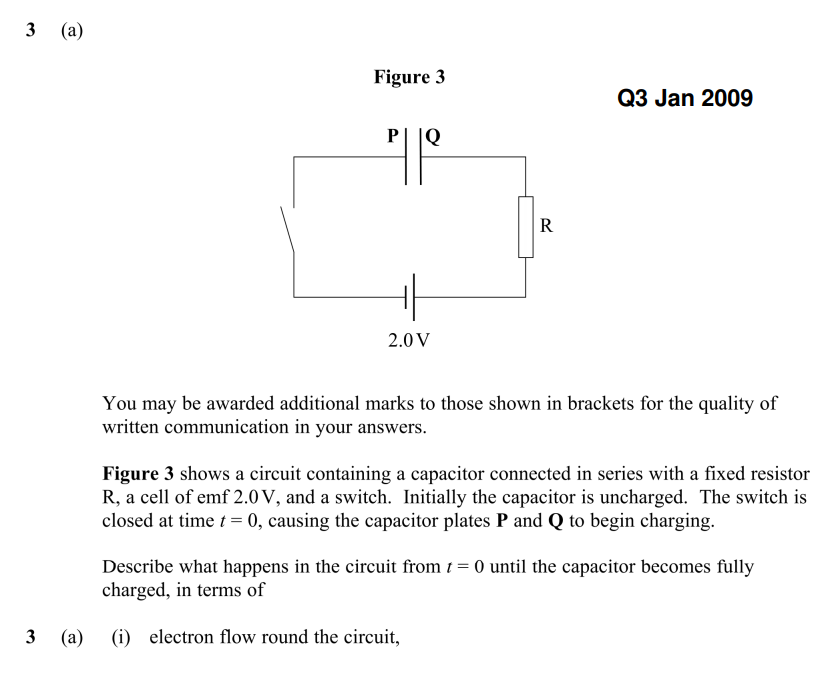

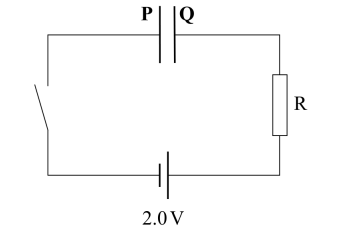
What happens to the p.d across capacitor and resistor as charging (4 marks)
p.d across capacitor increases
p.d across resistor decreases
Vr + Vc = 2v
Once fully charged, Vc = 2v and Vr = 0V
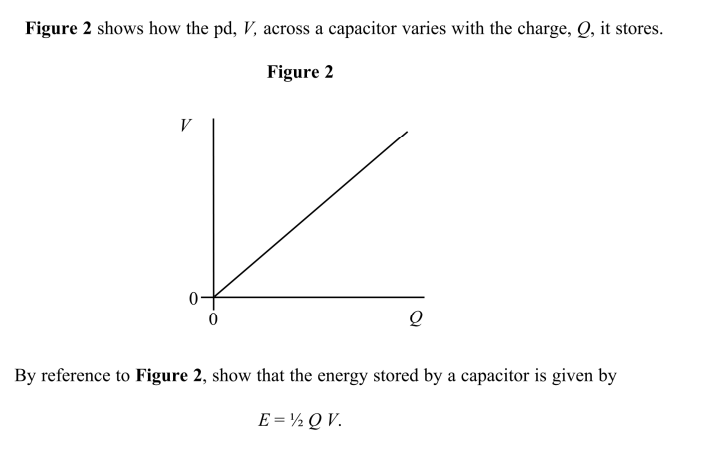
V = W/Q

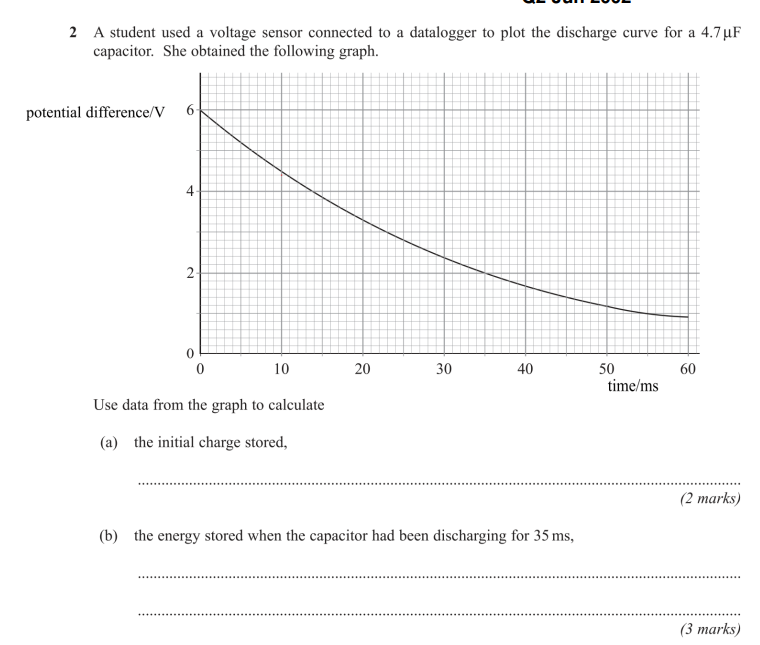
Part B
Use instantaneous voltage!

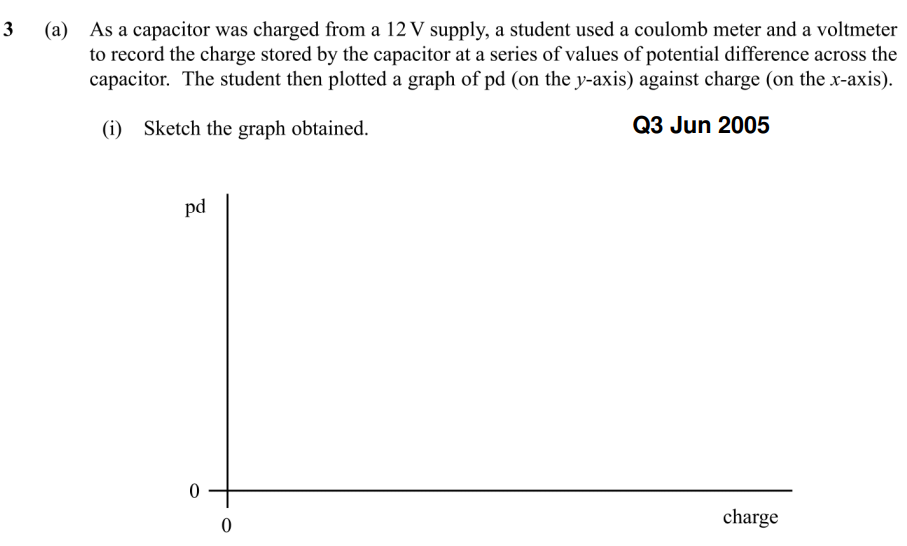
STRAIGHT LINE THROUGH ORIGIN! (Since Q directly proportional to V)
What is a dielectric constant?
The dielectric constant, also called relative permittivity (εr), is a measure of how much a material increases the capacitance of a capacitor compared to if it were filled with a vacuum (free space).
Why must a variable resistor, with varying resistance be used to keep current constant when charging a battery?
As the battery charges, its voltage gradually increases because more energy is stored in its chemical components.
If the battery voltage increases and the power supply voltage remains constant, the potential difference across the resistor decreases. To keep the current constant, the resistance must be increased
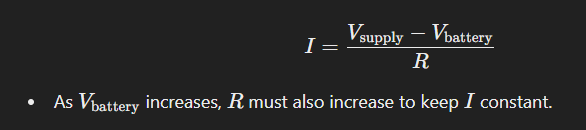
How much energy is lost as heat in a battery when charging a capacitor?
Half of the total amount.
Half wasted as heat, half stored.
(This question, 0.9J for energy and 1.8J for work done)
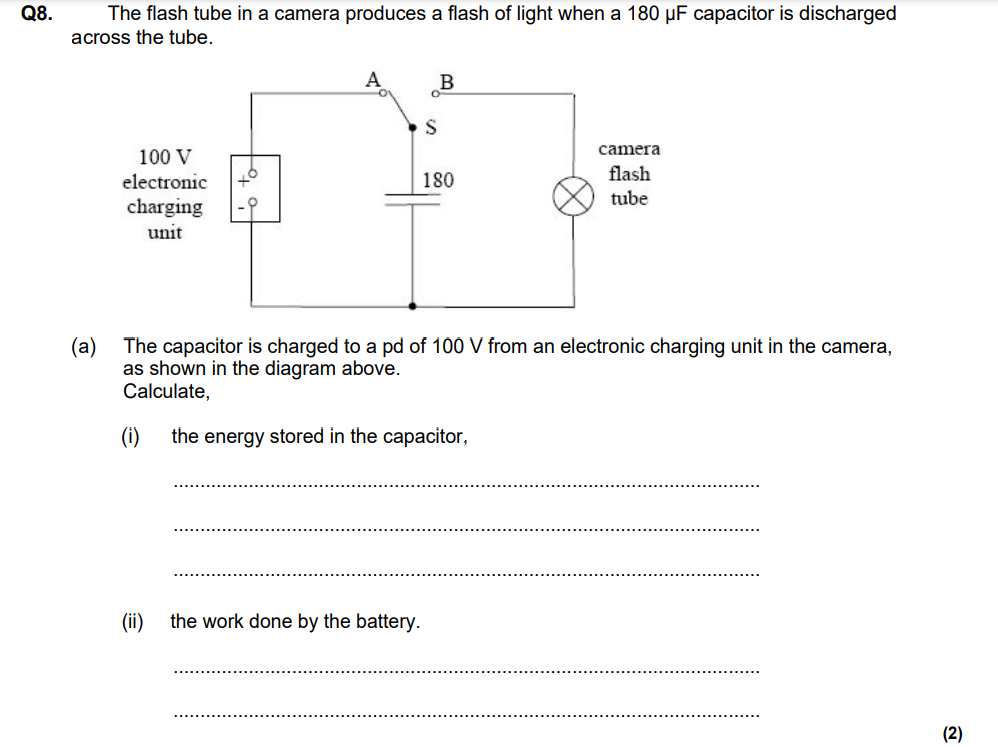
What are 3 differences between a capacitor and a battery?
Capacitors store potential energy in the electric field whereas Batteries as a chemical store
Capacitors stores relatively little charge, opposite for Batteries
Capacitors charges and discharges quickly, opposite for batteries.
What is capacitance?
The amount of charge stored in the object per unit potential difference used to store it (C = Q/V)
What is capacitance units?
Farads
What is the equation for capacitance?
C=Q/V, where V is the potential difference across the capacitor. (Charge is the same across circuit)
How would you keep the current charging a capacitor in a circuit constant?
Using a variable resistor, constantly change the resistance.
What are the 3 equations to use to work out the energy stored in a capacitor?
E = ½QV
E= ½Q²/C
E= ½CV²
Why does a build up of charge on a capacitor result in a build up of energy?
Like charges are forced onto the plates, and due to the electrostatic repulsion between the charges, some of that energy used in forcing them together is stored as electrical potential energy.
What type of energy is stored on a capacitor?
Electrical potential energy
What is the area under a charge-potential difference graph?
Energy. (V = W/Q so QV = W)
What is permittivity?
How difficult it is to generate an electric field in a medium. (The higher the number, the more charge required to generate an electric field)
What is relative permittivity?
The ratio of permittivity within a material over free space (vacuume).
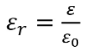
What happens to the size of the electric field between the parallel pates in a capacitor when charge flows through it?
Decreases, since the polar molecules when polarized (which occurs when charge flows) face the opposite directions to the plate charges, and since they create their own electric field, they reduce the overall electric field.
What happens to the capacitance when polar molecules are polarized?
Increases, since they reduce the overall electric field of the capacitor, which in turn reduces the potential difference (work done) to move the charge onto the plate.
Why does reducing an electric field reduce the potential difference of the capacitor?
Since V=E×d, where E is electric field, they are directly proportional to each other.
What is the equation for calculating capacitance, involving area of plate, permittivity of free space, relative permittivity and distance between plates?
C= AxE0xE/d
E0 is permittivity of free space
E is relative permittivity (ratio of permittivity of material and free space)
What is the permittivity of free space?
8.85 × 10^-12 Fm^-1
How can you increase the capacitance of a capacitor? (3 marks)
Increase area of plates
Increase permittivity of plate (which increases the relative permittivity)
Decrease the distance between the plates.
What is a Dielectric constant?
Another word for relative permittivity.
What is a dielectric material?
An electric insulator
What is meant by permittivity?
How difficult it is for an electric field of a given size to form in a medium.
What orientation are polar molecules when no charge is being stored in the capacitor?
Random
What orientation are polar molecules when charge is being stored in the capacitor?
They face towards their opposite charges (negative side to positive plate…)
What is the “form” of the 3 equations for calculating the charge, voltage and current when a capacitor is charging?
X = X0 × (1- e^-t/RC)
X = X at time t
X0 = final X
e = Euler’s number
t = time spent charging
R = resistance of fixed resistor in circuit
C = capacitance of capacitor
What do the graphs of current, voltage and charge respectively when a capacitor is charging?
Current: 1/e^x graph
Voltage and charge: e^x graph
What is the difference between charging and discharging equations?
Charging is 1- e
Discharging is just e!
What are the equations for discharging?
X = X0 x e^-t/RC
What do the 3 graphs of current, voltage and charge look like when a capacitor discharges?
1/e^x for all!
Explain how the polar molecules cause a change in capacitance. (3 marks)
Polar molecules align with their positive side facing the negative plate and vice versa with other side
Each molecule
If reducing the area of a capacitors plate, does it decrease linearly? If so, why?
Yes, since C is directly proportional to A.
D
Make sure to re arrange properly!

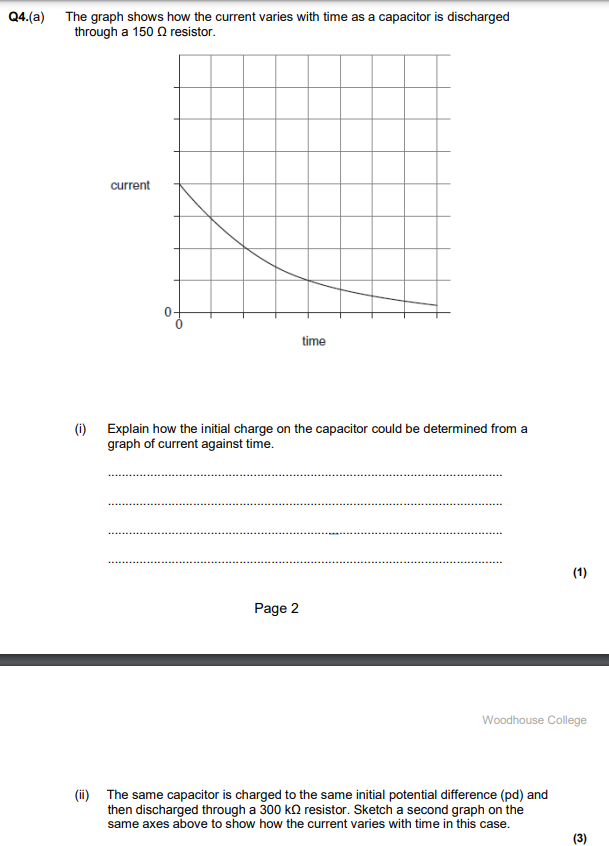
Part ii)
The current is half since I = V/R and if R doubles, I halves. I here is the intial.

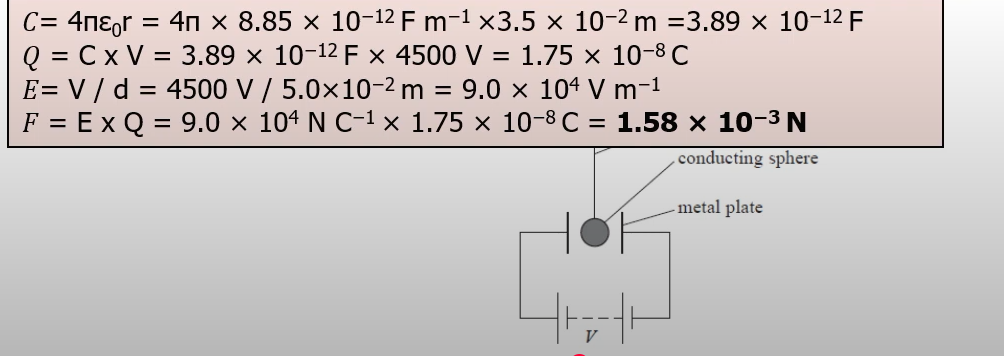
The capacitance of the capacitor is 0.12 F and it is charged to a pd of 9.0 V. The weight of the mass raised is 3.5 N. Calculate the maximum height to which the mass could be raised. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
With any question involving capacitance and energy, you must use E = 1/2cV² or another SPECIFIC energy equation using capacitance. NOT V= W/Q since remember only V/2 is stored in the capacitor, so you CAN use V/2 = W/Q


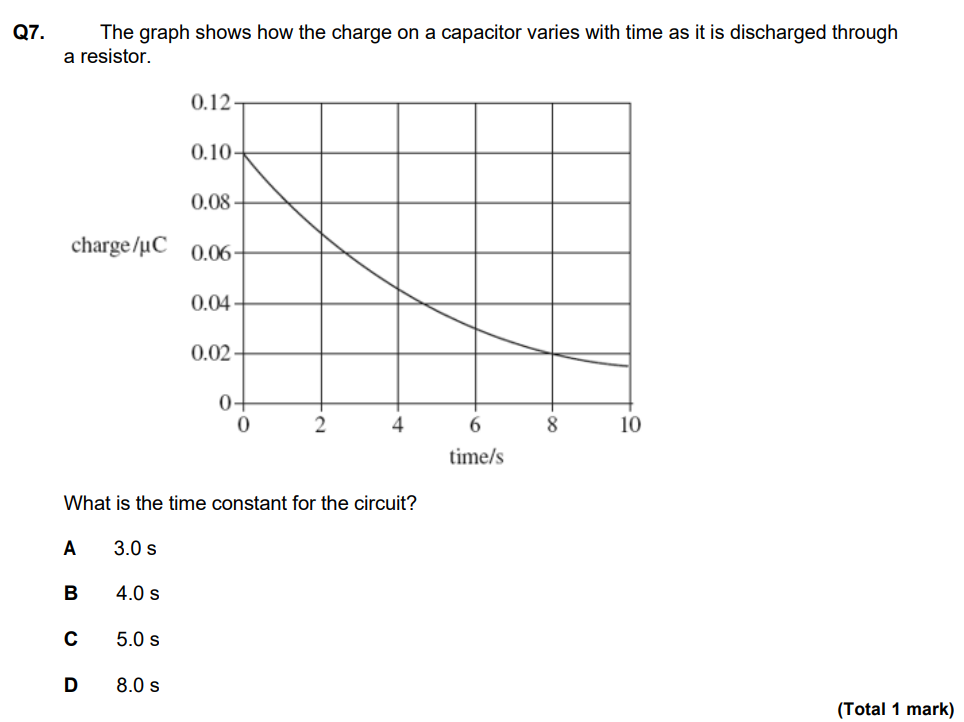
Remember time constant (T) is the time taken for the capacitance to fall to 37 % (C x 0.37) of original value.