BLOOD BANK 383 -438
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
383-A patient has symptoms indicating a possible hemolytic transfusion reaction. What should be done immediately?
C-stop the transfusion and call the patient's doctor to report the reaction
384-Posttransfusion purpura is usually caused by:
C-anti-HPA-1a
385-An unexplained fall in hemoglobin and mild jaundice in a patient transfused with Red Blood Cells 1 week previously would most likely indicate:
D-delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction
386-In a delayed transfusion reaction, the causative antibody is generally too weak to be detected in routine compatibility testing and antibody screening tests, but is typically detectable at what point after transfusion?
B-2 days-2 weeks
387-Which of the following is a potential complication of massive transfusions?
C-hypothermia due to 1-6*C storage temperature of red cells
388-Severe intravascular hemolysis is most likely caused by antibodies of which blood group system?
a- ABO
389-Which of the following blood group systems is most commonly associated with delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions?
B- JK
390-After receiving a unit of Red Blood Cells, a patient immediately develops flushing, nervousness, fever spike of 38.9°C, shaking, chills and back pain. The plasma hemoglobin is elevated and there is hemoglobinuria. Laboratory investigation of this adverse reaction would most likely show:
A-an error in ABO grouping
391-Atrauma patient who has just received 10 units of blood may develop:
D-thrombocytopenia
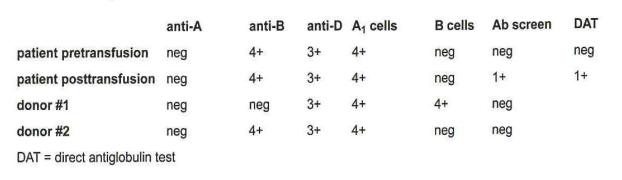
392-Five days after transfusion, a patient becomes mildly jaundiced and experiences a drop in 1S hemoglobin and hematocrit with no apparent hemorrhage. The results of the transfusion reaction workup are in this table:
DAT = direct antiglobulin test
In order to reach a conclusion, the MLS should:
D-perform an elution on the posttransfusion sample and identify the antibody in the eluate and the serum
393-The most appropriate laboratory test for early detection of acute posttransfusion hemolysis is:
A-visual inspection for free plasma hemoglobin
394-During initial investigation of a suspected hemolytic transfusion reaction, it is observed that Blood Bank paperwork and patient sample and blood component labels are correct, the postransfusion reaction plasma is yellow as is the pretransfusion sample, and the direct antiglobulin test is negative. Repeat ABO typing on the posttransfusion sample confirms the pretransfusion results. What is the next step in this investigation?
D- no further serological testing is necessary
395-Which of the following transfusion reactions is characterized by high fever, shock, hemoglobinuria, DIC and renal failure?
A- bacterial contamination
396-Hemoglobinuria, hypotension and generalized bleeding are symptoms of which of the following transfusion reactions?
C- hemolytic
397-Patients who are chronically transfused with red cell components can develop:
A-iron overload
398-A patient's record shows a previous anti-Jk(b), but the current antibody screen is negative. What further testing should be done before transfusion?
D-phenotype donor units and select Jk(b—) units for compatibility testing
399-Which of the following is associated with a risk of developing transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GVHD)?
B-direct donation from the first degree family members

400-A patient is readmitted to the hospital with a hemoglobin level of 7 g/dL (70 g/L) 3 weeks after receiving 2 units of red cells. The initial serological tests are:
Which test should be performed next?
C-perform an elution and identify the antibody in the eluate
401-In a delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction, the direct antiglobulin test on the posttransfusion sample can be:
B- mixed-field positive
402-To prevent donor lymphocytes from engraftment in the bone marrow of an immunosuppressed patient, all transfusion products must be:
D-irradiated
403-For a patient who has suffered an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction, the primary treatment goal should be to:
D-reverse hypotension and minimize renal damage
404-Nine days after being transfused with an HLA-matched platelet transfusion, a patient develops a fever, watery diarrhea, skin rash and demonstrates increased liver enzymes. This patient may have transfusion-associated:
C -graft-versus-host disease
405-Which of the following transfusion reactions occurs after infusion of only a few milliiters of blood and gives no history of fever?
C-anaphylactic
406-Fever and chills are symptoms of which of the following transfusion reactions?
D-febrile
407-Hives and itching are symptoms of which of the following transfusion reactions?
B-allergic
408-A temperature rise of 1°C or more occurring in association with a transfusion, with no abnormal results in the transfusion reaction investigation, usually indicates which of the following reactions?
A- febrile
409-A 65-year-old woman experienced shaking, chills, and a fever of 38.9°C approximately 40 minutes following the transfusion of a second unit of Red Blood Cells. The most likely explanation for the patients symptoms is
D-febrile transfusion reaction
410-Use of only male donors as a source of plasma intended for transfusion is advocated to reduce which type of reaction?
B- TRALI
411-Symptoms of dyspnea, hypoxemia, and pulmonary edema within 6 hours of transfusion is most likely which type of reaction?
D-TRALI (hypoxemia, and pulmonary)
412-Coughing, hypoxemia and difficult breathing are symptoms of which of the following transfusion reactions?
C- TACO
413-Congestive heart failure, severe headache and/or peripheral edema occurring soon after transfusion is indicative of which type of transfusion reaction?
D-TACO
414-A patient becomes hypotensive and goes into shock after receiving 50 mL of a unit of Red Blood Cells. She has a shaking chill and her temperature rises to 40.4°C. A transfusion reaction investigation is initiated but no abnormal results are seen. What additional testing should be performed?
A- Gram stain and culture of the donor unit
415-The most frequent transfusion-associated disease complication of blood transfusions is:
C-hepatitis
416-Which of the following patient groups is at risk of developing graft-versus-host disease?
D-recipients of blood donated by immediate family members
417-Transfusion-associated HTLV I/II incidence is low due to the following laboratory testing:
D-IgG antibody testing for HTLV I/Il by ELISA or ChLIA
418-which viral diseases have a lower incidence of transfusion-associated infections due to nucleic acid testing (NAT)?
A-HIV-1, HCV, WNV
419-Two hours after receiving a blood transfusion, the recipient experienced fever, chills, back pain and hypotension. Patient blood samples are collected along with a urine sample and sent to the laboratory. Which of the following results could indicate that an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction is taking place?
B-hemolysis in posttransfusion sample only
420-What can cause hypothermia in a blood recipient?
D- rapid infusion of cold blood
421-The preferred replacement fluid to maintain normal oncotic pressure and intravascular fluid levels for patients who have therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura is:
B-plasma
422-Which of the following disease states is treated with therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE)?
B-myasthenia gravis
423-50-Year-old patient with acute lymphocytic leukemia has symptoms of dyspnea, visual , abnormalities, and headache. The blast count is greater than 100,000/uL. What type of apheresis is indicated to treat this patient?
C- cytapheresis to remove immature lymphocytes
424-Therapeutic plasmapheresis is performed in order to:
D-treat patients with plasma abnormalities
425-Plasma exchange is recommended in the treatment of patients with macroglobulinemia in order to remove:
B-excess IgM
426-Extracorporeal photopheresis can be used to treat which of the following disorders?
A-solid organ transplant rejection
427-For patients with familial hypercholesterolemia, what type of therapeutic apheresis will remove by LDL cholesterol?
B-selective adsorption
428-Sickle cell anemia may be treated with:
D-erythrocytapheresis to remove sickled RBCs
429-Prior to initiating a blood transfusion, the transfusionist and another qualified individual must:
A-match the blood component to the recipient using 2 independent identifiers
430-Which of the following must be verified in the transfusion service prior to the issue of blood products?
D-expiration date and, if applicable, expiration time of the blood product
431-during the issue of an autologous unit of Whole Blood, the supernatant plasma is observed to be dark red. What would be the best course of action?
D-Quarantine the unit for further testing
432-Which of the following must be performed on a patient before, during, and after receiving a blood transfusion?
A-blood pressure, pulse, respiration rate and temperature
433-An intraoperative strategy for patient blood management is:
C-acute normovolemic hemodilution
434-The most important step in the safe administration of blood is to:
D- accurately identify the donor unit and recipient
435-What information related to receiving a blood transfusion needs to be documented in a patient's medical record?
C-signed patient consent for transfusi
436-In addition to verifying the blood recipient's 2 independent identifiers, ABO group and RA type, what else needs to be verified immediately before starting a transfusion?
D-donation identification number on unit and donor's ABO and Rh
437-Preoperative autologous blood donation can be used for patients who:
B-have an alloantibody to a high-incidence antigen
438-Intraoperative strategies for blood management include:
C-reinfusing shed blood recovered during surgery that has been washed with normal saline