3AIS1 SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 3-4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Enterprise Data Model
• Establishes the range and general contents of organizational databases.
• Create an overall picture or explanation of organizational data, not the design for a particular database.
• Specifies scope and general content
Information System
• Resources that enable information collection, management, control, and dissemination throughout an organization
Information System Architecture
• A conceptual blueprint or plan that expresses the desired future structure for the information systems in an organization.
System Development Life Cycle
• The traditional methodology used to develop, maintain, and replace information systems.
• is a conceptual model that describes the stages involved in an information system development project, from an initial feasibility study through maintenance of the completed application
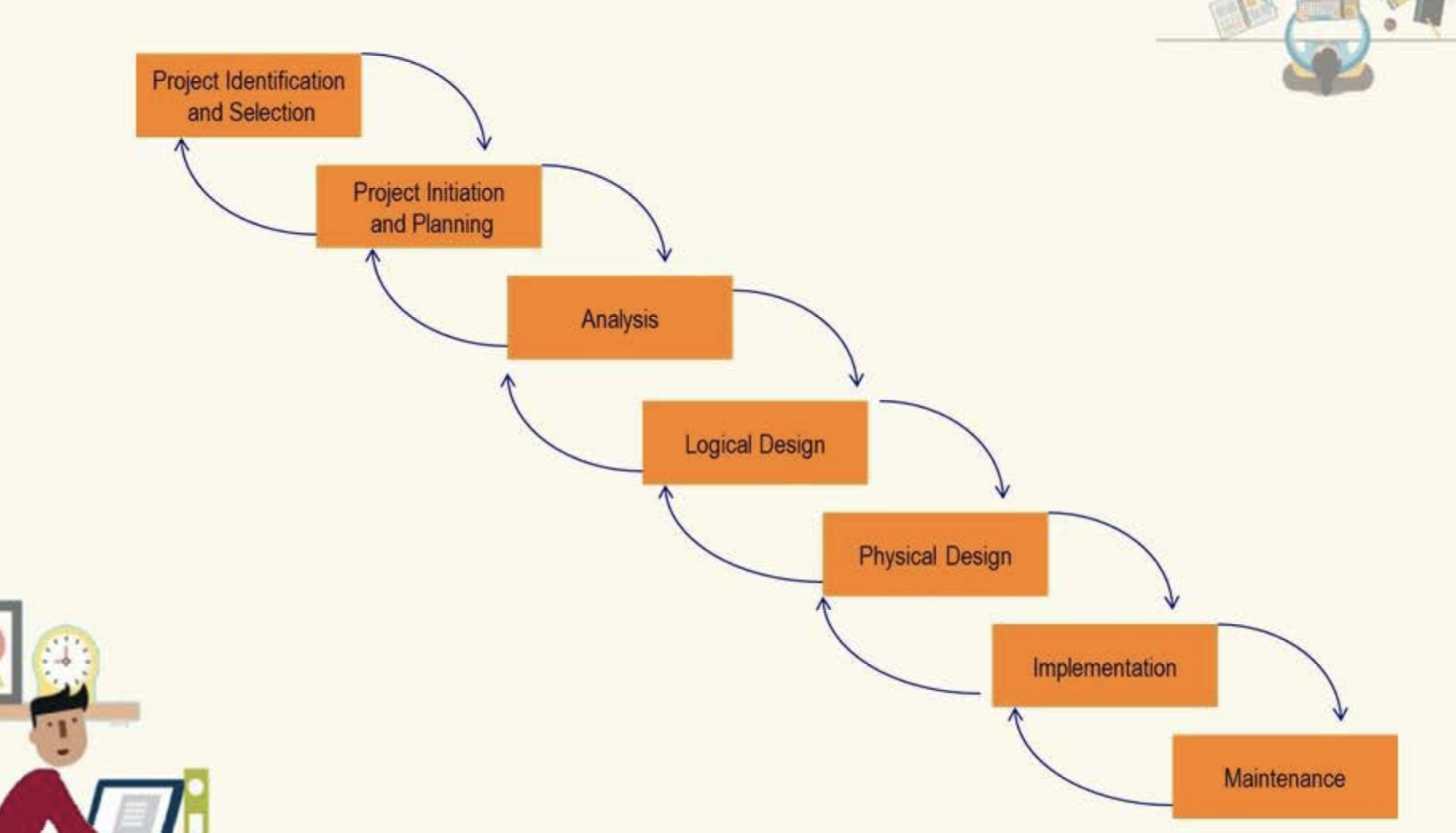
Waterfall Model
is the first SDLC method and is often considered the classic approach to systems development, which describes a development method that is linear and sequential.
Feasibility Study
can be considered as preliminary investigation that helps the management to take decision about whether study of system should be feasible for development or not.
- it identifies the possibility of improving an existing system, developing a new system, and produce refined estimates for further development of system.
- It is used to obtain the outline of the problem and decide whether a feasible or appropriate solution exists or not.
Objective of a Feasibility Study
to acquire problem scope instead of solving the problem.
Output of a Feasibility Study
is a formal system proposal act as decision document which includes the complete nature and scope of the proposed system.
Economic Feasibility
• Assesses a system's costs and benefits
• Team tallies tangible development and operating costs for the system and compares them with expected financial benefits of the system
• Keep in mind that an information system project that's feasible at the outset could become unfeasible later
Technical Feasibility
Concerned with technology to be used in the system
• Team needs to assess whether technology to support the new system is available or feasible to implement
• Lack of technical feasibility
- Can also stem from an organization lacking the expertise, time, or personnel to implement the new system
Operational Feasibility
Measure of: - How well the proposed solution will work in the organization - How internal and external customers will react to it • "Is the information system worth implementing?"
Schedule Feasibility
Whether the new system can be completed on time
Legal Feasibility
Concerned with legal issues
Conceptual Modeling
- The analyst develops a diagram and other documentation to outline the scope of data involved in this particular development project without considering what databases already exist
Conceptual schema
A detailed, technologyindependent specification of the overall structure of organizational data.
Logical Schema
The representation of a database for a particular data management technology.Physical schema
Physical Schema
is a set of specifications that describe how data from a logical schema are stored in a computer's secondary memory by a specific database management system.Corrective maintenance
Corrective Maintenance
Changes made to a system to repair flaws in its design, coding, or implementation
Adaptive Maintenance
Changes made to a system to evolve its functionality to changing business needs or technologiesPerfective maintenance
Perfective Maintenance
Changes made to a system to add new features or to improve performanceChanges made to a system to add new features or to improve performance
Preventive Maintenance
Changes made to a system to avoid possible future problemsPilot
Pilot
In this method, a working version of the system is implemented in one part of the organization, such as a single work area or a single department.
Phase
The phased method of conversion introduces the new system gradually.
Parallel
The phased method of conversion introduces the new system gradually.
This method is the safest conversion method since it guarantees that, should problems such as errors in processing or inability to handle certain types of transactions arise in using the new system, the organization can still fall back to the old system without loss of time or loss of service
Plunge
• The phased method of conversion introduces the new system gradually.
• It can be used when installing a new system throughout an organization is impossible all at once.
Rapid Application Development
• The initial emphasis is on creating a prototype that looks and acts like the desired product in order to test its usefulness.
Joint Application Development
a methodology that involves the end-users or clients in the design and development of an application, through a succession of collaborative workshops.Spiral Model
Spiral Model
combines the features of the prototyping model and the waterfa II model. The spira I model is favored for large, expensive, and complicated projects.
V Model
It is considered to be the extension of the waterfall model, but instead of moving down, the process is bent upwards after the coding stage to form the V shape.
• defines a uniform procedure for systems development wherein system validation is carried out through activities that occur throughout the entire development.
Synchronize and Stabilize Model
allows teams to work in parallel on individual application modules, frequently synchronizing their code with that of other teams and debugging (stabilizing) code regularly throughout the development processPrototyping
Prototyping
Is the rapid development and testing of working models of new applications in an interactive, iterative process that can be used by both IS specialists and business professionals
Agile Methods
• Less emphasis on team coding and more emphasis on limiting the project's scope • Focuses on setting a minimum number of requirements and turning them into a working product • Agile Alliance organization - Manifesto contains principles for this methodologySCRUM Methodology
SCRUM Methodology
a management framework that teams use to self-organize and work towards a common goal. It describes a set of meetings, tools, and roles for efficient project delivery.
KANBAN Methodology
an agile method that aims at continuous improvement, flexibility in task management, and enhanced workflow
Programmers
These individuals design and write computer programs with commands to maintain and access data in the embedded database
Database architects
These individuals establish standards for data in business units, striving to attain optimum data location, currency, and quality.
Data administrators
These individuals have responsibility for existing and future databases and ensure consistency and integrity across databases, and as experts on database technology, provide consulting and training to other project team members.
Project Managers
- Project managers oversee assigned projects, including team composition, analysis, design, implementation, and support of projects.