orgo rnx
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
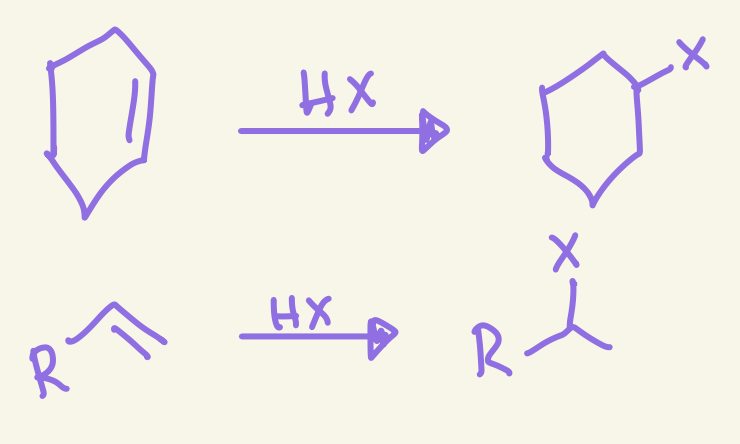
halohydrogenation
H-X added
X adds markovnikov
No sterochem
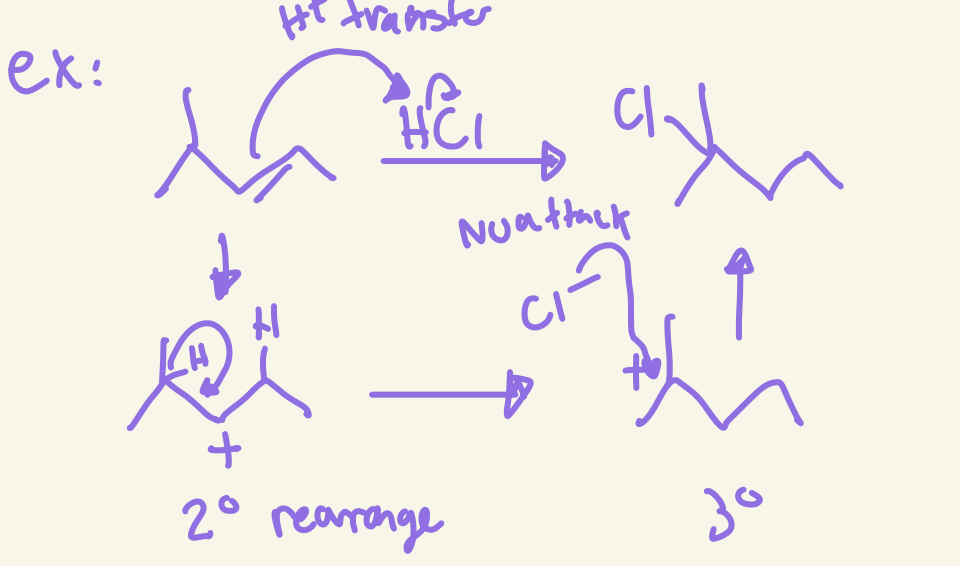
halohydrogenation mechanism
H+ transfer rearrange if possible then nu attack of X to most substituted carbon
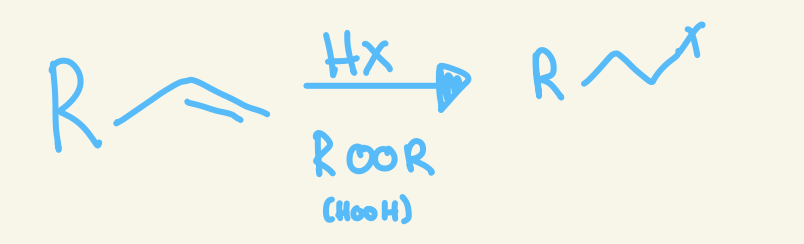
anti-markovnikov halohydrogenation
H-X
X adds anti markovnikov
No stereochem
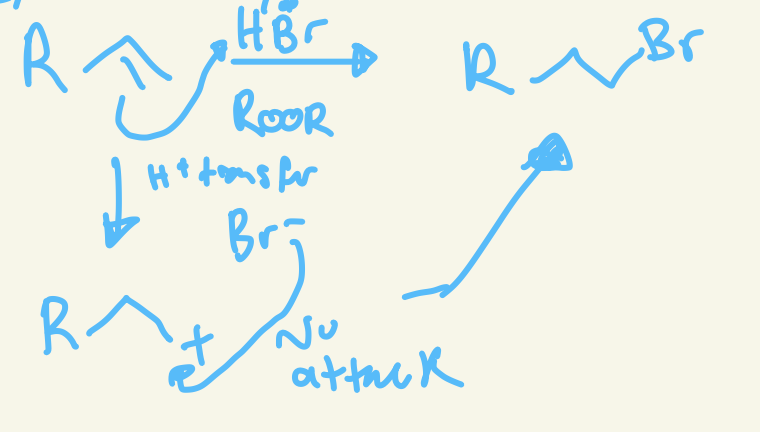
anti-markovnikov halohydrogenation mechanism
H+ transfer and H add to more substituted carbon so carbon cation is on less substituted carbon and then nu attack of X- on the less substituted carbon cation
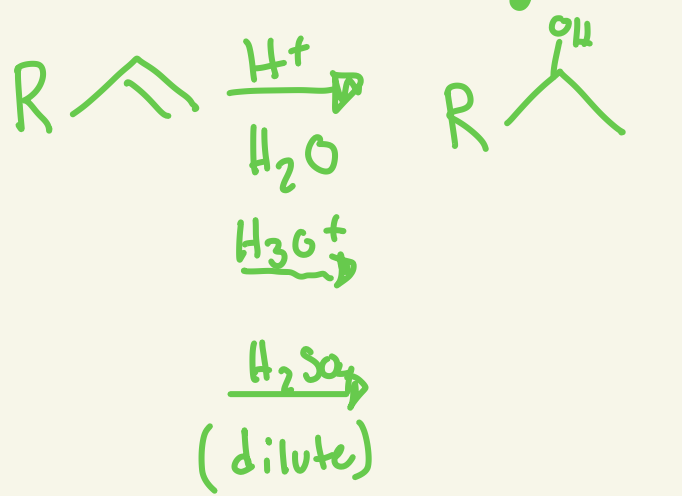
acid catalyzed hydration
H and OH
OH adds markovnikov
No stereochem but rearrangement can occur
H+/H2O or H3O+ or H2SO4 dilute
adds H and OH at more substituted spot with rearrangement
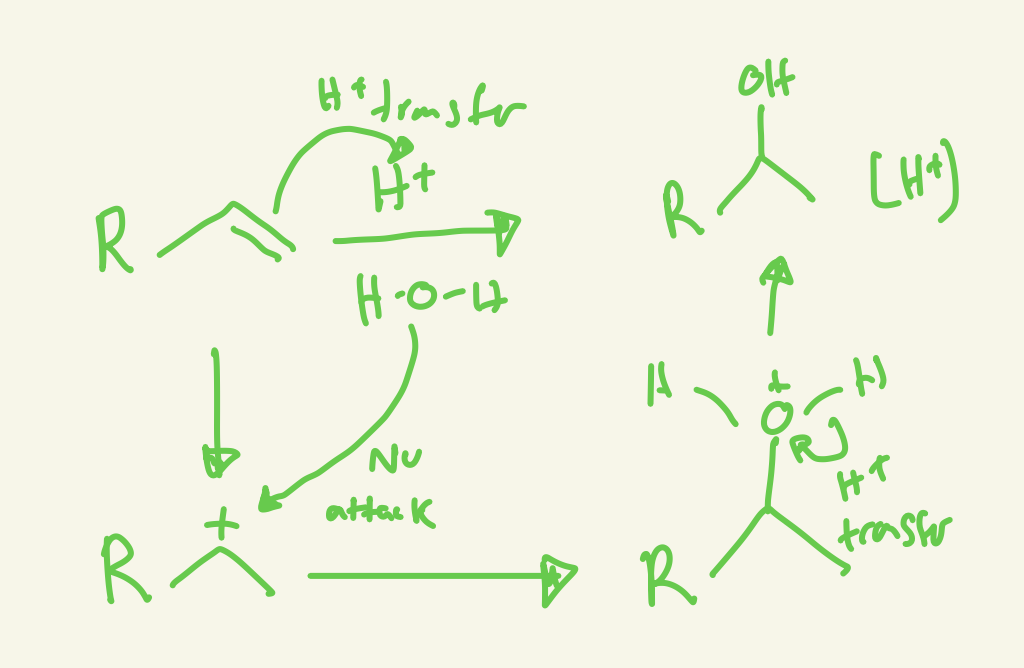
acid catalyzed hydration mechanism (H+/H2O or H3O+ or H2SO4 dilute)
H+ transfer and H2O attacks more substituted carbon cation and then H+ transfer on H2O
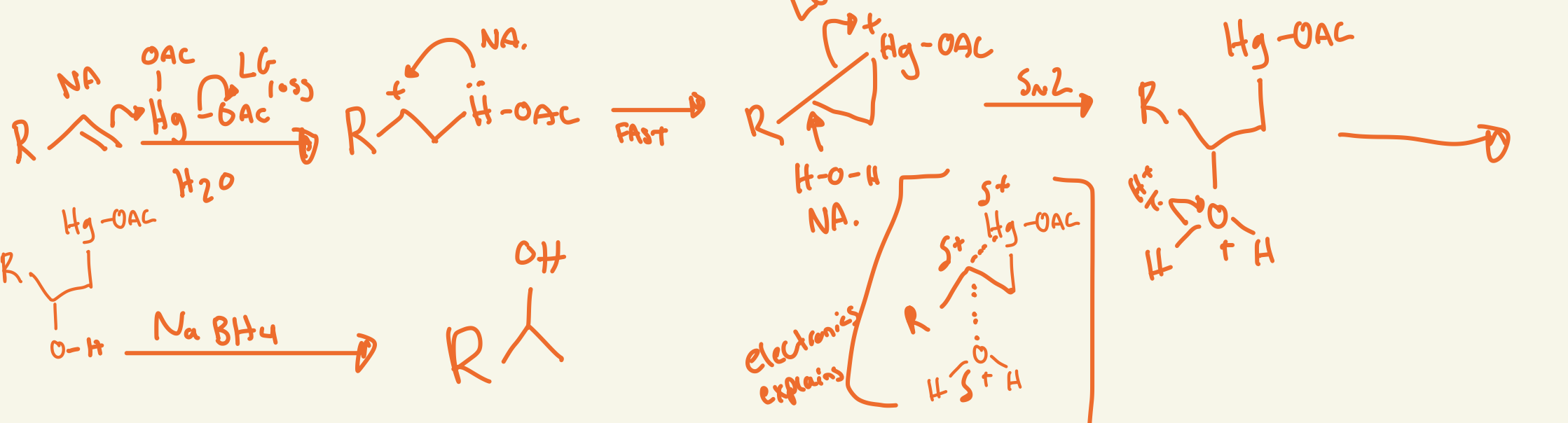
oxymercuration/demercuration
H and OH
OH adds markovnikov
No sterochem
Hg(Oac)2 H2O / NaBh4
adds H and OH at markovnikov but no rearrangement
oxymercuration/demercuration mechanism (Hg(Oac)2 H2O / NaBh4)
first double bond nu attacks the Hg at less substituted side and 1 OAc has LG loss and the lone pair on Hg nu attack the carbon cation then H2O nu attacks the carbon cation and LG loss of positive Hg-OAc then H2O H+ transfer then NaBH4 somehow removes Hg-OAc so then just OH on more substituted side
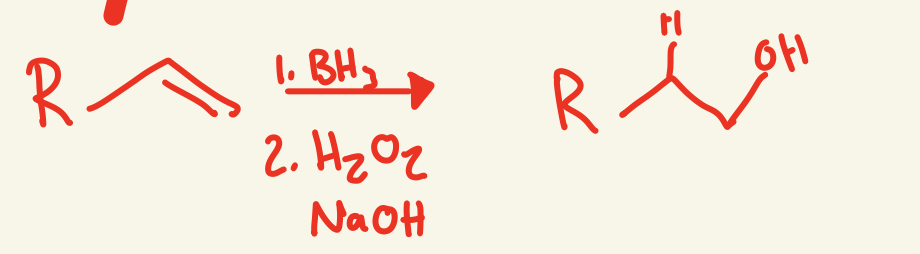
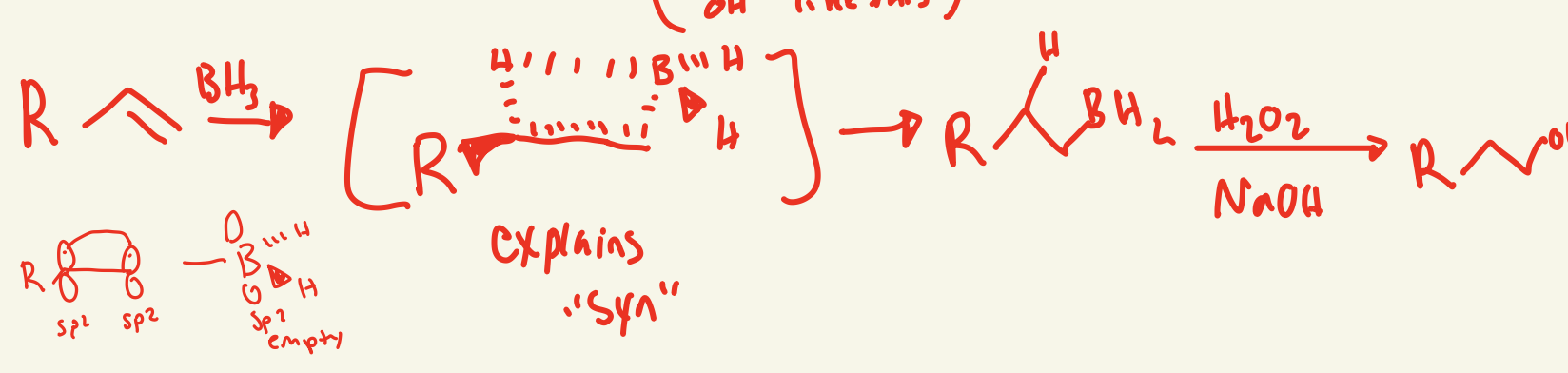
hydroboration/oxidation
H and OH
OH adds anti markovnikov
Stereo Yes adds syn
BH3 / H2O2 NaOH
adds OH on less substituted side and has same wedge/dash as H “syn”
hydroboration/oxidation mechanism (BH3 / H2O2 NaOH)
BH3 on less substituted carbon and then one H attaches to the more substituted carbon and then BH2 on less substituted side interacts with H2O2 and NaOH and OH replaces the BH2
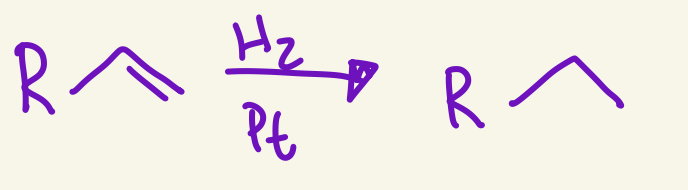
catalytic hydrogenation
H and H
No regio
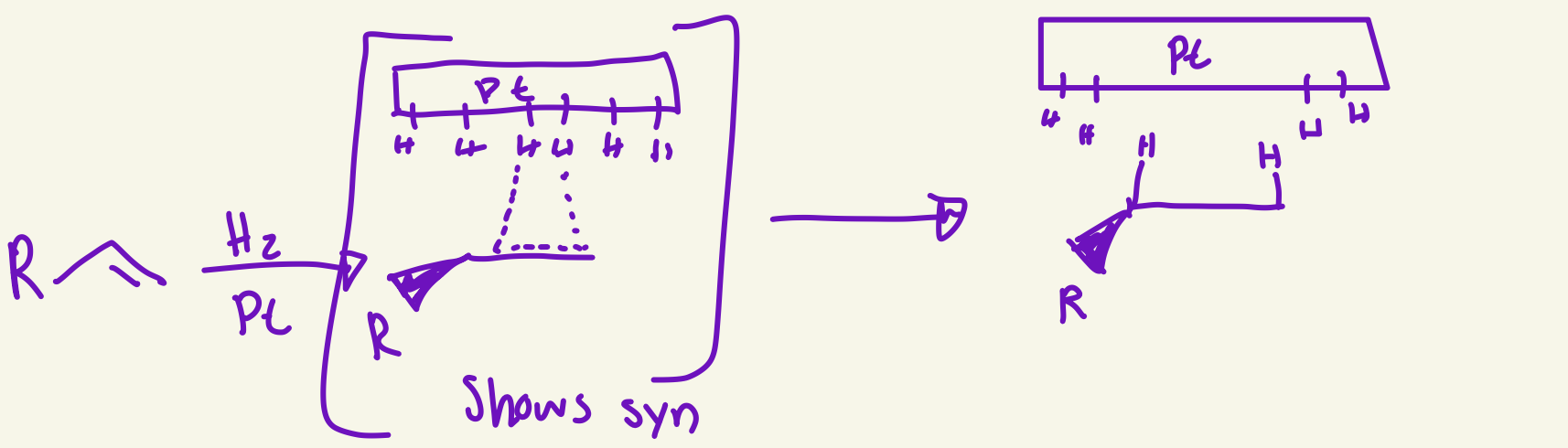
Stereocehm is syn addition
H2 / Pt
adds Hs with same sterochem '“syn”
catalytic hydrogenation mechanism (H2 / Pt)
the alkene interacts with Pt that have hydrogens on it then it breaks the double bond and uses that to create bonds with two Hs and the gets syn H attachments
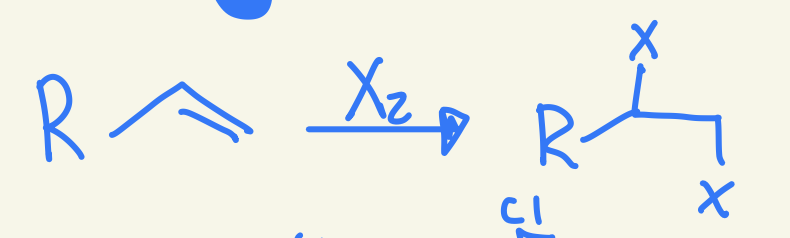
halogenation
X and X
No regio
Stero yes Xs add anti
X2
adds X on each side of double bound with trans stereochem
halogenation mechanism (X2)
double bond Nu attack on X at less substituted carbon cation and other X LG loss then lone pair on X attacks carbon cation then the free X- Nu attack more substituted carbon and LG loss of X+ and then creates anti product
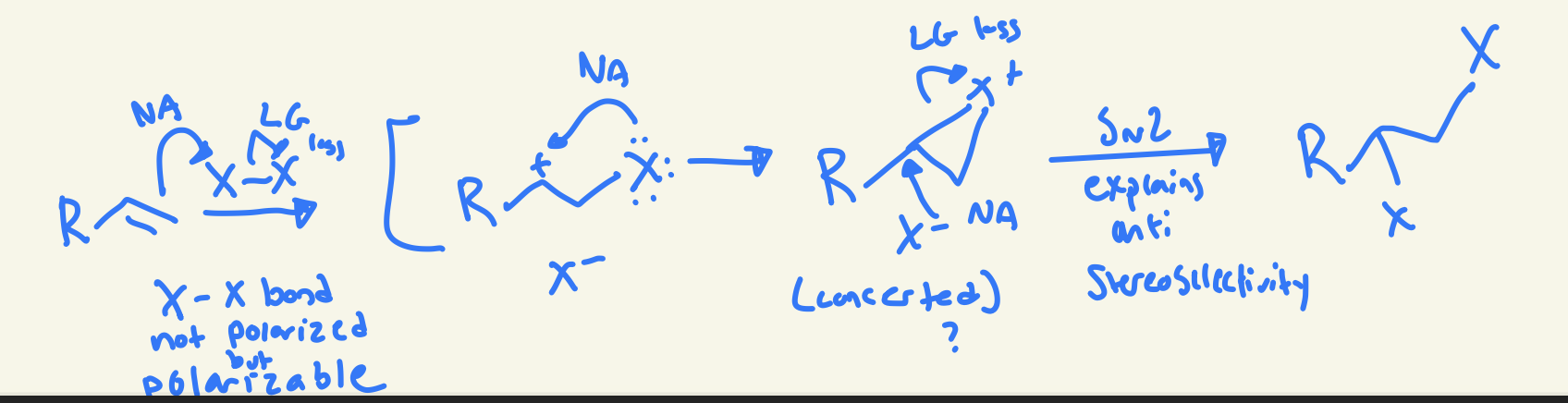
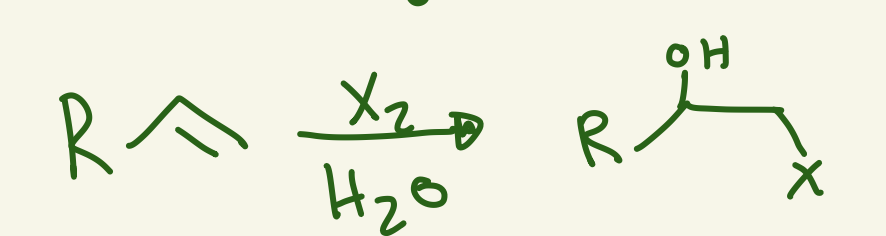
halohydrin
X and OH
OH adds markovnikov
Stereochem anti
X2 / H2O
adds OH on more substituted and X on less
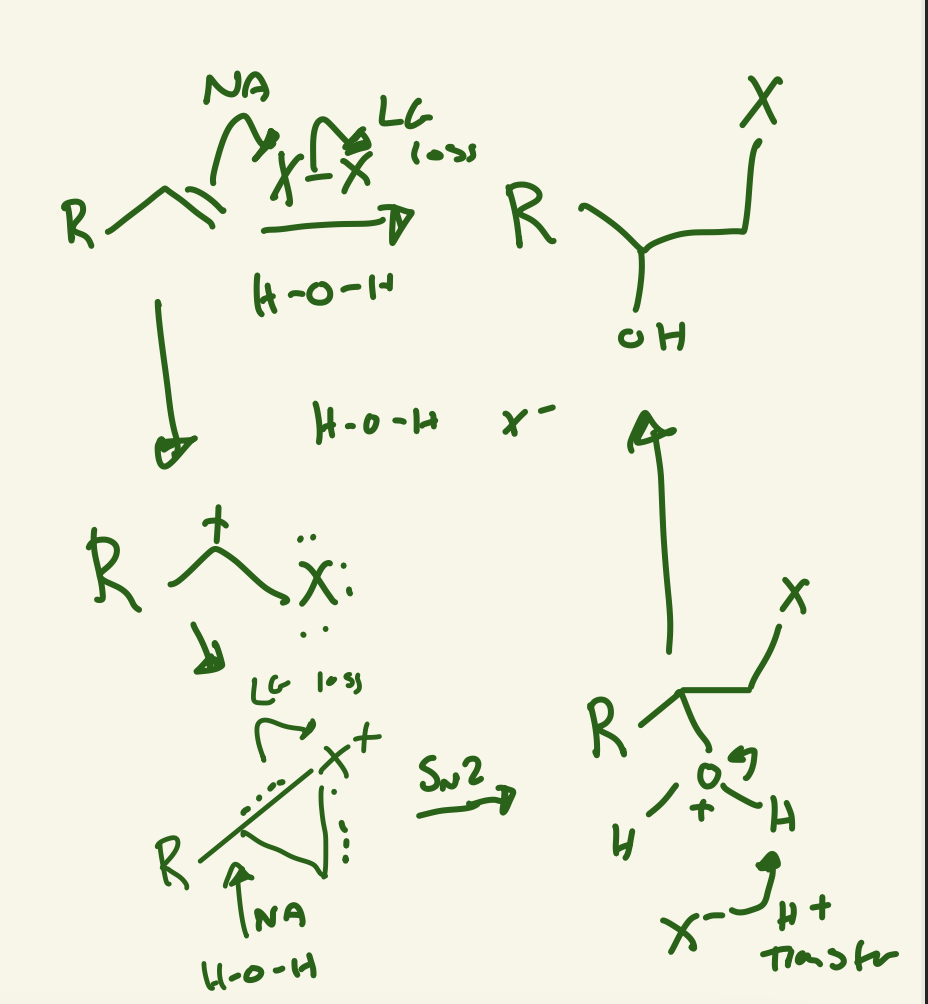
halohydrin mechanism (X2 / H2O)
Nu attack on X-X and LG of a X and X is on less substituted carbon and the lone pair of X attack carbon cation and then H2O Nu attack the more substituted carbon then H+ transfer with free X- and leaves OH
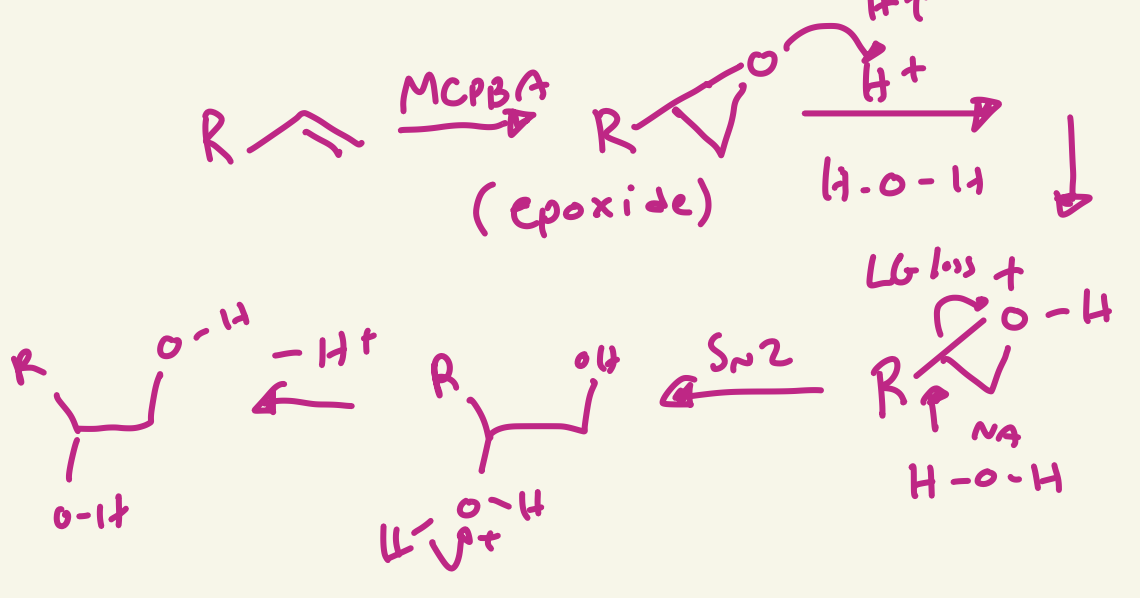
anti-dihydroxylation
OH and OH
no regio
Sterochem anti
RCO3H / H3O+ or McPBA / H3O+
OH and OH added trans
anti-dihydroxylation mechanism (RCO3H / H3O+ or McPBA / H3O+)
the RCO3H or McPBA adds O then O H+ transfer H+ from H3O+ then H2O Nu attack at more substituted carbon and LG loss of O+ then H+ transfer to leave OH
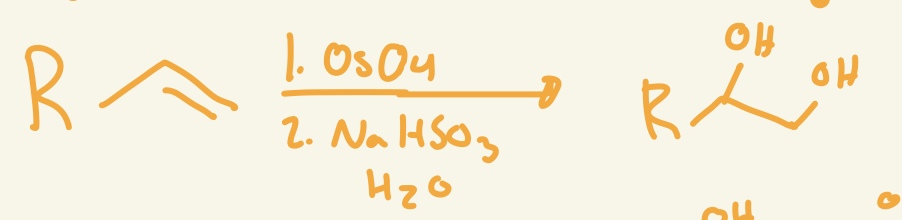
syn dihydroxylation
OH and OH
no regio
Stereo adds syn
OsO4 / NaHSO3 H2O
adds OH and OH cis
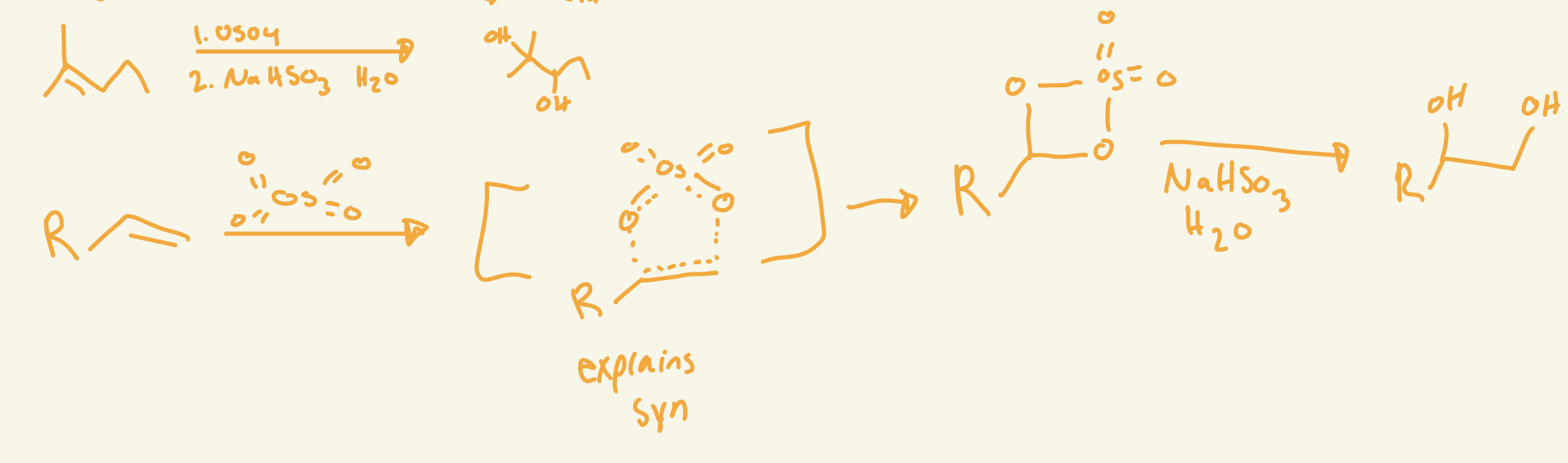
syn dihydroxylation mechanism (OsO4 / NaHSO3 H2O)
OsO4 adds 2 O on same side then interacts with NaHSO3 H2O removes the OsO2 and adds Hs on Os
ozonolysis (O3 / DMS)
breaks C=C bond and adds 2 Os double bonded to molcules