Second Trimester Normal/ Abnormal
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
What does aneuploidy mean?
Having an abnormal number of chromosomes
What is the most common chromosomal abnormalities among spontaneous abortions?
Turner’s syndrome
What are sonographic features of trisomy 21?
thickened nuchal fold, AVSD, hydronephrosis, double bubble sign (duodena atresia), shortened long bones
What are less specific trisomy 21 markers?
cystic hygromas, ventriculomegaly, sandal gap toes, omphalocele, single umbilical artery
What lab finding is decreased in trisomy 21?
b hCG
For quad screen which test is increased in trisomy 21?
increased inhibin A
What are sonographic appearances of trisomy 18?
Symmetrical IUGR with polyhydramnosis, CPC’s. clenched fists, clinodactyly, club feet/ rocket bottom feet, large VSD
What are less specific sonographic markers of trisomy 18?
cleft lip, omphalocele, strawberry shaped head, radial ray syndrome, micrognathia
What is radial ray syndrome?
absent radius resulting in a clubbed hand
What are sonographic features of trisomy 13?
holoprosencephaly, cleft lip/palate, microphthalmia, absent nose, omphalocele
What is holoprosencephaly?
severe abnormality of the forebrain cleavage
What is the most severe form of holoprosencephaly?
alobar
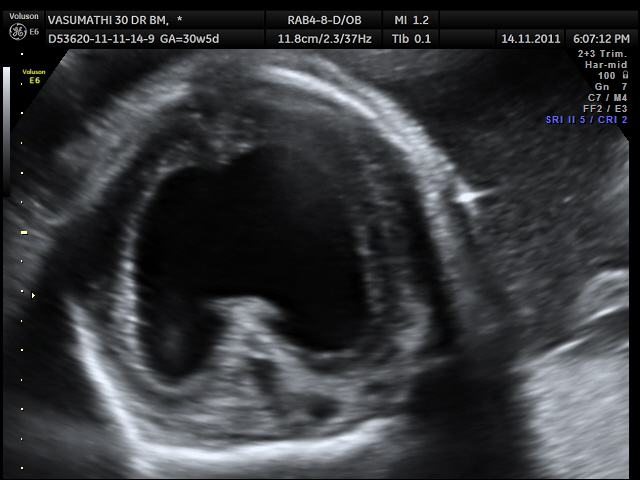
What is this an image of?
alobar holoprosencephaly
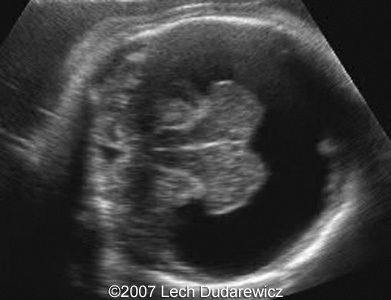
What is this an image of?
semilobar holoprosencephaly
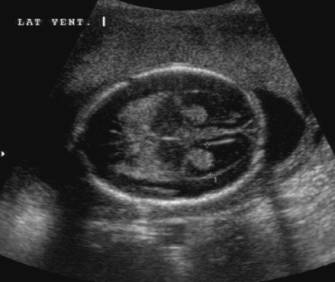
What is this an image of?
lobar holoprosencephaly
A paternal (partial molar pregnancy) placenta will have what appearance?
multiple cysts
a maternal molar pregnancy placenta will have what appearance?
small placenta
What are sonographic appearances of Turner’s syndrome?
cystic hygromas, short limbs, hydrops, heart defects, renal agenesis, horseshoe kidney, pelvic kidney
What is apert syndrome?
premature fusion of the skull and and feet bones.
What are sonographic features of apert syndrome?
prominent bulging forehead, hypertelorism, syndactyly
What is CHARGE syndrome?
a collection of rare malformations including coloboma, small eyes and cranial nerve damage
What does CHARGE syndrome stand for?
coloboma, heart defects, atresia, restriction in growth, genital and ear abnormalities
What is limb-wall body complex?
limb and ventral wall defects from amnion rupturing and sticking to fetus. Fetus commonly missing half its body for example.
What are sonographic characteristics of limb-wall defect complex?
fetus appears stuck to placenta, ventral wall defects, facial cleft, kyphoscoliosis, abnormal thumbs
What is Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome?
overgrowth syndrome with 5 findings: macroglossia, anterior wall defects, hyperglycemia, macrosomia, hemihyperplasia (renal abnormalities too)
What are sonographic characteristics of Meckel Gruber syndrome?
encephalocele, ARPKD, limb abnormalities, dandy walker syndrome
What are sonographic features of Potter sequence?
oligohydramnosis impairing normal development in: extremities, facial features and lungs (pulmonary hypoplasia)
What may cause pulmonary hypoplasia (underdeveloped lungs)?
olioghydramnosis, restricted rib cage, chest masses, pleural effusion
What is the most common cause of lack of amniotic fluid?
PROM or GU abnormalities
What is CPAM type 1
macrocystic areas in the lung
What is CPAM type 2?
macro and microcystic areas in the lungs
What is CPAM type 3?
microcystic areas in the lungs (can look hyperechoic)
What is pulmonary sequestration?
a mass of ectopic pulmonary tissue with no communication with the bronchial tree
What is the most common type of CPAM?
type 1
What type of CPAM can pulmonary sequestration mimic?
Type3
How can you tell the difference between pulmonary sequestration and CPAM 3?
pulmonary sequestration has its own blood supply (feeding stalk off the aorta)
What type of CPAM can bronchogenic cysts mimic?
Type 1
What does foramen of Bockdalek hernia usually contain?
stomach and bowel contents
What does foramen of Maorgagni hernia usually contain?
liver
What are sonographic appearances of tracheal atresia?
enlarged lungs, ascites, polyhydramnosis
What is a strong indicator a fetus has esophageal atresia?
no stomach is seen
What three sections of the spine do you see in transverse?
lamina, peduncle and centrum
What is spina bifidua occulta versus spina bifida aperta?
occulta includes only the deep layers and is a closed defect, aperta includes all layers and is an open defect
What content is in a myelomeningocele?
meninges, CSF and neural tissue
What is the most common type of spina bifida?
aperta
What is elevated in fetuses with a NTD?
AFP
Where is the most common location for NTD’s?
lumbosacral region
What is Rachischisis?
failure of fusion of the spine
What plane is the spine best assessed?
transverse
What is iniencephaly?
when the vertebrae in the neck and shortened causing dorsiflexion
what spinal defect is the “star-gazer” position seen in?
Ineiencephaly
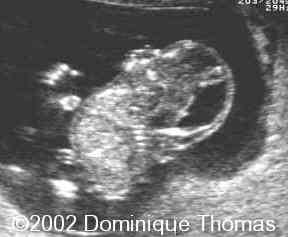
What is this an image of?
iniencephaly (star gazer position)
What are sonographic features of sirenomelia?
absence of sacrum, fusion of legs, renal agenesis, oligohydramnosis
What is the most severe form of caudal regression?
sirenomelia
What is the most common type of sacrococcygeal teratoma?
type I (external mass predominantly)
Where is CSF produced?
choroid plexus
What is the route that CSF takes?
lateral ventricles, interventricular foramen, 3rd ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, 4th ventricle, Magendie and Luchka
What is the upper limit of normal for lateral ventricles?
10mm
What is hydrocephalus?
increase in CSF that results in enlargement of the ventricular system
What is the most common cranial anomaly?
hydrocephalus
What is the difference between hydrocephalus and ventriculomegaly?
hydro is due to a CSF obstruction and ventriculomegaly is due to brain atrophy causing the ventricles to have space to enlarge
What are 3 causes of true hydrocephalus?
NTD, Dandy walker malformation, aqueduct stenosis
What is an aqueduct stenosis?
intraventricular obstruction between 3rd and 4th ventricle
What are examples of extraventricular obstruction?
Dandy Walker malformation and spina bifida
What are 3 sonographic signs of Arnold Chiari II?
lemon sign, obliterated cisterna magna, banana sign
What is Dandy Walker Malformation?
Enlarged cisterna magna where 4th ventricle directly communicates with it due to a defect in the cerebellum
What is AWM associated with?
agenesis of corpus callosum, heart defects, genitourinary, polydactyly
If you suspect the agenesis of the corpus callosum what structure should you try to see?
CSP
What trisomy is associated with CPC’s?
trisomy 18
What is acrania?
absence of the skull
What is exencephaly?
brain tissue exposed to amniotic fluid damages the brain tissue
What is an encephalocele?
brain herniates through the skull
What is Porencephaly?
hemorrhage or rupture causes brain tissue to damage
What is the most severe form of Porencephaly?
hydranencephaly
increase AFP can indicate what?
Encephalocele, omphalocele, gastroschisis, bladder extrophy, and neural tube defects
What is schizencephaly?
brain split into anterior and posterior segments of the brain
What is lissencephaly?
no sulci or gyri
What is craniosynostoses?
bizzare fusion of the cranial sutures
What is an omphalocele?
abdominal contents hernias into the umbilical cord
What is a small omphalocele associated with?
chromosomal abnormalities
What is a gastroschisis?
a defect in abdo to the right of the umbilical cord, bowel is free floating in amniotic fluid
What is gastroschisis associated with?
marijuana, smoking, younger women
What is bladder exstrophy?
bladder doesnt have a developed cloacal membrane. bladder develops outside fetus.
What is a cloacal exstrophy?
when the bladder, vagina, and rectus all connect together
What are sonographic features of cloacal exstrophy?
absence of bladder and unable to identify umbilical artery around the bladder
What are sonographic appearances of esophageal atresia?
absent or small stomach, polyhydramnosis, cystic area in neck
What does the double bubble sign suggest?
duodenal atresia
what is a normal colon diameter in a term fetus?
18mm
what is a normal small bowel diameter in a term fetus?
12mm
What disease can cause meconium ileus?
cystic fibrosis
What could cause hepatic calcifications in a fetus?
maternal TORCH infections
How many weeks does fetal urine production begin at?
11 weeks LMP
What should the length of the kidneys measure in fetuses?
similar to the gestational age
What is a normal renal pelvis measurement?
up to 5mm
What is bilateral renal agenesis associated with?
sirenonmelia, cardiac abnormalities, GI abnormalities, teratogens (Warfarin, cocaine type 1 diabetes)
What are two indirect sonographic features of bilateral renal agenesis?
absent bladder and oligohydramnosis
What is the difference between Potter’s sequence and syndrome?
syndrome referes to bilateral renal agenesis, sequence refers to a consequence of oligohydramnosis
Where is the obstruction if only the kidneys are dilated
UPJ
where is the obstruction if the ureters and kidneys are dilated?
UVJ
where is the obstruction if the bladder is dilated (keyhole appearance)
PUV (posterior urethral valve)